当前位置:网站首页>Gradle foundation | customize the plug-in and upload it to jitpack
Gradle foundation | customize the plug-in and upload it to jitpack
2022-07-02 03:22:00 【Drizzle in winter】
author :Petterp
introduction
Every use Gradle Classmate , Must have heard of or written plug-ins , Because it is not difficult in itself , But because the articles on the Internet are the same now , Most of them are older , The new student is just like me at first , Spent a lot of time in the most basic first step how to write a simple demo On . Moreover, if you use AndroidStudio BumBlebee To create a project , Compared with online tutorials, the difference is even greater , It takes time , And this article is to help you save these time .
This article mainly summarizes three ways to create plug-ins , And how to upload to JitPack in .
- The development environment is based on the latest Gradle7.0.4 , AndroidStudio BumBlebee ;
- The relevant sample code of this article ,github
https://github.com/Petterpx/GradlePluginSImple
What is a plug-in ?
stay Gradle in , The plug-in is equivalent to packaging some reusable construction fragments , Make it reusable for multiple projects to build . As shown below :
// New edition
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
}
// The old version
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
These are the two most common plug-ins , For example, when we are creating a android-model when , Will automatically add the corresponding library plug-in unit , The job of these plug-ins is to help us put some repetitive work or code , Introduce in the form of a sentence of code , It greatly reduces the amount of our code .
stay Gradle in , We can use Java ,Kotlin as well as Groovy To write their own plug-ins , generally speaking , Use Java and Koltin Compared to using Groovy The implementation effect will be better . Digression : In writing ,Java And kotlin It is also more in line with development habits .
