当前位置:网站首页>Restricted linear table
Restricted linear table
2022-07-07 23:43:00 【Min, Hello, Xun】
List of articles
Stack (Stack)
The basic concept of stack
- Follow the first in, last out rule
- Can not traverse
- The data elements in the stack comply with ” Last in, first out ”(First In Last Out) Principles , abbreviation FILO structure .
- Only insert and delete operations can be performed at the top of the stack .


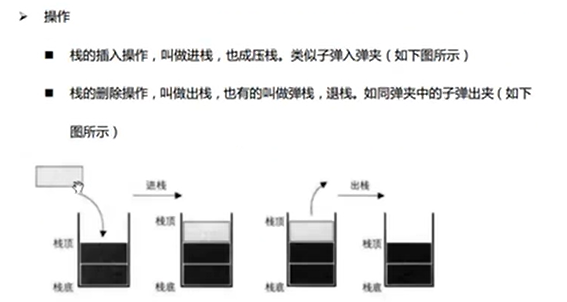
Sequential storage of stacks
 Example :
Example :
- Create a SeqStack.h The header file
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
// Array to simulate the sequential storage of stack
#define MAX_SIZE 1024
#define SEQSTACK_TRUE 1
#define SEQSTACK_FALSE 0
typedef struct SEQSTACK
{
void* data[MAX_SIZE];
int size;
}SeqStack;
// Initialization stack
SeqStack* Init_SeqStack();
// Push
void Push_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack, void* data);
// Back to top of stack element
void* Top_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack);
// Out of the stack
void Pop_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack);
// Determine whether it is null
int IsEmpty(SeqStack* stack);
// Returns the number of elements in the stack
int Size_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack);
// Empty stack
void Clear_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack);
// The destruction
void FreeSpace_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack);
- Build a SeqStack.c The source file
#include "SeqStack.h"
// Initialization stack
SeqStack* Init_SeqStack()
{
SeqStack* stack = (SeqStack*)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)
{
stack->data[i] = NULL;
}
stack->size = 0;
return stack;
}
// Push
void Push_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack, void* data)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (data == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (stack->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
return;
}
stack->data[stack->size] = data;
stack->size++;
}
// Back to top of stack element
void* Top_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (stack->size == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
return stack->data[stack->size-1];// From an array 0 At the beginning
}
// Out of the stack
void Pop_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (stack->size == 0)
{
return;
}
stack->data[stack->size-1] = NULL;
stack->size--;
}
// Determine whether it is null
int IsEmpty(SeqStack* stack)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
if (stack->size == 0)
return SEQSTACK_TRUE;
return SEQSTACK_FALSE;
}
// Returns the number of elements in the stack
int Size_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack)
{
return stack->size;
}
// Empty stack
void Clear_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < stack->size; i++)
{
stack->data[i] = NULL;
stack->size = 0;
}
}
// The destruction
void FreeSpace_SeqStack(SeqStack* stack)
{
if (stack == NULL)
{
return;
}
free(stack);
}
- Build a 03 Sequential storage of stacks .c The source file , To test
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include"SeqStack.h"
typedef struct PERSON
{
char name[21];
int age;
}person;
int main()
{
// Create a stack
SeqStack* stack = Init_SeqStack();
// Create data
person p[3]=//==
{
{
" Zhang San ",19},
{
" Li Si ",18},
{
" Wang Wu ",20}
};
// Data on the stack
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Push_SeqStack(stack, &p[i]);
}
//person p1 = { " Zhang San ",19 };//==
//person p2 = { " Li Si ",18 };
//person p3 = { " Wang Wu ",20 };
Data on the stack
//Push_SeqStack(stack, &p1);
//Push_SeqStack(stack, &p2);
//Push_SeqStack(stack, &p3);
// Output
while (Size_SeqStack(stack) > 0)
{
// Access the top element of the stack
person* person = Top_SeqStack(stack);
printf(" full name :%s Age :%d\n", person->name, person->age);
// Pop up top element , Out of the stack
Pop_SeqStack(stack);
}
// Free memory
FreeSpace_SeqStack(stack);
return 0;
}
result :
full name : Wang Wu Age :20
full name : Li Si Age :18
full name : Zhang San Age :19
Chain storage of stacks
Example :
- Build a LinkStack.h The header file
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct LINKNODE
{
struct LINKNODE* next;
}LinkNode;
// Chain stack
typedef struct LINKSTACK
{
LinkNode head;
int size;
}LinkStack;
// Initialization function
LinkStack* Init_LinkStack();
// Push
