当前位置:网站首页>Basic process of network transmission using tcp/ip four layer model
Basic process of network transmission using tcp/ip four layer model
2022-07-07 07:03:00 【abs(ln(1+NaN))】
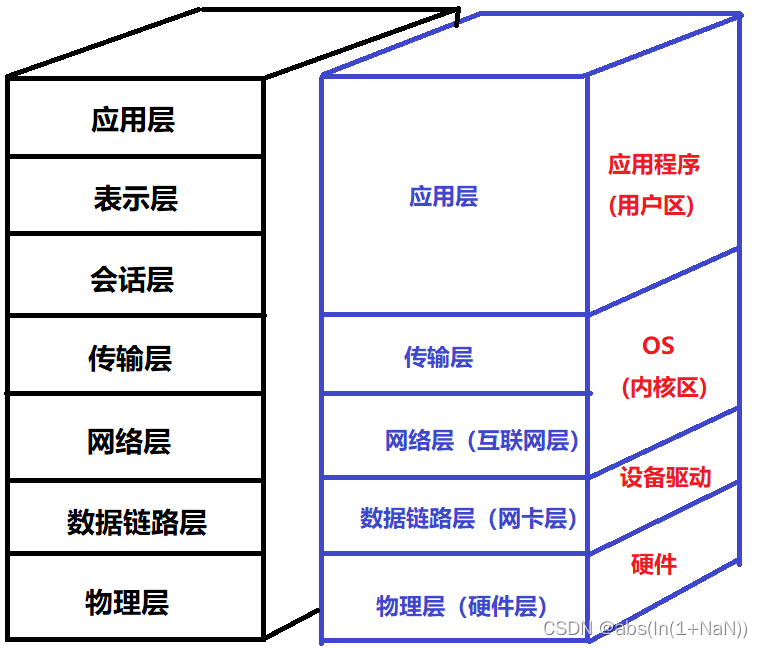
OSI The seven layer model logically divides the network into 7 layer , The main function is to realize two Communication between different hosts . actually OSI The seven layer model is not practical , We usually use the four or five layer protocol , The statement of the fourth floor is Just talk about software , We need to know the fourth floor , But software is based on hardware , So there are five layers .
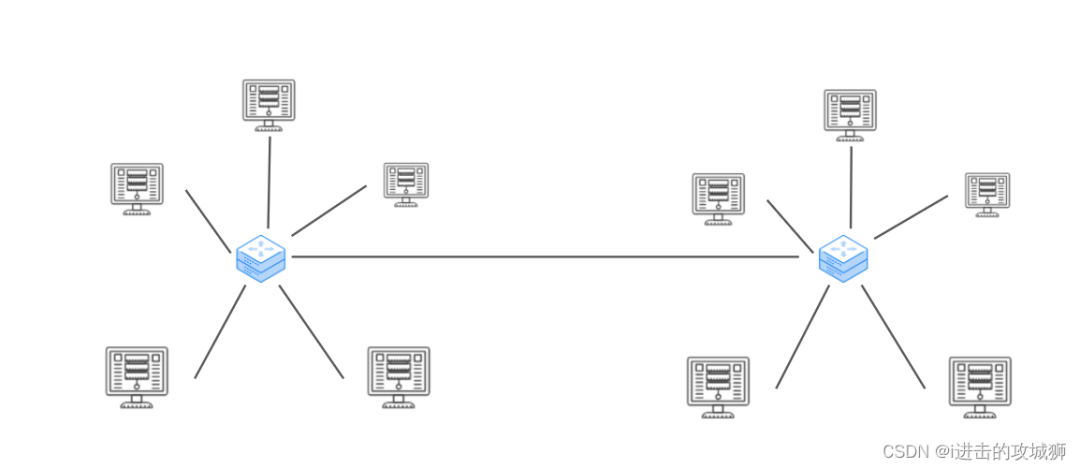
The lower left half is a seven layer model , The right half is a four layer model , We call these four floors “TCP/IP Five floors ( four layers ) Model ”. These four layers also have a certain corresponding relationship with the computer architecture
Catalog
Two 、TCP/IP Five floors ( four layers ) Model
3、 ... and 、 The basic flow of network transmission
One 、 What is an agreement
The so-called agreement is a kind of agreement , There are people from different places in a dormitory , If everyone just speaks their own dialect , It's impossible to communicate , At this time, someone made a suggestion , Everyone speaks Mandarin , After reaching this agreement , Everyone can communicate normally .