What are the uses of plug-ins ?
The role of plug-ins is to add some of our own logic to the project implementation process , This practice is in Gradle It is called task , Or say Task , So as to test the project 、 compile 、 Packing, etc ;
You can also add new extended attributes to existing object types in the project 、 Such method 、 You can also configure and optimize the construction of the project , For example, the common android{} Namely Android Gradle Plug in Project An extension of object addition .
Daily development , We also have many plug-ins that we will see in development , such as didibooster Plug in for , Alibaba routing plug-in , Some third-party management plug-ins .
There is an interesting question , I think you may have ?
These plug-ins are usually in model And then rely on other components , If I only use code components , Instead of enabling these plug-ins , Can it be used normally ?In fact, in general , It does not affect your normal use in development , One
qualifiedThree party Library , When the plug-in is not enabled, it will not affect the final use effect , It's just that the final implementation method will be different , For example, performance . Similar to Alibaba routing plug-in , If you do not enable plug-ins , Rely only on code components , When finally finding the routing table, you can only find it through reflection , Instead of path mapping generated during compilation , So in general, we are debug Some dependencies can be closed under , Thereby reducing debug Time , But in general , These plug-ins don't take much time , So it depends on your own needs .
Create a plug-in
Script plugin
We can directly include the source code of the plug-in in the build script , This is the easiest way to understand , Specific examples are as follows :
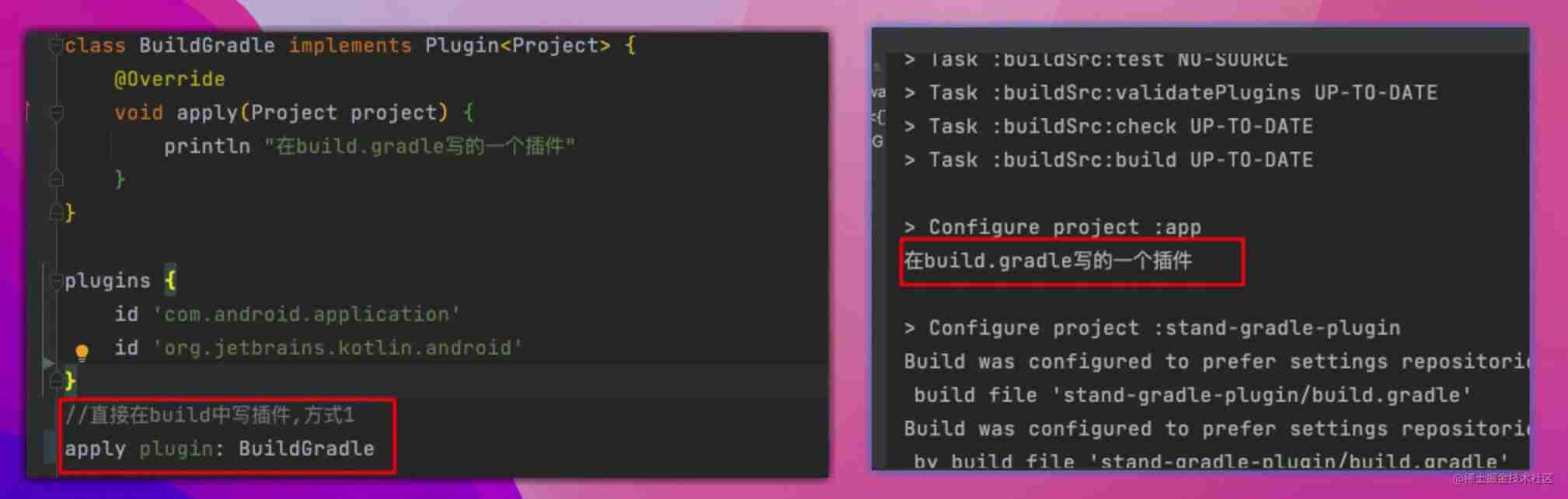
Directly in app model Chinese writing plug-in , The advantage of this is that the plug-in will be automatically compiled and included in the classpath of the build script , Without doing anything else . Corresponding , If you want to reuse across projects , It is more difficult to solve , And because of the lack of a unified maintenance path , It also increases the later cost .
buildSrc
The official suggestion is that we can put the code of local plug-ins into buildSrc In this directory . This directory is special , For every project , There is one and only one buildSrc Catalog , And must be located in the root directory of the project , If there is buildSrc This directory , that Gradle The code will be compiled and tested automatically at run time , And put it in the classpath of the build script , Compared with the above script plug-in , It is easier to maintain and manage tests .
Sample code :buildSrc
https://github.com/Petterpx/GradlePluginSImple/tree/main/buildSrc
Use the tutorial :
We have a new one called buildSrc The catalog of , Then create a build.gradle file , As shown below :
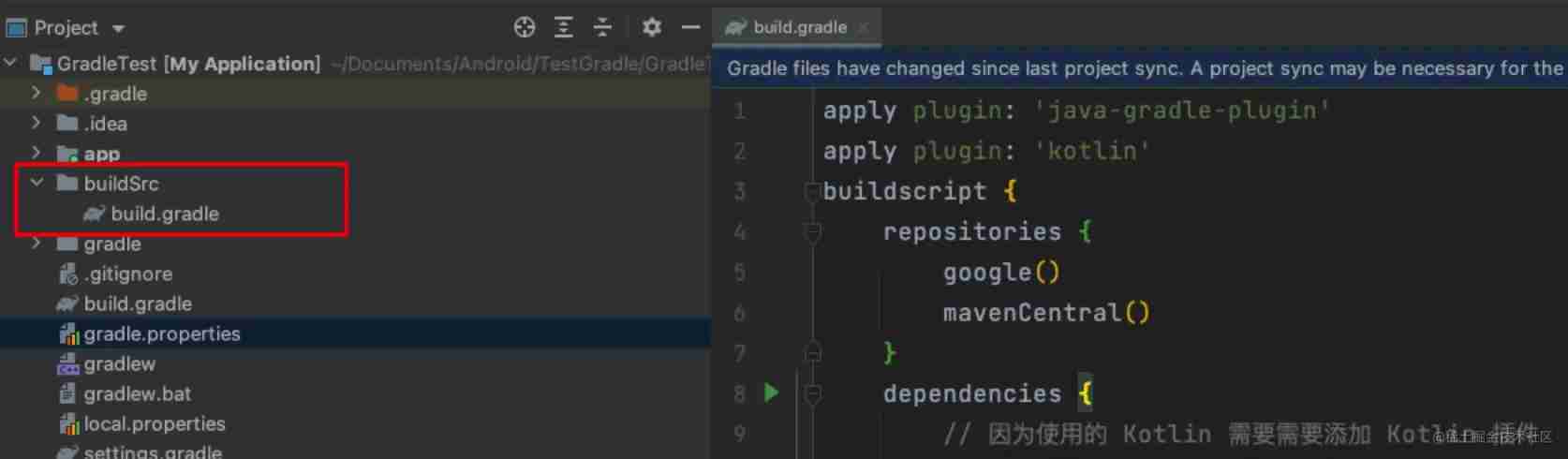
The code is as follows :
apply plugin: 'kotlin'
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
// Because I want to use kotlin, So here we add kotlin plug-in unit
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:1.6.10-RC"
}
}
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk8:1.6.10"
}
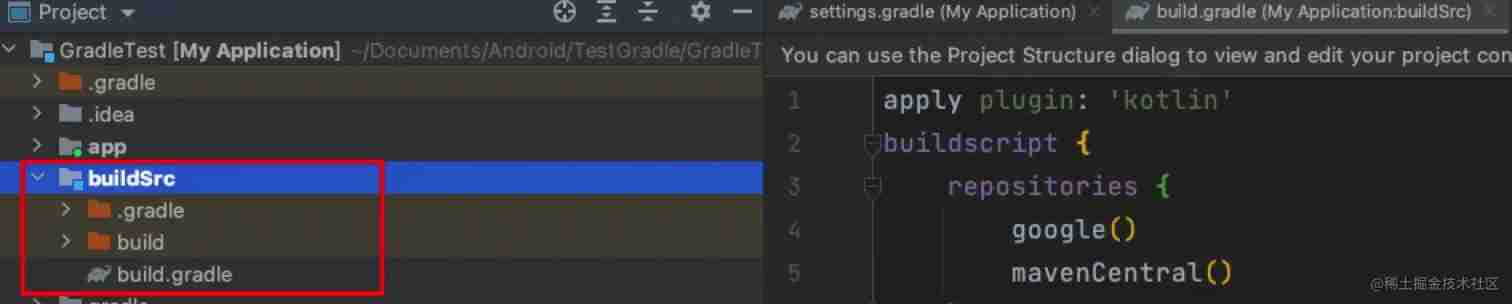
next sync once , Then you will find out , This buildSrc Has been Android Studio Automatic recognition for a java project . as follows :
Of course, you can also create one directly
