当前位置:网站首页>Thread hierarchy in CUDA
Thread hierarchy in CUDA
2022-07-02 06:28:00 【Little Heshang sweeping the floor】
Thread hierarchy
For convenience ,threadIdx It's a 3 Component vector , Therefore, one dimension can be used 、 Two or three-dimensional thread index to identify threads , Form a one-dimensional 、 2D or 3D thread block , be called block. This provides a cross domain element ( For example, vector 、 Matrix or volume ) Call the method of calculation .
The index of the thread and its thread ID Relate to each other in a direct way : For one-dimensional blocks , They are the same ; For size (Dx, Dy) 2D block of , The index for (x, y) Thread of thread ID by (x + y*Dx); For size (Dx, Dy, Dz) Three dimensional blocks , The index for (x, y, z) Thread of thread ID by (x + y*Dx + z*Dx*Dy).
for example , The following code will have two sizes NxN Matrix A and B Add up , And store the results in the matrix C in :
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = threadIdx.x;
int j = threadIdx.y;
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation with one block of N * N * 1 threads
int numBlocks = 1;
dim3 threadsPerBlock(N, N);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}
The number of threads per block is limited , Because all threads of a block should reside on the same processor core , And must share the limited memory resources of the core . In the current gpu On , A thread block may contain up to 1024 Threads .
however , A kernel can be executed by multiple thread blocks with the same shape , Therefore, the total number of threads is equal to the number of threads per block multiplied by the number of blocks .
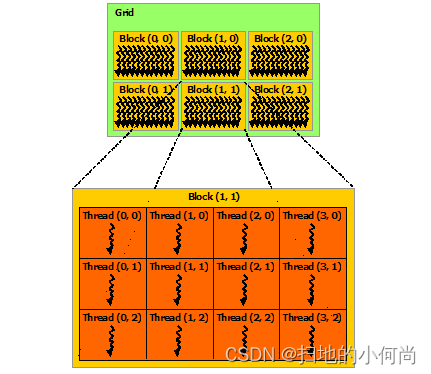
Blocks are organized into one dimension 、 2D or 3D threaded block mesh (grid), As shown in the figure below . The number of thread blocks in a grid is usually determined by the size of the data being processed , It usually exceeds the number of processors in the system .
<<<...>>> The number of threads per block and the number of blocks per grid specified in the syntax can be int or dim3 type . As shown in the example above , You can specify 2D blocks or meshes .
Each block in the grid can be represented by a one-dimensional 、 A unique index identifier for two or three dimensions , The index can be accessed through the built-in blockIdx Variables are accessed in the kernel . The dimension of thread block can be through the built-in blockDim Variables are accessed in the kernel .
Expand previous MatAdd() Example to handle multiple blocks , The code is as follows .
// Kernel definition
__global__ void MatAdd(float A[N][N], float B[N][N],
float C[N][N])
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (i < N && j < N)
C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
int main()
{
...
// Kernel invocation
dim3 threadsPerBlock(16, 16);
dim3 numBlocks(N / threadsPerBlock.x, N / threadsPerBlock.y);
MatAdd<<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>(A, B, C);
...
}
The thread block size is 16x16(256 Threads ), Although it is arbitrarily changed in this case , But this is a common choice . The mesh is created with enough blocks , In this way, each matrix element has a thread to process . For the sake of simplicity , This example assumes that the number of threads per grid in each dimension can be divided by the number of threads per block in this dimension , Although this is not the case .
The process block needs to be executed independently : It must be possible to execute them in any order , Parallel or serial . This independence requires that thread blocks can be scheduled in any order across any number of cores , As shown in the figure below , Enable programmers to write code that expands with the number of kernels .

Threads in the block can share data through some shared memory and coordinate memory access by synchronizing their execution . More precisely , You can call __syncthreads() Internal function to specify the synchronization point in the kernel ; __syncthreads() Act as a barrier , All threads in the block must wait , Before we can continue . Shared Memory An example of using shared memory is given . except __syncthreads() outside ,Cooperative Groups API It also provides a rich set of thread synchronization examples .
For efficient collaboration , Shared memory is low latency memory near each processor core ( It's like L1 cache ), also __syncthreads() It's lightweight .
边栏推荐
- eslint配置代码自动格式化
- 【程序员的自我修养]—找工作反思篇二
- 栈(线性结构)
- 稀疏数组(非线性结构)
- It is said that Kwai will pay for the Tiktok super fast version of the video? How can you miss this opportunity to collect wool?
- 标签属性disabled selected checked等布尔类型赋值不生效?
- virtualenv和pipenv安装
- In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (I) what is JUC
- Find the highest value of the current element Z-index of the page
- CUDA用户对象
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
kali最新更新指南
代码技巧——Controller参数注解@RequestParam
Kotlin - 验证时间格式是否是 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
unittest.TextTestRunner不生成txt测试报告
Sudo right raising
浅谈三点建议为所有已经毕业和终将毕业的同学
分布式事务 :可靠消息最终一致性方案
20201002 VS 2019 QT5.14 开发的程序打包
AWD学习
2020-9-23 QT的定时器Qtimer类的使用。
注解和反射详解以及运用
Three suggestions for all students who have graduated and will graduate
奇葩pip install
Redis——缓存击穿、穿透、雪崩
Alibaba cloud MFA binding Chrome browser
FE - 微信小程序 - 蓝牙 BLE 开发调研与使用
深入学习JVM底层(四):类文件结构
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘jieba.analyse‘; ‘jieba‘ is not a package
Linked list (linear structure)
Learn about various joins in SQL and their differences