From the perspective of network , On the transport layer TCP and UDP agreement , This agreement is to choose whether there is connected transmission or connectionless transmission .
Two 、TCP/IP Five floors ( four layers ) Model
TCP/IP Is a synonym for a group of agreements , You can understand that almost every layer has its own agreement .
- application layer : Responsible for communication between applications , Such as simple email Transfer Protocol (SMTP)、 File transfer protocol (FTP)、 Network remote access protocol (Telnet).
- Transport layer : Decide how to transmit data between two hosts , Such as transmission control protocol (TCP).
- The network layer : Responsible for address management and routing . It can be understood as the way to transfer data to the other host . For example, in IP Agreement , adopt IP Address to identify a host , And through the way of routing table Draw the data transmission line between the two hosts . The router works on this layer .
- Data link layer : Responsible for the transmission and identification of data frames between devices . For example, conflict detection ( If a conflict is detected , It will automatically resend )、 Data error checking, etc . The switch works at the data link layer .
- The physical layer : Responsible for light / How electrical signals are transmitted . We often say coaxial cable 、 Optical fiber 、wifi All belong to the content of this layer . It can be simply understood that most of the contents of the physical layer have entities . The physical layer determines the maximum transmission rate 、 Anti interference, etc . The hub works on the physical layer ( Enlarge data , Reduce data loss ).
3、 ... and 、 The basic flow of network transmission
You may think , Still a little obscure , Here is a simple example to get familiar with the functions of the above layers , At the same time, I have a preliminary understanding of network transmission .
Network transmission can be seen as the relationship between sellers and buyers , Suppose you buy a bottle of shampoo from Taobao , So the mainframe A The application layer of is equivalent to the seller , host B The application layer of is equivalent to the buyer .
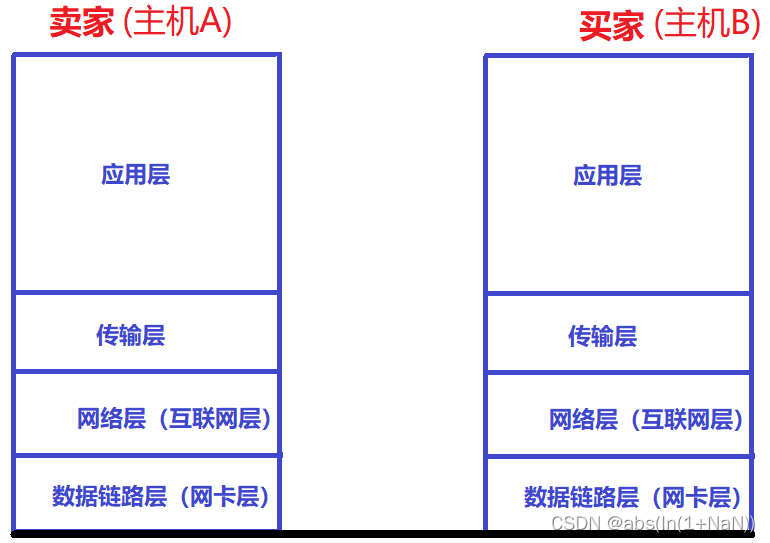
1、 The seller ( host A)
(1) application layer
The seller puts shampoo in a box , This process is equivalent to the application layer adding a data header to the data , This header contains the length of the header 、 Length of load 、 What is the upper layer protocol . In fact, it is equivalent to putting it in the product box , The product box has the quality of the product 、 Production date and other information .
The application layer is equivalent to OS Users in , No matter how the data is sent 、 And how the data is delivered . Only deal with the details of the application .

(2) Transport layer
After the goods arrive at the express station , The express station should affix the express bill to the goods , The delivery address is on the express bill . This process is actually equivalent to adding a data header to the data at the transport layer .
After that it ? That is to decide which express to send . The transport layer is equivalent to OS The kernel part of , The details of communication are here , There is also the network layer of the next layer . The transport layer determines the transmission mode of data , yes TCP still UDP.

(3) The network layer
Now that you have decided which express to send , Now it's time to decide the route . This floor also needs to add a header .
The network layer determines the transmission route of data .
(4) Data link layer
The express is on the way , Suppose we arrive in Nanjing now , The express station in Nanjing will send you to the next stop, Zhejiang . The data link layer determines the process of transferring data from the transfer station .
