当前位置:网站首页>【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
2022-07-04 10:04:00 【weixin_ forty-five million nine hundred and sixty-five thousand】
Get!New
1.super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs): This sentence calls nn.Block Of __init__ function , It provides prefix( Name ) and params( Specify model parameters )
net3 = MLP(prefix='another_mlp_')
2.net.name_scope(): call nn.Block Provided name_scope() function .nn.Dense The definition of is put in this scope Inside . Its function is to prefix the names of all layers and parameters inside (prefix) Make them unique in the system .
Convolutional neural networks
Convolution :input/output 2channel
Pooling (pooling): It's similar to convolution , Look at a small window at a time , Then select the largest or average element in the small window as the output .
LeNet
Two layer convolution + Two layers are all connected
Weight format :input_filter×output_filter×height×width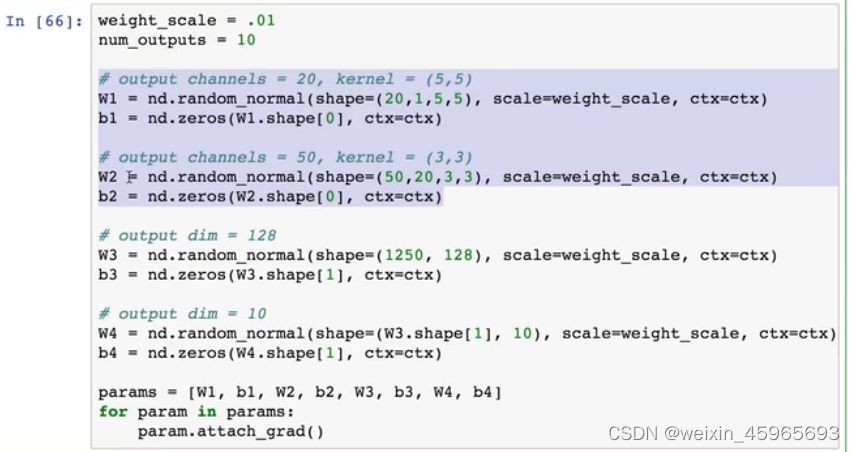
When the input data has multiple channels , Each channel will have a corresponding weight , Then it will convolute each channel and sum them up
c o n v ( d a t a , w , b ) = ∑ i c o n v ( d a t a [ : , i , : , : ] , w [ 0 , i , : , : ] , b ) conv(data,w,b)=\sum_{i}conv(data[:,i,:,:],w[0,i,:,:],b) conv(data,w,b)=i∑conv(data[:,i,:,:],w[0,i,:,:],b)
Convolution modules are usually “ Convolution layer - Activation layer - Pooling layer ”. And turn it into 2D The matrix is output to the following full connection layer .
def net(X, verbose=False):
X = X.as_in_context(W1.context)
# The first convolution
h1_conv = nd.Convolution(data=X, weight=W1, bias=b1, kernel=W1.shape[2:], num_filter=W1.shape[0])
h1_activation = nd.relu(h1_conv)
h1 = nd.Pooling(data=h1_activation, pool_type="max", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))
# The second convolution
h2_conv = nd.Convolution(data=h1, weight=W2, bias=b2, kernel=W2.shape[2:], num_filter=W2.shape[0])
h2_activation = nd.relu(h2_conv)
h2 = nd.Pooling(data=h1_activation, pool_type="max", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))
h2 = nd.flatten(h2)
# The first layer is fully connected
h3_linear = nd.dot(h2, W3) + b3
h3 = nd.relu(h3_linear)
# Layer 2 full connectivity
h4_linear = nd.dot(h3, W4) + b4
if verbose:
print('1st conv block:', h1.shape)
print('2nd conv block:', h2.shape)
print('1st dense:', h3.shape)
print('2nd dense:', h4_linear.shape)
print('output:', h4_linear)
return h4_linear

gluon
Ignore the input size
net = gluon.nn.Sequential()
with net.name_scope():
net.add(gluon.nn.Conv2D(channels=20, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'))
net.add(gluon.nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2))
net.add(gluon.nn.Conv2D(channels=50, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
net.add(gluon.nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2))
net.add(gluon.nn.Flatten())
net.add(gluon.nn.Dense(128,activation="relu"))
net.add(gluon.nn.Dense(10))
Creating neural networks block
nn.block What is it? ?– Provide flexible network definitions
stay gluon in ,nn.block It is a general component . The whole neural network can be a nn.Block, A single layer is also a nn.Block. We can ( The approximate ) Infinitely 【 nesting 】nn.Block To build new nn.Block. Mainly provide :
- Store parameters
- describe
forwardHow to execute - Automatic derivation
class MLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with self.name_scope():
self.dense0 = nn.Dense(256)
self.dnese1 = nn.Dense(10)
def forward(self, x):
return self.dense1(nd.relu(self.dense0(x)))
class FancyMLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(FancyMLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
with self.name_scope():
self.dense = nn.Dense(256)
self.weight = nd.random_uniform(shape=(256,20))
def forward(self, x):
x = nd.relu(self.dense(x))
print('layer 1:',x)
x = nd.relu(nd.dot(x, self.weight)+1)
print('layer 2:',x)
x = nd.relu(self.dense(x))
return x
fancy_mlp = FancyMLP()
fancy_mlp.initialize()
y = fancy_mlp(x)
print(y.shape)
nn.Sequential What is it? ?– The definition is simpler nn.Sequential It's a nn.Block Containers , It passes through add To add nn.Block. It automatically generates forward() function , It is added nn.Block Run one by one .
