当前位置:网站首页>深入理解 SQL 中的 Grouping Sets 语句
深入理解 SQL 中的 Grouping Sets 语句
2022-07-03 16:06:00 【InfoQ】
前言
Group Bydealer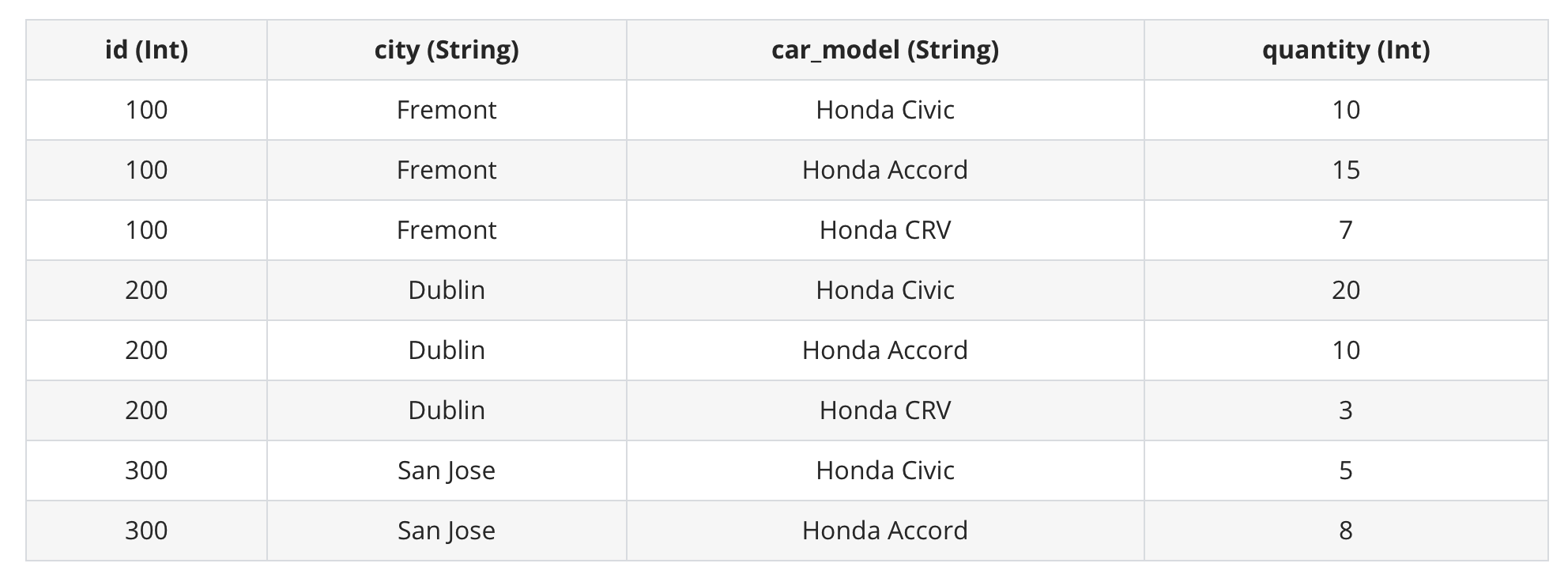
SELECT id, sum(quantity) FROM dealer GROUP BY id ORDER BY id+---+-------------+
| id|sum(quantity)|
+---+-------------+
|100| 32|
|200| 33|
|300| 13|
+---+-------------+
idquantityGroup ByGrouping SetsRollUpCubeRollUpCubeGrouping SetsGrouping SetsRollUpCubeGrouping SetsGrouping SetsGrouping Sets 简介
Grouping SetsUNION ALLUNION ALLGROUPING SETSGrouping SetsGroup ByGroup By dealerGroup By Grouping Sets ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ())Union All((Group By city, car_model), (Group By city), (Group By car_model), 全局聚合)spark-sql> SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer
> GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ())
> ORDER BY city, car_model;
+--------+------------+---+
| city| car_model|sum|
+--------+------------+---+
| null| null| 78|
| null|Honda Accord| 33|
| null| Honda CRV| 10|
| null| Honda Civic| 35|
| Dublin| null| 33|
| Dublin|Honda Accord| 10|
| Dublin| Honda CRV| 3|
| Dublin| Honda Civic| 20|
| Fremont| null| 32|
| Fremont|Honda Accord| 15|
| Fremont| Honda CRV| 7|
| Fremont| Honda Civic| 10|
|San Jose| null| 13|
|San Jose|Honda Accord| 8|
|San Jose| Honda Civic| 5|
+--------+------------+---+
spark-sql> (SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city, car_model) UNION ALL
> (SELECT city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city) UNION ALL
> (SELECT NULL as city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY car_model) UNION ALL
> (SELECT NULL as city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer)
> ORDER BY city, car_model;
+--------+------------+---+
| city| car_model|sum|
+--------+------------+---+
| null| null| 78|
| null|Honda Accord| 33|
| null| Honda CRV| 10|
| null| Honda Civic| 35|
| Dublin| null| 33|
| Dublin|Honda Accord| 10|
| Dublin| Honda CRV| 3|
| Dublin| Honda Civic| 20|
| Fremont| null| 32|
| Fremont|Honda Accord| 15|
| Fremont| Honda CRV| 7|
| Fremont| Honda Civic| 10|
|San Jose| null| 13|
|San Jose|Honda Accord| 8|
|San Jose| Honda Civic| 5|
+--------+------------+---+
Grouping Sets 的执行计划
Grouping SetsUnion AllGrouping SetsUnion Allexplain extendedspark-sql> explain extended (SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city, car_model) UNION ALL (SELECT city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city) UNION ALL (SELECT NULL as city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY car_model) UNION ALL (SELECT NULL as city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer) ORDER BY city, car_model;
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
...
