当前位置:网站首页>C language - pointer one touch ※
C language - pointer one touch ※
2022-07-26 04:43:00 【minghanhan778】
C Language pointer is a big difficulty for beginners to learn and understand , The pointer to C Language can be called C The soul of language , For beginners, the standard to judge whether it is a pointer is whether there is * , But is it true ? Or what are the types of pointers , This article uses easy to understand language to help beginners learn pointer , Understand the pointer , Use pointer !
Then let's start !
Catalog
1. Initial understanding of pointer
2. What is a pointer variable ?
Two 、 Initial order of pointer
3.1 The origin of wild pointer
0. About array names ( About arr And &arr The difference between them, etc )
One 、 What is a pointer ?
1. Initial understanding of pointer
There are two points to understand pointer .
First , A pointer is a pointer in memory The number of the smallest unit , In a nutshell “ Address ”
secondly , Usually said pointer , Is usually Pointer to the variable , Variables used to store memory addresses
In short , It's memory , It's the address
2. What is a pointer variable ?
Before understanding what pointer variables are , We need to understand every value , Every quantity needs space to be stored in the computer , The name of this space can be called address , adopt &( Fetch address operator ) You can take out the address of this quantity . The following example :


adopt VS The monitoring function of , Be able to find a The value of is 10,a The address of is 0x00effac, Namely &a yes 0x00effac.
Here we must Strictly distinguish between a The value of is equal to a The address of
a The value of is int The type is 10 a The address is 0x00effac The type is int*( Get to know )
So for storage a The variable of the address of is the pointer variable !!
So the value of the pointer variable here is the address of a variable , The address of the pointer variable is its own address !!
Examples are as follows :


Create a Pointer to the variable p, take a The address of is assigned to p, Through monitoring ,p The value is &a ,&p Namely p The address of
Only this and nothing more , I have a certain understanding of pointers
To sum up :
Pointer to the variable , The variable used to hold the address .( The values stored in the pointer are treated as addresses ).
Pointer to the variable , It's also a variable ! It can be changed ! Only the address is stored , Not a certain value !
The pointer is used to Storage address Of , An address is a unique identifier of an address space .
The size of all pointers is 32 Bit platform is 4 Bytes , stay 64 Bit platform is 8 Bytes .
Two 、 Initial order of pointer
1. Pointer and pointer type
The data types are int float double char short long etc.
Does the pointer have a corresponding pointer type ? The answer is yes ! Corresponding to the following :


The type of pointer variable , To correspond to the type of the corresponding stored variable , Storage int type Just apply int* To define the pointer
Here you can see , The way pointers are defined is : type + * So the meaning of the corresponding pointer below should be understood 
Secondly, the meaning of pointer type is not just to Type of storage , also Other special meanings , The demonstration is as follows :

summary : The type of pointer determines how big the pointer moves forward or backward ( distance ).
2. Dereference of pointer *
As mentioned earlier &( Fetch address operator ) Then it's equivalent to finding Your room number, ! Then you need to open the door The key , So that is Dereference operation *
We can understand first *&a The meaning of

So contrast &( Address operation )* We can understand it as value taking operation ,* The object of is the address , Can be accessed !
We put &a Assign to a pointer variable p1, therefore p1 Equivalent to &a, We can get *p1
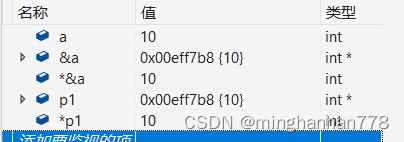
From the above case, we can get *p1 Namely a p1 yes a The address of , adopt * You can find a 了 !
3. Wild pointer
Many beginners have heard of wild pointer from his population , Have you heard of the power of wild pointer . If the pointer can be compared to an arrow , It refers to the address of a variable , Re pass * You can find this variable for assignment and other operations . As the name suggests , The wild pointer is just pointing *, Proceed again * Dereference will change the uncertain quantity , Will cause great harm !
Concept : The position of the pointer is unknown ( Random 、 incorrect 、 There is no definite limit to )
3.1 The origin of wild pointer
Pointer not initialized Examples are as follows :

I want to pass the pointer p1 receive a The address of , Proceed again * Dereference operation pair a Assign values to , But if there is no assignment to the pointer , Then the object pointed to by the pointer is unknown , Extremely dangerous !
If we want to define a pointer , But now I don't know the object , Then we can do it first NULL assignment

The pointer is out of bounds Examples are as follows :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {0};
int *p = arr;
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<=11; i++){
// When the pointer points to an array arr The scope of time ,p It's a wild pointer
*(p++) = i;
}
return 0;
}
3.2 Avoid wild pointer
1. Pointer initialization
2. Watch out for the pointer
3. Pointer to space release even if set to NULL
4. Avoid returning the address of a local variable // Avoid returning the address of a local variable when calling a function
5. Check the validity of the pointer before using it
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int *p = NULL;
//....
int a = 10;
p = &a;
if(p != NULL)// Check pointer validity
{
*p = 20;
}
return 0;
}Sum up : We have learned what pointer is , What is a pointer variable , The type of pointer variable , Two meanings of pointer variables ,& Fetch address operator ,* Dereference operator , What is the wild pointer , The origin of wild pointer , How to avoid wild pointer . It's almost enough to learn about the initial application of so many pointers , Next is the higher-order learning of pointer , More difficult operation , More brainstorming !
are you ready !Are you ready?

