当前位置:网站首页>MySQL Architecture
MySQL Architecture
2022-07-07 23:38:00 【Clock in the opposite direction 197】
Review notes
Install here docker Installation is not elaborated here :Docker install mysql5.7( Turn on binlog function 、 Modify character )_ Clock in the opposite direction 197 The blog of -CSDN Blog _docker mysql Turn on binlog
Catalog
1.MySQL Character set related operations
3.SQL_mode Setting up reasonable
5. The relationship between database and file system
6. Representation of database in file system
7. User and permission management
13. Storage engine introduction
1.MySQL Character set related operations
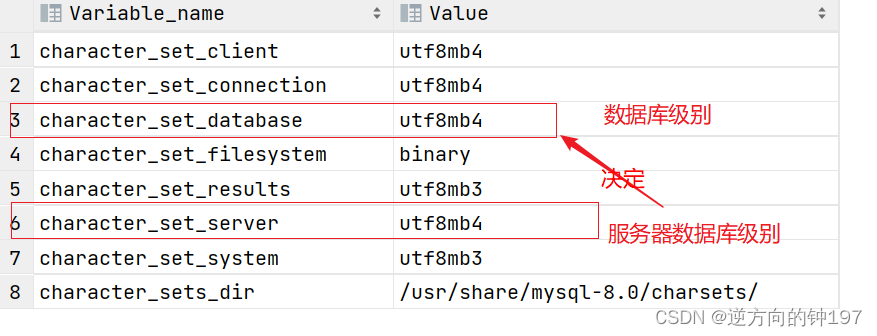
Add :5.7 Version of view character set :
show variables like 'character%';
or
show variables like '%char%';Character sets at all levels
1 Server level 、2 Database level 、3 Table level 、4 Column level Character sets can be set for each character set
 、
、
2.SQL Case specification
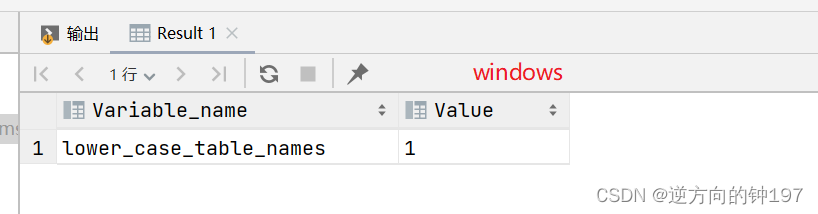
windows Case insensitive , stay linux Lower case sensitivity
0 Indicates case sensitivity ,1 Indicates case insensitive
# Check whether it is sensitive
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%lower_case_table_names%'windows
linux
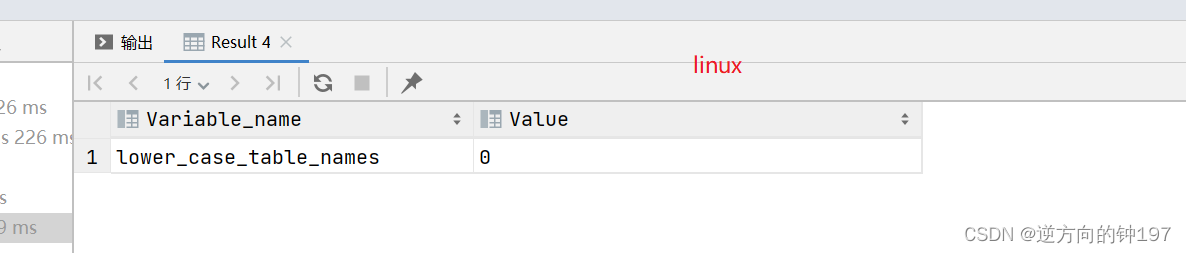
Linux The rules :
Widows The rules :
Case insensitive in
Set up Linux Case sensitive
stay mysql5.7 in : need my.cnf Configuration of [mysqlId] Add lower_case_table_names=1 And restart the server
stay mysql8.0 in : You need to delete /var/lib/mysql Catalog , Then modify the configuration file , start-up mysql
SQL Write suggestions
1. Then all keywords and function names are capitalized
2. Database name , Table name , Table alias , All field names are lowercase
3.sql Statement must be in ; ending
3.SQL_mode Setting up reasonable
The main function is to set different levels of data verification
Loose mode :
give an example : Set up name char(3), There are too many insertion times 3, such as abc123, At this time, the insertion will not report an error , And only insert abc
