当前位置:网站首页>【DIoU CIoU】DIoU和CIoU损失函数理解及代码实现
【DIoU CIoU】DIoU和CIoU损失函数理解及代码实现
2022-08-03 05:27:00 【寻找永不遗憾】
1 引言
目标检测任务的损失函数由Classificition Loss和Bounding Box Regeression Loss两部分构成。
Bounding Box Regression Loss Function的演进路线是:
Smooth L1 Loss --> IoU Loss --> GIoU Loss --> DIoU Loss --> CIoU Loss
之前写到了 Smooth L1 Loss 、 IoU Loss 和 GIoU Loss。
本文介绍DIoU Loss 和 CIoU Loss。
2 问题分析
GIoU Loss 存在的问题:
- 出现下图中的情况时,IoU和GIoU的值都一样,此时GIoU退化为IoU, 无法区分其相对位置关系。
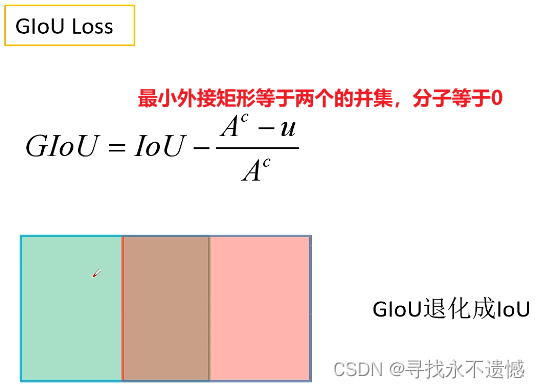
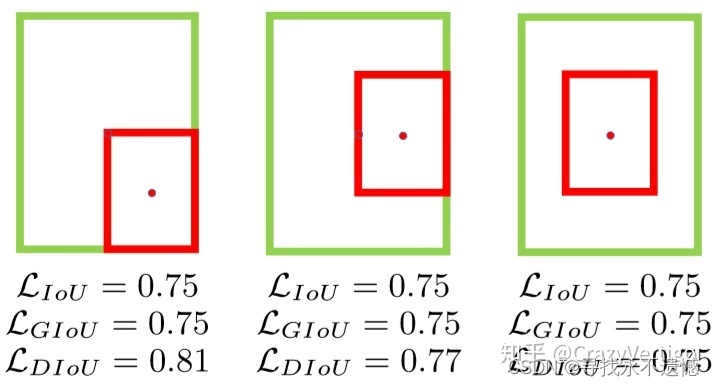
- 收敛的比较慢
- 回归的还不够准确
3 作者思考
基于IoU和GIoU存在的问题,作者提出了两个问题:
- 问题一:直接最小化预测框与目标框之间的归一化距离是否可行,以达到更快的收敛速度。
- 问题二:如何使回归在与目标框有重叠甚至包含时更准确、更快。
好的目标框回归损失应该考虑三个重要的几何因素:重叠面积,中心点距离,长宽比。
针对问题一,作者提出了DIoU Loss,相对于GIoU Loss收敛速度更快,DIoU Loss考虑了重叠面积(IoU)和中心点距离( d 2 c 2 \frac{d^{2}}{c^{2}} c2d2),但没有考虑到长宽比;
针对问题二,作者提出了CIoU Loss,其收敛的精度更高,以上三个因素都考虑到了。
4 DIoU Loss计算过程
Distance-IoU(DIoU) Loss计算过程如下: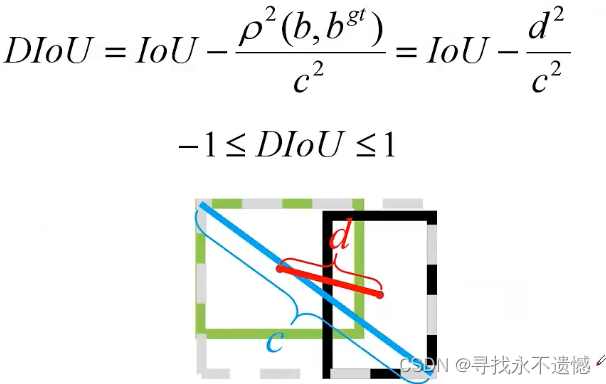
图中,b表示预测框中心点坐标, b g t b^{gt} bgt表示GT框中心点坐标。 ρ 2 ( b , b g t ) ρ^2(b, b^{gt}) ρ2(b,bgt)表示两中心点的距离的平方, c 2 c^2 c2表示两矩形最小外接矩形的对角线长度的平方。
DIoU损失能直接最小化两个box之间的距离,因此收敛速度更快。
L D I o U = 1 − D I o U L_{DIoU}=1-DIoU LDIoU=1−DIoU
当两个框重合时, L D I o U = 0 L_{DIoU}=0 LDIoU=0;当两个框相距无穷远时, L D I o U = 2 L_{DIoU}=2 LDIoU=2,故 0 ≤ L D I o U < 2 0≤L_{DIoU}<2 0≤LDIoU<2。
可以将DIoU替换IoU用于NMS算法当中,也即论文提出的DIoU-NMS, 实验结果表明有一定的提升。
DIoU相比于GIoU的优点:
DIoU Loss可以直接优化2个框之间的距离,比GIoU Loss收敛速度更快
对于目标框包裹预测框的情况,DIoU Loss可以收敛的很快,而GIoU Loss此时退化为IoU Loss收敛速度较慢