java-model, And then changebuildfile , The advantage of this is that it saves the effort of manually creating folders , Corresponding , You also need to gosettings.gradleDelete this model Statement of , as a result of :buildSrc It's a special directory , It is forbidden to declare manually ;
Here we are. , How do we create our own plug-in files , Directly in src Create the corresponding folder under , Then create our own plug-in file , As shown below :
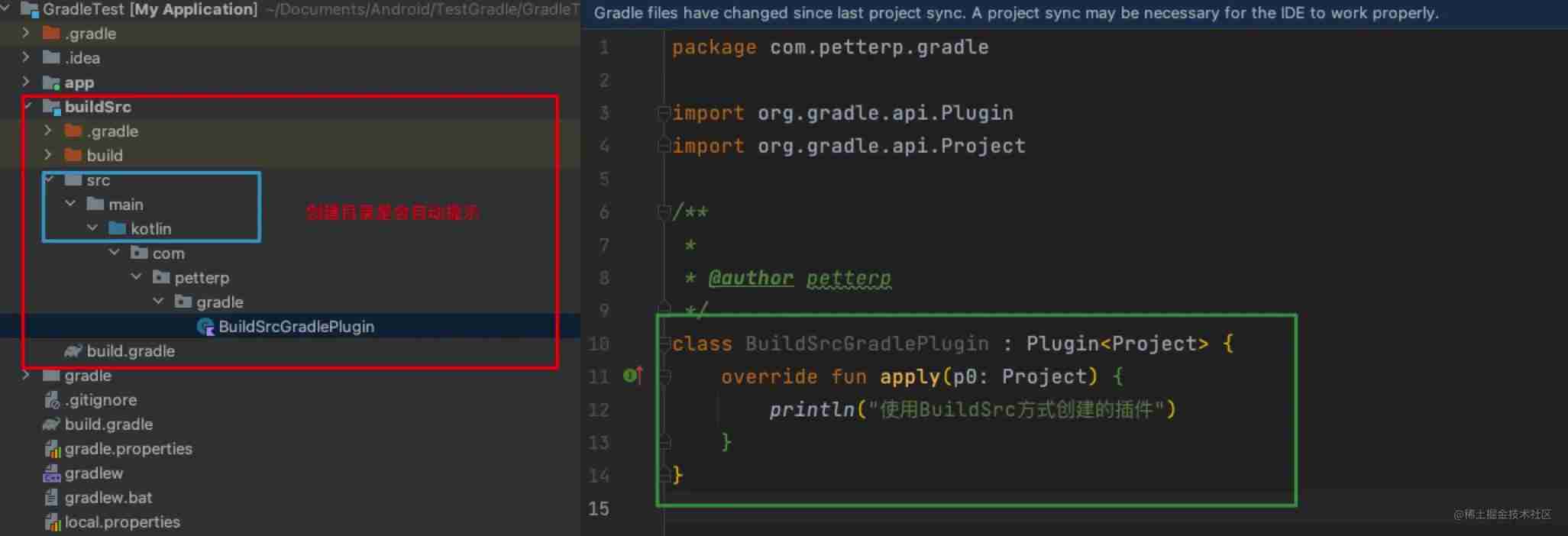
The above directory format , It depends on your own way of writing , For example, here I want to use kotlin Write plug-in code , Just use the following , By default, three directory configuration methods are officially recommended :
- src/main/kotlin
- src/main/java
- src/main/groovy
ps: When using As stay buildSrc When creating a directory , It will automatically prompt you to select the appropriate directory .
Above we created a custom plug-in implementation class , Now go and change our build.gradle file , Add the following code :
//java-gradle plug-in unit
apply plugin: 'java-gradle-plugin'
...
// Use when relying on plug-ins locally
gradlePlugin {
plugins {
// The plugin name , Every plug-in can have
buildSrcTestPlugin {
// Your plugin id, External project reference requires
id = 'com.petterp.gradle.buildSrc'
// Specific implementation classes of plug-ins
implementationClass = 'com.petterp.gradle.BuildSrcGradlePlugin'
}
// Second plug-in
// test2Plugin {
// id = xxx
// implementationClass = xxx
// }
}
}
After a change , And then in our app-build.gradle( It depends on where you use it ) You can import dependencies in :
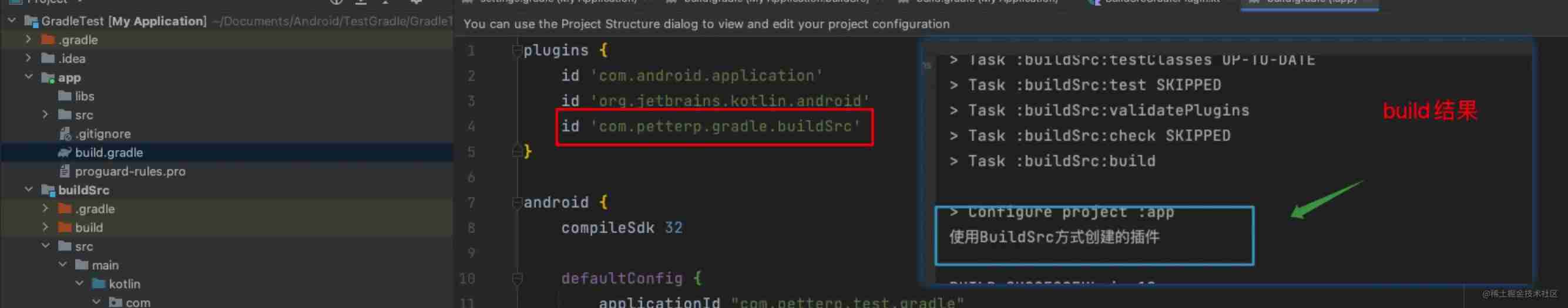
It's over here , Isn't it super simple , If you have searched the old tutorial , You will find that you need Manually create resource namely META-xxx wait .