The main use of : Data migration
Strict mode :
For the loose model, this error reporting is the strict model
View and set up
see
select @@session.sql_mode;
or
select @@global.sql_mode;
or
show variables like 'sql_mode';Temporary settings
set SESSION sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; # overall situation
set GLOBAL sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; # Current session Permanent settings
stay my.cnf Modify... In configuration file , Restart again
[mysqld]
sql_mode=ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR _DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION4.MySQL Data directory for
windows Next
Linux Next
linux see mysql Related documents find / -name mysql
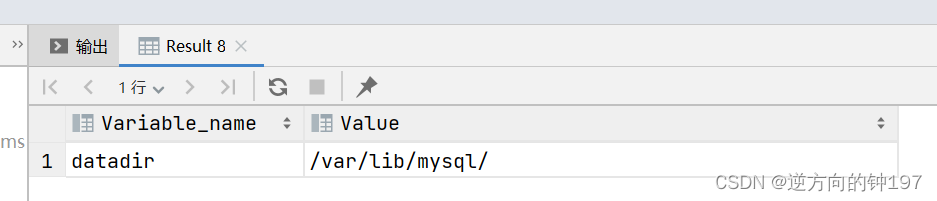
View the database storage path show variables like 'datadir'
5. The relationship between database and file system
View the default database show database
6. Representation of database in file system
Two storage engines Innodb,MyIsAM
Innodb :
5.7:
ibdata1 Location :/var/lib/mysql/qing Table space of the system , Storing table data
SYSTEM tablespace and independent tablespace settings , stay my.cnf
[server]
innodb_file_per_table=0 # 0: Represents the use of system tablespaces ; 1: Represents the use of independent tablespaces Check the default
show variables like 'innodb_file_per_table';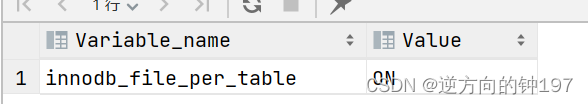
8.0:
stay 8.0 in .frm and .ibd Amalgamated , Only .ibd 了
Proof of merger :
ibd2sdi --dumpfile= Create a piece name by yourself .txt The file to parse .ibd
MyIsAM:
characteristic : Data and indexes are stored separately
Create table :
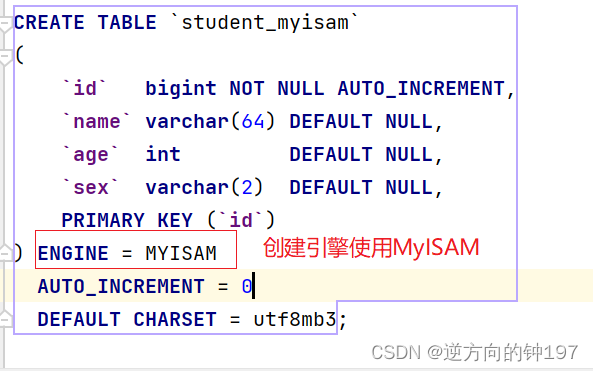
5.7:
There are three files after creation
student_myisam.MYD # Save table data
student_myisam.MYI # Storage index
student_myisam_363.frm8.0:
difference 5.7 .frm Turned into .sdi

7. User and permission management
7.1 User management
Usually use mysql -u root -p password
Full version login
mysql -h Host name ( Default localhost) -P Port number -p password Database name -e sql sentence ;To view the user
