当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode之单词搜索(回溯法求解)
LeetCode之单词搜索(回溯法求解)
2022-07-05 04:50:00 【little亮_】
题目
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true
示例 2:
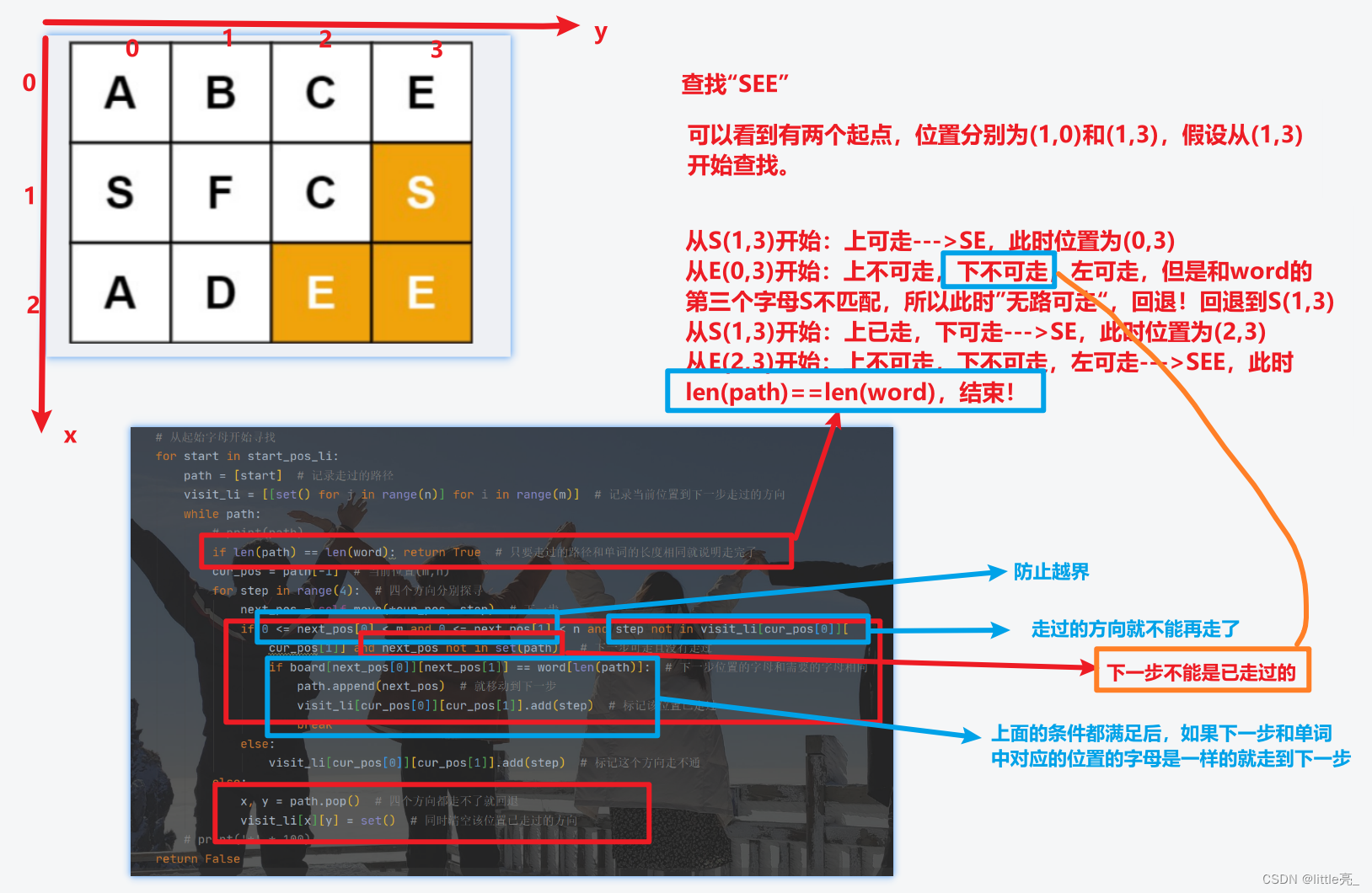
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
输出:false
提示:
m == board.length
n = board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 6
1 <= word.length <= 15
board 和 word 仅由大小写英文字母组成来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
因为前不久刚做过一个走迷宫的问题,所以在读完这题后,就发现它与走迷宫惊奇的相似,只不过在走下一步的时候条件有所改变。但是,它还是花了我2个多接近3个小时才写出来的!
,唉,不说了,还是我太菜了。
言归正传(菜不能做为我懒惰的理由)
首先,不管是走迷宫还是这一题,都得有一个起点,对于这一题,如果一个一个去试的话,那样就太费时了,所以我首先遍历了整个网格, 找到和要查找的单词的第一个字母一样的字母的位置:
start_pos_li = [] # 记录单词首字母的位置 word_set = set() # 表格中的所有字母 m, n = len(board), len(board[0]) for i in range(m): for j in range(n): word_set.add(board[i][j]) if board[i][j] == word[0]: start_pos_li.append((i, j))找到的字母添加到start_pos_li这个列表中,方便以后查找直接从这些位置开始。
同时我也设置了一个集合word_set,保存网格中所有出现的字母,在正式查找之前,可以做一个简单的判断来快速得出一些栗子的答案:
for s in word: if s not in word_set: return False # 只要有一个字母不在表格中就返回False如代码所示,遍历需要查找的单词,只要有一个字母不在集合中就直接返回False。
下面就开始正式的查找
1.首先定义一个移动规则:
# 移动(四个方向) def move(self, x, y, direction): if direction == 1: return (x - 1, y) elif direction == 2: return (x + 1, y) elif direction == 3: return (x, y - 1) else: return (x, y + 1)1代表上移,2代表下移,3代表左移,4代表右移;我这里是以横轴作为y轴,纵轴作为x轴,所以 上下移动的时候x轴发现变化,左右移动的时候y轴发生变化。
2.开始试探性的走
a.定义一个“栈”来保存走过的路径
path = [start] # 记录走过的路径其实这里就是一个列表,但是只使用append()和pop()方法,那么它的行为就像栈。
b.定义一个列表保存每一个格子走过的方向
visit_li = [[set() for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)] # 记录当前位置到下一步走过的方向这里每一个格子走过的方向我用的是一个集合来存储的,一个格子最多存储四个方向,即上下左右;与走迷宫不一样的是,在走迷宫中就用来两个值来表示:0代表当前格子没有走过,1代表当前格子已走;因为这里的是一个单词,它要求的是一个连续的序列,当前格子从这个方向过来可能不行,但是从另外一个方向过来就可以。(即从不同的方向取格子,所得到的序列都是不同的)
c.试探+回溯
# 从起始字母开始寻找 for start in start_pos_li: path = [start] # 记录走过的路径 visit_li = [[set() for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)] # 记录当前位置到下一步走过的方向 while path: # print(path) if len(path) == len(word): return True # 只要走过的路径和单词的长度相同就说明走完了 cur_pos = path[-1] # 当前位置(m,n) for step in range(4): # 四个方向分别探寻 next_pos = self.move(*cur_pos, step) # 下一步 if 0 <= next_pos[0] < m and 0 <= next_pos[1] < n and step not in visit_li[cur_pos[0]][ cur_pos[1]] and next_pos not in set(path): # 下一步可走且没有走过 if board[next_pos[0]][next_pos[1]] == word[len(path)]: # 下一步位置的字母和需要的字母相同 path.append(next_pos) # 就移动到下一步 visit_li[cur_pos[0]][cur_pos[1]].add(step) # 标记该位置已走过 break else: visit_li[cur_pos[0]][cur_pos[1]].add(step) # 标记这个方向走不通 else: x, y = path.pop() # 四个方向都走不了就回退 visit_li[x][y] = set() # 同时清空该位置已走过的方向从起点开始,依次试探四个方向是否可走,如果可走更新可走点为当前位置,然后继续试探,如果到某一点,四个方向都行不通,则回溯,退回到上一步;继续上次没有走完的方向,以下面这个栗子为例:
源码
