当前位置:网站首页>MySQL in-depth learning - index creation and deletion, index design principles, index failure scenarios, query optimization, index push down ICP
MySQL in-depth learning - index creation and deletion, index design principles, index failure scenarios, query optimization, index push down ICP
2022-07-05 04:33:00 【Incarnate robber_ Bandit】
List of articles
- 6、 ... and 、 Index creation and deletion
- 7、 ... and 、 Index design principles
- 8、 ... and 、 Index failure scenario
- 1. Violation of the leftmost prefix principle
- 2. Use operations on index columns 、 function 、 Type conversion causes invalidation
- 3.LIKE Wildcard problem
- 4. The column index to the right of the range condition fails
- 5.<>、NOT、IN、NOT EXISTS invalid
- 6. OR Index invalidation is caused by non indexed columns before and after
- Nine 、 Query optimization
- Ten 、 Index push down ICP
In the past :
- MySQL Learn more — mysql Logical architecture ,SQL The implementation process of , Database buffer pool
- MySQL Learn more — MySQL Storage engine ,InnoDB、MyISAM The data structure of the index
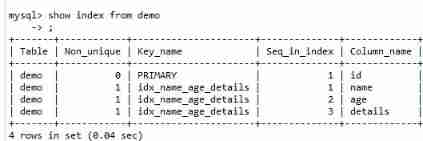
6、 ... and 、 Index creation and deletion
Classification of indexes :
- from
Functional logicSay above , The index mainly includes 4 Kind of , They are ordinary indexes 、 unique index 、 primary key 、 Full-text index - according to
Physical implementation, The index can be divided into 2 Kind of : Clustered index and non clustered index - according to
Number of action fieldsdivision , Divided into single column index and joint index
Different storage engines support different index types
- InnoDB : Support B-tree、Full-text Wait for the index , I won't support it Hash Indexes ;
- MyISAM : Support B-tree、Full-text Wait for the index , I won't support it Hash Indexes ;
- Memory : Support B-tree、Hash Wait for the index , I won't support it Full-text Indexes ;
- NDB : Support Hash Indexes , I won't support it B-tree、Full-text Wait for the index ;
- Archive : I won't support it B-tree、Hash、Full-text Wait for the index ;
6.1 Index creation
1. When creating a table
CREATE TABLE table_name [col_name data_type]
[UNIQUE | FULLTEXT | SPATIAL] [INDEX | KEY] [index_name] (col_name [length]) [ASC | DESC]
UNIQUE unique index、FULLTEXT Full-text index、SPATIAL Spatial indexINDEXAndKEYSynonyms , Both have the same effectindex_nameSpecify the name of the index , Is an optional parameter , If you don't specify , that MySQL Default col_name For index namecol_nameFor the field columns that need to be indexed , The column must be selected from multiple columns defined in the data table , You can select multiple columns to form a joint indexlengthIs an optional parameter , Indicates the length of the index , Only fields of string type can specify index lengthASCorDESCSpecifies the index value store in ascending or descending order
CREATE TABLE book(
book_id INT,
book_name VARCHAR(100),
year_publication YEAR,
INDEX(year_publication) # General index , It is also a single column index
INDEX multi_idx(book_id,book_name) # Multi column index
UNIQUE INDEX uk_idx_id(book_id) # unique index
);
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT(10) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT,
student_no VARCHAR(200),
student_name VARCHAR(200),
PRIMARY KEY(id) # primary key
);
CREATE TABLE `papers` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
`content` text,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
FULLTEXT KEY `title` (`title`,`content`) # Full-text index
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
# differ like Mode query
SELECT * FROM papers WHERE content LIKE ‘% Query string %’;
# Full text index can be used match+against Mode query :
SELECT * FROM papers WHERE MATCH(title,content) AGAINST (‘ Query string ’);
CREATE TABLE test5(
geo GEOMETRY NOT NULL,
SPATIAL INDEX spa_idx_geo(geo) # Spatial index
) ENGINE=MyISAM;
- Before using full-text indexing , Find out the version support ;
- Full text index ratio like + % fast N times , But there may be precision problems ;
- If you need a large amount of data for full-text indexing , It is recommended to add data first , Then create the index .