use mysql;
select Host,User from user;Add users
# % Indicates that any address can be accessed
create user 'qing' identified by '123456';
# Indicates that only local connections are supported
create user 'qing'@'localhost' identified by '83348535';View current user permissions
# View permissions
show grants ;Change user name
# Change user name
update mysql.user set User='ming' where User='qing';Refresh the permissions
# Refresh the permissions
flush privileges ;Delete account
# Delete account
drop user 'ming';
drop user 'ming'@'localhost';Change the current user password
# Set the password of the current user
alter user user() identified by '83348535';
# Change the current password
set password ='abc';Change other user passwords
use mysql;
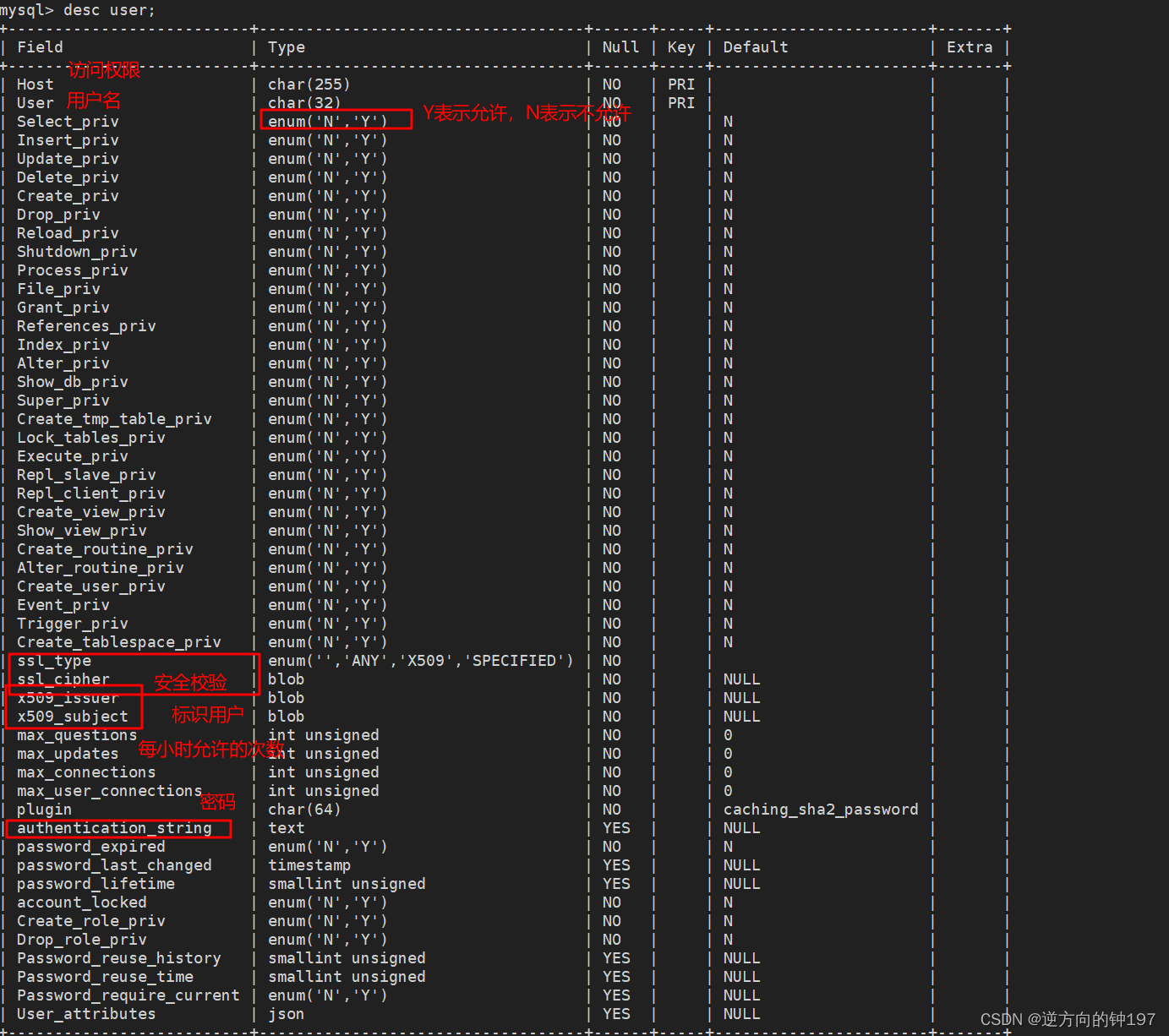
desc user;
# The password is specially encrypted
select Host,User,authentication_string from user;
# Change other user passwords
alter user 'qing'@'%' identified by '123456';
set password for 'qing'@'%'=' password ';
7.2 Rights management
When you first started creating users , At this time, you need to give permission to Yongfu
Show the current user permissions
# View permissions
show grants ;
# or
SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_USER;
# or
SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_USER();
# View all permission lists
show privileges;
View the user's global permissions
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'user'@' The host address ' ;Authority granting principle :
1. The minimum authority to meet the requirements
2. Restrict the user's Login Host , limit io Or the Internet IP paragraph
3. Set a password that meets the password complexity
4. Clean up unwanted users regularly
Authority granted to
ps: The created user has no way to create another user , If you give your permission to others
REVOKE jurisdiction 1, jurisdiction 2,… jurisdiction n ON Database name . The name of the table FROM user name @ Address of the user ;Need to add parameters
