当前位置:网站首页>Window function method for FIR filter design
Window function method for FIR filter design
2022-08-02 16:44:00 【Zhi Zhao】
前言
FIRfilter refers to finite length impulse response filter.It can be designed into a strict linear phase,Can avoid the phase distortion of the processed signal,Therefore, in data communication、语音信号处理、Widely used in image processing and other fields.
一、The basic principle of the window function method
Given an ideal zero-phase low-pass filter,Its frequency characteristic can be expressed as:
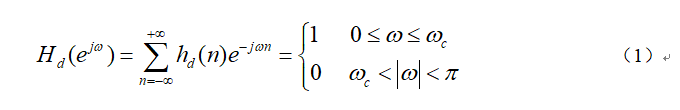
The characteristics of the zero-phase filter are:
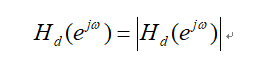
The corresponding unit impulse response is:
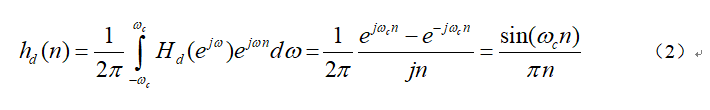
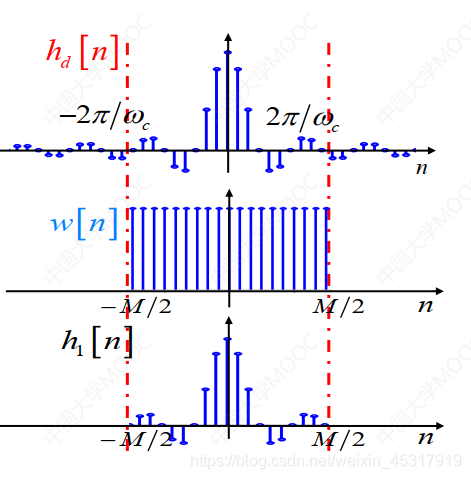
式(1)和式(2)分别对应图1frequency and time domains in,The above process is the inverse Fourier transform.
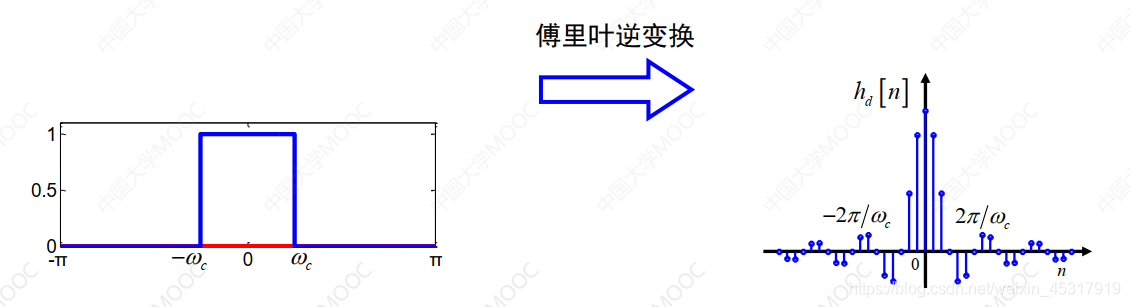
由于 是一个无限长序列,Computers are often unable to handle,So use a functionw(n)对其进行截断,into a finite-length sequenceh(n),即:
是一个无限长序列,Computers are often unable to handle,So use a functionw(n)对其进行截断,into a finite-length sequenceh(n),即:
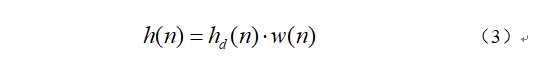
w(n)称为窗函数,其表达式如下:
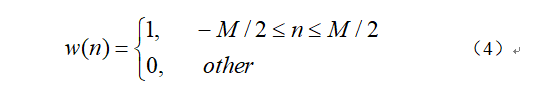
The process of truncating an infinite-length sequence into a finite-length sequence is shown in the figure2所示.
由于此时的h(n)is a non-causal sequence,是不可实现的,shift it in the time domain,得到新的h(n)如下式:
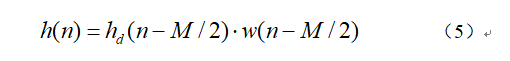
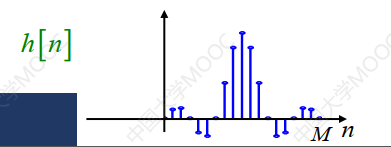
式(5)is the time-domain expression for the achievable low-pass filter,The waveform diagram as shown in figure3所示.