2. Create... On an existing table
1. Use ALTER TABLE Statement to create an index
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD
[UNIQUE | FULLTEXT | SPATIAL] [INDEX | KEY] [index_name] (col_name[length],...) [ASC | DESC]
2. Use CREATE INDEX Create index
CREATE [UNIQUE | FULLTEXT | SPATIAL] INDEX index_name
ON table_name (col_name[length],...) [ASC | DESC]
6.2 The deletion of the index
1. Use ALTER TABLE Delete
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX index_name;
2. Use DROP INDEX Delete
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name;
7、 ... and 、 Index design principles
7.1 Which situations are suitable for indexing
- The value of the field has
UniquenessThe limitation of- The value of the uniqueness index is unique , Can be indexed faster
determineA record
- The value of the uniqueness index is unique , Can be indexed faster
- Frequent act
WHERE Query criteriaField of- A field is in SELECT Of the statement WHERE Conditions are often used in , Then you need to create an index for this field
- often
GROUP BYandORDER BYThe column of- Sorting operations waste a lot of time , If you index it , Can effectively avoid sorting operations , It is equivalent to sorting them by index in advance
- UPDATE、DELETE Of WHERE Conditional column
- stay UPDATE or DELETE when , First of all, use WHERE Find out , If an index is added , The efficiency of finding the record to be modified or deleted will be improved
- But the subsequent update operation , If the updated field is non indexed, the efficiency will be higher , Because non indexed fields do not need to maintain indexes
- therefore ,WHERE Conditions lead to , Try not to modify the index fields
DISTINCTFields need to be indexed- If you need to go heavy , Creating an index on this field will also improve query efficiency
- Use string
Prefix create index- If the value of the index field is long , It's best to use the prefix of the value to index
High discrimination ( High hashability )The column of is suitable as an index- High discrimination , finger hash The distribution range should be as large as possible after operation , Like gender , Only men and women are indistinguishable , Not suitable for indexing
- When multiple fields need to be indexed , Joint index is better than single value index
- The most frequently used columns are placed on the left side of the federated index
- According to the leftmost prefix principle ,MySQL The scan index is from left to right , Sorting is also from left to right
- such as :
index(k1,k2)Such a joint index , The index tree will be given first k1 Sort , Guarantee k1 Give it in an orderly way k2 Sort
7.2 What is not suitable for indexing
- stay
where Not used inField of , Don't set the index WatchIt's better not to use indexes- Yes
Large amount of duplicate dataDo not index the columns of- give an example : Gender , This kind of discrimination is not high , Not suitable for indexing
- Avoid being right
Frequently updated tablesCreate too many indexes - Unordered values are not recommended as indexes
- For example, ID card 、UUID( In index comparison, it needs to be converted to ASCII, And the insertion may cause page splitting )、MD5、HASH、 Disordered long word Character string, etc
- Delete indexes that are no longer or rarely used
- Do not define redundant or duplicate indexes
8、 ... and 、 Index failure scenario
First create a table :
CREATE TABLE `demo`(
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`age` INT(2) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`details` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`comment` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`),
#INDEX idx_age(age),
#INDEX idx_age_name(age,name),
#INDEX idx_name(name),
INDEX idx_age_name_details(age,name,details)
) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
1. Violation of the leftmost prefix principle
MySQL Matching is from left to right , about idx_age_name_details(age,name,details), stay where Columns in the index are not skipped from left to right in the condition column , It conforms to the leftmost prefix principle , Is a valid index
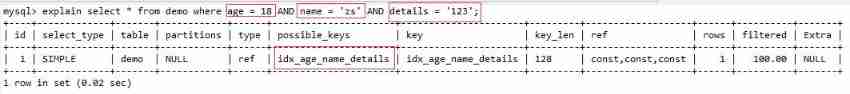
Cases of violating principles :
Not starting from the leftmost column , Index failure
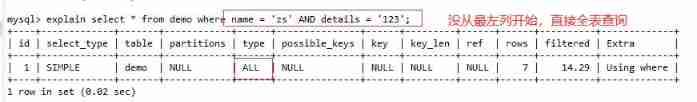
Skip index middle column , It only took Partial index
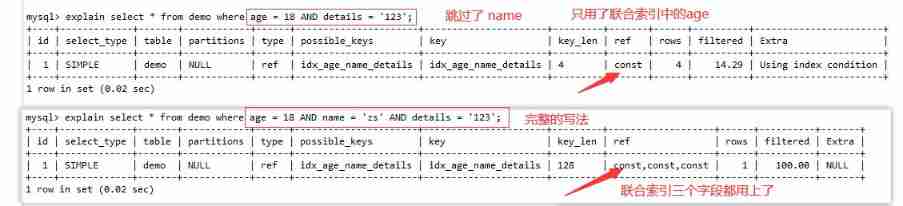
Conclusion : Leading brother can't die , The middle brother can't break
2. Use operations on index columns 、 function 、 Type conversion causes invalidation
2.1 Use operations on index columns

where age + 1 = 18 Using functions , Didn't go idx_age_name_details(age,name,details) Indexes , Used Full table scan
2.2 Index columns use functions
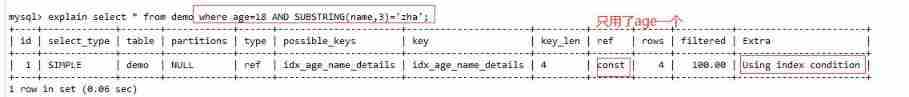
where age=18 AND SUBSTRING(name,3)='zha' , The function is used on the second parameter of the index , So the index only goes age One parameter .