class Solution:
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
'''
类似于走迷宫,设置4个移动方向,同时标记走过的地方
'''
start_pos_li = [] # 记录单词首字母的位置
word_set = set() # 表格中的所有字母
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
word_set.add(board[i][j])
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
start_pos_li.append((i, j))
for s in word:
if s not in word_set: return False # 只要有一个字母不在表格中就返回False
# 从起始字母开始寻找
for start in start_pos_li:
path = [start] # 记录走过的路径
visit_li = [[set() for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)] # 记录当前位置到下一步走过的方向
while path:
# print(path)
if len(path) == len(word): return True # 只要走过的路径和单词的长度相同就说明走完了
cur_pos = path[-1] # 当前位置(m,n)
for step in range(4): # 四个方向分别探寻
next_pos = self.move(*cur_pos, step) # 下一步
if 0 <= next_pos[0] < m and 0 <= next_pos[1] < n and step not in visit_li[cur_pos[0]][
cur_pos[1]] and next_pos not in set(path): # 下一步可走且没有走过
if board[next_pos[0]][next_pos[1]] == word[len(path)]: # 下一步位置的字母和需要的字母相同
path.append(next_pos) # 就移动到下一步
visit_li[cur_pos[0]][cur_pos[1]].add(step) # 标记该位置已走过
break
else:
visit_li[cur_pos[0]][cur_pos[1]].add(step) # 标记这个方向走不通
else:
x, y = path.pop() # 四个方向都走不了就回退
visit_li[x][y] = set() # 同时清空该位置已走过的方向
# print('*' * 100)
return False
# 移动(四个方向)
def move(self, x, y, direction):
if direction == 1:
return (x - 1, y)
elif direction == 2:
return (x + 1, y)
elif direction == 3:
return (x, y - 1)
else:
return (x, y + 1)通过截图
同步更新于个人博客系统:LeetCode之单词搜索(回溯法求解)
边栏推荐
- 2021 huashubei mathematical modeling idea + reference + paper
- Cookie learning diary 1
- Emlog blog theme template source code simple good-looking responsive
- Wenet: E2E speech recognition tool for industrial implementation
- AutoCAD - Zoom previous
- Mode in BST (binary tree & Notes on question brushing)
- AutoCAD -- dimension break
- Raki's notes on reading paper: code and named entity recognition in stackoverflow
- [groovy] closure (closure call is associated with call method | call () method is defined in interface | call () method is defined in class | code example)
- Error statuslogger log4j2 could not find a logging implementation
猜你喜欢