class Sequential(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Sequential, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def add(self, block):
self._children.append(block)
def forward(self, x):
for block in self._children:
x = block(x)
return x
add layer
net = nn.Sequenctial()
with net.name_scope():
net.add(nn.Dense(256, activation="relu"))
net.add(nn.Dense(10))
net.initialize()
nn The following classes are basically nn.Block Subclass , They can be nested and used easily
class RecMLP(nn.Block):
def __init__(self. **kwargs):
super(RecMLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.net = nn.Sequential()
with self.name_scope():
self.net.add(nn.Dense(256, activation="relu"))
self.net.add(nn.Dense(128, activation="relu"))
self.net.add(nn.Dense(64, activation="relu"))
def forward(self, x):
return nd.relu(self.dense(self.net(x)))
rec_mlp = nn.Sequential()
rec_mlp.add(RecMLP())
rec_mlp.add(nn.Dense(10))
print(rec_mlp)
Initialize model parameters
visit :params = net.collect_params()
class MyInit(init.Initializer):
def __init__(self):
super(MyInit, self).__init__()
self._verbose = True
def __init__weight(self, __, arr):
# Initialization weight , Use out=arr Then we don't need to specify the shape
nd.random.uniform(low=5, high=10, out=arr)
def __init__bias(self, __, arr):
# Initialize offset
arr[:] = 2
params.initialize(init=MyInit(), force_reinit=True)
print(net[0].weight.data(), net[0].bias.data())
Shared model parameters
net.add(nn.Dense(4, in_units=4, activation="relu"))
net.add(nn.Dense(4, in_units=4, activation="relu", params=net[-1].params))
Define a simple layer
The following code defines a layer to subtract the average value from the input .
from mxnet import nd
from mxnet.gluon import nn
class CenteredLayer(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(CenteredLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def forward(self, x):
return x - x.mean()
layer = CenteredLayer()# No model parameters , no need initialize
layer(nd.array([1,2,3,4,5]))
Alexnet: Deep convolution neural network
net = nn.Sequential()
# Use larger 11 x 11 Window to capture objects . Use strides at the same time 4 To greatly reduce the output height and width . The output used here is through
# Channel number ratio LeNet The middle is also much larger
net.add(nn.Conv2D(96, kernel_size=11, strides=4, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# Reduce the convolution window , Use padding as 2 To make the height and width of input and output consistent , And increase the number of output channels
nn.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=5, padding=2, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# continuity 3 Convolution layers , And use smaller convolution windows . Except for the final convolution layer , Further increase the number of output channels .