You can see Extra It says using index condition, intend Although the index column appears in the search criteria , But there are some conditions that cannot use indexes , It will search once according to the conditions that can use the index, and then match the conditions that cannot use the index .
2.3 Index column type conversion

First, in the name Add an index to it
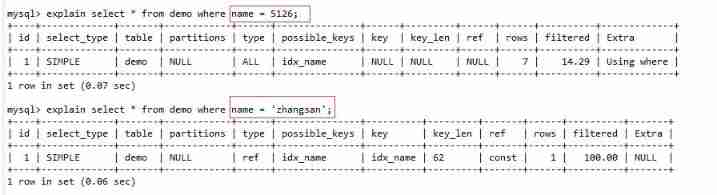
It is obvious that , Use type conversion without index
3.LIKE Wildcard problem
stay SQL In the sentence LIKE The following wildcards % or _ The location is also exquisite
WHERE name LIKE 'zhang%', Wildcards are written after , Can walk the indexWHERE name LIKE '%zhang', Wildcards are written in front , Don't go by index , Will scan the whole table

4. The column index to the right of the range condition fails
Create a joint index :idx_name_age_details(name,age,details)

Obviously , Use in the middle age>20 after , Indexed key_len Just forget it name and age, didn't carry out details 了
5.<>、NOT、IN、NOT EXISTS invalid
When the query condition is equivalent query or range query , The index can find the corresponding entries according to the query conditions .
But with <>、NOT、IN、NOT EXISTS It means that the full table scan query is not equal to , Not belong to
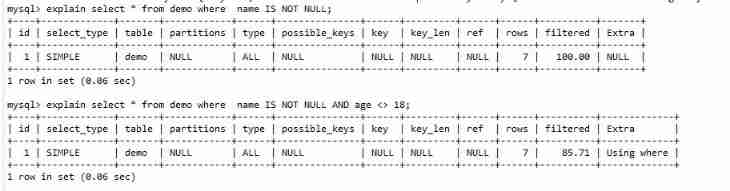
Be careful :IS NULL You can use index , and IS NOT NULL Can not be
Pictured , All used are full table scans
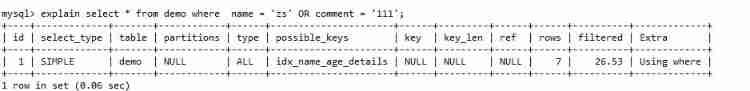
6. OR Index invalidation is caused by non indexed columns before and after
name There's an index on , and comment There is no index on it , At this time, the index fails
Nine 、 Query optimization
9.1 Association query optimization
JOIN The principle of sentences
Look at the following sentence :
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1 STRAIGHT_JOIN t2 ON (t1.a=t2.a);
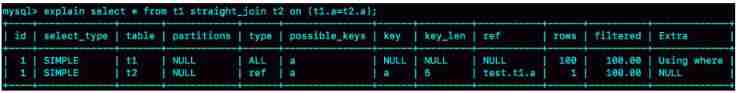
If used directly join sentence ,MySQL The optimizer may select tables t1 or t2 As a driving table . change to the use of sth. straight_join Give Way MySQL Use Fixed connection Execute the query , In this way, the optimizer will only follow the way we specify join. therefore , In this way ,t1 It's the drive meter ,t2 It's driven watch
This article SQL The flow corresponding to the statement is :
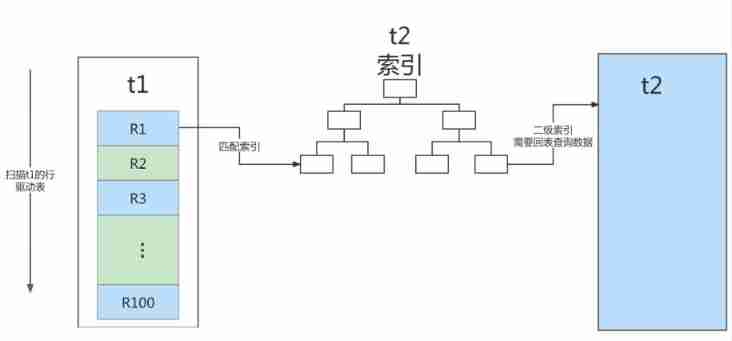
- From the table t1 Read in a row of data R;
- From the data line R in , Take out a Field to table t2 Go to find ;
- Take out the watch t2 The line that satisfies the condition in , Follow R Form a line , As part of the result set ;
- Repeat steps 1 To 3, Until the watch t1 At the end of the loop .
