当前位置:网站首页>[merge array] 88 merge two ordered arrays
[merge array] 88 merge two ordered arrays
2022-07-05 05:16:00 【lee2813】
One 、 subject
Here are two buttons Non decreasing order Array of arranged integers nums1 and nums2, There are two other integers m and n , respectively nums1 and nums2 The number of elements in .
Would you please Merge nums2 To nums1 in , Make the merged array press Non decreasing order array .
Be careful : Final , The merged array should not be returned by the function , It's stored in an array nums1 in . In response to this situation ,nums1 The initial length of is m + n, The top m Elements represent the elements that should be merged , after n Elements are 0 , It should be ignored .nums2 The length of is n .
Example 1:
Input :nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output :[1,2,2,3,5,6]
explain : Need merger [1,2,3] and [2,5,6] .
The combined result is [1,2,2,3,5,6] , In which, bold italics indicates nums1 The elements in .
Example 2:
Input :nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
Output :[1]
explain : Need merger [1] and [] .
The combined result is [1] .
Example 3:
Input :nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
Output :[1]
explain : The array to be merged is [] and [1] .
The combined result is [1] .
Be careful , because m = 0 , therefore nums1 No elements in .nums1 The only remaining 0 Just to ensure that the merged results can be successfully stored in nums1 in .
Two 、 Answer key
Solution 1 : Violence solution
This problem can be solved without double pointers , Point to inserting another array completely after the first array , And then sort .
Solution 2 : Double pointer
Although this question points to two arrays , In each array, you find an element , And they are all orderly , So we can use double pointers .
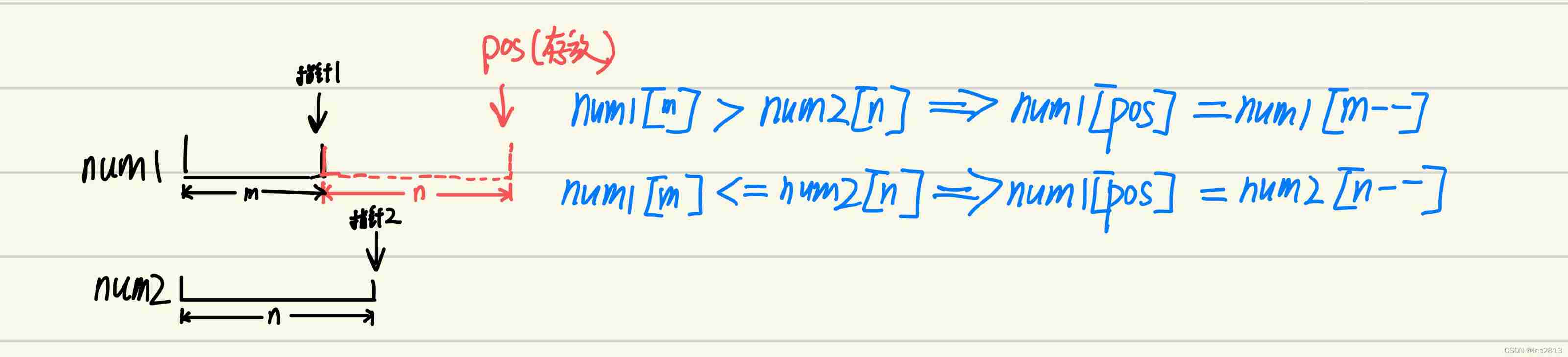
- First , The initialization pointer points to the initial position of the two pointers , Because the length of the last interval is m + n So you can point the first pointer to the last bit of the first array , The second pointer points to the last bit of the second array . Compare in turn , Put the larger number forward by the last digit after expansion .
- secondly , Because the length of the two arrays may be different , There are two situations (1) The first array element is finished , The second array is not finished : At this time, you need to put all the values of the second array into (2) The first array element is not finished , The second array is finished : There is no need to deal with , Because this means that the elements in the first array are in the final position
3、 ... and 、 Code
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {
int pos = m-- + n-- - 1;
while(m>=0 & n>=0 & pos>=0){
nums1[pos--] = nums1[m] > nums2[n] ?nums1[m--]:nums2[n--];
}
while(n>=0){
nums1[pos--] = nums2[n--];
}
}
};
边栏推荐
- Research and investment forecast report of adamantane industry in China (2022 Edition)
- 2022年上半年国家教师资格证考试
- Unity shot tracking object
- A complete attack chain
- Basic knowledge points of dictionary
- 3dsmax snaps to frozen objects
- room数据库的使用
- Panel panel of UI
- 被舆论盯上的蔚来,何时再次“起高楼”?
- Stm32cubemx (8): RTC and RTC wake-up interrupt
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
A three-dimensional button
Sixth note
Django reports an error when connecting to the database. What is the reason
2022 / 7 / 1 Résumé de l'étude
Optimization scheme of win10 virtual machine cluster
How much do you know about 3DMAX rendering skills and HDRI light sources? Dry goods sharing
Unity sends messages and blocks indecent words
When will Wei Lai, who has been watched by public opinion, start to "build high-rise buildings" again?
Applet Live + e - commerce, si vous voulez être un nouveau e - commerce de détail, utilisez - le!
Cocos2dx screen adaptation
对象的序列化
Ue4/ue5 illusory engine, material part (III), material optimization at different distances
[turn to] MySQL operation practice (I): Keywords & functions
C # perspective following
Time format conversion
Unity enables mobile phone vibration
Reverse one-way linked list of interview questions
django连接数据库报错,这是什么原因
PMP考生,请查收7月PMP考试注意事项
This article is good