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
...
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Sort [city#93 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#94 ASC NULLS FIRST], true
+- Union false, false
:- Aggregate [city#93, car_model#94], [city#93, car_model#94, sum(quantity#95) AS sum#79L]
: +- Project [city#93, car_model#94, quantity#95]
: +- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#92, city#93, car_model#94, quantity#95], Partition Cols: []]
:- Aggregate [city#97], [city#97, null AS car_model#112, sum(quantity#99) AS sum#81L]
: +- Project [city#97, quantity#99]
: +- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#96, city#97, car_model#98, quantity#99], Partition Cols: []]
:- Aggregate [car_model#102], [null AS city#113, car_model#102, sum(quantity#103) AS sum#83L]
: +- Project [car_model#102, quantity#103]
: +- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#100, city#101, car_model#102, quantity#103], Partition Cols: []]
+- Aggregate [null AS city#114, null AS car_model#115, sum(quantity#107) AS sum#86L]
+- Project [quantity#107]
+- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#104, city#105, car_model#106, quantity#107], Partition Cols: []]
== Physical Plan ==
...
- 执行每个子查询语句,计算得出查询结果。其中,每个查询语句的逻辑是这样的:
- 在HiveTableRelation节点对
dealer表进行全表扫描。
- 在Project节点选出与查询语句结果相关的列,比如对于子查询语句
SELECT NULL as city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer,只需保留quantity列即可。
- 在Aggregate节点完成
quantity列对聚合运算。在上述的 Plan 中,Aggregate 后面紧跟的就是用来分组的列,比如Aggregate [city#902]就表示根据city列来进行分组。
- 在Union节点完成对每个子查询结果的联合。
- 最后,在Sort节点完成对数据的排序,上述 Plan 中
Sort [city#93 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#94 ASC NULLS FIRST]就表示根据city和car_model列进行升序排序。

explain extendedspark-sql> explain extended SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ()) ORDER BY city, car_model;
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
...
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
...
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Sort [city#138 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#139 ASC NULLS FIRST], true
+- Aggregate [city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L], [city#138, car_model#139, sum(quantity#133) AS sum#124L]
+- Expand [[quantity#133, city#131, car_model#132, 0], [quantity#133, city#131, null, 1], [quantity#133, null, car_model#132, 2], [quantity#133, null, null, 3]], [quantity#133, city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L]
+- Project [quantity#133, city#131, car_model#132]
+- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe, Data Cols: [id#130, city#131, car_model#132, quantity#133], Partition Cols: []]
== Physical Plan ==
...
