当前位置:网站首页>Information System Project Manager - Chapter VII project cost management
Information System Project Manager - Chapter VII project cost management
2022-06-27 06:06:00 【lufei0920】
Information system project manager — Chapter vii. Project cost management
The process of project cost management
Through project cost management, try to control the actual cost of the project within the budget range . Ensure that projects are completed within a comparable budget .


One 、 Planning cost management
Planning cost management : The project cost structure has been formulated 、 Estimate 、 Standards of budget and control .

1、 Type of cost
• Variable cost : With production 、 The cost that varies with workload or time is variable cost . Variable cost is also called variable cost .
• fixed cost : Not with production 、 Non recurring costs that change due to changes in workload or time are fixed costs .
• Direct cost : The cost directly attributable to the project work is the direct cost . Such as project team travel expenses 、 Wages 、 Fees for materials and equipment used in the project .
• Indirect costs : Expenses allocated to the project from the general management expense account or the project cost shared by several projects , It forms the indirect cost of the project , Such as tax 、 Additional benefits and security costs, etc .
• Opportunity cost : Is the use of a certain time or resources to produce a commodity , The lost opportunity to use these resources to produce other best alternatives is the opportunity cost , It generally refers to one of the biggest losses after making a choice .
• Sunk cost : It refers to what has happened due to past decisions , And costs that cannot be changed by any decision now or in the future . Sunk cost is a kind of historical cost , It's an uncontrollable cost to an existing decision , Will greatly affect people's behavior and decision-making , The interference of sunk cost should be eliminated in investment decision-making .
2、 Example cost management plan

Two 、 Estimated cost
cost estimation : The process of preparing an approximate estimate of the funds required to complete the project activities .

1、 There are three main steps in project cost estimation
1) Identify and analyze component accounts of project cost , That is, the category of resources or services included in the project cost , for example : Labor cost 、 Material cost 、 Consulting fee, etc .
2) Accounts are formed according to the identified project cost , Estimate the cost size of each cost account .
3) Analyze the cost estimation results , Find various alternative costs , Coordinate the proportional relationship between various costs .
2、 Tool technology for cost estimation
2.1 Analogical estimation
Analogy estimation method is also called “ Top down estimation ”.
The basic operation steps of this method are :
First , The upper management personnel collect historical information about similar projects ;
secondly , Work with relevant cost experts to estimate the total cost of the current project ;
Again , Transfer the estimation results to the adjacent next level management personnel according to the hierarchy of the project work breakdown structure diagram , On this basis , They estimate the cost of their work and activities ;
Last , Continue to pass on their estimates to the next level of Management , Until the grass-roots personnel of the project .
Scope of application : Previous projects for analogy are very similar in form and substance ; When the project information is difficult to obtain ( Little mastery of project details ).
advantage : It's easy , Less time-consuming 、 Low cost .
shortcoming ( limitations ): Due to the uniqueness of the project , The estimation accuracy of this method may be low .
2.2 Parameter estimation method
Parameter estimation is the use of historical data and other variables ( For example, the square meter cost during construction , Number of coding lines in software programming , Required man hours , Function point method in software project estimation, etc ) The statistical relationship between ,
An estimation technique to calculate the cost of activity resources . The accuracy of this technical estimation depends on the complexity of the model and the amount of resources and cost data involved .
2.3 Reserve analysis
Emergency reserve
Emergency reserve : Many cost estimation experts are used to adding provisions or contingency reserves to the cost estimation of planned activities . Emergency reserve is the estimated cost freely used by the project manager , Used to deal with expected but uncertain events , These events are called “ Known unknown events ”, Is part of the project scope and cost baseline .
Manage reserves
Manage reserves : Planned for the future , But the budget reserved for possible cost changes . Not part of the cost benchmark , Used for processing “ Unknown unknown events ”.
The difference is shown in the table below 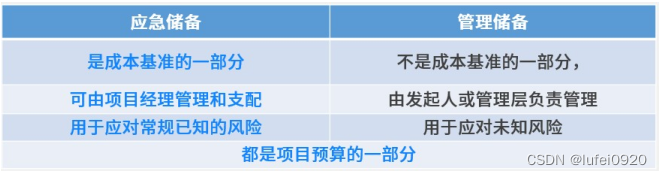
2.4 Bottom-up estimating
Bottom-up estimating : It is also called Bill of quantities . First, the cost of a single work package or activity is specified 、 Careful estimation ; Then report to the higher levels .
advantage : detailed 、 accuracy .
shortcoming : Time consuming 、 The cost of estimating itself is high .
2.5 quality cost
quality cost : Quality cost considerations and assumptions .
The cost of prevention : Prevent non conformance ( train );
Evaluate costs : The cost of evaluating to ensure compliance ;
rework ( Failure ) cost : Rework and repair 、 guarantee .
The first two items are consistency costs .
2.6 Seller's bid analysis
Seller's bid analysis : According to the bidding situation of the qualified seller , Analyze project cost .
3、 Estimated cost output
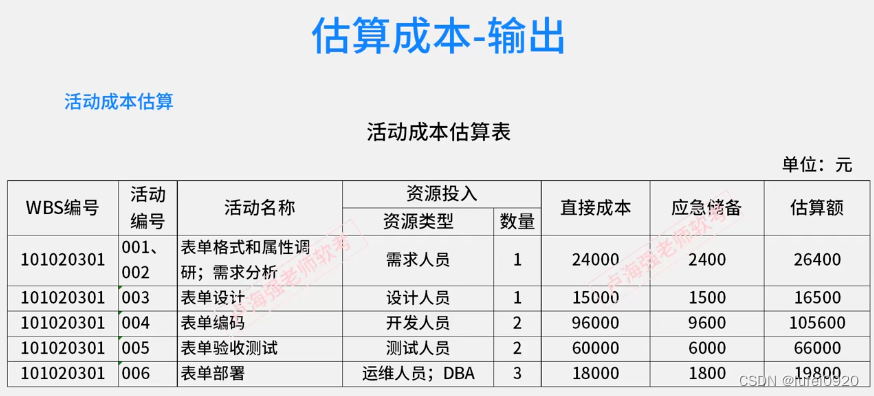
3、 ... and 、 Budget making
Cost budget : Aggregate estimated costs for all individual activities or work packages , To establish a cost benchmark .