2、 buyers ( host B)
The buyer received the goods , What we need may be wrapped in many layers , Now we need to dismantle it layer by layer . This process is unpacking .
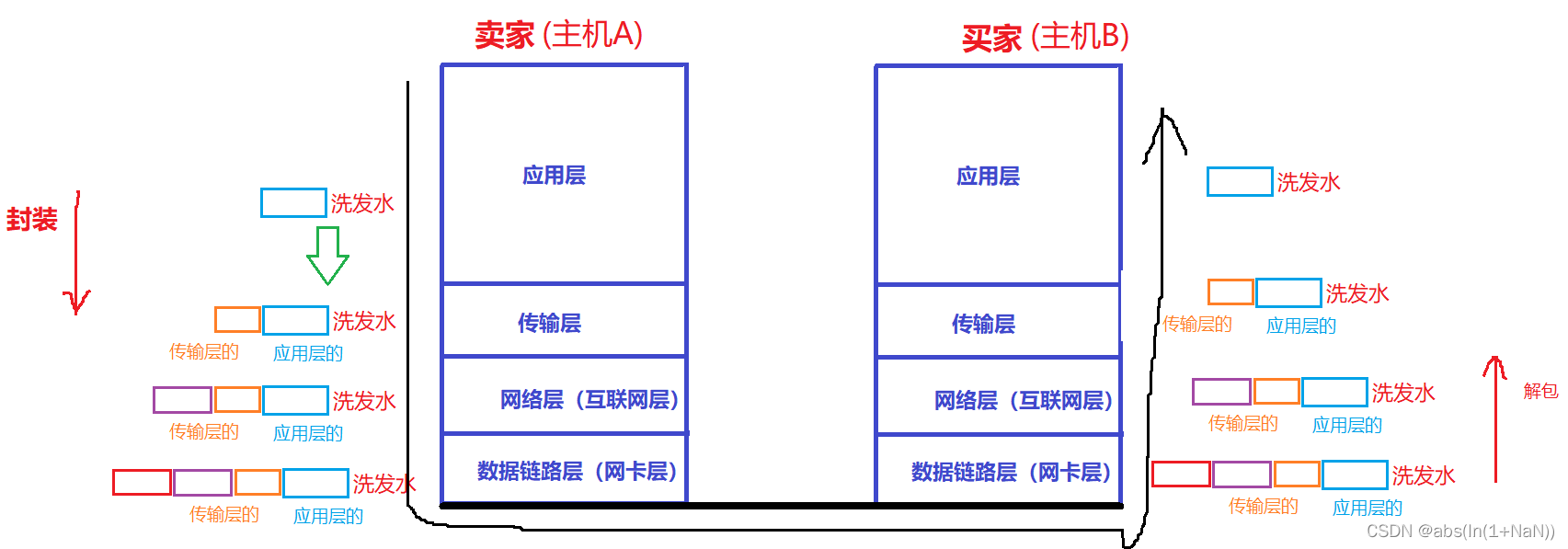
For the process of encapsulation and unpacking, please refer to the following blog .
边栏推荐
- [noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)
- What books can greatly improve programming ideas and abilities?
- Kotlin之 Databinding 异常
- Abnova 免疫组化服务解决方案
- 使用net core优势/为什么使用
- Jetpack Compose 远不止是一个UI框架这么简单~
- 常用函数detect_image/predict
- MySQL user permissions
- Abnova循环肿瘤DNA丨全血分离,基因组DNA萃取分析
- from . onnxruntime_ pybind11_ State Import * noqa ddddocr operation error
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
场馆怎么做体育培训?
Maze games based on JS
工具类:对象转map 驼峰转下划线 下划线转驼峰
mysql查看bin log 并恢复数据
CompletableFuture使用详解
MySQL view bin log and recover data
JWT的基础介绍
中英文说明书丨ProSci LAG-3 重组蛋白
main函数在import语句中的特殊行为
[noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)
from .onnxruntime_pybind11_state import * # noqa ddddocr运行报错
Bus message bus
偏执的非合格公司
Abnova 体外转录 mRNA工作流程和加帽方法介绍
Data of all class a scenic spots in China in 2022 (13604)
Brand · consultation standardization
impdp的transform参数的测试
Learning records on July 4, 2022
LC 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 & LC142. 环形链表II
LM11丨重构K线构建择时交易策略
 https://blog.csdn.net/challenglistic/article/details/125643881?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/challenglistic/article/details/125643881?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501