另外,也可以对 First do the shift in the time domain,Then use the window function to intercept,And the sequence remains symmetric during interception.此时的序列h(n)is a finite-length causal sequence.
First do the shift in the time domain,Then use the window function to intercept,And the sequence remains symmetric during interception.此时的序列h(n)is a finite-length causal sequence.
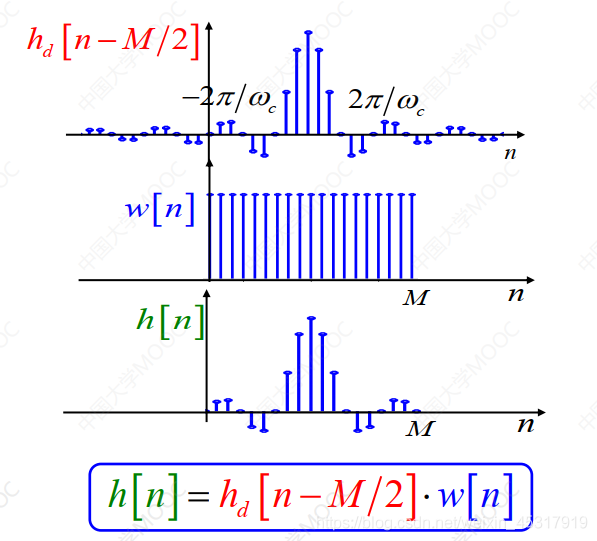
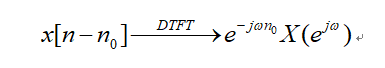
According to the time domain shift property:Amplitude frequency constant,Phase frequency linear change.
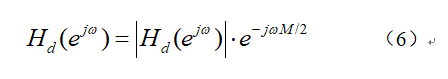
窗函数w(n)的频域表达式为:
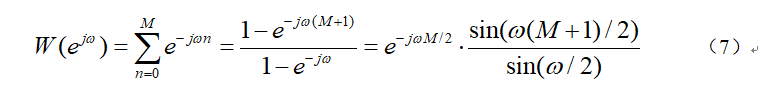
根据时域相乘等于频域卷积,The frequency domain expression of the achievable filter is:
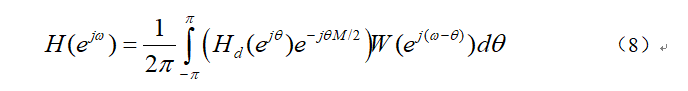
with ideal linear phase and window functionw(n)The spectrum of5所示.
and window functionw(n)The spectrum of5所示.
主瓣宽度为4π/N,Nis the length of the window function,N=M+1,M为滤波器的阶数.
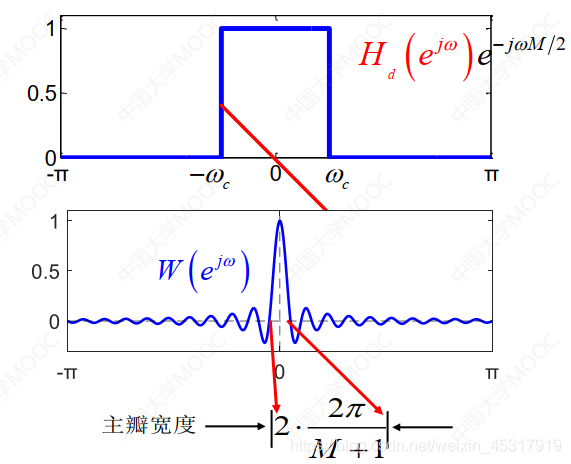
The resulting the filter for the ideal filter can be realized and window functionw(n)的卷积,如图6所示.
and window functionw(n)的卷积,如图6所示.
窗函数法设计的滤波器有如下结论:
1)旁瓣积分决定阻带和通带内的纹波;
2)主瓣积分决定过渡带的宽度.
3)通带的幅度取决于主、旁瓣积分.
二、Window function method design steps
Because of the influence of the shape of the window main lobe and side lobe,So according to design filterRipple size to determine the shape of the window;The length of the window affects the main lobe,which in turn affects the width of the transition band,So according to design filterThe width of the transition band determines the length of the window.