1、 Comparison between cost estimate and cost budget

2、 Budget making — Tool technology
2.1 Cost summary

explain : The cost base includes contingency reserves but does not include management reserves ; The project budget includes management reserves .
2.2 Historical relations
Historical relations : There may be some historical relationships between relevant variables that can be used for parameter estimation or analogy estimation . Based on these historical relationships , Use project features ( Parameters ) To build a mathematical model , Forecast the total cost of the project .
2.3 Capital limit balance
Capital limit balance : Should be based on any restrictions on project funding , To balance capital expenditure . If you find a difference between the capital limit and the planned expenditure , The work schedule may need to be adjusted , To balance the level of capital expenditure . This can be achieved by adding mandatory dates to the project schedule .
3、 Output — Cost basis
Cost baseline ( Also called cost benchmark ) It is a time phased budget used to measure and monitor project cost performance . Usually, the S Curve form display . When to plan how much to spend , It is the scale of cost in time .
A project ( Especially big projects ) There can be multiple cost benchmarks , To measure all aspects of project cost performance . For example, expenditure plan or cash flow forecast is the cost benchmark for measuring expenditure ; In large projects , Management may require the project manager to monitor internal costs separately ( artificial ) And external costs ( Contractor's cost ) wait , Multiple baselines can be set .
3.1 Project cost budget table ( Cost basis )


explain : Total project budget = Cost basis + Manage reserves
Total capital requirements = Cost basis + Manage reserves
The project budget and fund demand amount are equal , The former is S curve , The latter is ladder like .
Four 、 cost control
cost control : Monitor project status , To update project costs : The process of managing cost baseline changes .