# After the first two convolution layers, no pooling layer is used to reduce the input height and width
nn.Conv2D(384, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.Conv2D(384, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, padding=1, activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2),
# Here, the output ratio of the full connection layer is LeNet A few times as big as . Use the discard layer to alleviate over fitting
nn.Dense(4096, activation="relu"), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(4096, activation="relu"), nn.Dropout(0.5),
# Output layer . Because of the use of Fashion-MNIST, So the number of categories is 10, Not in the paper 1000
nn.Dense(10))

trick: The law of abandonment dropout —— Coping with over fitting
The following operations are usually performed on the input layer or hidden layer :
- Randomly select a part of the output of this layer as the discard element
- Multiply the discarded element by 0
- Stretch the non discarded elements
Activate a part of the model run every time
def dropout(X, drop_prob):
assert 0 <= drop_prob <= 1
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
# In this case, all elements are discarded
if keep_prob == 0:
return X.zeros_like()
# Randomly select a part of the output of this layer as the discard element
mask = nd.random.uniform(0, 1, X.shape) < keep_prob
return mask * X / keep_prob
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2 = 784, 10, 256, 256
W1 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_inputs, num_hiddens1))
b1 = nd.zeros(num_hiddens1)
W2 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_hiddens1, num_hiddens2))
b2 = nd.zeros(num_hiddens2)
W3 = nd.random.normal(scale=0.01, shape=(num_hiddens2, num_outputs))
b3 = nd.zeros(num_outputs)
params = [W1, b1, W2, b2, W3, b3]
for param in params:
param.attach_grad()
drop_prob1, drop_prob2 = 0.2, 0.5
def net(X):
X = X.reshape((-1, num_inputs))
H1 = (nd.dot(X, W1) + b1).relu()
if autograd.is_training(): # The discard method is used only when training the model
H1 = dropout(H1, drop_prob1) # Add discard layer after the first layer is fully connected
H2 = (nd.dot(H1, W2) + b2).relu()
if autograd.is_training():
H2 = dropout(H2, drop_prob2) # Add and discard layers after layer 2 is fully connected
return nd.dot(H2, W3) + b3
VGG: Very deep networks using repeating elements
def vgg_block(num_convs, num_channels):
blk = nn.Sequential()
for _ in range(num_convs):
blk.add(nn.Conv2D(num_channels, kernel_size=3,
padding=1, activation='relu'))
blk.add(nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2))
return blk
def vgg(conv_arch):
net = nn.Sequential()
# Convolution layer part
for (num_convs, num_channels) in conv_arch:
net.add(vgg_block(num_convs, num_channels))
# The whole connection layer
net.add(nn.Dense(4096, activation='relu'), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(4096, activation='relu'), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Dense(10))
return net
net = vgg(conv_arch)
Batch normalization batch-norm
benefits : Convergence is faster
Each layer is normalized
Every channel normalization
mean value 0, variance 1
The mean and variance of the whole data are used in the test
But when the Party training data is huge , This calculation costs a lot . therefore , We use the moving average method to approximate (mvoing_mean and moving_variance)
def batch_norm(X, gamma, beta, is_training, moving_mean, moving_variance, eps = 1e-5, moving_momentum = 0.9):
assert len(X.shape) in (2,4)
# Full connection :batch_size x feature
if len(X.shanpe) == 2:
# The average and variance of each input dimension on the sample
mean = X.mean(axis=0)
variance = ((X - mean)**2.mean(axis=0))
# 2D Convolution :batch_size × channel × height × width
else:
# Calculate the mean and variance for each channel , Need to keep 4D The shape makes it possible to broadcast correctly
mean = X.mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)
variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)
# Deformation makes it possible to broadcast correctly
moving_mean = moving_mean.reshape(mean.shape)
moving_variance = moving_variance.reshape(mean.shape)
# Homogenization
if is_training:
X_hat = (X - mean) / nd.sqrt(variance + eps)
#!!! Update the global mean and variance
moving_mean[:] = moving_momentum * moving_mean + (1.0 - moving_momentum) * mean
moving_variance[:] = moving_momentum * moving_variance + (1.0 - moving_momentum) * variance
else:
#!!! The test phase uses the global mean and variance
X_hat = (X - moving_mean) / nd.sqrt(moving_variance + eps)
# Stretch and offset
return gamma.reshape(mean.shape) * X_hat + beta.reshape(mean.shape)
stay gluon Use in 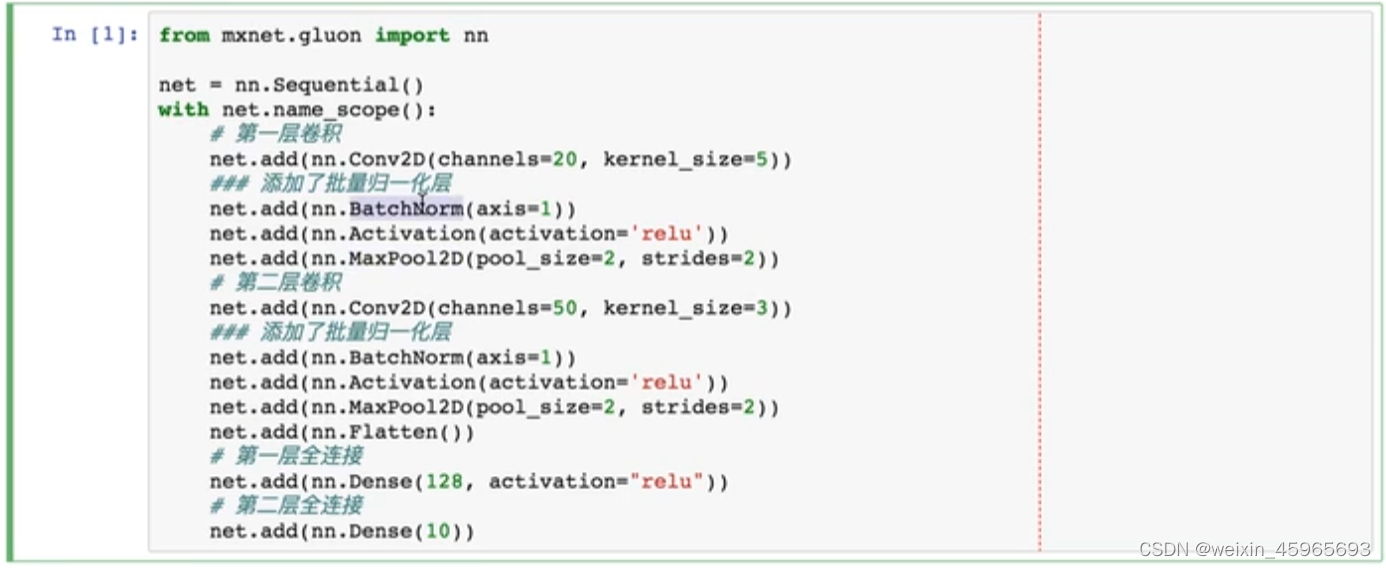
边栏推荐
- 用数据告诉你高考最难的省份是哪里!