5 CIoU Loss计算过程
Complete-IoU(CIoU) Loss计算过程如下:在DIoU的基础上,考虑长宽比 α v αv αv。
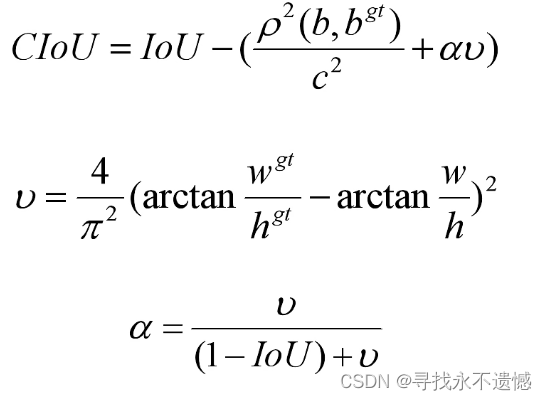
其中, α α α是用于做trade-off的参数, v v v是用来衡量长宽比一致性的参数。
CIoU Loss function的定义为
L C I o U = 1 − C I o U L_{CIoU}=1-CIoU LCIoU=1−CIoU
!注意!: CIoU loss的梯度类似于DIoU loss,但还要考虑 v v v的梯度。在长宽在 [0, 1] 的情况下, w 2 + h 2 w^2+h^2 w2+h2的值通常很小,会导致梯度爆炸,因此在 1 w 2 + h 2 \frac{1}{w^2+h^2} w2+h21实现时将替换成1。
6 IoU/GIoU/DIoU/CIoU代码实现可视化
import numpy as np
import cv2
import torch
import math
def CountIOU(RecA, RecB):
xA = max(RecA[0], RecB[0])
yA = max(RecA[1], RecB[1])
xB = min(RecA[2], RecB[2])
yB = min(RecA[3], RecB[3])
# 计算交集部分面积
interArea = max(0, xB - xA + 1) * max(0, yB - yA + 1)
# 计算预测值和真实值的面积
RecA_Area = (RecA[2] - RecA[0] + 1) * (RecA[3] - RecA[1] + 1)
RecB_Area = (RecB[2] - RecB[0] + 1) * (RecB[3] - RecB[1] + 1)
# 计算IOU
iou = interArea / float(RecA_Area + RecB_Area - interArea)
return iou
def Giou(rec1,rec2):
# 分别是矩形左上、右下的坐标
x1,y1,x2,y2 = rec1
x3,y3,x4,y4 = rec2
iou = CountIOU(rec1,rec2)
area_C = (max(x1,x2,x3,x4)-min(x1,x2,x3,x4))*(max(y1,y2,y3,y4)-min(y1,y2,y3,y4))
area_1 = (x2-x1)*(y1-y2)
area_2 = (x4-x3)*(y3-y4)
sum_area = area_1 + area_2
w1 = x2 - x1 #第一个矩形的宽
w2 = x4 - x3 #第二个矩形的宽
h1 = y1 - y2
h2 = y3 - y4
W = min(x1,x2,x3,x4)+w1+w2-max(x1,x2,x3,x4) # 交叉部分的宽
H = min(y1,y2,y3,y4)+h1+h2-max(y1,y2,y3,y4) # 交叉部分的高
# 交叉的面积
Area = W * H
# 两矩形并集的面积
add_area = sum_area - Area
