当前位置:网站首页>Collection of practical string functions
Collection of practical string functions
2022-07-04 10:25:00 【sqjddb】
String function
>> Find the string length
strlen

String to ‘\0’ As an end sign ,strlen Function returns in a string ‘\0’ The number of characters that appear before ( It doesn't contain ‘\0’ )
The string that the argument points to must be in ‘\0’ end
Note that the return value of the function is size_t, It's unsigned
Classic examples ( Fallible ):
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
const char*str1 = "abcdef";
const char*str2 = "bbb";
if(strlen(str2)-strlen(str1)>0)
{
printf("str2>str1\n");
}
else
{
printf("srt1>str2\n");
}
return 0;
}
because strlen The return value is size_t type , therefore strlen(str2)-strlen(str1) It's also size_t type , Must be greater than zero
strlen Simulation Implementation of
List three ways
The way 1:
// Counter mode
int my_strlen(const char * str)
{
int count = 0;
while(*str)
{
count++;
str++;
}
return count;
}
The way 2:
// Cannot create temporary variable counter
int my_strlen(const char * str)
{
if(*str == '\0')
return 0;
else
return 1+my_strlen(str+1);
}
The way 3:
// The pointer - The way of the pointer
int my_strlen(char *s)
{
char *p = s;
while(*p != ‘\0’ )
p++;
return p-s;
}
>> Unlimited length string function
strcpy ( Copy string )

The source string must be in ‘\0’ end
In the source string ‘\0’ Copy to target space
The target space has to be variable , So the source string cannot be copied into the constant string
The target space has to be large enough , To ensure that the source string can be stored
strcpy Simulation Implementation of :
char *my_strcpy(char *dest, const char*src)
{
char *ret = dest;
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(src != NULL);
while((*dest++ = *src++))
{
;
}
return ret;
}
strcat ( Append string )

The source string must be in ’\0’ end
The target space has to be large enough , It can accommodate the source string
In the source string ‘\0’ Copy to target space
The target space must be modifiable
String cannot be used behind itself strcat Additional , Because first put the... Of the target string ’\0’ Cover , There is no in the string ’\0’, There will be mistakes
strcat Simulation Implementation of :
char *my_strcat(char *dest, const char*src)
{
char *ret = dest;
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(src != NULL);
while(*dest)
{
dest++;
}
while((*dest++ = *src++))
{
;
}
return ret;
}
strcmp ( Compare strings )
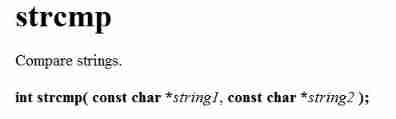
The first string is larger than the second string , Return greater than 0 The number of
The first string is equal to the second string , Then return to 0
The first string is less than the second string , Then return less than 0 The number of
strcmp Simulation Implementation of :
clever , Worthy of taste
int my_strcmp (const char * src, const char * dst)
{
assert(src != NULL);
assert(dest != NULL);
while( *src == *dst)
{
if(*str=='\0')
return 0;
++src;
++dst;
}
return( *scr-*dst);
}
>> String function with limited length
The use method is similar to the string function with unlimited length , Just specify a length , Some special requirements can be achieved , It is also safer
strncpy ( Copy the specified characters to the target space )

If the length of the source string is less than count, After copying the source string , Add... After the target 0, until count individual
strncpy Implementation method in the Library :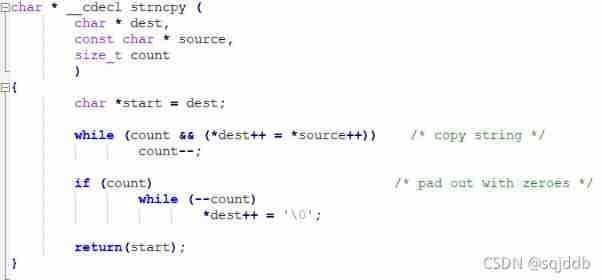
strncat ( Append the specified characters to the target space )

After addition , Add one more ’\0’
If the number of characters in the source string is less than count, After appending the source string , Just one more ’\0’
strncat Implementation method in the Library :
strncmp ( Compare the specified number of characters )