This process is similar to the nested query when we write a program , And you can use the index of the driven table , So we call it “Index Nested-Loop Join” , abbreviation NLJ.
In this flow , A full table scan of the drive table
MySQL in Nested-Loop Join There are three ways :
- Simple Nested-Loop Join. Simple nested loop join
- Index Nested-Loop Join. Index nested loop join
- Block Nested-Loop Join. Cache block nested loop connection
Simple Nested-Loop Join
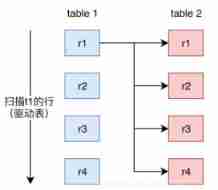
The whole process is a two-level cycle , Traverse the left nested traverse the right , If there are 10000 pieces of data on the left , There are 10000 pieces of data on the right , Whole Join It's 10000 times 10000
Index Nested-Loop Join
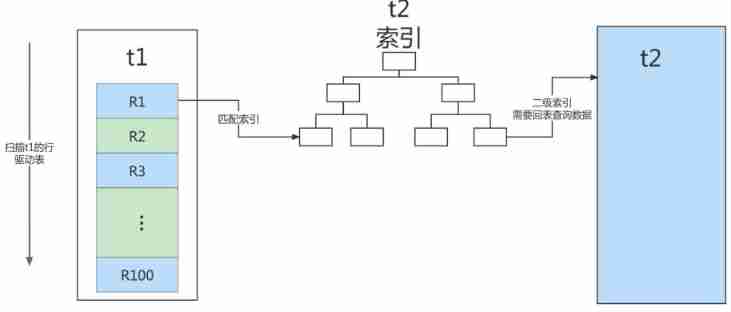
For the kind mentioned at the beginning , Traverse left , When the index is matched, go to the right to query , Reduce inner circulation
Block Nested-Loop Join
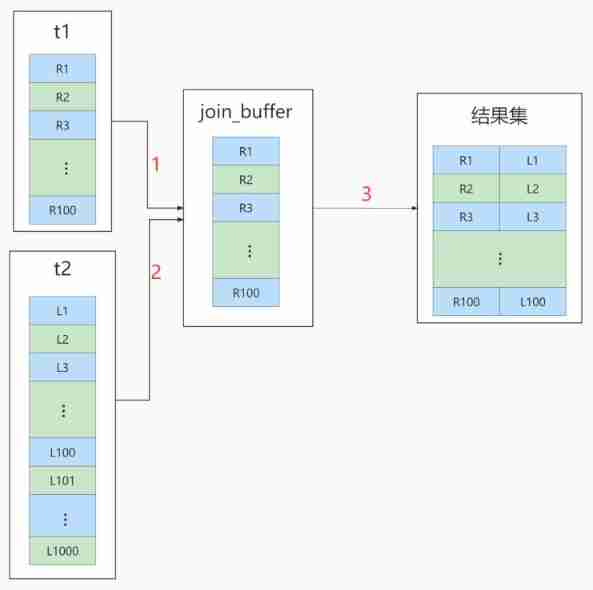
This way uses buffer pools ,t1 You can cache multiple pieces of data to Join Buffer, And then Join Buffer Data batch in and t2 Contrast , Thus reducing the number of internal cycles
Join Buffer It can be modified by join_buffer_size Parameter adjust cache size
Summary
- Make sure that the driven meter
JOIN FieldAlready createdIndexes - need JOIN Field of ,
data typeBe absolutely consistent . LEFT JOINwhen , choiceSmall table as drive table,Big watch as driven watch. Reduce the number of outer cyclesINNER JOINwhen ,MySQL Will automaticallyThe table of the small result set is selected as the driving table. Choose to believe MySQL Optimization strategy .- If you can directly associate multiple tables, try to associate directly , No sub query .( Reduce the number of queries )
- Subqueries are not recommended , It is suggested that sub query SQL Open the combination program many times , Or use JOIN Instead of subquery .