设计一个FIRThe filter is usually done as follows:
1)According to filter design requirements,Determining the filter's stopband attenuation requirements and transition band width,Then choose the type of window function and estimate the length of the windowN;
2)According to the transition zone width to determine the ideal filter cutoff frequency,get the unit impulse response ;
;
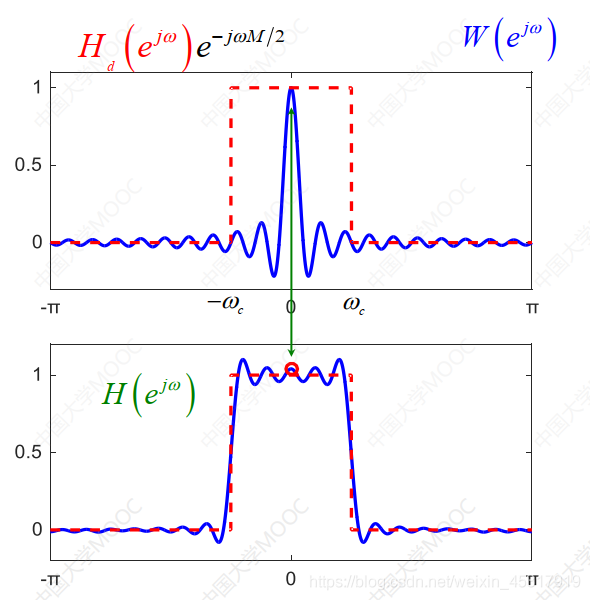
3)According to the obtained realizable filterh(n)的表达式,Find out the frequency response:
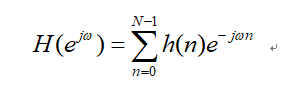
4)Verify that specifications are met based on frequency response;
5)If the index requirements are not met,then the window function type or length should be adjusted,然后重复以上步骤,直到满足要求为止.
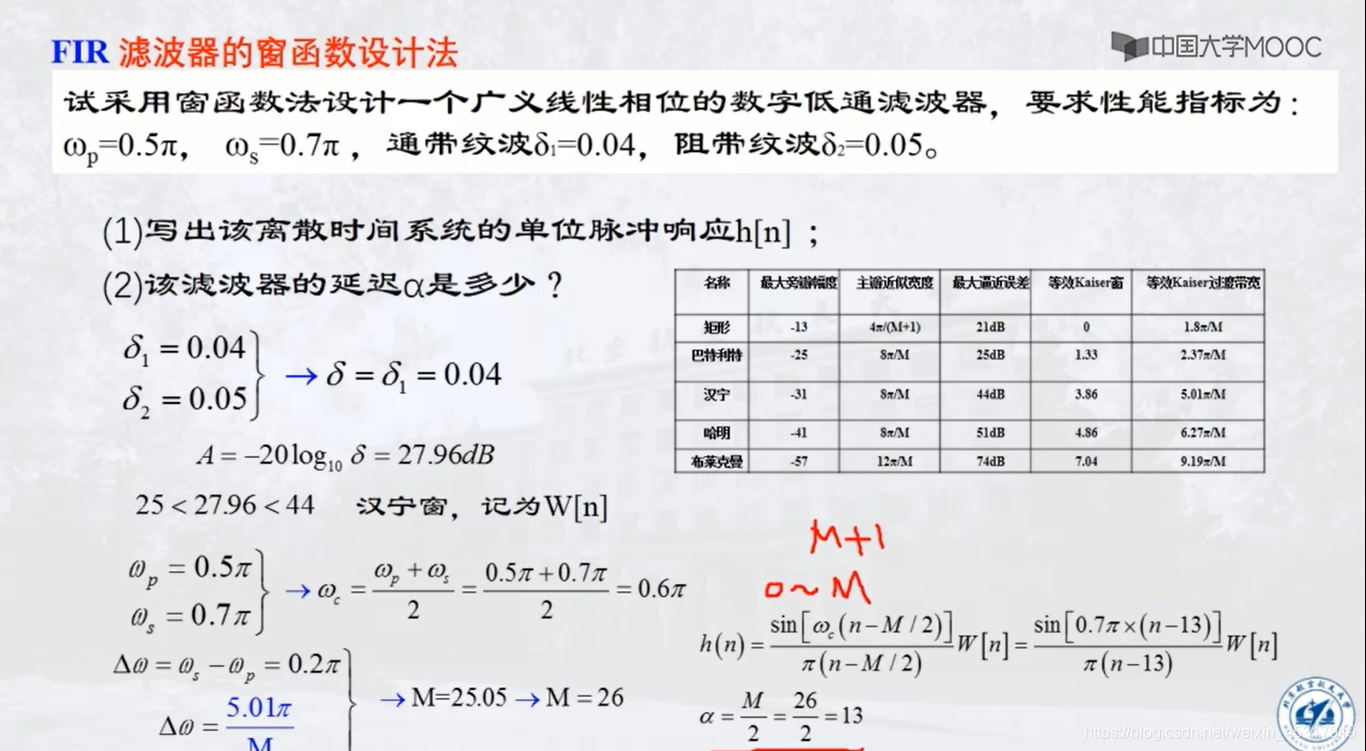
三、案例分析


四、MATLAB代码
function [h] = useFIR(mode,n,fp,fs,window,r,sample)
% mode:模式(1——高通,2——低通,3——带通,4——带阻)
% n:阶数,The number of points for windowing is the order plus1
% fp:Indicates the cutoff frequency at high pass and low pass,Indicates the lower limit frequency in band pass and band stop
% fs:Upper limit frequency bandpass and band stop instructions
% window:加窗(1——矩形窗,2——三角窗,3——Bart window,4——海明窗,
% 5——汉宁窗,6——布莱克曼窗,7——凯塞窗,8——切比雪夫窗)
% r:代表加kaiserWhen the windowbetavalue and addchebyshev窗的r值
% sample:采样率
% h:Return to design goodFIR滤波器系数
if window == 1
w = boxcar(n+1);
end
if window == 2
w = triang(n+1);
end
if window == 3
w = bartlett(n+1);