void Push_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack, LinkNode* data);
// Out of the stack
void Pop_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack);
// Back to top of stack element
LinkNode* Top_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack);
// Returns the number of stack elements
int Size_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack);
// Empty stack
void Clear_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack);
// Destroy the stack
void FreeSpace_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack);
- Build a LinkStack.c The source file
#include"LinkStack.h"
// Initialization function
LinkStack* Init_LinkStack()
{
LinkStack* lstack = (LinkStack*)malloc(sizeof(LinkStack));
lstack->head.next= NULL;
lstack->size = 0;
return lstack;
}
// Push
void Push_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack, LinkNode* data)
{
if (lstack == NULL )
{
return;
}
if (data == NULL)
{
return;
}
data->next = lstack->head.next;// When inserting the linked list , First arrange who is connected to the right side of the node to be inserted
lstack->head.next = data;
lstack->size++;
}
// Out of the stack
void Pop_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack)
{
if (lstack == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (lstack->size == 0)
{
return;
}
// The first valid node
LinkNode* pnext = lstack->head.next;
lstack->head.next =pnext->next;
lstack->size--;
}
// Back to top of stack element
LinkNode* Top_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack)
{
if (lstack == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (lstack->size == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
return lstack->head.next;
}
// Returns the number of stack elements
int Size_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack)
{
if (lstack == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
return lstack->size;
}
// Empty stack
void Clear_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack)
{
if (lstack == NULL)
{
return;
}
lstack->head.next = NULL;
lstack->size = 0;
}
// Destroy the stack
void FreeSpace_LinkStack(LinkStack* lstack)
{
if (lstack == NULL)
{
return;
}
free(lstack);
}
- Build a 04 Chain storage of stacks Source file
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include"LinkStack.h"
typedef struct PERSON
{
LinkNode node;
char name[21];
int age;
}person;
int main()
{
// Create a stack linked list
LinkStack* lstack = Init_LinkStack();
// Create data
person p1, p2, p3,p4,p5;
strcpy(p1.name, " One by one ");
strcpy(p2.name, " Two two ");
strcpy(p3.name, " sensei ");
strcpy(p4.name, " Wanton ");
strcpy(p5.name, " Wu Wu ");
p1.age = 19;
p2.age = 30;
p3.age = 20;
p4.age = 18;
p5.age = 22;
// Push
Push_LinkStack(lstack, (LinkNode*)&p1);// When writing elements , You need to convert the element into , Initial data type , Such as LinkNode*
Push_LinkStack(lstack,(LinkNode*)&p2);
Push_LinkStack(lstack, (LinkNode*)&p3);
Push_LinkStack(lstack, (LinkNode*)&p4);
Push_LinkStack(lstack, (LinkNode*)&p5);
// Output
while (Size_LinkStack(lstack) > 0)
{
// Take out the top element of the stack
person* person = Top_LinkStack(lstack);
printf(" full name :%s Age :%d\n", person->name, person->age);
// Pop up top element , Out of the stack
Pop_LinkStack(lstack);
}
// Destroy the stack
FreeSpace_LinkStack(lstack);
return 0;
}
result :
full name : Wu Wu Age :22
full name : Wanton Age :18
full name : sensei Age :20
full name : Two two Age :30
full name : One by one Age :19
queue (Queue)
Basic concept of queue

Sequential storage of queues
- Array simulates the sequential storage of queues
Example :
- Create a SeqQueue.h The header file
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1024
typedef struct SEQQUEUE
{
void* data[MAX_SIZE];
int size;
}SeqQueue;
// initialization
SeqQueue* Init_SeqQueue();
// The team
void Push_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue, void* data);
// Return to team leader element
void* Front_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
// Out of the team
void Pop_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
// Return to the end of the team
void* Back_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
// Return size
int Size_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
// Clear queue
void Clear_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
// The destruction
void Free_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue);