strncmp The implementation in the library is somewhat complicated :
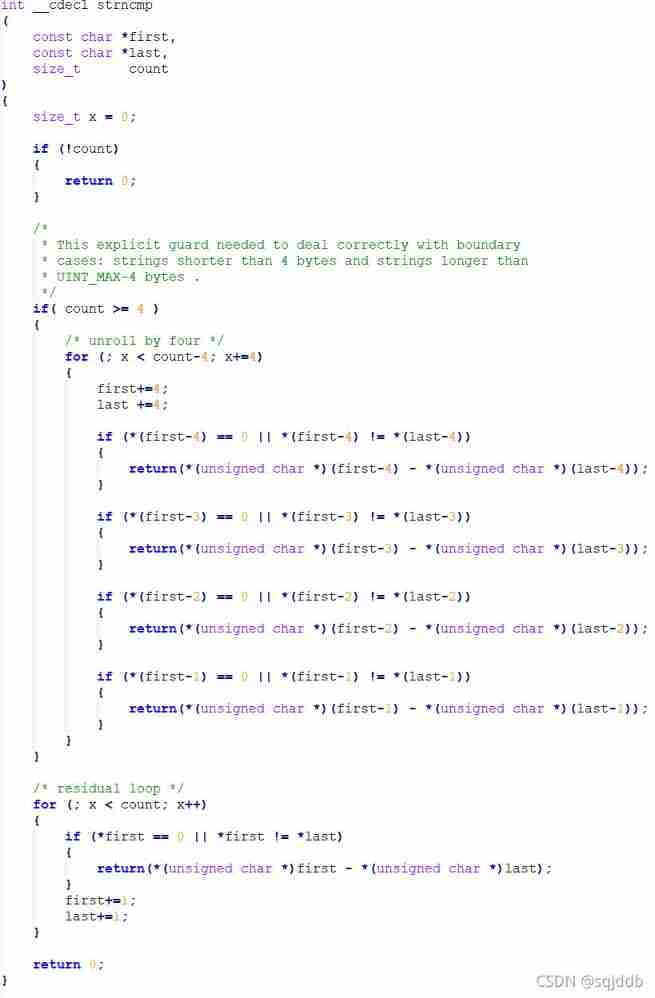
>> String search
strstr ( Find the string in the string )

strstr The implementation of the :
char *my_strstr(const char* str1, const char* str2 )
{
assert(str1);
assert(str2);
char *cp = NULL; // Point to str1 China and str2 The starting position of the comparison
char *s1 = NULL; // Point to str1 Characters being compared in
char *s2 = NULL; // Point to str Characters being compared in
if(*str2 == '\0')
return((char *)str1); // This is handled in the library function
while(*cp)
{
s1 = cp;
s2 = str2;
while(*s1 && *s2 && (*s1 == *s2))
{
s1++;
s2++;
}
if(*substr == '\0')
return cp;
cp++;
}
}
>> String segmentation
strtok ( Divide the string according to the specified character )

strDelimit Points to a collection of defined delimiters
The first parameter specifies a string , It contains 0 One or more specified delimiters
strtok Function found str Next separator in , Replace with \0 , Return a pointer to this position . ( notes :strtok Function changes the string being manipulated , So it's using strtok The string cut by the function is usually a temporary copy and can be modified .)
strtok The first argument of the function is not NULL , Function will find str The first separator in the ,strtok Function will hold its position in the string
strtok The first argument to the function is NULL , The function will start at the same position in the string that is saved , Find next separator
If there are no more tags in the string , Then return to NULL The pointer
Examples of use : use @ and . Split mailbox "[email protected]"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *p = "[email protected]";
const char* sep = "[email protected]"; // Specify the separator as '.' and '@'
char arr[30];
char *str = NULL;
strcpy(arr, p);// Make a copy of the data , Handle arr Contents of array
for (str = strtok(arr, sep); str != NULL; str = strtok(NULL, sep))
{
printf("%s\n", str);
}
}
Running results :
>> Error message report
strerror ( Return the error information corresponding to the error code )
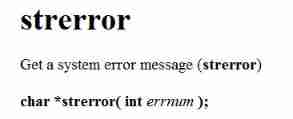
When there is an error in the program , Error labels are stored in variables errno( Standard error number , It's defined in errno.h in ), hold errno Pass to strerror function , Will return an error message
For example, open a file that does not exist :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
FILE * pFile;
pFile = fopen("unexist.txt", "r");
if (pFile == NULL)
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
//errno: Last error number
return 0;
}
Running results :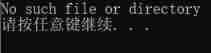
边栏推荐
- Advanced technology management - how to design and follow up the performance of students at different levels
- Hands on deep learning (42) -- bi-directional recurrent neural network (BI RNN)
- 2020-03-28
- Ruby时间格式转换strftime毫秒匹配格式
- leetcode1229. Schedule the meeting
- The time difference between the past time and the present time of uniapp processing, such as just, a few minutes ago, a few hours ago, a few months ago
- MPLS: multi protocol label switching
- 六月份阶段性大总结之Doris/Clickhouse/Hudi一网打尽
- Rhcsa12
- Latex learning insertion number - list of filled dots, bars, numbers
猜你喜欢

Hands on deep learning (44) -- seq2seq principle and Implementation
Hands on deep learning (37) -- cyclic neural network
Dynamic address book
Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)