with grant option
give an example :
GRANT SELECT,INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE ON database . surface TO '[email protected]'@'%'
# Assign all permissions to qing user
grant all privileges on *.* to 'qing'@'%';Take back authority
REVOKE jurisdiction 1, jurisdiction 2,… jurisdiction n ON Database name . The name of the table FROM user name @ Address of the user ;give an example :
ps: Re login is useful
# Take back all permissions of the whole database and table
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM [email protected]'%';
# Take back mysql Insert, delete, modify and query permissions for all tables under the database
REVOKE SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE ON mysql.* FROM [email protected];7.3 Permissions on the table
mysql Control users' access to data through permission table , The permission table is stored and then mysql In the database ,mysql According to the contents of the permission table, give each user the corresponding permission , These permissions are important for ,user surface ,db surface ,prcs_priv( Set operation permissions for stored procedures and stored functions ),tables_priv( Table authority ),colums_priv( List of permissions )
user surface :
db surface :
It indicates the problem of permission to a specific database
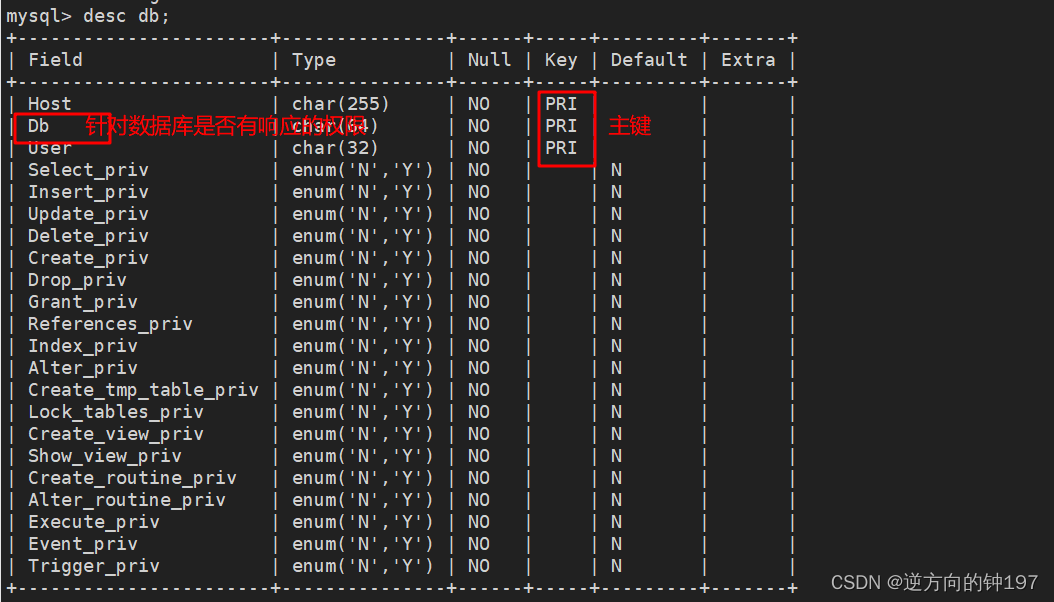
desc tables_priv;
Indicates the corresponding permissions of a table 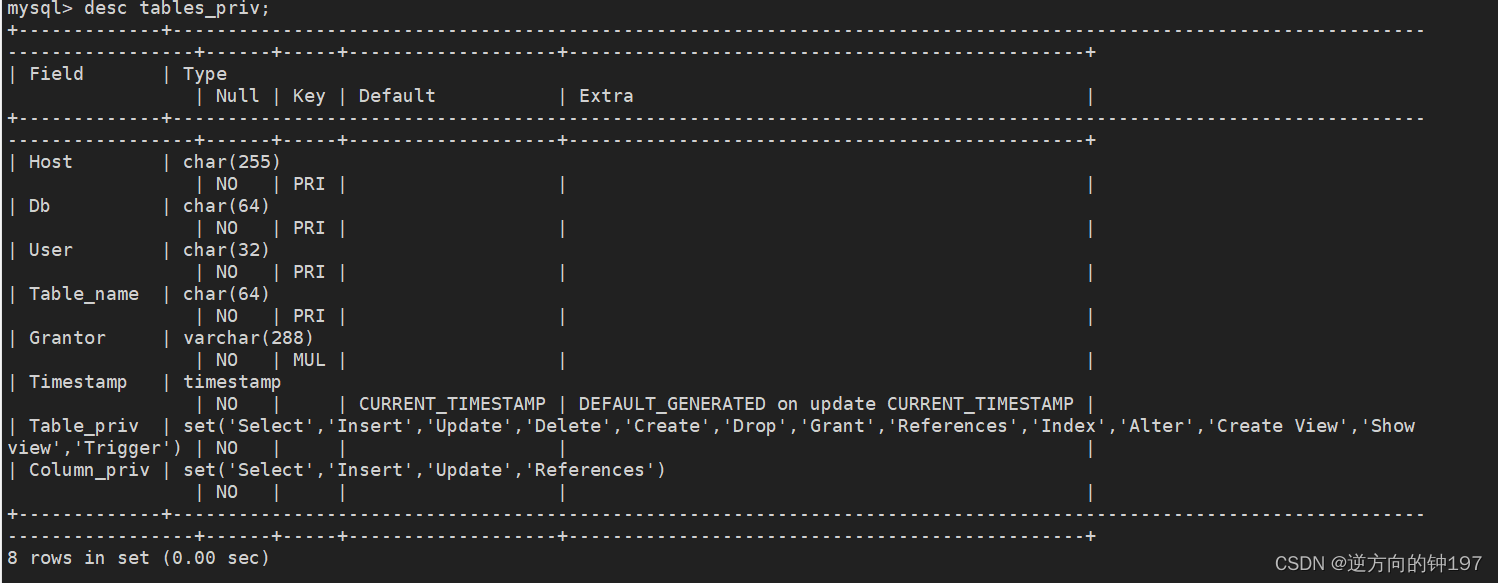
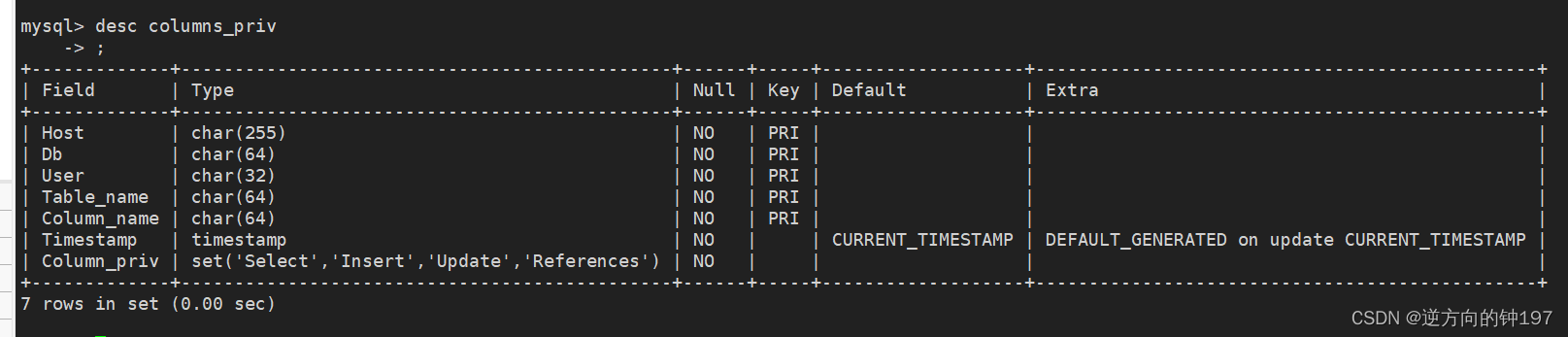
desc columns_priv;
Whether the corresponding field of the corresponding data table has permission
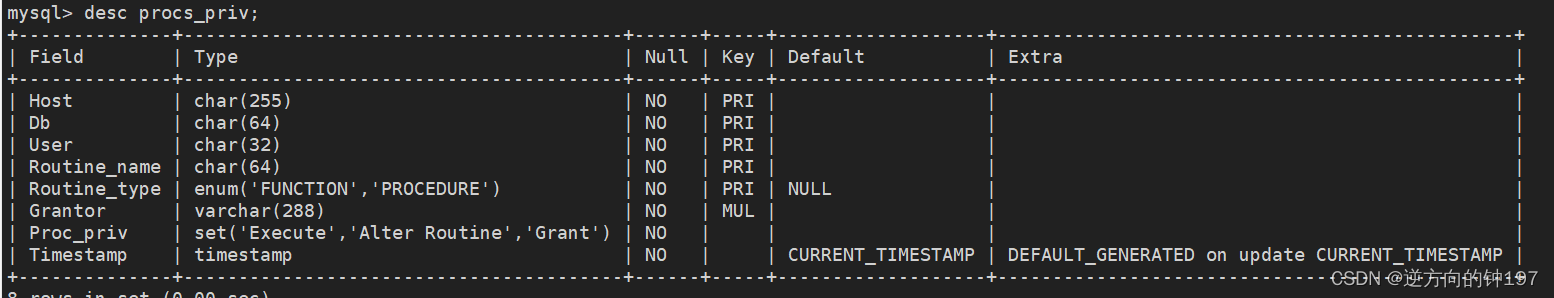
desc procs_priv;
Set operation permissions for stored procedures and stored functions
8. Role management
8.0 Newly introduced concept , from oracle Borrowed concepts
Concept : Roles are sets of permissions , You can add or move permissions for roles , Users are given roles , At the same time, they are also given the right to feel . And like an account , Role ownership is granted and revoked .