It's not that we didn't create , It's what we use java-gradle-plugin The plug-in will be created automatically , And take api Way to introduce gradleApi() , It will automatically help us realize the above steps . The specific final generation is here , As shown in the figure below :
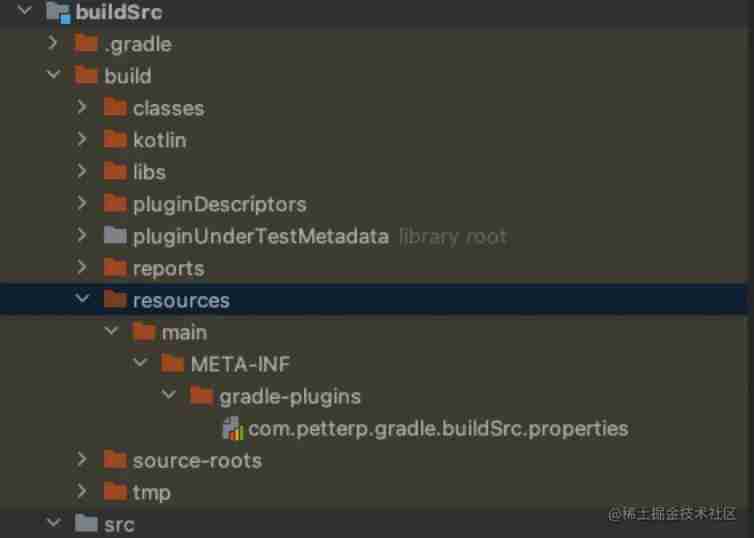
Standalone project
The above two methods can only be used in the current project , If we want to use it in other projects , At this time, we usually publish the plug-in to Maven On , Share with others , This is also the most commonly used way to develop plug-ins , This article will be uploaded to JitPack On .
Sample code :standlone
https://github.com/Petterpx/GradlePluginSImple/tree/main/stand-gradle-plugin
We copy and paste the above tutorial buildSrc package , And rename it as follows , For example, change to stand-gradle-plugin , Then in our project settings.build This is introduced in model, As shown below :

It seems too simple , It's no different , You might think , So in that case , that buildSrc What is the use of ? Anyway, it seems that any name is ok ?
Let's change it first stand-gradle-plugin Of plug-in unit id , And the corresponding Plug in implementation class name , As shown below :

Then go straight to app-model Introduce in , What happens at this point ?
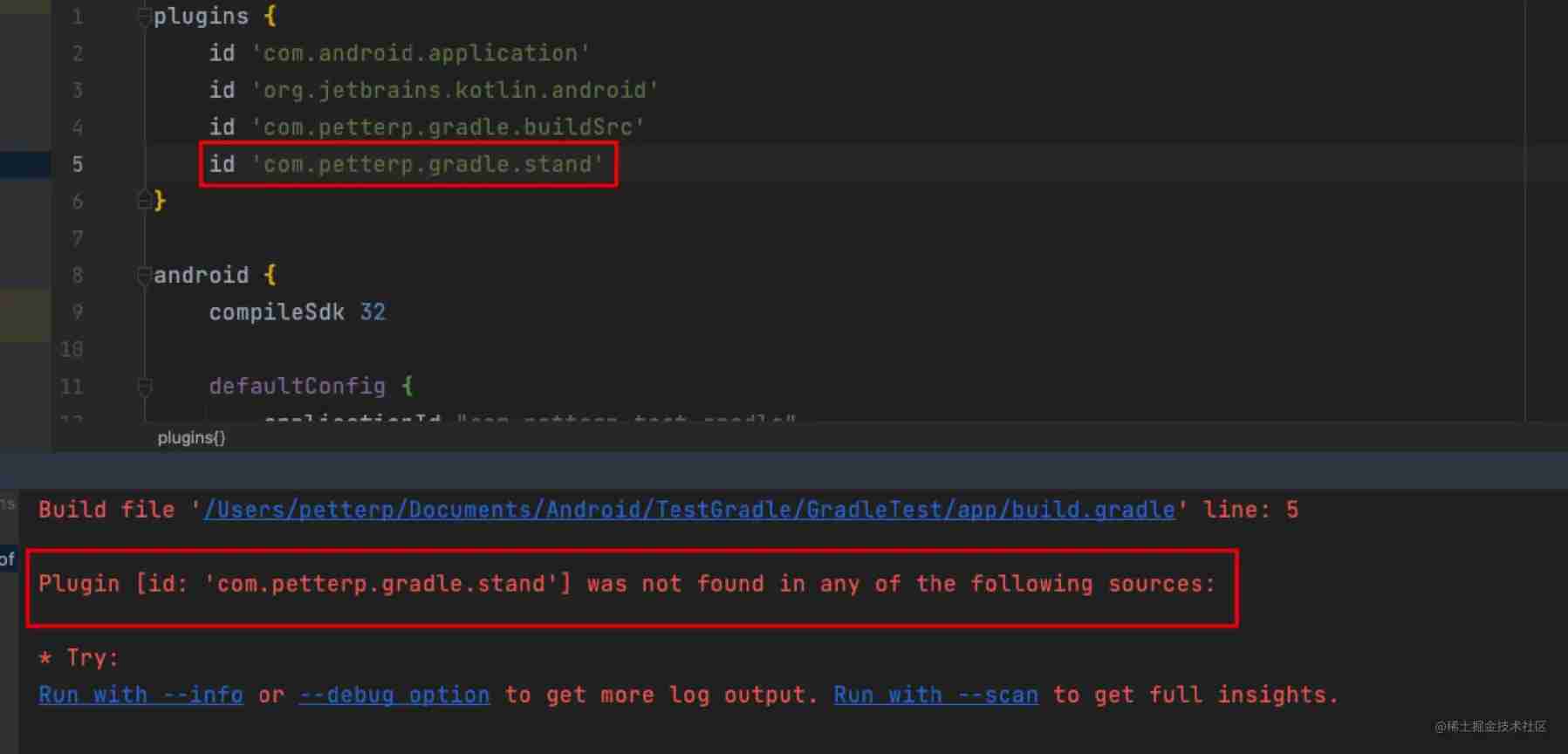
Prompt: the plug-in cannot be found , Why? ? I'm not settings.gradle Is it introduced in ?
We said at the top ,buildSrc Itself is a special project ,Gradle Will automatically compile and introduce . Other plug-ins , If you don't use maven Way to introduce , You need to configure it separately , As shown below :
Let's change settings.gradle file :