By * Anyone who points to it can learn !
3、 ... and 、 Advanced pointer
0. About array names ( About arr And &arr The difference between them, etc )
Before further studying pointers , Review the little knowledge about array names , Sometimes the array name represents the address of the first element of the array , Sometimes it means the whole array , Often confused , Here is a little summary !
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
return 0;
}
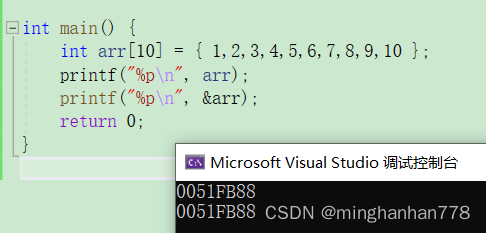
Ask yourself a question first ? You can distinguish arr And &arr The difference between ?
Through the above code, you will find that the results are consistent , But are they really the same ? Let's demonstrate the following code
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
printf("arr = %p\n", arr);
printf("arr+1 = %p\n", arr+1);
printf("&arr = %p\n", &arr);
printf("&arr+1 = %p\n", &arr+1);
return 0;
}

Through the above code, we can find that :
arr+1 Skip is a int The length of and &arr+1 Skip the length of the entire array Namely int*10 The length of
arr The real meaning is arr[0] The address of , Is the whole array The first address of the first element
&arr The real meaning is The address of the entire array
Is there any exception ? The answer is yes ! But not much Just remember if sizeof( Array name ) What you get is the length of the entire array

Summary : About Array name
except sizeof( Array name ) Represents the length of the entire array , Other times The array name indicates Address of the first element of the array .
Array name +1 Skip the first element of the array
& Array name Represents the address of the entire array
& Array name +1 Skip the address of the entire array
1. Character pointer char*
Among the types of pointers, we know that one pointer type is Character pointer char* ;
General usage :
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'w';
char* p = &ch;
*p = 'm';
return 0;
}

besides ,char* There is another way to use character pointers
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
const char* pstr = "hello cainiao.";// Here is to put a string into pstr Is it in the pointer variable ?
printf("%s\n", pstr);
return 0;
}
Many students will put const char* pstr = "hello cainiao."; This code is understood as hold hello cainiao. On the pstr in
It's actually the address of the first element h It's in storage The pointer pstr in !
To help better understand const char* Demonstrate the following code !
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
char str1[] = "hello cainiao.";
char str2[] = "hello cainiao.";
const char* str3 = "hello cainiao.";
const char* str4 = "hello cainiao.";
if (str1 == str2)
printf("str1 and str2 are same\n");
else
printf("str1 and str2 are not same\n");
if (str3 == str4)
printf("str3 and str4 are same\n");
else
printf("str3 and str4 are not same\n");
return 0;
}

Did you send out soul torture ???what?
About first if() It should be well understood
Even if the contents of two character arrays are consistent , But the content of comparing characters and numbers cannot be used == To compare ( Use strcmp), here == The comparison is the address ,str1 And str2 It represents the address of the first element , Two character array , The address must be different , So it's definitely not equal
About the second if()
Through the above code, you will find , The addresses of two constant character arrays are actually the same ???
0. here str3 and str4 Points to the same constant string .
1. actually C/C++ The constant string is stored in a separate memory area , When a few pointers . When pointing to the same string , They actually point to the same block of memory .
2. But use the same constant string to Initializing different arrays will open up different memory blocks . therefore str1 and str2 Different ,str3 and str4 Different .

So if str3 And str4 Refers to different constant strings , Then it won't be the same , Another simple test .

understand char*,const char* And the storage of constant strings in memory !
2. Pointer array
First, play a word game , whether Distinguished pointer array still Array pointer The central word of .
Pointer array The understanding of should be compared integer array , Floating point array , A character array ......, So the central word is Array
Compare and understand , It can be clearly concluded that An array of pointers is an array , The data type stored in the array is pointer !
Compare and define pointer arrays
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
char str1[] = "hello cainiao.";// A character array
int a[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };// integer array
float b[10] = { 1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0 };// Floating point array
//......
char* pstr[10]; // Character pointer array
int* pint[10]; // Array of integer pointers
float* pf[10]; // Floating point pointer array
//......
return 0;
}
The application of pointer array
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
int c = 0;
int d = 1;
int e = 1;
int f = 9;
int* pint[6] = {&a,&b,&c,&d,&e,&f}; // Array of integer pointers
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
printf("%d", *pint[i]);
}
return 0;
}