In short :mysql There are multiple accounts , There are multiple roles in the account
ps: When a role is created, it does not have corresponding permissions , You need to activate yourself
Create the role
# Create the role For more than one character , Connection No
create role 'manager'@'%';
# To give permission
grant select,update on database .* to ' role ';View role permissions
show grants for ' role '@'%';Recycling permissions
REVOKE jurisdiction ON Table name FROM ' role ';give an example :
# Revoke authority
REVOKE INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON school.* FROM 'school_write';
# View permissions
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'school_write';Delete the role
# Multiple use , Connected to a
DROP ROLE ' role ';Give permission to the user
GRANT ' role ' TO ' Roles granted '@'localhost';
SHOW GRANTS FOR ' Roles granted '@'localhost';Activate role
1. Administrator activation
# Use set default role The command activates the character
SET DEFAULT ROLE ALL TO ' role '@'localhost';2. Parameter setting , Default activation
# Check to see if
show variables like 'activate_all_roles_on_login';
# hold off Change to on
SET GLOBAL activate_all_roles_on_login=ON;
Revoke user activation
REVOKE role FROM user;give an example :
# Revoke user information
# revoke kangshifu User school_read role .
REVOKE 'school_read' FROM ' role '@'localhost';
# see
SHOW GRANTS FOR ' role '@'localhost';Set mandatory roles (mandatory role)