- 在HiveTableRelation节点对
dealer表进行全表扫描。
- 在Project节点选出与查询语句结果相关的列。
- 接下来的Expand节点是关键,数据经过该节点后,多出了
spark_grouping_id列。从 Plan 中可以看出来,Expand 节点包含了Grouping Sets里的各个 grouping set 信息,比如[quantity#133, city#131, null, 1]对应的就是(city)这一 grouping set。而且,每个 grouping set 对应的spark_grouping_id列的值都是固定的,比如(city)对应的spark_grouping_id为1。
- 在Aggregate节点完成
quantity列对聚合运算,其中分组的规则为city, car_model, spark_grouping_id。注意,数据经过 Aggregate 节点后,spark_grouping_id列被删除了!
- 最后,在Sort节点完成对数据的排序。

spark_grouping_idspark_grouping_id- Expand 的实现逻辑是怎样的,为什么能达到
Union All的效果?
- Expand 节点的输出数据是怎样的?
spark_grouping_id列的作用是什么?
Expand== Physical Plan ==
AdaptiveSparkPlan isFinalPlan=false
+- Sort [city#138 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#139 ASC NULLS FIRST], true, 0
+- Exchange rangepartitioning(city#138 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#139 ASC NULLS FIRST, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=422]
+- HashAggregate(keys=[city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L], functions=[sum(quantity#133)], output=[city#138, car_model#139, sum#124L])
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L, 200), ENSURE_REQUIREMENTS, [plan_id=419]
+- HashAggregate(keys=[city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L], functions=[partial_sum(quantity#133)], output=[city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L, sum#141L])
+- Expand [[quantity#133, city#131, car_model#132, 0], [quantity#133, city#131, null, 1], [quantity#133, null, car_model#132, 2], [quantity#133, null, null, 3]], [quantity#133, city#138, car_model#139, spark_grouping_id#137L]
+- Scan hive default.dealer [quantity#133, city#131, car_model#132], HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#130, city#131, car_model#132, quantity#133], Partition Cols: []]
ExpandExpand 算子的实现
ExpandExecXxxExecXxxProjectExec/**
* Apply all of the GroupExpressions to every input row, hence we will get
* multiple output rows for an input row.
* @param projections The group of expressions, all of the group expressions should
* output the same schema specified bye the parameter `output`
* @param output The output Schema
* @param child Child operator
*/
case class ExpandExec(
projections: Seq[Seq[Expression]],
output: Seq[Attribute],
child: SparkPlan)
extends UnaryExecNode with CodegenSupport {
...
// 关键点1,将child.output,也即上游算子输出数据的schema,
// 绑定到表达式数组exprs,以此来计算输出数据
private[this] val projection =
(exprs: Seq[Expression]) => UnsafeProjection.create(exprs, child.output)
// doExecute()方法为Expand算子执行逻辑所在
protected override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
val numOutputRows = longMetric("numOutputRows")
// 处理上游算子的输出数据,Expand算子的输入数据就从iter迭代器获取
child.execute().mapPartitions { iter =>
// 关键点2,projections对应了Grouping Sets里面每个grouping set的表达式,
// 表达式输出数据的schema为this.output, 比如 (quantity, city, car_model, spark_grouping_id)
// 这里的逻辑是为它们各自生成一个UnsafeProjection对象,通过该对象的apply方法就能得出Expand算子的输出数据
val groups = projections.map(projection).toArray
new Iterator[InternalRow] {
private[this] var result: InternalRow = _
private[this] var idx = -1 // -1 means the initial state
private[this] var input: InternalRow = _
override final def hasNext: Boolean = (-1 < idx && idx < groups.length) || iter.hasNext
override final def next(): InternalRow = {
// 关键点3,对于输入数据的每一条记录,都重复使用N次,其中N的大小对应了projections数组的大小,
// 也即Grouping Sets里指定的grouping set的数量
if (idx <= 0) {
// in the initial (-1) or beginning(0) of a new input row, fetch the next input tuple
input = iter.next()
idx = 0
}
// 关键点4,对输入数据的每一条记录,通过UnsafeProjection计算得出输出数据,
// 每个grouping set对应的UnsafeProjection都会对同一个input计算一遍
result = groups(idx)(input)
idx += 1
if (idx == groups.length && iter.hasNext) {
idx = 0
}
numOutputRows += 1
result
}
}
}
}
...