# 闭包区域中不属于两个框的区域占闭包区域的比重
end_area = (area_C - add_area)/area_C
giou = iou - end_area
return giou
def Diou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
dious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:#
return dious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
dious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
# #xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax->[:,0],[:,1],[:,2],[:,3]
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
dious = inter_area / union - (inter_diag) / outer_diag
dious = torch.clamp(dious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
dious = dious.T
return dious
def bbox_overlaps_ciou(bboxes1, bboxes2):
rows = bboxes1.shape[0]
cols = bboxes2.shape[0]
cious = torch.zeros((rows, cols))
if rows * cols == 0:
return cious
exchange = False
if bboxes1.shape[0] > bboxes2.shape[0]:
bboxes1, bboxes2 = bboxes2, bboxes1
cious = torch.zeros((cols, rows))
exchange = True
w1 = bboxes1[:, 2] - bboxes1[:, 0]
h1 = bboxes1[:, 3] - bboxes1[:, 1]
w2 = bboxes2[:, 2] - bboxes2[:, 0]
h2 = bboxes2[:, 3] - bboxes2[:, 1]
area1 = w1 * h1
area2 = w2 * h2
center_x1 = (bboxes1[:, 2] + bboxes1[:, 0]) / 2
center_y1 = (bboxes1[:, 3] + bboxes1[:, 1]) / 2
center_x2 = (bboxes2[:, 2] + bboxes2[:, 0]) / 2
center_y2 = (bboxes2[:, 3] + bboxes2[:, 1]) / 2
inter_max_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
inter_min_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