The mandatory role is the default role for each account created , No need to set it manually , Mandatory roles cannot be revoke( revoke ) perhaps drop( Delete )
The way 1: modify my.cnf To configure , Set before service startup
[mysqld]
mandatory_roles='role1,[email protected],[email protected]%.atguigu.com'The way 2: Runtime settings
# After the system restarts, it still It works
SET PERSIST mandatory_roles = 'role1,[email protected],[email protected]%.example.com';
# Failure after system restart
SET GLOBAL mandatory_roles = 'role1,[email protected],[email protected]%.example.com'; 9. Configuration file usage
9.1 Profile format
# Specific startup options
[server]
# Specific startup options
[mysqld]
[mysqld_safe]
[client]
[mysql]
[mysqladmin]
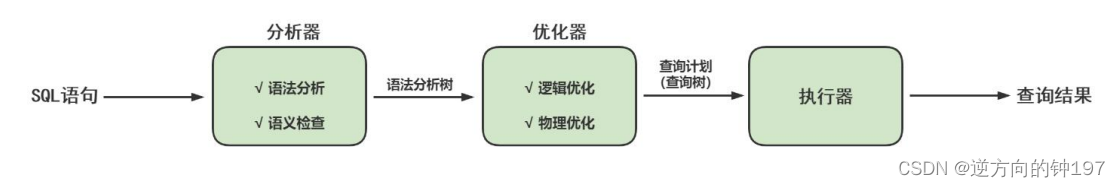
10. Logical architecture
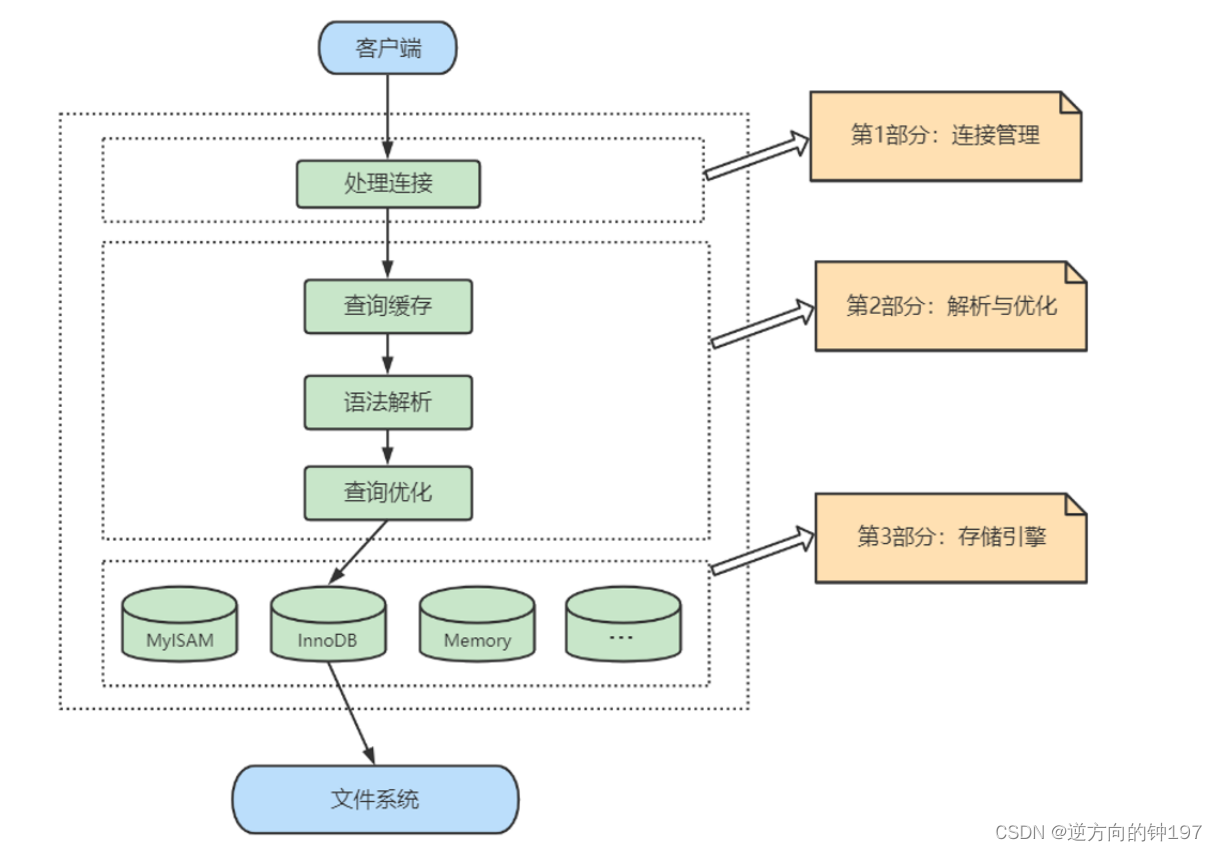
Execution order
1.Mysql Client programs outside the server -> 2. Connection pool -> 3.SQL Interface -> 4. The query cache -> 5. Parser -> 6. Optimizer -> 7. Plug in storage engine -> 8. file system -> 9. The query cache -> 10.sql Interface 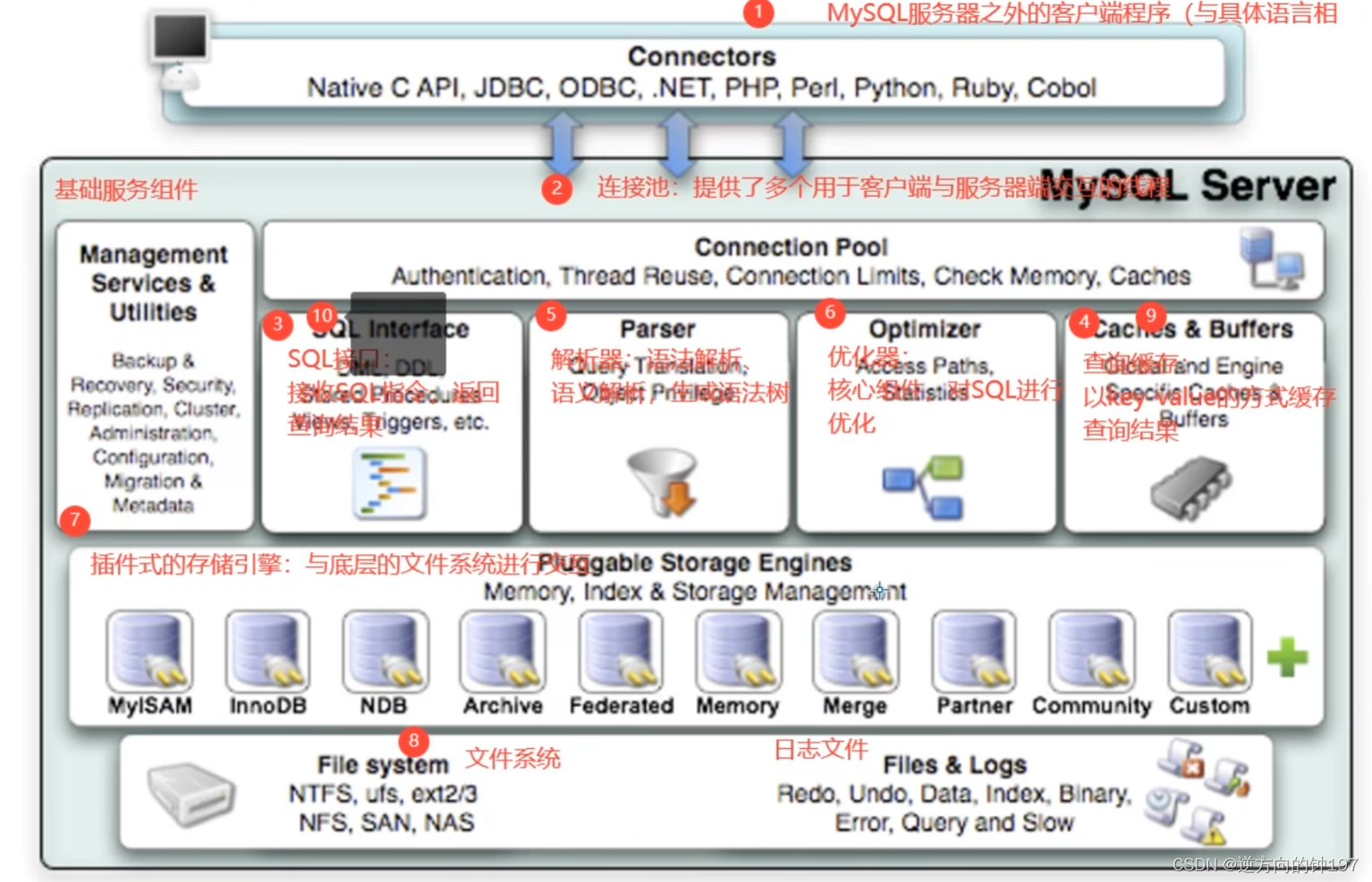
The main body is divided into three layers
adjoining course -> Service layer -> Engine layer 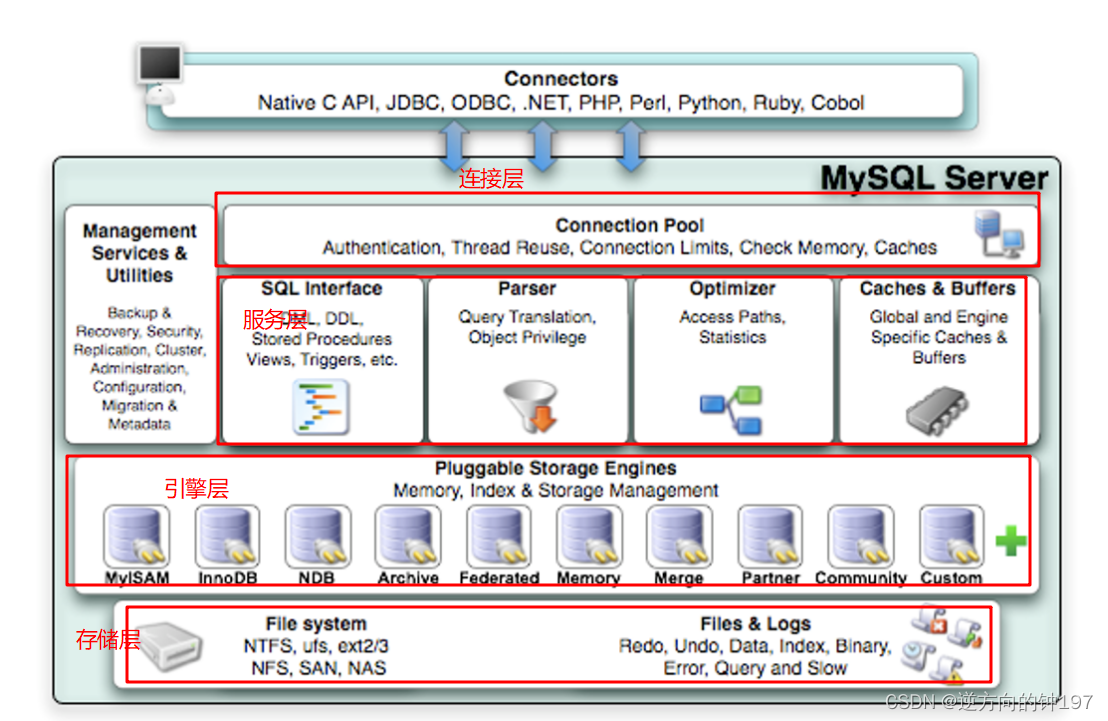
adjoining course
Connect MYSQL Before server , do TCP Connect , Verify the account number and password after three handshakes
