当前位置:网站首页>C# LINQ源码分析之Count
C# LINQ源码分析之Count
2022-07-05 08:39:00 【懒人Ethan】
概要
LINQ代码库中的Count方法作为数据统计的关键方法,经常被使用。在统计数据时候,Count方法是否每次都要遍历整个序列来获取序列元素个数,Count方法内容是否存在优化机制。为了更好的了解该方法的工作原理,我们从源码的角度对其进行分析。
本文的内容是以C# LINQ源码分析之Select和
C# LINQ源码分析之Where为基础,对Count方法的源码进行分析。
Count方法介绍
Count方法的基本功能是获取序列中元素个数。LINQ代码库提供了2个Count的重载方法如下:
| 方法名称 | 基本介绍 |
|---|---|
| Count(IEnumerable) | 获取序列中元素的个数 |
| Count(IEnumerable, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | 返回序列中满足条件的元素个数 |
Count关键源码分析
Count方法是 IEnumerable的一个扩展方法,支持一个TSource泛型参数。
public static int Count<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
if (source == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.source);
}
if (source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft)
{
return collectionoft.Count;
}
if (source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv)
{
return listProv.GetCount(onlyIfCheap: false);
}
if (source is ICollection collection)
{
return collection.Count;
}
int count = 0;
using (IEnumerator<TSource> e = source.GetEnumerator())
{
checked
{
while (e.MoveNext())
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
- 如果序列为空,抛出异常;
- 如果序列是实现ICollection接口的实例,例如List的实例,直接返回实例中的Count属性;
- 如果序列是I实现IListProvider接口的实例,调用该接口的GetCount方法,参数默认传入false,IListProvider接口在下文介绍;
- 如果序列是实现ICollection接口的实例,例如List的实例,直接返回实例中的Count属性;
- 如果source是一个迭代器,并且该迭代器没有实现IListProvider,调用该迭代器,则完成迭代,并统计元素个数。
Count的另一个重载方法代码与之类似,不再赘述。
Count方法的工作方式
为了检验Count方法的工作原理,本文对Count方法和其关联的内容进行了代码抽取,定义了Count2方法,以增加各种log,具体代码件附录。
实现ICollection接口的对象调用Count方法
Student类详见附录。
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
执行结果如下: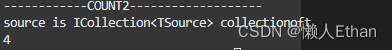
从结果我们可以看出,获取List对象内的元素个数,并不需要遍历整个List,只是返回ICollection接口的Count属性值。
实现IListProvider接口的对象调用Count方法
对于一个List泛型序列xx,如果存在xx.Where().Count()的调用,我们希望过滤和计算元素个数两个操作在一次遍历中完成,不希望通过两次遍历实现。
要实现上述目标的关键就是IListProvider接口,它主要是定义了ToList,ToArray和GetCount三个方法的规范,本文主要讨论GetCount方法。
之前的文章我们讨论过,LINQ的主要实现基础就是在扩展方法内部,使用各种迭代器来实现具体的操作,例如Where方法的WhereListIterator迭代器,可以实现List元素的过滤操作。
IListProvider就是让各种迭代器去实现它接口中的GetCount方法,从而将GetCount操作附加到各种迭代操作中。
关键代码如下,其中ToList和ToArray不再本文讨论范围内,已经略去。
private sealed partial class WhereListIterator<TSource> : Iterator<TSource>, IIListProvider<TSource>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
if (onlyIfCheap)
{
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _source.Count; i++)
{
TSource item = _source[i];
if (_predicate(item))
{
checked
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
我们可以看到,密封类WhereListIterator实现了IIListProvider中的GetCount,在该方法中将过滤和统计个数两个操作合二为一。
List泛型序列xx.Where().Count()的实现原理
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Where2(s=>s.MathResult >= 90)
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- 进入Where2扩展方法,返回WhereListIterator迭代器对象。
- 进入Count2扩展方法,WhereListIterator已经实现了IIListProvider方法。
- 调用WhereListIterator对象的GetCount方法,onlyIfCheap参数为false。
- 完成过滤和统计操作。
执行结果如下,符合预期: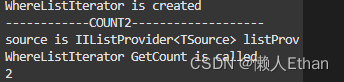
List泛型序列xx.Select().Count()的实现原理
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Select2(s => new {
Name= s.Name, Math = s.MathResult})
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- 进入Select2扩展方法,返回SelectListIterator对象
- 进入Count2扩展方法,SelectListIterator已经实现了IIListProvider方法。
- 调用SelectListIterator对象的GetCount方法,onlyIfCheap参数为false。
- 完成投影和统计操作,SelectListIterator类相关源码如下:
private sealed partial class SelectListIterator<TSource, TResult> : IPartition<TResult>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
// In case someone uses Count() to force evaluation of
// the selector, run it provided `onlyIfCheap` is false.
int count = _source.Count;
if (!onlyIfCheap)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
_selector(_source[i]);
}
}
return count;
}
}
List泛型序列xx.Where().Select().Count()的实现原理
在之前文章的讨论中,我们已经了解到,xx.Where().Select()中的过滤和投影操作会被合并成,通过WhereSelectListIterator迭代器,在遍历List泛型序列时,将满足Where条件的元素进行投影,一次遍历实现。
同样WhereSelectListIterator也实现了IIListProvider泛型接口,代码如下,其中ToList和ToArray不再本文讨论范围内,已经略去。
private sealed partial class WhereSelectListIterator<TSource, TResult> : IIListProvider<TResult>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
// In case someone uses Count() to force evaluation of