3. Array pointer
Array pointer The understanding of is to compare Integer pointer , Floating point pointer , Character pointer ...... The central word is The pointer
therefore Array pointer It's a pointer to an array , Namely A pointer stores the address of the array !
int *p1[10];
int (*p2)[10];
//p1, p2 What are the differences ?int *p1[10]; Pointer array
* The priority of is relatively low, so p1 With the first [] Combine with * combination , therefore int* Is the type of contents stored in the array It's the pointer
int (*p2)[10]; Array pointerstay () With the first * combination , therefore p2 It's a pointer , The type pointed to is int (*)[10]
Compare and define array pointers
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int* a ;// Integer pointer
float* b ;// Floating point pointer
double* c ;
char* d ;// Character pointer
//......
int arr1[6] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
float arr2[6] = { 1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0 };
char arr3[6] = { 'n','i','h','a','o','\0' };
int(*pint)[6] = &arr1;// Integer array pointer The type is int(*)[6]
float(*pf)[6] = &arr2;// Floating point array pointer The type is float(*)[6]
char(*pch)[6] = &arr3;// Character array pointer The type is char(*)[6]
//......
return 0;
}
Array pointer , Is the address used to receive the array , therefore We must add & Fetch address operator , If not , Is to get the address of the first element of the array , There will be big mistakes , want Note note !
Application of array pointer
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
void print_arr1(int arr[3][5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_arr2(int(*arr)[5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
print_arr1(arr, 3, 5);
// Array name arr, Represents the address of the first element
// But the first element of a two-dimensional array is the first row of a two-dimensional array
// So the message here is arr, It's actually equivalent to the address on the first line , Is the address of a one-dimensional array
// You can use an array pointer to receive
print_arr2(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}4. A function pointer
Pointers are used to store addresses , Then you can see that every function also has an address with a function pointer !
Let's start with a piece of code
#include <stdio.h>
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", test);
printf("%p\n", &test);
return 0;
} 
So let's say Function name and & Function name All means Address of function
The definition of function pointer applies
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*p)(int, int) = add;
printf("%d", p(1, 2));
return 0;
}int (*p)(int, int) = add;
A function pointer p The type is int(*)(int,int) first int Is the return type ,(int,int) It's a parameter list
5. Function pointer array
int Add(int x,int y) {
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y) {
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
int Diy(int x, int y) {
return x / y;
}
int main() {
int (*pfArr[])(int, int) = { 0, Add, Sub, Mul, Diy };// Function pointer array
printf("%d\n", (pfArr[1])(2, 4));
printf("%d\n", (pfArr[2])(2, 4));
printf("%d\n", (pfArr[3])(2, 4));
printf("%d\n", (pfArr[4])(2, 4));
return 0;
}
summary
That's what we're going to talk about today , This article only briefly introduces the use of pointers , There is an initial order of pointer , Higher order of pointer , I hope students can get what they need , The study of pointer cannot stop at reading articles , It is more important to practice , Code friends, come on !
边栏推荐
- Calculate the curvature of discrete points (matlab)
- Build a maker Education Laboratory for teenagers
- Analyzing the curriculum design evaluation system of steam Education
- 补位,稍后补上
- Creative design principle of youth maker Education
- mongoDB为什么快
- FFmpeg 视频添加水印
- 创建MySQL数据库的两种方式
- Yapi installation
- Postman imports curl, exports curl, and exports corresponding language codes
猜你喜欢

Yapi installation

Optimization analysis and efficiency execution of MySQL

Keil V5 installation and use

数据库启动报:ORA-29702: error occurred in Cluster Group Service

IEC61131 数据类型与 C#数据类型的对应

「游戏引擎 浅入浅出」4. 着色器

Study of const of constant function

Face database collection summary

User defined type details

can 串口 can 232 can 485 串口转CANbus总线网关模块CAN232/485MB转换器CANCOM
随机推荐
Keil V5 installation and use
数组排序2
[300 + selected interview questions from big companies continued to share] big data operation and maintenance sharp knife interview question column (VIII)
Vector explanation and iterator failure
2022河南萌新联赛第(三)场:河南大学 A - 玉米大炮
7、 Restful
Phaser(一):平台跳跃收集游戏
Throttling anti shake function of JS handwritten function
Codeforces Round #807 (Div. 2)
2022 Henan Mengxin League game (3): Henan University B - reverse pair count
UE4 键盘控制开关灯
一个sql server查询截止某个日期最新的记录
Spark Structured Streaming HelloWorld
The auxiliary role of rational cognitive educational robot in teaching and entertainment
Weights & biases (II)
Postman imports curl, exports curl, and exports corresponding language codes
Whether the SQL that fails to execute MySQL is counted into the slow query?
Postman 导入curl 、导出成curl、导出成对应语言代码
AWS Support Plan
egg-sequelize JS编写