Special information | finance, accounting, audit - 22.1.23

SQL set operation

10 programming habits that web developers should develop
![[groovy] closure (closure call | closure default parameter it | code example)](/img/61/754cee9a940fd4ecd446b38c2f413d.jpg)
[groovy] closure (closure call | closure default parameter it | code example)

Minor spanning tree

2022-2028 global and Chinese video coding and transcoding Market Research Report
Invalid bound statement (not found) in idea -- problem solving
![Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]](/img/e7/f699ee982ea325b8d04f8bd467a559.jpg)
Rip notes [rip three timers, the role of horizontal segmentation, rip automatic summary, and the role of network]
The principle of attention mechanism and its application in seq2seq (bahadanau attention)

Wan broadband access technology V EPON Technology
随机推荐
AutoCAD - feature matching
【acwing】837. Number of connected block points
[Business Research Report] Research Report on male consumption trends in other economic times -- with download link
2022 thinking of mathematical modeling a problem of American college students / analysis of 2022 American competition a problem
Key review route of probability theory and mathematical statistics examination
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
775 Div.1 C. Tyler and strings combinatorial mathematics
Inline built-in function
Neural networks and deep learning Chapter 2: machine learning overview reading questions
Invalid bound statement (not found) in idea -- problem solving
[groovy] closure (closure parameter binding | curry function | rcurry function | ncurry function | code example)
[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | this, owner, delegate member assignment and source code analysis)
2022-2028 global and Chinese FPGA prototype system Market Research Report
中国溶聚丁苯橡胶(SSBR)行业研究与预测报告(2022版)
windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
[PCL self study: feature9] global aligned spatial distribution (GASD) descriptor (continuously updated)
2021 electrician Cup - high speed rail traction power supply system operation data analysis and equivalent modeling ideas + code
Data security -- 14 -- Analysis of privacy protection governance
计组笔记(1)——校验码、原补码乘除计算、浮点数计算
[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | closure parametertypes and maximumnumberofparameters member usage)