// the selector, run it provided `onlyIfCheap` is false.
if (onlyIfCheap)
{
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _source.Count; i++)
{
TSource item = _source[i];
if (_predicate(item))
{
_selector(item);
checked
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
从代码中不难看出,GetCount方法将过滤,投影和统计元素,在一次遍历中实现。
所以,下面代码的实现逻辑就很清晰了,具体如下:
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Where2(s=>s.MathResult >= 90)
.Select2(s => new {
Name= s.Name, Math = s.MathResult})
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- 进入扩展方法Where2,返回WhereListIterator迭代器实例。
- 进入扩展方法Select2,WhereListIterator是一个迭代器实例,调用该实例自己的Select方法,返回WhereSelectListIterator实例。
- 进入扩展方法Count2,WhereSelectListIterator实现了 IIListProvider接口,所以调用实例自己的GetCount方法,将过滤,投影和统计元素,在一次遍历中实现。
执行结果符合预期:
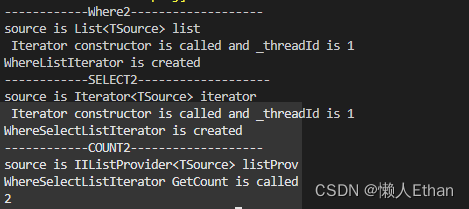
结论
Count方法在处理List,Array等集合数据类型时候,会直接返回它们实现ICollection接口中的Count属性值;在和其他扩展方法Where, Select等配合使用时候,会把统计操作和其他扩展方法的操作,进行合并,避免出现多次遍历同一个序列的情况。
附录
Count2方法:
public static int Count2<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
Console.WriteLine("------------COUNT2-------------------");
if (source == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.source);
}
if (source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft");
return collectionoft.Count;
}
if (source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv");
return listProv.GetCount(onlyIfCheap: false);
}
if (source is ICollection collection)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is ICollection collection");
return collection.Count;
}
Console.WriteLine("source is Iterator");
int count = 0;
using (IEnumerator<TSource> e = source.GetEnumerator())
{
checked
{
while (e.MoveNext())
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
Student类
public class Student {
public string Id {
get; set; }
public string Name {
get; set; }
public string Classroom {
get; set; }
public int MathResult {
get; set; }
}
边栏推荐
- Example 005: three numbers sorting input three integers x, y, Z, please output these three numbers from small to large.
- 实例002:“个税计算” 企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%;利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可提成7.
- MATLAB小技巧(28)模糊综合评价
- Business modeling of software model | overview
- Arduino+a4988 control stepper motor
- leetcode - 445. 两数相加 II
- Mathematical modeling: factor analysis
- 關於線性穩壓器的五個設計細節
- [three tier architecture]
- STM32 summary (HAL Library) - DHT11 temperature sensor (intelligent safety assisted driving system)
猜你喜欢
Example 001: the number combination has four numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4. How many three digits can be formed that are different from each other and have no duplicate numbers? How many are each?
Numpy pit: after the addition of dimension (n, 1) and dimension (n,) array, the dimension becomes (n, n)
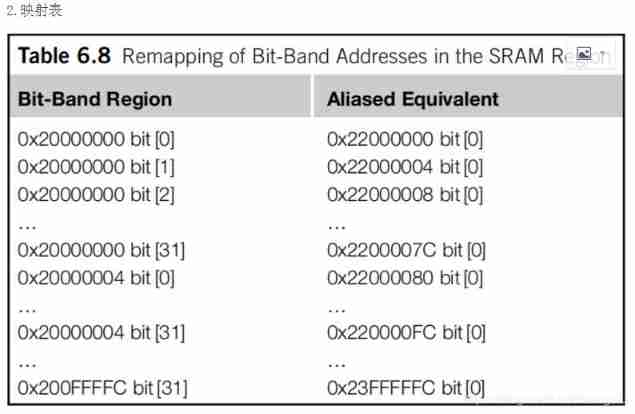
STM32 single chip microcomputer - bit band operation
Run menu analysis

实例002:“个税计算” 企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%;利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可提成7.
实例001:数字组合 有四个数字:1、2、3、4,能组成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数?各是多少?

Illustration of eight classic pointer written test questions

Guess riddles (6)
Business modeling of software model | vision
Example 009: pause output for one second
随机推荐
Some pitfalls of win10 network sharing
Example 001: the number combination has four numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4. How many three digits can be formed that are different from each other and have no duplicate numbers? How many are each?
Shift operation of complement
实例003:完全平方数 一个整数,它加上100后是一个完全平方数,再加上168又是一个完全平方数,请问该数是多少?
【三层架构】
暑假第一周
[formation quotidienne - Tencent Selection 50] 557. Inverser le mot III dans la chaîne
猜谜语啦(2)
Digital analog 1: linear programming
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
【日常训练】1200. 最小绝对差
Count the number of inputs (C language)
Example 009: pause output for one second
猜谜语啦(10)
696. 计数二进制子串
猜谜语啦(6)
Guess riddles (10)
Cinq détails de conception du régulateur de tension linéaire
STM32 single chip microcomputer - bit band operation
每日一题——输入一个日期,输出它是该年的第几天