}
ExpandExec关键点 1关键点 2关键点 2groupsUnsafeProjection[N]UnsafeProjectionGrouping Sets// A projection that returns UnsafeRow.
abstract class UnsafeProjection extends Projection {
override def apply(row: InternalRow): UnsafeRow
}
// The factory object for `UnsafeProjection`.
object UnsafeProjection
extends CodeGeneratorWithInterpretedFallback[Seq[Expression], UnsafeProjection] {
// Returns an UnsafeProjection for given sequence of Expressions, which will be bound to
// `inputSchema`.
def create(exprs: Seq[Expression], inputSchema: Seq[Attribute]): UnsafeProjection = {
create(bindReferences(exprs, inputSchema))
}
...
}
UnsafeProjectionapplyexprsinputSchemaGROUPING SETS ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ())groups
AttributeReferenceIteral关键点 3关键点 4ExpandExec关键点 4groups(idx)(input)groups(idx).apply(input)GROUPING SETS ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ())
- Expand 的实现逻辑是怎样的,为什么能达到
Union All的效果?
- 如果说
Union All是先聚合再联合,那么 Expand 就是先联合再聚合。Expand 利用groups里的 N 个表达式对每条输入记录进行计算,扩展成 N 条输出记录。后面再聚合时,就能达到与Union All一样的效果了。
- Expand 节点的输出数据是怎样的?
- 在 schema 上,Expand 输出数据会比输入数据多出
spark_grouping_id列;在记录数上,是输入数据记录数的 N 倍。
spark_grouping_id列的作用是什么?
spark_grouping_id给每个 grouping set 进行编号,这样,即使在 Expand 阶段把数据先联合起来,在 Aggregate 阶段(把spark_grouping_id加入到分组规则)也能保证数据能够按照每个 grouping set 分别聚合,确保了结果的正确性。
查询性能对比
// Grouping Sets 版本执行10次的耗时信息
// SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ()) ORDER BY city, car_model;
Time taken: 0.289 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.251 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.259 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.258 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.296 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.247 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.298 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.286 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.292 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.282 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
// Union All 版本执行10次的耗时信息
// (SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city, car_model) UNION ALL (SELECT city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY city) UNION ALL (SELECT NULL as city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY car_model) UNION ALL (SELECT NULL as city, NULL as car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer) ORDER BY city, car_model;
Time taken: 0.628 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.594 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.591 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.607 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.616 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.64 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.623 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.625 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.62 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
Time taken: 0.62 seconds, Fetched 15 row(s)
RollUp 和 Cube
Group ByRollUpCubeRollUpRollUpROLLUPGROUPING SETSRollUpGrouping SetsRollUp(A, B, C) == Grouping Sets((A, B, C), (A, B), (A), ())Group By RollUp(city, car_model)Group By Grouping Sets((city, car_model), (city), ())expand extendedspark-sql> explain extended SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY ROLLUP(city, car_model) ORDER BY city, car_model;
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
...
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
...
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Sort [city#2164 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#2165 ASC NULLS FIRST], true
+- Aggregate [city#2164, car_model#2165, spark_grouping_id#2163L], [city#2164, car_model#2165, sum(quantity#2159) AS sum#2150L]
+- Expand [[quantity#2159, city#2157, car_model#2158, 0], [quantity#2159, city#2157, null, 1], [quantity#2159, null, null, 3]], [quantity#2159, city#2164, car_model#2165, spark_grouping_id#2163L]
+- Project [quantity#2159, city#2157, car_model#2158]
+- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#2156, city#2157, car_model#2158, quantity#2159], Partition Cols: []]
== Physical Plan ==
...
RollUpRollUpGrouping SetsExpand [[quantity#2159, city#2157, car_model#2158, 0], [quantity#2159, city#2157, null, 1], [quantity#2159, null, null, 3]]RollUpCubeCubeCUBEGROUP BYCUBEGROUPING SETSCubeGrouping SetsCube(A, B, C) == Grouping Sets((A, B, C), (A, B), (A, C), (B, C), (A), (B), (C), ())Group By Cube(city, car_model)Group By Grouping Sets((city, car_model), (city), (car_model), ())expand extendedspark-sql> explain extended SELECT city, car_model, sum(quantity) AS sum FROM dealer GROUP BY CUBE(city, car_model) ORDER BY city, car_model;
== Parsed Logical Plan ==
...