- Build a SeqQueue.c Source file
#include "SeqQueue.h"
// initialization
SeqQueue* Init_SeqQueue()
{
SeqQueue* squeue = (SeqQueue*)malloc(sizeof(SeqQueue));
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; i++)// because data It's an array , So every array element has to be NULL
{
squeue->data[i] = NULL;
}
squeue->size = 0;
return squeue;
}
// The team
void Push_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue, void* data)
{
// The left side of the array is the head of the team , Add elements at the end
if (squeue == NULL || data == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (squeue->size == MAX_SIZE)
{
return;
}
squeue->data[squeue->size] = data;
squeue->size++;
}
// Return to team leader element
void* Front_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
if (squeue == NULL||squeue->size==0)
{
return NULL;
}
return squeue->data[0];
}
// Out of the team
void Pop_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
// Start at the head of the team , You need to move elements
if (squeue == NULL || squeue->size == 0)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < squeue->size-1; i++)// Put the following elements , Move to the front , Overwrite the previous
{
squeue->data[i] = squeue->data[i + 1];
}
squeue->size--;
}
// Return to the end of the team
void* Back_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
if (squeue == NULL||squeue->size==0)
{
return NULL;
}
return squeue->data[squeue->size-1];
}
// Return size
int Size_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
if (squeue == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
return squeue->size;
}
// Clear queue
void Clear_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
if (squeue == NULL)
{
return;
}
squeue->size = 0;
}
// The destruction
void Free_SeqQueue(SeqQueue* squeue)
{
if (squeue == NULL)
{
return;
}
free(squeue);
}
- Build a 05 Sequential storage of queues .c Source file
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include "SeqQueue.h"
typedef struct PERSON
{
char name[21];
int age;
}person;
int main()
{
// Create a queue
SeqQueue* squeue = Init_SeqQueue();
person p[3] =
{
{
" Hee hee ",25},
{
" ha-ha ",24},
{
" ha-ha ",26}
};
// Data in queue
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Push_SeqQueue(squeue,&p[i]);
}
// Output
while (Size_SeqQueue(squeue) > 0)
{
// Take out the team leader element
person* p = Front_SeqQueue(squeue);
printf(" full name :%s Age :%d\n", p->name, p->age);
// Pop up element from team head
Pop_SeqQueue(squeue);
}
// The destruction
Free_SeqQueue(squeue);
return 0;
}
result :
full name : Hee hee Age :25
full name : ha-ha Age :24
full name : ha-ha Age :26
Chain storage of queues
- Nodes include data field and pointer field .
- The data field is void* type , There are header nodes and nodes .
- The header node is of pointer type , When joining the team, you need to create a new node , And open up space for it .
Example :
- Create a LinkQueue.h The header file
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
// The node of the chain queue
typedef struct LINKNODE
{
void* data;// Node data
struct LINKNODE* next;
}LinkNode;
// Chain queues
typedef struct LINKQUEUE
{
LinkNode* head;
LinkNode* tail;// Caudal node
int size;
}LinkQueue;
// Initialize queue
LinkQueue* Init_LinkQueue();
// The team
void Push_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue, void* data);
// Go back to team leader
void* Front_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue);
// Out of the team
void Pop_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue);
// Return to the end of the team
void* Back_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue);
// Return size
int Size_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue);
// Clear queue
void Clear_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue);
// The destruction
void Free_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lququ);
- establish LinkQueue.c Source file
#include"LinkQueue.h"
// Initialize queue
LinkQueue* Init_LinkQueue()
{
LinkQueue* lqueue = (LinkQueue*)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueue));
lqueue->head= NULL;
lqueue->tail = NULL;
lqueue->size = 0;
}
// The team , Add elements from the end of the team
void Push_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue, void* data)
{
if (lqueue == NULL || data == NULL)
{
return;
}
// Create a new node
