当前位置:网站首页>Numpy array index slice
Numpy array index slice
2022-07-06 01:38:00 【Lao Xiao of Buddhism】

List of articles
NumPy Array index
Accessing array elements
Array index is the same as accessing array elements .
You can access an array element by referencing its index number .
NumPy The index in the array is in 0 start , This means that the index of the first element is 0, The index of the second element is 1, And so on .
example 1 Get the first element from the following array :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(arr[0])
Running results :
1
example 2 Get the second element from the following array .
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(arr[1])
Running results :
2
example 3 Get the third and fourth elements from the following array and add them .
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(arr[2] + arr[3])
Running results :
7
visit 2-D Array
To access elements from a two-dimensional array , We can use comma separated integers to represent the dimension and index of elements .
Think of a two-dimensional array as a table containing rows and columns , Where rows represent dimensions , The index represents the column .
example : Access the elements on the first row and the second column :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print(' The elements on the first row and the second column are : ', arr[0, 1])
Running results :
The elements on the first row and the second column are : 2
example 2: Access No. 2 Xing di 5 Elements in columns :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print(' The first 2 Xing di 5 The elements in the column are : ', arr[1, 4])
Running results :
The first 2 Xing di 5 The elements in the column are : 10
visit 3-D Array
To access elements from a 3D array , We can use comma separated integers to represent the dimension and index of elements .
example 1 Access the third element of the second array of the first array :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
print(arr[0, 1, 2])
Running results :
6
example
The first number represents the first dimension , It contains two arrays :
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
and :
[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
Because we chose 0 , Represents that we have selected the array :
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
The second number represents the second dimension , It also contains two arrays :
[1,2,3]
and :
[4,5,6]
Because we chose 1, Represents that we selected the second array :
[4,5,6]
The third number represents the third dimension , It contains three values :
4
5
6
Because we chose 2 , We finally get the third value :
6
Negative index
Use a negative index to access the array from the end .
example Print the second dim Last element of :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print(' the second dim Last element of : ', arr[1, -1])
Running results :
the second dim Last element of : 10
NumPy Array slice
Slice array
Python Slicing in means bringing elements from one given index to another .
We pass slices instead of indexes , As shown below :.[start:end]
We can also define steps , As shown below :.[start:end:step]
If we don't set start, Says from the 0 Start
If we don't set end, Indicates the length of the array
If we don't set step, The default is 1
example : Index the elements from the following array 1 Slice to index 5:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[1:5])
Running results :
[2 3 4 5]
Be careful : result Include Starting index , but barring End index .
example : Remove elements from the index 4 Slice to the end of the array :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[4:])
Running results :
[5 6 7]
Example : From start to index 4( barring ) Slice elements :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[:4])
Running results :
[1 2 3 4]
Negative slice
Use the minus operator to reference the index from the end :
example : Index from the end 3 Cut to the index from the end 1:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[-3:-1])
Running results :
[5 6]
step step
Use step Determine the slice length :
example : Return from index 1 To the index 5 All other elements of :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[1:5:2])
Running results :
[2 4]
Example Returns all odd elements from the entire array :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(arr[::2])
Running results :
[1 3 5 7]
2-D Array section
example Start with the second element , Remove elements from the index 1 Slice to index 4( Not included ):
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr[1, 1:4])
Running results :
[7 8 9]
example Return the index from these two elements 2:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr[0:2, 2])
Running results :
[3 8]
Example : From two elements , Slice indices 1 To the index 4( Not included ), This will return to a 2-D Array :
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
print(arr[0:2, 1:4])
Running results :
[[2 3 4]
[7 8 9]]
边栏推荐
- Leetcode skimming questions_ Verify palindrome string II
- 【详细】快速实现对象映射的几种方式
- Flowable source code comments (36) process instance migration status job processor, BPMN history cleanup job processor, external worker task completion job processor
- Electrical data | IEEE118 (including wind and solar energy)
- leetcode刷题_反转字符串中的元音字母
- 3D vision - 4 Getting started with gesture recognition - using mediapipe includes single frame and real time video
- Maya hollowed out modeling
- SPIR-V初窺
- 电气数据|IEEE118(含风能太阳能)
- What is weak reference? What are the weak reference data types in ES6? What are weak references in JS?