- 百度研发三面惨遭滑铁卢:面试官一套组合拳让我当场懵逼
- Daughter love: frequency spectrum analysis of a piece of music
- ASP. Net to access directory files outside the project website
- Golang 类型比较
- Laravel文档阅读笔记-How to use @auth and @guest directives in Laravel
- uniapp 处理过去时间对比现在时间的时间差 如刚刚、几分钟前,几小时前,几个月前
- Lauchpad x | MODE
- C语言指针经典面试题——第一弹
- Hands on deep learning (34) -- sequence model
猜你喜欢
MySQL develops small mall management system
Svg image quoted from CodeChina
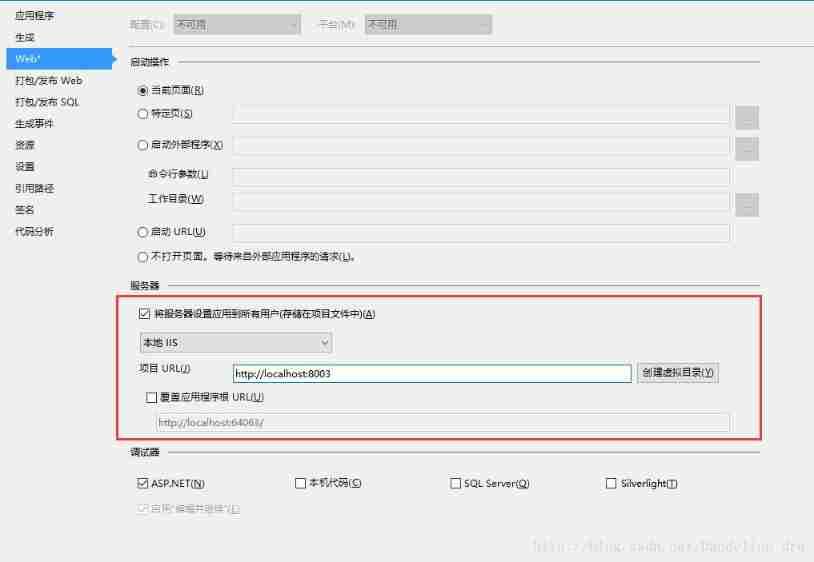
ASP. Net to access directory files outside the project website

Servlet基本原理与常见API方法的应用
MongoDB数据日期显示相差8小时 原因和解决方案
Hands on deep learning (41) -- Deep recurrent neural network (deep RNN)
libmysqlclient.so.20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
C语言指针经典面试题——第一弹
QTreeView+自定义Model实现示例

A little feeling
随机推荐
Write a jison parser from scratch (2/10): learn the correct posture of the parser generator parser generator
Pcl:: fromrosmsg alarm failed to find match for field 'intensity'
品牌连锁店5G/4G无线组网方案
Legion is a network penetration tool
C # use gdi+ to add text with center rotation (arbitrary angle)
Implementing expired localstorage cache with lazy deletion and scheduled deletion
智慧路灯杆水库区安全监测应用
Baidu R & D suffered Waterloo on three sides: I was stunned by the interviewer's set of combination punches on the spot
leetcode1-3
六月份阶段性大总结之Doris/Clickhouse/Hudi一网打尽
2. Data type
Kotlin 集合操作汇总
按键精灵跑商学习-商品数量、价格提醒、判断背包
什么是 DevSecOps?2022 年的定义、流程、框架和最佳实践
7-17 crawling worms (15 points)
Write a jison parser (7/10) from scratch: the iterative development process of the parser generator 'parser generator'
智能网关助力提高工业数据采集和利用
Leetcode (Sword finger offer) - 35 Replication of complex linked list
回复评论的sql
Ruby时间格式转换strftime毫秒匹配格式