1、 cost control — Tool technology
1.1 Earned value management
Earned value management : It is a comprehensive range 、 Time 、 Methods of cost performance measurement . The workload will be planned 、 The actual cost is compared with the income of the actual earned value , Determine whether the cost and schedule are implemented as planned .
2、 Example of earned value calculation
1、 scene
For general planning 10 Tianzhong 100 A tree , The completion budget is 10000 element ;
The specific plan is to plant... Every day 10 star , The budget for each tree is 100 element , Spend every day 1000 element ;
2、 Now it's number one 5 The day is over , Budget and implementation :
According to the plan 50 A tree , Spending budget 5000 element ;
Actually planted 30 A tree , It actually cost 4500 element .
| The term | explain | give an example |
|---|---|---|
| Completion budget BAC | Project completion budget ( Without management reserves ) | Planning use 10 Tianzhong 100 A tree , The completion budget is 10000 element |
| actual cost AC | Actual cost of work done | Actually planted 30 A tree , The actual cost 4500 element |
| Plan value PV | The planned value of the work to be done | The first 5 The day is over , According to the plan 50 A tree , Spending budget 5000 element |
| Earned value EV | The planned value of the work actually done ( Approved budget value of completed work ) | Planted 30 A tree , It is planned to cost =30*100 element =3000 element ( Actually planted 30 A tree , According to the plan, a tree costs 100 element ) |
| Schedule deviation SV | EV-PV: Less than 0, Behind schedule ; Greater than 0 Ahead of schedule | EV3000 element -PV5000 element , Less than 0, Behind schedule |
| Progress performance index SPI | EV/PV: Less than 1, backward ; Greater than 1, advance | 3000/5000, Less than 1, Behind schedule |
| Cost deviation CV | EV-AC: Less than 0, Cost overruns ; Greater than 0, Cost savings | EV3000 element -AC4500 element , Less than 0, Cost overruns |
| Cost performance index CPI | EV/AC: Less than 1, Overspending ; Greater than 1, save | 3000/4500, Less than 1, Cost overruns |
| to complete performance index TCPI | Achieve the efficiency to be maintained according to the plan :TCPI=(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) The efficiency to be maintained by the current completion estimate : TCPI=(BAC-EV)/(EAC-AC) | Greater than 1 Difficult to accomplish equals 1 Just finished less than 1 It's easy to do |
| ETC( Atypical ) | The completion of the project needs to be estimated ( Atypical / Special circumstances of the original budget , It won't happen again , Just planting trees is not skilled , Not in the future ):ETC=BAC-EV | ETC=10000-3000=7000 |
| ETC ( A typical ) | The completion of the project needs to be estimated ( Typical , Not in special circumstances , There will always be , For example, the ground is hard to open Ken ):ETC=(BAC-EV)/CPI | ETC=(10000-3000)/0.6667≈10499 |
| ETC ( Dual effects ) | SPI and CPI At the same time influence :ETC=(BAC- EV)/(CPI*SPI), It can be set according to actual conditions SPI and CPI The weight of | ETC=(10000-3000)/(0.6667*0.6)≈17499 |
| ETC ( re-calculate ) | ETC, There is something wrong with the estimate , Re estimate | There is a problem with the early estimation , Manual revaluation |
| EAC | Completion estimate :EAC=AC+ETC Or a quick formula for typical cases :{EAC=BAC/CPI} | EAC=4500+7000=11500( According to the atypical situation ) ;EAC=4500+10499=14999( As a typical case ) |
| Total completion time forecast | Supplementary knowledge : Planned total construction period /SPI ( A typical ); Atypical : The actual construction period that has occurred + Planned remaining duration | The original planned construction period 10 Months , at present SPI by 0.5, Then the predicted completion period =10/0.5=20 |
| VAC Deviation from completion | The difference between the completion budget and the new completion estimate :VAC=BAC-EAC | VAC=BAC-EAC |
explain :
The advantages of earned value technology : If you only look at the budget and actual expenses , There seems to be no overspending , because AC4500 It seems less than PV5000, But in terms of scope , Actually, it's overspending : Planted 30 A tree , According to the plan, it should take 3000 element , But it actually took 4500 element (EV<AC ).
Three reference rules for Earned Value Management estimation
There are three ways to estimate the implementation value of a work package (EV) The law of :
0-100: The most conservative . Only when it is completely completed will it be recorded as completed .
100-100: The most aggressive . As long as the work starts, it is recorded as done .
50-50: frequently-used . Remember to finish the work at the beginning 50%, Write it down after the work is finished 50%( Another kind of view : Remember to finish the work at the beginning 50%, Over work 50% Remember to complete ) .
Description of schedule deviation and cost deviation
Less than is not a good thing (SV、CV Less than 0, or API、CPI Less than 1): Behind schedule , Cost overruns
Greater than is a good thing (SV、CV Greater than 0, or API、CPI Greater than 1): Ahead of schedule , Cost savings
Is full of EV start

边栏推荐
- Webrtc series - Nomination and ice of 7-ice supplement for network transmission_ Model
- Wechat applet refreshes the current page
- 数据库-索引
- JVM的垃圾回收机制
- Two position relay hjws-9440
- Free SSH and telnet client putty
- NEON优化1:软件性能优化、降功耗怎么搞?
- Kubesphere cluster configuration NFS storage solution - favorite
- openstack实例重启状态就会变成错误处理方法,容器搭建的openstack重启计算节点compute服务方法,开机提示Give root password for maintenance处理方法
- expect脚本中使用scp命令的方法,expect脚本中scp命令获取不了值的问题完美解决方法
猜你喜欢
![Senior [Software Test Engineer] learning route and necessary knowledge points](/img/51/1be2e0812a6bca9e5e8d14bf254254.png)
Senior [Software Test Engineer] learning route and necessary knowledge points

30 SCM common problems and solutions!
Two position relay hjws-9440

Dev++ 环境设置C语言关键字显示颜色

Leetcode298 weekly race record

Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)

使用CSDN 开发云搭建导航网站

Implementation of easyexcel's function of merging cells with the same content and dynamic title

Open the door small example to learn ten use case diagrams

思维的技术:如何破解工作生活中的两难冲突?
随机推荐
Double position relay jdp-1440/dc110v
openresty使用文档
【Cocos Creator 3.5.1】event.getButton()的使用
IP网络通信的单播、组播和广播
Unicast, multicast and broadcast of IP network communication
Assembly language - Wang Shuang Chapter 3 notes and experiments
【合辑】点云基础知识及点云催化剂软件功能介绍
【QT小记】QT元对象系统简单认识
Wechat applet websocket use case
我对于测试团队建设的意见
Small program of C language practice (consolidate and deepen the understanding of knowledge points)
Double position relay rxmd2-1mrk001984 dc220v
[FPGA] design and implementation of frequency division and doubling based on FPGA
426 binary tree (513. find the value in the lower left corner of the tree, 112. sum of paths, 106. construct a binary tree from the middle order and post order traversal sequence, 654. maximum binary
Wholestagecodegen of spark
IAR Systems全面支持芯驰科技9系列芯片
QListWidget中的内容不显示
30个单片机常见问题及解决办法!
Functional continuous
JVM overall structure analysis