猜你喜欢
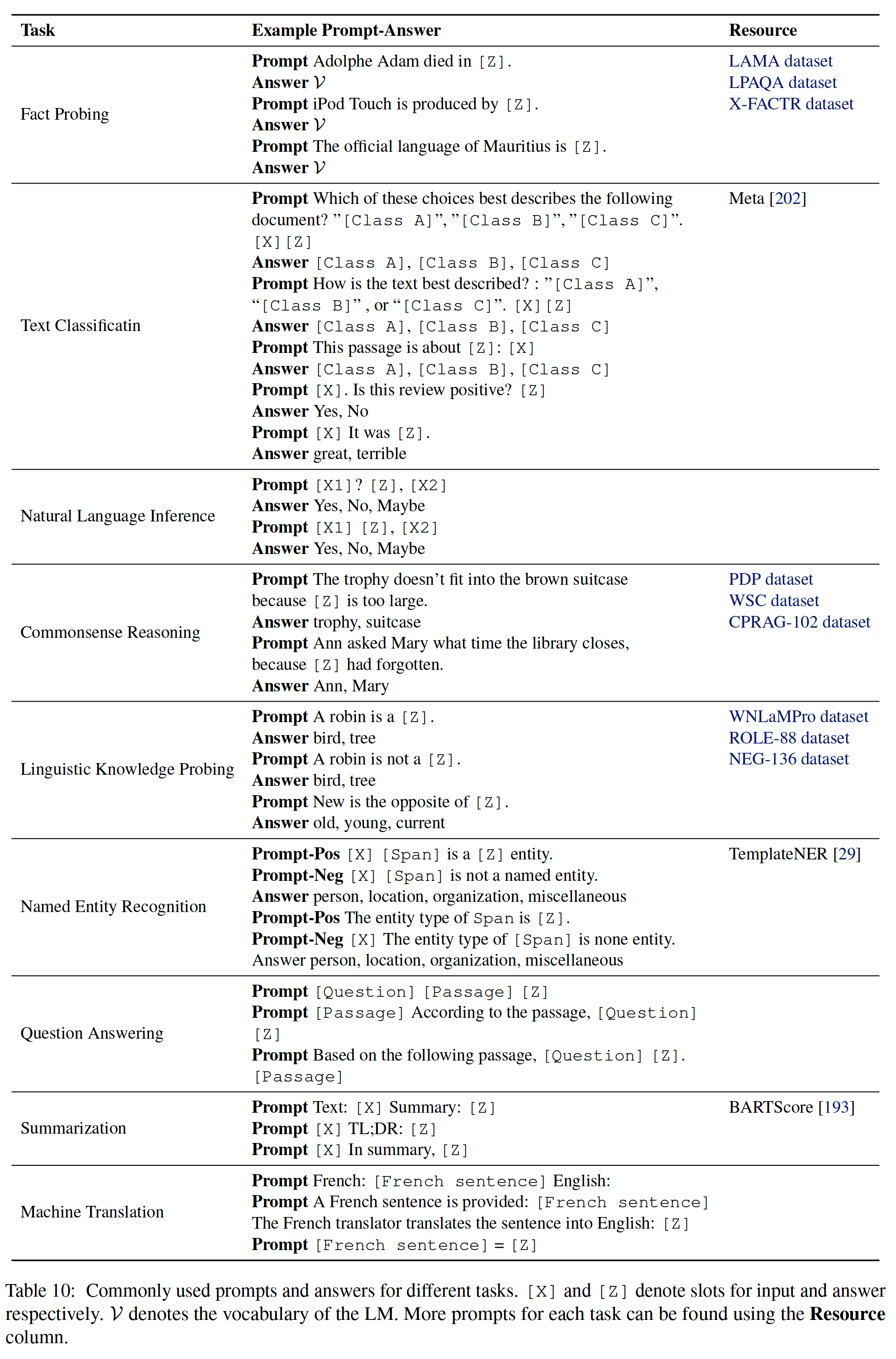
NLP第四范式:Prompt概述【Pre-train,Prompt(提示),Predict】【刘鹏飞】
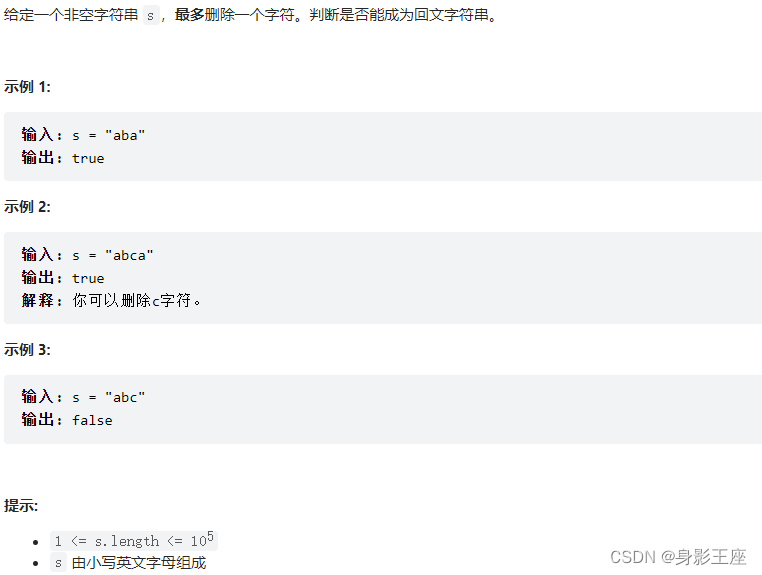
Leetcode skimming questions_ Verify palindrome string II
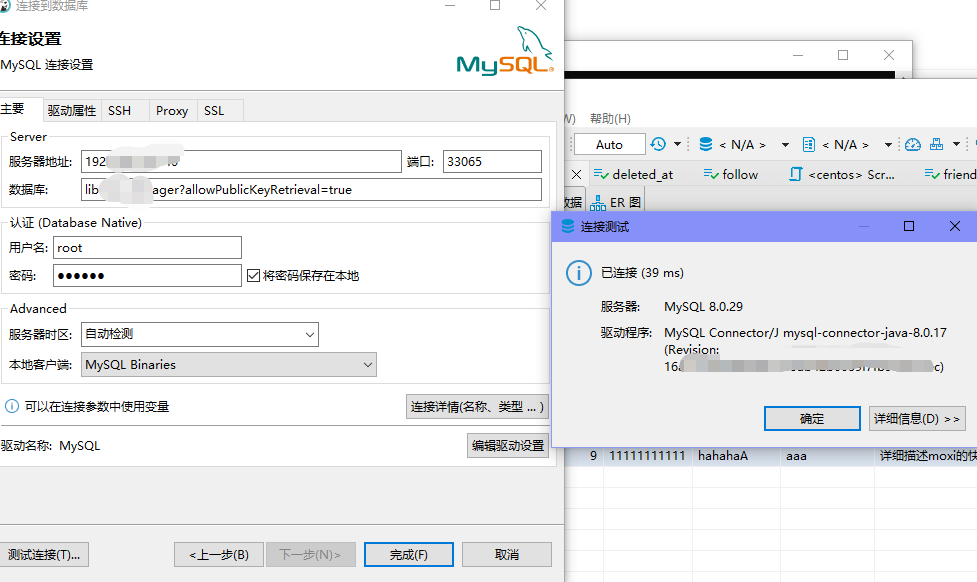
Docker compose配置MySQL并实现远程连接

插卡4G工业路由器充电桩智能柜专网视频监控4G转以太网转WiFi有线网速测试 软硬件定制
NiO related knowledge (II)
ORA-00030
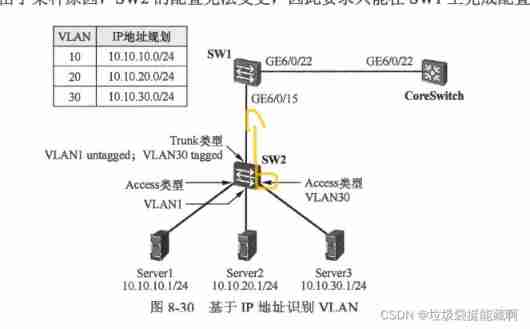
Huawei Hrbrid interface and VLAN division based on IP

A picture to understand! Why did the school teach you coding but still not
【已解决】如何生成漂亮的静态文档说明页

General operation method of spot Silver
随机推荐
【Flask】官方教程(Tutorial)-part1:项目布局、应用程序设置、定义和访问数据库
Unity VR solves the problem that the handle ray keeps flashing after touching the button of the UI
ClickOnce 不支持请求执行级别“requireAdministrator”
Comments on flowable source code (XXXV) timer activation process definition processor, process instance migration job processor
NLP第四范式:Prompt概述【Pre-train,Prompt(提示),Predict】【刘鹏飞】
干货!通过软硬件协同设计加速稀疏神经网络
Loop structure of program (for loop)
一圖看懂!為什麼學校教了你Coding但還是不會的原因...
dried food! Accelerating sparse neural network through hardware and software co design
Unreal browser plug-in
1. Introduction to basic functions of power query
About error 2003 (HY000): can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost' (10061)
Alibaba canal usage details (pit draining version)_ MySQL and ES data synchronization
ctf. Show PHP feature (89~110)
037 PHP login, registration, message, personal Center Design
Superfluid_ HQ hacked analysis
Code Review关注点
Reasonable and sensible
[flask] obtain request information, redirect and error handling
National intangible cultural heritage inheritor HD Wang's shadow digital collection of "Four Beauties" made an amazing debut!