- Derivative tables cannot be indexed
9.2 Sub query optimization
Sub query execution efficiency is not high , reason :
- When executing a subquery , Will create a
A temporary tableSave inner query , Undo these tables after the query . This will consume too much CPU and IO resources , Cause slow query There is no index in the temporary table, Poor query performance
stay MySQL in , You can use connections (JOIN) Query instead of subquery
9.3 Sort optimization
- SQL in , Can be in WHERE Clause and ORDER BY Use index in clause
- Aimed at WHERE clause
Avoid full table scanning, stay ORDER BY Clause Avoid usingFileSortSort . - Of course , In some cases, full table scanning , perhaps FileSort Sorting is not necessarily slower than indexing .
- But on the whole , We still have to avoid , To improve query efficiency .
- Aimed at WHERE clause
- Use as much as possible Index complete ORDER BY Sort . If WHERE and ORDER BY The same column is followed by a single column index ; If different, use a federated index .
- Can't use Index when , Need to be right FileSort Way to tune .
INDEX a_b_c(a,b,c)
order by Can use index leftmost prefix
- ORDER BY a
- ORDER BY a,b
- ORDER BY a,b,c
- ORDER BY a DESC,b DESC,c DESC
If WHERE The leftmost prefix of the index is defined as a constant , be order by Can use index
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY b,c
- WHERE a = const AND b = const ORDER BY c
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY b,c
- WHERE a = const AND b > const ORDER BY b,c
Can't use index to sort
- ORDER BY a ASC,b DESC,c DESC /* The order is inconsistent */
- WHERE g = const ORDER BY b,c /* The loss of a Indexes */
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY c /* The loss of b Indexes */
- WHERE a = const ORDER BY a,d /*d Not part of the index */
- WHERE a in (...) ORDER BY b,c /* For sorting , Multiple equality conditions are also range queries */
give an example :
SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM student
WHERE age = 30 AND stuno <101000
ORDER BY NAME ;
For something like this SQL, We can
Build an index and remove filesort,
idx_age_name(age,name)Further optimization ,
idx_age_stuno_name(age,stuno,name)about filesort The optimization of the
- Try to improve sort_buffer_size
- Try to improve max_length_for_sort_data
- Order by when
select *It's a big taboo . Better just Query Required fields
9.4 Group By Optimize
- group by The principle of using indexes is almost the same as order by Agreement ,group by Even if no filter conditions are used, the index , You can also use the index directly
- group by Sort first and then group , Follow the best left prefix rule for indexes
- When index columns cannot be used , increase
max_length_for_sort_dataandsort_buffer_sizeParameter settings - where Efficiency is higher than having, It can be written in where Don't write the limited conditions in having It's in
- Reduce use order by, Communication with business can not be sorted , Or put the sorting on the program side .Order by、group by、distinct These statements are more expensive CPU, Database CPU Resources are extremely valuable .
- Contains order by、group by、distinct Statements for these queries ,where Please keep the result set filtered by the condition in 1000 That's ok within , otherwise SQL It's going to be slow .
9.5 Override index first
The overlay index is select The data columns of can be obtained only from the index , You don't have to read rows of data , In other words, the query column will be overwritten by the index created .
for instance :
select * from demo where id = 1,id It's the primary key , The clustered index tree established by the primary key contains the fields of all tables , No need to return table query , This is an overlay indexAgain for instance : Set up a joint index
idx_name_age_details(name,age,details)perform sql sentence
select name,age from demo where age = xxx AND name = xxx AND details = xxx.