out_max_xy = torch.max(bboxes1[:, 2:],bboxes2[:, 2:])
out_min_xy = torch.min(bboxes1[:, :2],bboxes2[:, :2])
inter = torch.clamp((inter_max_xy - inter_min_xy), min=0)
inter_area = inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
inter_diag = (center_x2 - center_x1)**2 + (center_y2 - center_y1)**2
outer = torch.clamp((out_max_xy - out_min_xy), min=0)
outer_diag = (outer[:, 0] ** 2) + (outer[:, 1] ** 2)
union = area1+area2-inter_area
u = (inter_diag) / outer_diag
iou = inter_area / union
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)), 2)
S = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (S + v)
w_temp = 2 * w1
ar = (8 / (math.pi ** 2)) * arctan * ((w1 - w_temp) * h1)
cious = iou - (u + alpha * ar)
cious = torch.clamp(cious,min=-1.0,max = 1.0)
if exchange:
cious = cious.T
return cious
img = np.zeros((512,512,3), np.uint8)
img.fill(255)
# 分别是矩形左上、右下的坐标
RecA = [30,30,300,300]
RecB = [60,60,350,340]
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecA[0],RecA[1]), (RecA[2],RecA[3]), (0, 255, 0), 5)
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecB[0],RecB[1]), (RecB[2],RecB[3]), (255, 0, 0), 5)
IoU = CountIOU(RecA,RecB)
GIoU = Giou(RecA,RecB)
RecA_tensor,RecB_tensor = torch.tensor([RecA]), torch.tensor([RecB])
DIoU = Diou(RecA_tensor,RecB_tensor)