includeBuild('stand-gradle-plugin')
change Project root build.gradle:
plugins {
...
id 'com.petterp.gradle.stand' apply false
}
again sync It won't be wrong , The results are shown in the following figure :

This is actually equivalent to using a local plug-in , If you have used composite build to configure your project dependency configuration , Maybe I'm very familiar with this way .
Upload to JitPack in
generally speaking , We will upload the plug-in to Maven On , Easy to use across projects . We use Standalone Project Take this method as an example , change Standalone In the way build.gradle, As shown below , Add the following code :
Sample code :stabdlobe-build.gradle
https://github.com/Petterpx/GradlePluginSImple/blob/main/stand-gradle-plugin/build.gradle
apply plugin: 'maven-publish'
// Group name , It can be understood that the plug-in is placed in that group , Finally, it is a folder
// com/petterp/gradle/plugins/xxx
group = 'com.petterp.gradle'
// describe
description = ' This is an independent plug-in '
// Version number
version = '1.0.0'
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_11
publishing {
publications {
maven(MavenPublication) {
// edition id, Eventually, according to this id-version Generate corresponding plug-ins
artifactId = 'com.petterp.gradle.plugin'
from components.java
}
}
repositories {
maven {
// Generated plug-in location
url = uri('../repo')
}
}
}
change settings.gradle The plug-in depends on
include ':stand-gradle-plugin'
Then execute... On the command line :gradlew publish
At this time, there will be one more in our project repo Folder , As shown in the figure below , This is the plug-in package we finally packed .