The user password is not correct , received Access denied for user error , The client program completes execution
User password authentication passed , From the permission table, you will find out the permission of the account and the connection Association , The following permission judgment logic , All rely on the supervision authority at this time
Mainly create two pools 1) Connection pool 2) Thread pool
Service layer
SQL Interface: SQL Interface
1) Receive the user's SQL command , And returns the result of the query that the user needs . such as SELECT ... FROM It's called SQL Interface
#mysql8.0 Check whether the execution plan is enabled
select @@profiling;
#profiling=0 Means closing ,1 Open for indication
show variables like 'profiling';
# Start the implementation plan
set profiling=1;Caches & Buffers: Query cache component
# Display storage engine
show engines;11.SQL Execute the process
ps: The query cache 8.0 Abandoned , Hit ratio is low , The two statements must be the same , Off by default
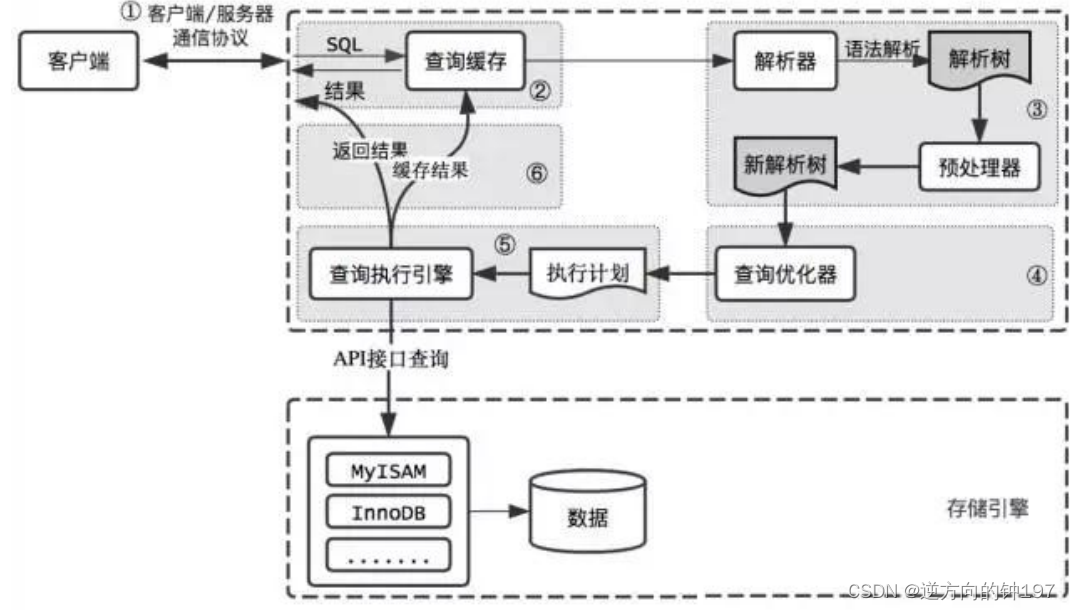 The query cache
The query cache
Instructions
# Check whether the cache is enabled
show variable like '%query_cache_type'
# View cache
show status like'%Qcache%'Parser
Yes sql Perform analytical analysis
Lexical analysis : Those are keywords , Those are fields
Syntax analysis : Whether the grammar meets
Optimizer
It will be determined in the optimizer that SQL Statement execution path , For example, according to Full search , Or according to Index search etc. .