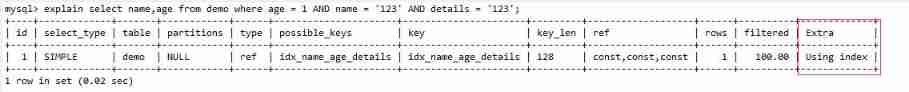
stay Extra It shows that Using index It means the overlay index is used , There is no need to query back to the table
The benefits of covering indexes :
- avoid Innodb The table makes a secondary query for the index ( Back to the table )
- You can take the random IO Into order IO Speed up query
9.6 Prefix index of string
Alibaba In the specification of , String is to establish prefix index
【 mandatory 】 stay varchar When indexing on a field , Index length must be specified , There's no need to index all fields , Determine the index length according to the actual text differentiation .
It is important to choose the length of the prefix , Define the length , You can save space , There is no need to add too much query cost .
give an example :
alter table teacher add index index1(email);
# or
alter table teacher add index index2(email(6));
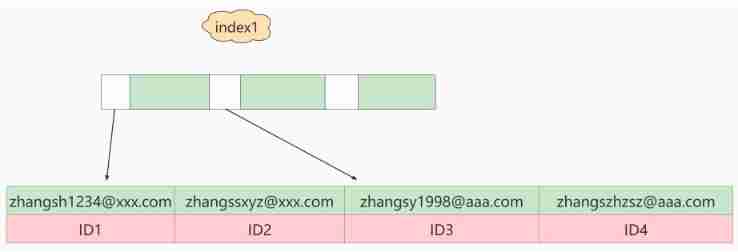
about index1:
- from index1 The index tree is found to satisfy the index value ’ [email protected] ’ This record of , obtain ID2 Value ;
- The primary key value is found on the primary key ID2 The line of , Judge email The value of is correct , Add this line of record to the result set ;
- take index1 The next record of the location just found in the index tree , The discovery is not satisfied email=’ [email protected] ’ The condition of the , The loop ends .
- In the process , You only need to retrieve data from the primary key index once , So the system thinks it only scanned one line .
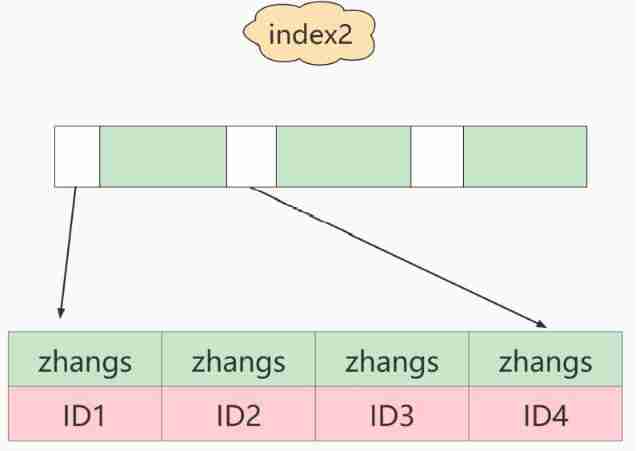
about index2:
- from index2 The index tree is found to satisfy the index value ’zhangs’ The record of , The first one we found was ID1;
- The primary key value is found on the primary key ID1 The line of , Determine the email The value is not ’ [email protected] ’, This record is discarded ;
- take index2 The next record on the location just found , The discovery is still ’zhangs’, Take out ID2, Until then ID Round up the row on the index Post judgment , This time it was right , Add this line of record to the result set
- Repeat the previous step , Until idxe2 The value taken up is not ’zhangs’ when , The loop ends .
- In the process , Repeated scanning for many times , The performance is not very good
Conclusion :
The prefix index is not as short as possible , It is necessary to ensure the differentiation , Hash

Be careful : The influence of prefix index on overlay index
Using prefix index can't optimize query performance with covering index , This is also a factor to consider when choosing whether to use prefix index or not .
Ten 、 Index push down ICP
Index Condition Pushdown(ICP) yes MySQL 5.6 China new features , It's an optimized way to use indexes to filter data in the storage engine layer .ICP It can reduce the number of times the storage engine accesses the base table and MySQL The number of times the server has access to the storage engine .