Next go github hit Tag, And open Jitpack Website , Search our project name , Build .

After that, we can quote in the project , As shown in the figure below :
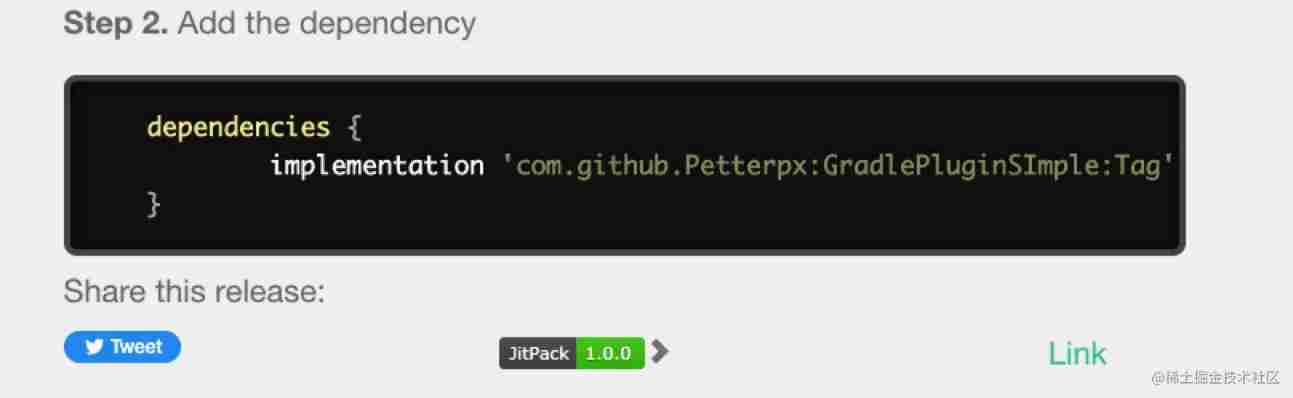
Because we generate plug-ins , So the corresponding dependency method is changed to classpath
classpath "com.github.Petterpx:GradlePluginSImple:1.0.0"
And then in the corresponding model Just introduce it into the
plugins {
...
id 'com.petterp.gradle.stand'
}
So far , Even if a simple plug-in is created .
边栏推荐
- Global and Chinese markets for ultrasonic probe disinfection systems 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Grpc快速实践
- [golang] leetcode intermediate bracket generation & Full Permutation
- C#联合halcon脱离halcon环境以及各种报错解决经历
- Verilog 避免 Latch
- Screenshot literacy tool download and use
- Download and use of the super perfect screenshot tool snipaste
- PMP personal sprint preparation experience
- Baohong industry | 6 financial management models at different stages of life
- Just a few simple steps - start playing wechat applet
猜你喜欢

浅谈线程池相关配置

How to develop digital collections? How to develop your own digital collections

JIT deep analysis

C shallow copy and deep copy
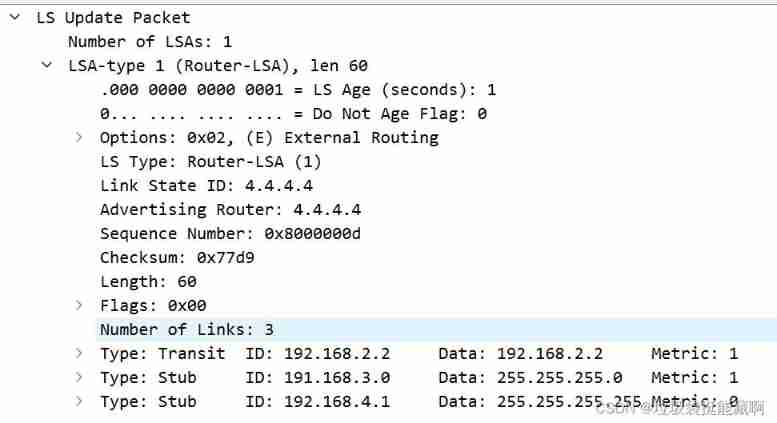
OSPF LSA message parsing (under update)
![[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol](/img/03/83c883afb63b7c63f6879b5513bac3.jpg)