In the query optimizer , Can be divided into Logical query Optimization phase and Physical query Optimization stage .
actuator
View permissions 、 Call the storage engine, such as InnoDB、MyISAM Wait, and then call the storage engine system
Main process
12. Storage engine operation
A storage engine is a structure that represents a table , Different storage engines represent different structures
View engine
show engines;
# perhaps
show engines \G;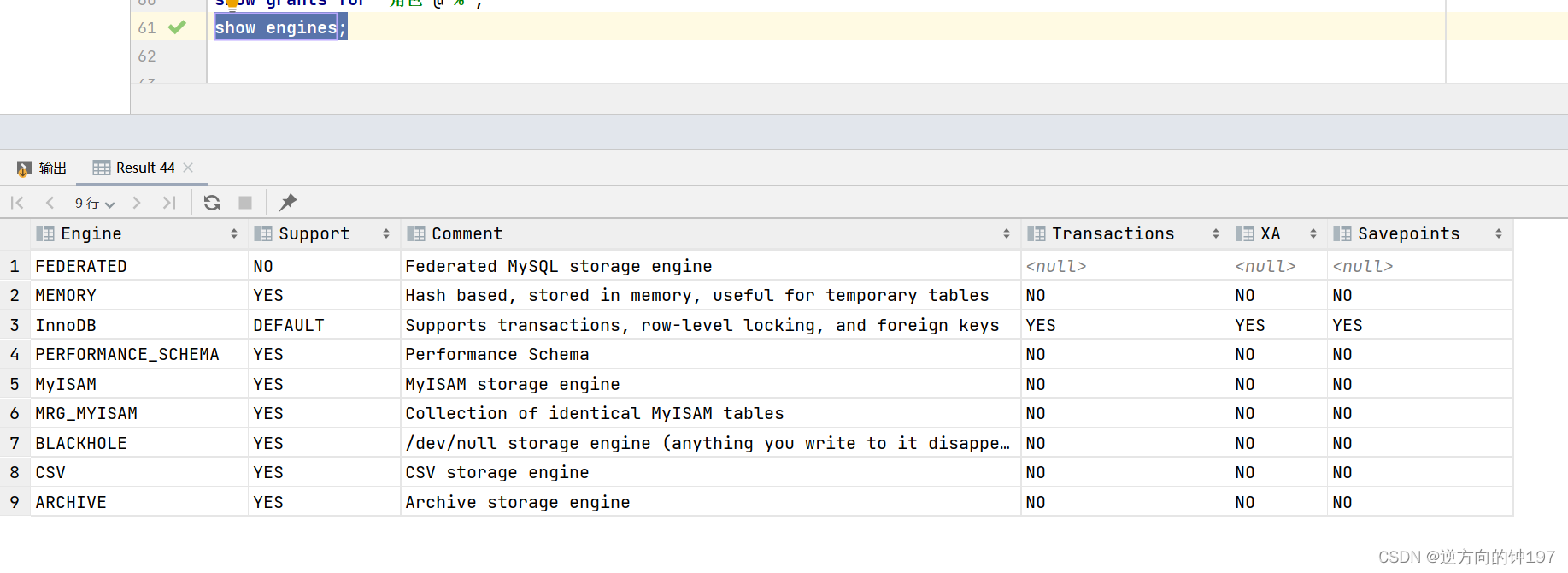
View the default storage engine
show variables like '%storage_engine%';
# or
SELECT @@default_storage_engine;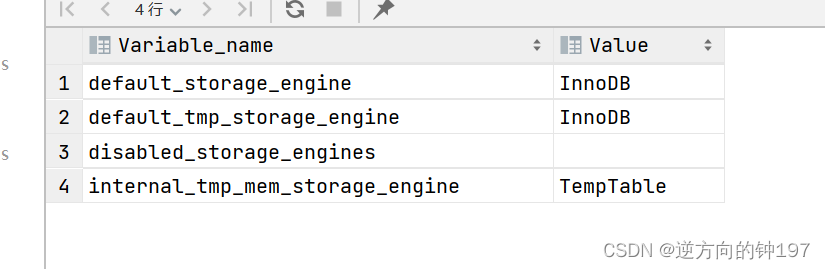
Modify the default storage engine
1) Directly modifying
SET DEFAULT_STORAGE_ENGINE=MyISAM;2) Modify the configuration file
default-storage-engine=MyISAM
# Restart the service
systemctl restart mysqld.serviceCreate the specified storage engine
CREATE TABLE Table name (
Create table statement ;
) ENGINE = Storage engine name ;Modify the storage engine of the table
ALTER TABLE Table name ENGINE = Storage engine name ;
# After modifying the view table structure
SHOW CREATE TABLE Table name 13. Storage engine introduction
3. There is additional constant storage for data statistics . so count(*) The query efficiency is very high
4. Table structure surface .frm Storage table structure surface .MyD Store the data surface .MYI Storage index
application : Read only applications or read-only businesses
Archive engine : For data archiving
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Mobile heterogeneous computing technology - GPU OpenCL programming (basic)
伸展树(一) - 图文解析与C语言实现

C inheritance and interface design polymorphism

2022注册测绘师备考开始 还在不知所措?手把手教你怎么考?
UE4_ Ue5 combined with Logitech handle (F710) use record

产业共融新势能,城链科技数字峰会厦门站成功举办
ASP. Net core middleware request processing pipeline

Anxin can internally test offline voice module vb-01 to communicate with esp-c3-12f
C cat and dog

【实验分享】通过Console口登录到Cisco设备
随机推荐
Unity3d learning notes 5 - create sub mesh
C number of words, plus ¥, longest word, average value
[stm32+esp8266 connect Tencent cloud IOT development platform 2] stm32+esp8266-01s connect Tencent cloud
USB (XVII) 2022-04-15
Open source hardware small project: anxinco esp-c3f control ws2812
Slam interview summary
B_QuRT_User_Guide(36)
移动端异构运算技术 - GPU OpenCL 编程(基础篇)
Oracle string sorting
Understand TCP's three handshakes and four waves with love
Unity3d learning notes 4 - create mesh advanced interface
USB (XV) 2022-04-14
One week learning summary of STL Standard Template Library
Dependency injection
First week of July
IDEA 2021.3. X cracking
C method question 1
USB (XIV) 2022-04-12
Experience sharing of system architecture designers in preparing for the exam: the direction of paper writing
PCB wiring rules of PCI Express interface