10.1 give an example :
Take the previous table for example , We set up a joint index idx_name_age_details(name,age,details)
Then there is a demand , The age of the matching surname Zhang is 20 Year old user :
SELECT * FROM demo WHERE name LIKE ' Zhang %' AND age = 20
stay Mysql5.6 Before , The process goes like this :
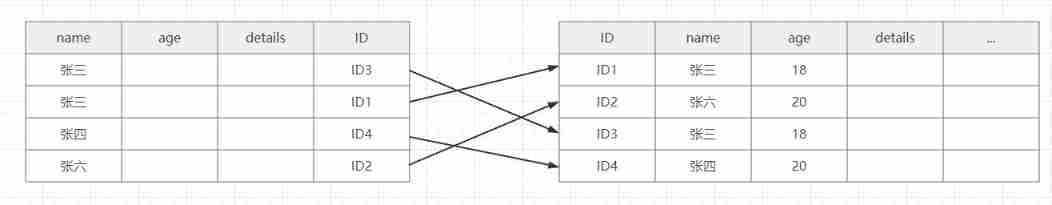
First, find the name and surname of Zhang , Then ignore age, Take this 4 individual ID, Query directly back to the table
A total of four times is required
stay Mysql5.6 after , The process goes like this :
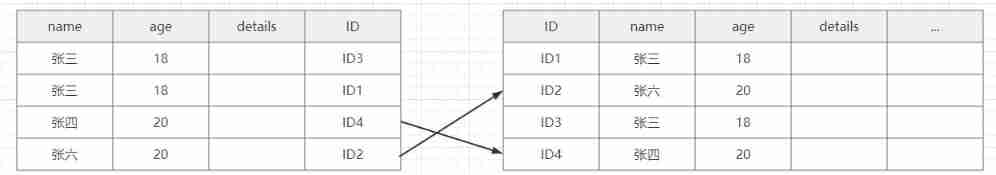
First, find the name and surname of Zhang , And then directly The next field of the union index age To filter , Skip the age Not for 18 Two records of
You only need to return the form twice in total
10.2 Use ICP Internal processes before and after
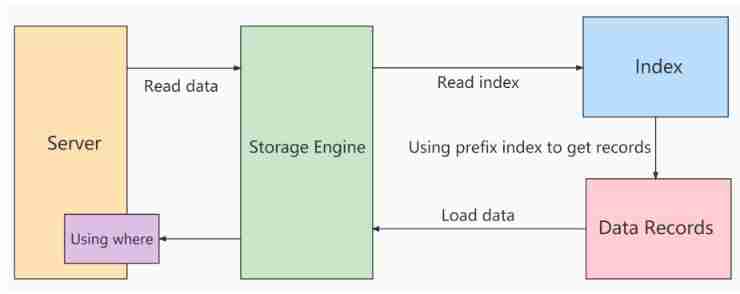
Don't use ICP The process of index scanning :
storage layer : Will only satisfy index key Retrieve the entire row of records corresponding to the index record of the condition , Return to server layer
server layer : For the returned data , Use the following where filter , Until you return to the last line .
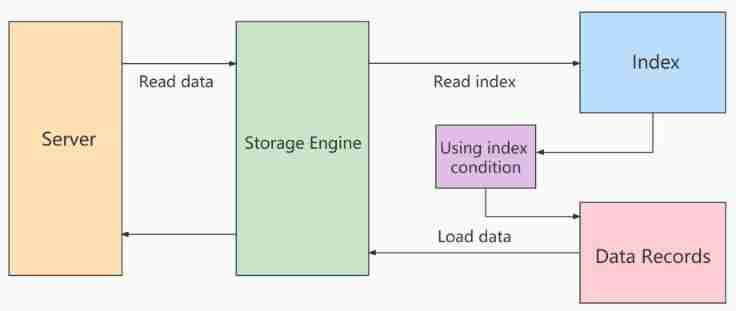
Use ICP The process of index scanning :
- storage layer : First of all, will index key Determination of index record interval satisfying conditions , Then use... On the index index filter To filter . Will satisfy index filter The conditional index records go back to the table, take out the whole row of records, and return server layer . dissatisfaction index filter The index record of the condition is discarded , Don't return the form 、 And will not return server layer .
- server layer : For the returned data , Use table filter Condition for final filtering .
Cost difference before and after use :
- Before using , The storage layer returns more information that needs to be index filter Filtered out entire line of records
- Use ICP after , Directly get rid of dissatisfaction index filter Record of conditions , It saves them from going back to the table and passing it to server The cost of the layer .
- ICP Of
Acceleration effectDepends on passing through the storage engineICP ScreeningThe proportion of data dropped .