OSPF summary

Application of safety monitoring in zhizhilu Denggan reservoir area
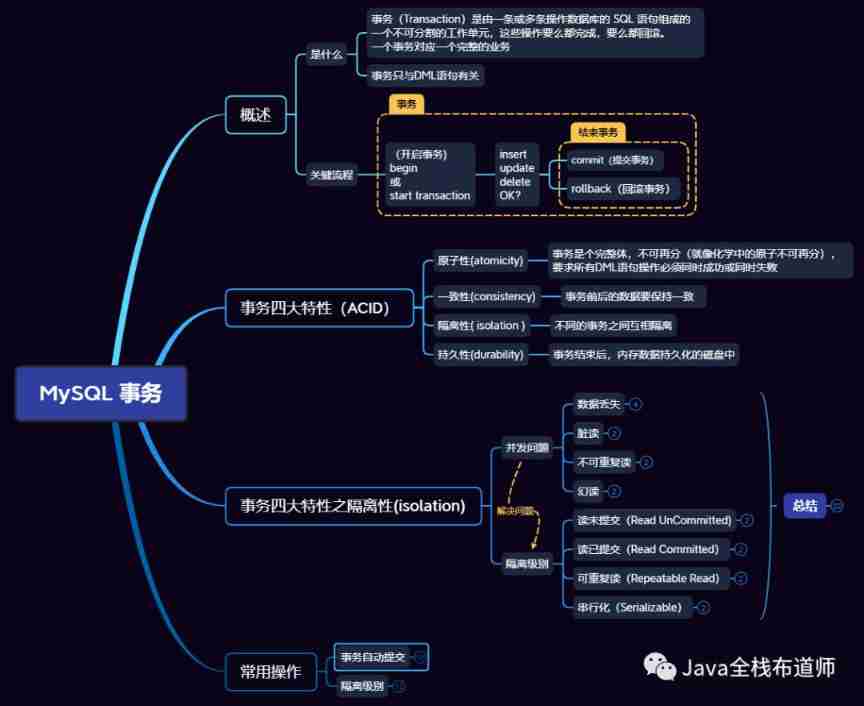
Four characteristics and isolation levels of database transactions
Hands on deep learning (45) -- bundle search

For programmers, if it hurts the most...
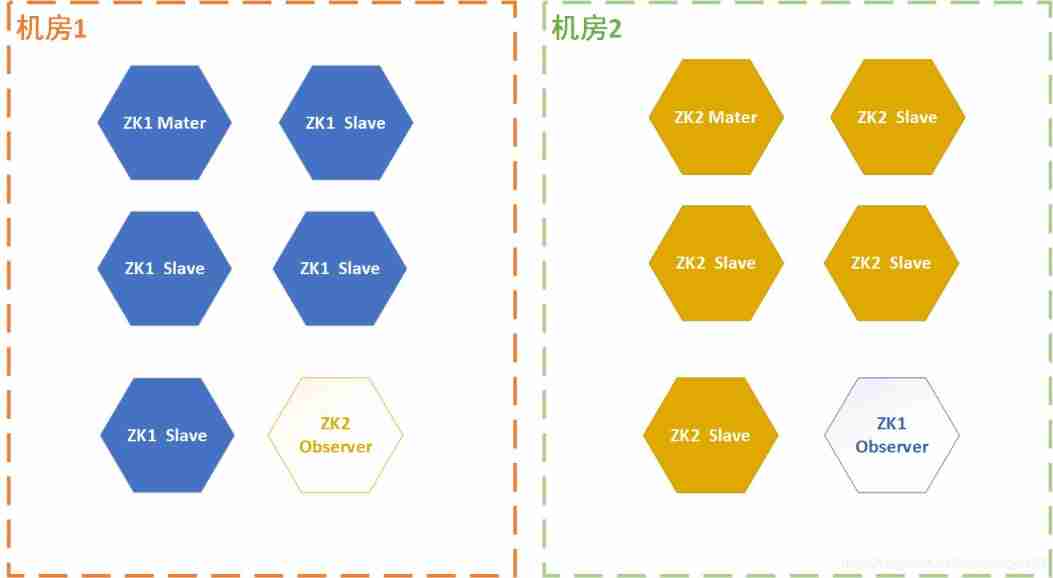
Three schemes of ZK double machine room
随机推荐
Exercise 8-10 output student grades (20 points)
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
Network disk installation
leetcode842. Split the array into Fibonacci sequences
The time difference between the past time and the present time of uniapp processing, such as just, a few minutes ago, a few hours ago, a few months ago
Number of relationship models
DCL statement of MySQL Foundation
Exercise 9-3 plane vector addition (15 points)
AUTOSAR从入门到精通100讲(106)-域控制器中的SOA
uniapp 小于1000 按原数字显示 超过1000 数字换算成10w+ 1.3k+ 显示
Exercise 9-1 time conversion (15 points)
Whether a person is reliable or not, closed loop is very important
System. Currenttimemillis() and system Nanotime (), which is faster? Don't use it wrong!
Hands on deep learning (43) -- machine translation and its data construction
leetcode1-3
OSPF comprehensive experiment
Dynamic memory management
Talk about scalability
Rhcsa day 10 operation
RHCE - day one