当前位置:网站首页>[uvalive 6663 count the regions] (DFS + discretization) [easy to understand]
[uvalive 6663 count the regions] (DFS + discretization) [easy to understand]
2022-07-07 20:59:00 【Full stack programmer webmaster】
Hello everyone , I meet you again , I'm the king of the whole stack .
The main idea of the topic :
There are... On a plane n (1<=n<=50) A rectangle . Give you the coordinates of the upper left corner and the lower right corner (0<=x<=10^6, 0<=y<=10^6). Ask how many blocks these rectangles divide the plane .
Their thinking :
because n A very small , It can compress the whole graph . Just don't change the relative position of each side . It has no effect on the answer .
The coordinates of these rectangles can be discretized , Then mark the dot on the side . After that, simple dfs Can .( Pay attention to discretization , There should be at least a distance between the two sides )
Code :
/*
ID: [email protected]
PROG:
LANG: C++
*/
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define INF (1<<30)
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define For(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000007;
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
struct node {
int a, b, c, d;
} rec[600];
int x[1200], y[1200];
int xp[1000100], yp[1000100];
int mp[240][240], n;
int lx, ly;
void gao() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int A = xp[rec[i].a];
int B = yp[rec[i].b];
int C = xp[rec[i].c];
int D = yp[rec[i].d];
for (int j = A; j <= C; j++) mp[j][D] = mp[j][B] = 1;
for (int j = D; j <= B; j++) mp[A][j] = mp[C][j] = 1;
}
}
int dir[4][2] = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, { -1, 0}};
bool in(int x, int y) {
return (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < 2 * lx + 1 && y < 2 * ly + 1);
}
void dfs(int x, int y) {
mp[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dir[i][0];
int yy = y + dir[i][1];
if (in(xx, yy) && !mp[xx][yy]) {
dfs(xx, yy);
}
}
}
int main() {
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &rec[i].a, &rec[i].b, &rec[i].c, &rec[i].d);
x[2 * i] = rec[i].a;
x[2 * i + 1] = rec[i].c;
y[2 * i] = rec[i].b;
y[2 * i + 1] = rec[i].d;
}
sort(x, x + 2 * n);
sort(y, y + 2 * n);
lx = unique(x, x + 2 * n) - x;
ly = unique(y, y + 2 * n) - y;
for (int i = 0; i < lx; i++) {
xp[x[i]] = 2 * i + 1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < ly; j++) {
yp[y[j]] = 2 * j + 1;
}
memset(mp, 0, sizeof(mp));
gao();
int fk = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * lx; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2 * ly; j++) if (mp[i][j] == 0) {
dfs(i, j);
fk++;
}
}
cout << fk << endl;
}
return 0;
}Publisher : Full stack programmer stack length , Reprint please indicate the source :https://javaforall.cn/116289.html Link to the original text :https://javaforall.cn
边栏推荐
- 阿洛的烦恼
- 刚开户的能买什么股票呢?炒股账户安全吗
- 华为CE交换机下载文件FTP步骤
- AADL Inspector 故障树安全分析模块
- Deep learning model compression and acceleration technology (VII): mixed mode
- Is it safe to open an account of BOC shares in kainiu in 2022?
- 字符串中数据排序
- Small guide for rapid formation of manipulator (12): inverse kinematics analysis
- 部署、收回和删除解决方式—-STSADM和PowerShell「建议收藏」
- 现在网上开户安全么?想知道我现在在南宁,到哪里开户比较好?
猜你喜欢
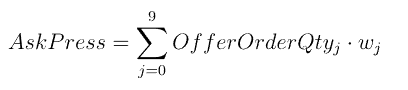
复杂因子计算优化案例:深度不平衡、买卖压力指标、波动率计算
Implement secondary index with Gaussian redis

How to meet the dual needs of security and confidentiality of medical devices?
Intelligent software analysis platform embold
![嵌入式系统真正安全了吗?[ OneSpin如何为开发团队全面解决IC完整性问题 ]](/img/af/61b384b1b6ba46aa1a6011f8a30085.png)
嵌入式系统真正安全了吗?[ OneSpin如何为开发团队全面解决IC完整性问题 ]

CodeSonar网络研讨会

Measure the height of the building
MySQL storage expression error
MySQL约束之默认约束default与零填充约束zerofill
C language helps you understand pointers from multiple perspectives (1. Character pointers 2. Array pointers and pointer arrays, array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing 3. Function point
随机推荐
Mongodb learn from simple to deep
Numerical method for solving optimal control problem (0) -- Definition
2022年在启牛开中银股票的账户安全吗?
复杂因子计算优化案例:深度不平衡、买卖压力指标、波动率计算
H3C S7000/S7500E/10500系列堆叠后BFD检测配置方法
Is it safe to open an account online now? I want to know where I can open an account in Nanning now?
Phoenix JDBC
Helix QAC 2020.2 new static test tool maximizes the coverage of standard compliance
神兵利器——敏感文件发现工具
Codeforces 474 F. Ant colony
如何满足医疗设备对安全性和保密性的双重需求?
部署、收回和删除解决方式—-STSADM和PowerShell「建议收藏」
MySQL storage expression error
Nebula importer data import practice
Lingyun going to sea | yidiantianxia & Huawei cloud: promoting the globalization of Chinese e-commerce enterprise brands
Intelligent transportation is full of vitality. What will happen in the future? [easy to understand]
凌云出海记 | 易点天下&华为云:推动中国电商企业品牌全球化
Codeforces Round #275 (Div. 2) C – Diverse Permutation (构造)[通俗易懂]
awk处理JSON处理
SQL注入报错注入函数图文详解