CIoU = bbox_overlaps_ciou(RecA_tensor,RecB_tensor)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(img,"IOU = %.2f"%IoU,(130, 150),font,0.8,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.putText(img,"GIOU = %.2f"%GIoU,(130, 180),font,0.8,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.putText(img,"DIOU = %.2f"%DIoU,(130, 210),font,0.8,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.putText(img,"CIOU = %.2f"%CIoU,(130, 240),font,0.8,(0,0,0),2)
cv2.imshow("image",img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果输出: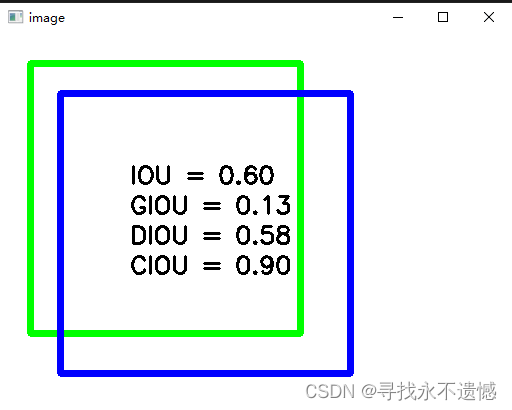
7 感谢链接
DIoU和CIOU用于目标检测与实例分割,作者已开源,可参考:
https://github.com/Zzh-tju?tab=repositories
其它感谢链接:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/94799295
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/104236411
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1yi4y1g7ro?p=4
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Unity Animation从UAS获取动画资产到编制状态机控制简单的人物动画
宝塔负载均衡配置及nfs共享
Eight, the difference between the interface of the abstract class
【面试】摸鱼快看:关于selenium/ui自动化的面试题
Oracle 11g静默安装
ue4入门学习笔记1(操作界面)
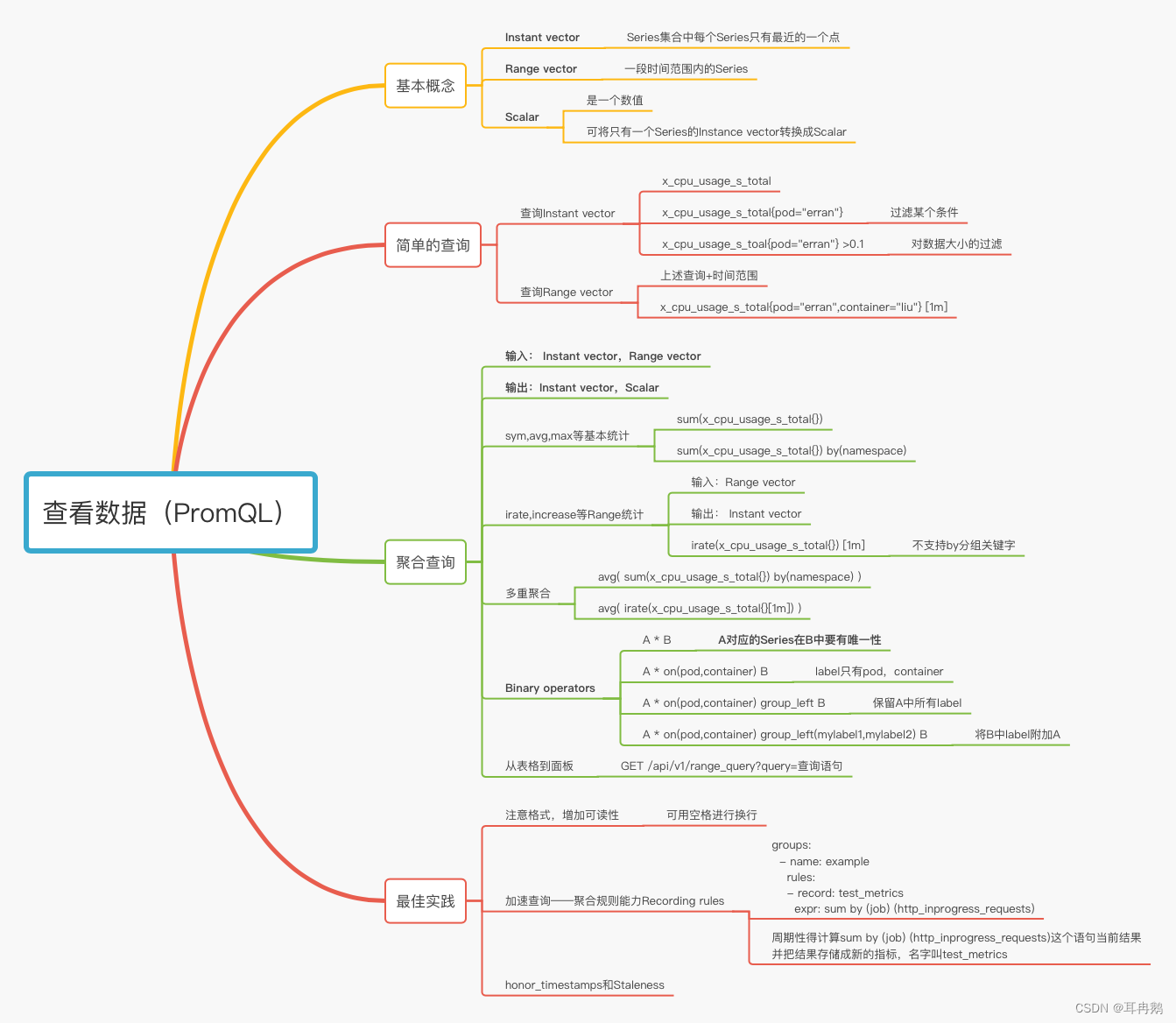
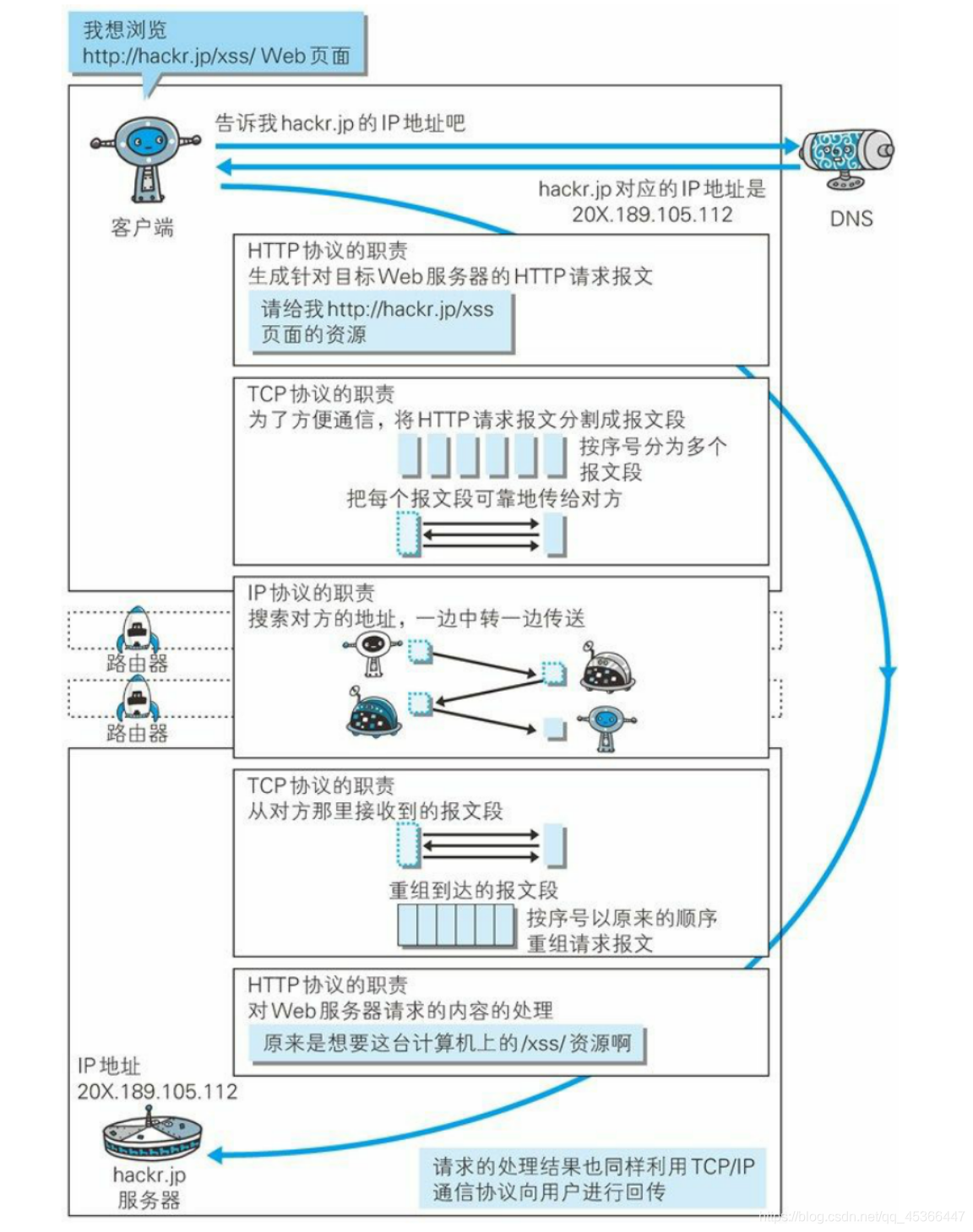
【入职第一篇知识总结- Prometheus】
802.1AS 时钟同步原理理解
次世代建模到底需要哪些美术基础
使用Powershell批量导入Task
【面试准备】游戏开发中的几个岗位分别做什么&考察侧重点
php 数组元素移动
交换机access口,hybrid口,trunk口的区别
2021-06-15
cobalt strike 的基础使用
C # program with administrator rights to open by default
./autogen.sh: 4: ./autogen.sh: autoreconf: not found
Oracle 数据库集群常用巡检命令
Zabbix历史数据清理(保留以往每个项目每天一条数据)
内网渗透之PPT票据传递攻击(Pass the Ticket)