end
if window == 4
w = hamming(n+1);
end
if window == 5
w = hanning(n+1);
end
if window == 6
w = blackman(n+1);
end
if window == 7
w = kaiser(n+1,r);
end
if window == 8
w = chebwin(n+1,r);
end
wp = 2*fp/sample;
ws = 2*fs/sample;
if mode == 1
h = fir1(n,wp,'high',w);
end
if mode == 2
h = fir1(n,wp,'low',w);
end
if mode == 3
h = fir1(n,[wp,ws],w);
end
if mode == 4
h = fir1(n,[wp,ws],'stop',w);
end
m = 0:n;
subplot(1,3,1);plot(m,h);
xlabel('n');ylabel('h(n)');title('冲激响应');axis([0 n 1.1*min(h) 1.1*max(h)]);grid on;
freq_response = freqz(h,1);
magnitude = 20*log10(abs(freq_response));
m = 0:511;
f = m * sample/(2*511);
subplot(1,3,2);plot(f,magnitude);
xlabel('频率/Hz');ylabel('f幅值');title('幅频特性');axis([0 sample/2 1.1*min(magnitude) 1.1*max(magnitude)]);grid on;
phase = angle(freq_response);
subplot(1,3,3);plot(f,phase);
xlabel('频率/Hz');ylabel('相位');title('相频特性');axis([0 sample/2 1.1*min(phase) 1.1*max(phase)]);grid on;
end边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
The DOM event type
webrtc 数据接收流程图解
makefile——杂项
常见(MySQL)面试题(含答案)
集成电路实践----D触发器
这几年让你大呼惊人的AI应用,都离不开这项技术
webrtc 有关 SDP 部分的解析流程分析
二、QT界面开发--新建C语言工程
页面返回顶部和固定导航栏js基础案例
只出现一次的数字||| —— 哈希映射、异或位运算+分治思想
smart_rtmpd 的 NAT 映射方式使用说明
2022-07-21 第六小组 瞒春 学习笔记
【时间序列模型】AR模型(原理剖析+MATLAB代码)
2022-07-19 第五小组 瞒春 学习笔记
支付系列文章:PCI合规能力建设
网络运维系列:远程服务器登录、配置与管理
2022-0801 第六小组 瞒春 学习笔记
【数据读写】csv文件与xls/xlsx文件
【IP基本原理-ARP原理】
makefile——pattern rule