[HCIA continuous update] overview of dynamic routing protocol
![[HCIA continuous update] working principle of OSPF Protocol](/img/bc/4eeb091c511fd563fb1e00c8c8881a.jpg)
[HCIA continuous update] working principle of OSPF Protocol

Tupu software has passed CMMI5 certification| High authority and high-level certification in the international software field
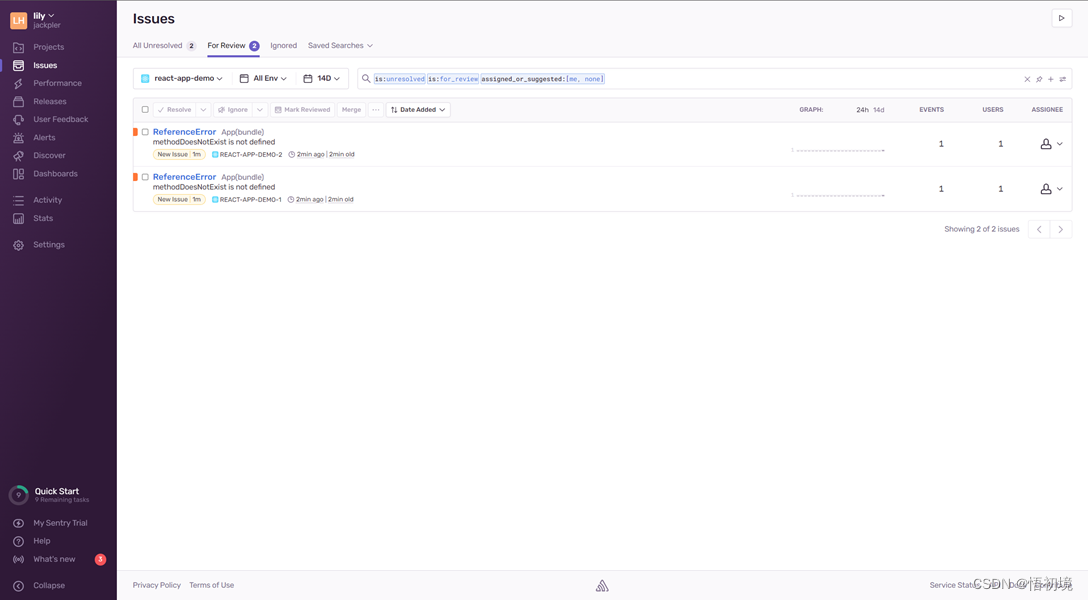
初出茅庐市值1亿美金的监控产品Sentry体验与架构
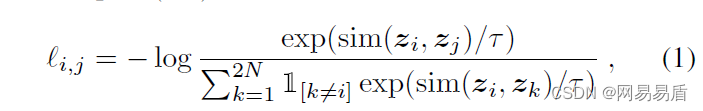
知物由学 | 自监督学习助力内容风控效果提升
随机推荐
West digital decided to raise the price of flash memory products immediately after the factory was polluted by materials
Verilog wire type
GSE104154_scRNA-seq_fibrotic MC_bleomycin/normalized AM3
高并发场景下缓存处理方案
On redis (II) -- cluster version
MMSegmentation系列之训练与推理自己的数据集(三)
Framing in data transmission
JS introduction < 1 >
Design details of SAP e-commerce cloud footernavigationcomponent
verilog 并行块实现
创业了...
C # joint Halcon's experience of breaking away from Halcon environment and various error reporting solutions
Redis set command line operation (intersection, union and difference, random reading, etc.)
Pointer array & array pointer
跟着CTF-wiki学pwn——ret2shellcode
[C Advanced] brother Peng takes you to play with strings and memory functions
32, 64, 128 bit system
Verilog 过程连续赋值
Verilog state machine
Aaaaaaaaaaaa