== Analyzed Logical Plan ==
...
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Sort [city#2202 ASC NULLS FIRST, car_model#2203 ASC NULLS FIRST], true
+- Aggregate [city#2202, car_model#2203, spark_grouping_id#2201L], [city#2202, car_model#2203, sum(quantity#2197) AS sum#2188L]
+- Expand [[quantity#2197, city#2195, car_model#2196, 0], [quantity#2197, city#2195, null, 1], [quantity#2197, null, car_model#2196, 2], [quantity#2197, null, null, 3]], [quantity#2197, city#2202, car_model#2203, spark_grouping_id#2201L]
+- Project [quantity#2197, city#2195, car_model#2196]
+- HiveTableRelation [`default`.`dealer`, ..., Data Cols: [id#2194, city#2195, car_model#2196, quantity#2197], Partition Cols: []]
== Physical Plan ==
...
CubeCubeGrouping SetsRollUpCubeGrouping Sets最后
Group ByGroupings SetsGroupings SetsUnion AllGrouping Setsspark_grouping_idUnion AllGrouping SetsGroup ByRollUpCubeGrouping SetsGrouping Sets文章配图
参考
边栏推荐
- A Fei's expectation
- 工资3000,靠“视频剪辑”月入40000:会赚钱的人,从不靠拼命!
- "Everyday Mathematics" serial 56: February 25
- “用Android复刻Apple产品UI”(2)——丝滑的AppStore卡片转场动画
- 【OpenCV 例程200篇】217. 鼠标交互获取多边形区域(ROI)
- Redis在Windows以及Linux系统下的安装
- Microservice - fuse hystrix
- [web security] - [SQL injection] - error detection injection
- Detailed explanation of four modes of distributed transaction (Seata)
- Qt插件之自定义插件构建和使用
猜你喜欢

Slam learning notes - build a complete gazebo multi machine simulation slam from scratch (III)
![[redis foundation] understand redis master-slave architecture, sentinel mode and cluster together (Demo detailed explanation)](/img/1f/3dd95522b8d5f03dd763a6779e3db5.jpg)
[redis foundation] understand redis master-slave architecture, sentinel mode and cluster together (Demo detailed explanation)
Introduction series of software reverse cracking (1) - common configurations and function windows of xdbg32/64

Distributed task scheduling XXL job

嵌入式开发:避免开源软件的7个理由
![[系统安全] 四十三.Powershell恶意代码检测系列 (5)抽象语法树自动提取万字详解](/img/cd/00954b9c592c253d42e6a3b8298999.jpg)
[系统安全] 四十三.Powershell恶意代码检测系列 (5)抽象语法树自动提取万字详解

Microservices Seata distributed transactions

Unity function - unity offline document download and use
Redis在Windows以及Linux系统下的安装
uploads-labs靶场(附源码分析)(更新中)
随机推荐
Famous blackmail software stops operation and releases decryption keys. Most hospital IOT devices have security vulnerabilities | global network security hotspot on February 14
半监督学习
深度学习之三维重建
Shell script import and export data
坚持输出需要不断学习
Advanced Mathematics (Seventh Edition) Tongji University exercises 2-1 personal solutions
用同花顺炒股开户安全吗?
一些事情的反思
Find mapping relationship
First!! Is lancet hungry? Official documents
高等数学(第七版)同济大学 习题2-1 个人解答
Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server; consider upgrading MySQL client
"Remake Apple product UI with Android" (3) - elegant statistical chart
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(HAL 库)—— 实验5 外部中断实验(学习笔记)
[list to map] collectors Tomap syntax sharing (case practice)
[redis foundation] understand redis master-slave architecture, sentinel mode and cluster together (Demo detailed explanation)
Rk3399 platform development series explanation (WiFi) 5.54. What is WiFi wireless LAN
Is it safe to open an account with tongdaxin?
From the 18th line to the first line, the new story of the network security industry
[200 opencv routines] 217 Mouse interaction to obtain polygon area (ROI)