LinkNode* newnode = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (lqueue->head== NULL)
{
lqueue->head = lqueue->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
lqueue->tail->next = newnode;
lqueue->tail = lqueue->tail->next;
}
lqueue->size++;
}
// Go back to team leader
void* Front_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL||lqueue->size==0)
{
return NULL;
}
return lqueue->head->data;
}
// Out of the team
void Pop_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL || lqueue->size == 0)
{
return;
}
LinkNode* pdel = lqueue->head;
//LinkNode* pnext = lqueue->head;
lqueue->head = lqueue->head->next;;
lqueue->size--;
free(pdel);
}
// Return to the end of the team
void* Back_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL || lqueue->size == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
return lqueue->tail->data;//
}
// Return size
int Size_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
return lqueue->size;
}
// Clear queue
void Clear_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL)
{
return;
}
lqueue->size = 0;
}
// The destruction
void Free_LinkQueue(LinkQueue* lqueue)
{
if (lqueue == NULL)
{
return;
}
free(lqueue);
}
- establish 06 Chain storage of queues .c Source file
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include"LinkQueue.h"
typedef struct PERSON
{
char name[21];
int age;
int score;
}person;
int main()
{
// Create a queue
LinkQueue* lqueue = Init_LinkQueue();
// Create data
person p[3]=
{
{
" tearful ",25,98},
{
" Grass ",23,89},
{
" Tree tree ",26,99}
};
// Data in the team
for (int i = 0; i < 3;i++)
{
Push_LinkQueue(lqueue, &p[i]);
}
// Take out the team leader element
person* fnode = Front_LinkQueue(lqueue);
printf(" The element of the team head is —— full name :%s Age :%d achievement :%d\n", fnode->name, fnode->age, fnode->score);
// Take out the tail element
person* bnode = Back_LinkQueue(lqueue);
printf(" The element at the end of the team is —— full name :%s Age :%d achievement :%d\n", bnode->name, bnode->age, bnode->score);
while (lqueue->size>0)
{
// Output
person* per = Front_LinkQueue(lqueue);
printf(" full name :%s Age :%d achievement :%d\n", per->name, per->age, per->score);
Pop_LinkQueue(lqueue);
}
// The destruction
Free_LinkQueue(lqueue);
return 0;
}
result :
The element of the team head is —— full name : tearful Age :25 achievement :98
The element at the end of the team is —— full name : Tree tree Age :26 achievement :99
full name : tearful Age :25 achievement :98
full name : Grass Age :23 achievement :89
full name : Tree tree Age :26 achievement :99
边栏推荐
- JNI uses asan to check memory leaks
- SAP HR奖罚信息导出
- Chisel tutorial - 02 Chisel environment configuration and implementation and testing of the first chisel module
- Access database query all tables SQL
- Extract the file name under the folder under win
- HB 5469民用飞机机舱内部非金属材料燃烧试验方法
- Design and implementation of spark offline development framework
- How to login and enable synchronization function in Google browser
- Home appliance industry channel business collaboration system solution: help home appliance enterprises quickly realize the Internet of channels
- Display the server hard disk image to the browser through Servlet
猜你喜欢

B_QuRT_User_Guide(38)
SAP HR family member information
Anxinco EC series modules are connected to the multi protocol access products of onenet Internet of things open platform

Interface
Summary of SQL single table query 2020.7.27

2022 certified surveyors are still at a loss when preparing for the exam? Teach you how to take the exam hand in hand?
Chisel tutorial - 02 Chisel environment configuration and implementation and testing of the first chisel module
SAP memory parameter tuning process

B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(38)
MySQL架构
随机推荐
Map operation execution process
Open source hardware small project: anxinco esp-c3f control ws2812
平衡二叉树【AVL树】——插入、删除
[untitled]
BSS 7230 航空内饰材料阻燃性能测试
ASP. Net query implementation
postgis学习
Slam interview summary
HDU - 1260 Tickets(线性DP)
2022.7.7-----leetcode.648
Lm12 rolling heikin Ashi double K-line filter
二叉排序树【BST】——创建、查找、删除、输出
B_QuRT_User_Guide(38)
Arbre binaire équilibré [Arbre AVL] - Insérer et supprimer
Summary of SQL single table query 2020.7.27
Apng2gif solutions to various problems
Sequence of entity layer, Dao layer, service layer and controller layer
受限线性表
Download AWS toolkit pycharm
archery安装测试