10.3 ICP Conditions of use
- Can only be used for secondary index (secondary index)
- explain In the displayed execution plan type value (join type ) by
range、ref、eq_refperhapsref_or_null - Not all of them where All conditions can be used ICP Screening , If where The field of the condition is not in the index column , Or read the records of the whole table To server End to do where Filter .
- ICP It can be used for
MyISAMandInnnoDBStorage engine - MySQL 5.6 The version of does not support partition tables ICP function ,5.7 The beginning of the version supports
- When SQL Use
Overlay indexwhen ,I won't support itICP An optimization method
边栏推荐
- 【UNIAPP】系统热更新实现思路
- SPI read / write flash principle + complete code
- Kwai, Tiktok, video number, battle content payment
- PR video clip (project packaging)
- 函数(易错)
- 网络安全-记录web漏洞修复
- windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
- File upload bypass summary (upload labs 21 customs clearance tutorial attached)
- 这是一个不确定的时代
- Moco is not suitable for target detection? MsrA proposes object level comparative learning target detection pre training method SOCO! Performance SOTA! (NeurIPS 2021)...
猜你喜欢
Construction d'un Cluster redis sous Windows
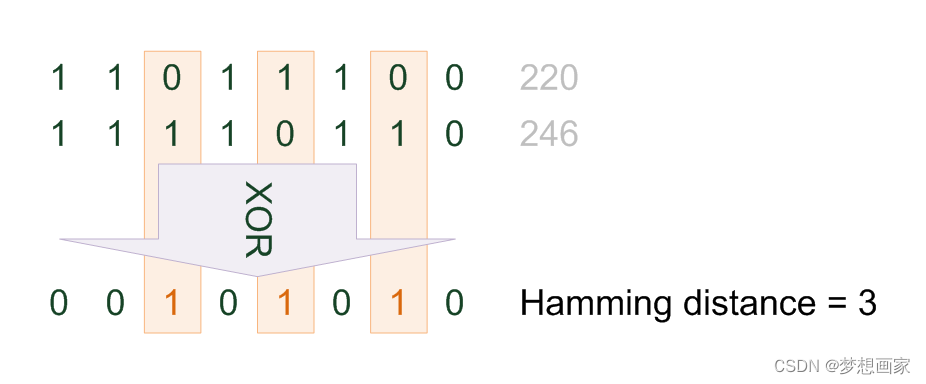
介绍汉明距离及计算示例
Mxnet imports various libcudarts * so、 libcuda*. So not found

直播预告 | 容器服务 ACK 弹性预测最佳实践
![[phantom engine UE] the difference between running and starting, and the analysis of common problems](/img/e2/49d6c4777c12e9f4e3f8b6ca6db41c.png)
[phantom engine UE] the difference between running and starting, and the analysis of common problems
Function (basic: parameter, return value)
![[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording](/img/11/b55f85ef9e1f22254218cb9083b823.png)
[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording

2022-2028 global and Chinese virtual data storage Market Research Report
Reading and visualization of DICOM, MHD and raw files in medical imaging
揭秘技术 Leader 必备的七大清奇脑回路
随机推荐
level18
WeNet:面向工业落地的E2E语音识别工具
Official announcement! The third cloud native programming challenge is officially launched!
解密函数计算异步任务能力之「任务的状态及生命周期管理」
[uniapp] system hot update implementation ideas
A solution to the problem that variables cannot change dynamically when debugging in keil5
C26451: arithmetic overflow: use the operator * on a 4-byte value, and then convert the result to an 8-byte value. To avoid overflow, cast the value to wide type before calling the operator * (io.2)
Discussion on the dimension of confrontation subspace
How to get the first few pieces of data of each group gracefully
【UNIAPP】系统热更新实现思路
About the prompt loading after appscan is opened: guilogic, it keeps loading and gets stuck. My personal solution. (it may be the first solution available in the whole network at present)
A應用喚醒B應該快速方法
Looking back on 2021, looking forward to 2022 | a year between CSDN and me
Learning MVVM notes (1)
线上故障突突突?如何紧急诊断、排查与恢复
揭秘技术 Leader 必备的七大清奇脑回路
CUDA Programming atomic operation atomicadd reports error err:msb3721, return code 1
程序员应该怎么学数学
Live broadcast preview | container service ack elasticity prediction best practice
Interview related high-frequency algorithm test site 3