当前位置:网站首页>[set theory] relational closure (relational closure solution | relational graph closure | relational matrix closure | closure operation and relational properties | closure compound operation)
[set theory] relational closure (relational closure solution | relational graph closure | relational matrix closure | closure operation and relational properties | closure compound operation)
2022-07-03 06:11:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 Closure method
- Two 、 Find an example of closure ( Diagram angle )
- 3、 ... and 、 Find an example of closure ( Relationship matrix angle )
- Four 、 Closure operation and relation properties
- 5、 ... and 、 Closure compound operation
One 、 Closure method
R
R
R The relationship is
A
A
A Binary relations on sets ,
R
⊆
A
R \subseteq A
R⊆A , And
A
A
A Set is not empty ,
A
≠
∅
A \not= \varnothing
A=∅
Find reflexive closure :
r
(
R
)
=
R
∪
I
A
r(R) = R \cup I_A
r(R)=R∪IA , Add a ring to each vertex ;
- If
R
R
R Relationships are reflexive , If and only if ,
I
A
⊆
R
I_A \subseteq R
IA⊆R
Find symmetric closure :
s
(
R
)
=
R
∪
R
−
1
s(R) = R \cup R^{-1}
s(R)=R∪R−1
- original There is no edge ( Ordered pair ) , Naturally, there is no corresponding inverse , Do not add edges at this time
- original There is a directed side ( Ordered pair ) , Add a reverse directed edge , form In the diagram Between vertices Two way directed edge
- original There are two directed edges ( Ordered pair ) , At this time, there is no need to add other edges
- If
R
R
R The relationship is symmetrical , If and only if ,
R
=
R
−
1
R = R^{-1}
R=R−1
Finding transitive closure :
t
(
R
)
=
R
∪
R
2
∪
R
3
∪
⋯
t(R) = R \cup R^2 \cup R^3 \cup \cdots
t(R)=R∪R2∪R3∪⋯
take
R
R
R Relate all the power operation values together , Is its transitive closure ,
R
R
R Relational
1
1
1 The next power ,
R
R
R Relational
2
2
2 The next power ,
R
R
R Relational
3
3
3 The next power ,
⋯
\cdots
⋯ ,
R
R
R Relational
n
n
n The next power , And get up , Is its transitive closure ;
If
A
A
A It's a poor set , The relationship is also poor , Find out all
n
n
n The next power , There is no need to find many power operations , Because the power operation of the relationship is followed by a cycle , Find all known
n
n
n The next power take Union is enough ;
If
R
R
R Relationships are transitive , If and only if ,
R
2
⊆
R
R^2 \subseteq R
R2⊆R
Two 、 Find an example of closure ( Diagram angle )
aggregate
A
=
{
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
}
A = \{ a, b, c , d \}
A={ a,b,c,d}
Relationship
R
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
,
<
c
,
d
>
}
R = \{ <a,b> , <b,a> , <b,c> , <c,d> \}
R={ <a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>,<c,d>}
Seeking relationship
R
R
R Reflexive closure of
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) , Symmetric closure
s
(
R
)
s(R)
s(R) , Pass closures
t
(
R
)
t(R)
t(R)
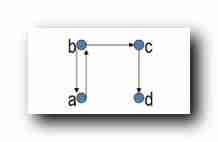
Find reflexive closure : Is to add a ring to each vertex :

Find symmetric closure : take Between vertices Change one-way edge to two-way edge , No matter Two way edges between vertices and There are no edges between vertices The situation of ;
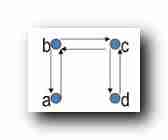
Finding transitive closure : Connect the accessible points directly ;
- a You can go to b , route a -> b ; a You can go to c , The path is a a -> b -> c ; a You can go to d , The path is a a -> b -> c -> d ; So add a To c , d The directed side of ;
- b You can go to a , route b -> a ; b You can go to c , The path is a b -> c ; b You can go to d , The path is a b -> c -> d ; So add b To d The directed side of ;
- c You can go to d , route c -> d ; There are no connectable edges ;
- d I can't get anywhere , There are no connectable edges ;
- In addition, when two-way edges appear , Two vertices must be looped ;
3、 ... and 、 Find an example of closure ( Relationship matrix angle )
Relationship
R
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
,
<
c
,
d
>
}
R = \{ <a, b> , <b,a> , <b,c> , <c,d> \}
R={ <a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>,<c,d>}
Use the relation matrix method to find its Reflexive closure , Symmetric closure , Pass closures ;
Write the above relationship in matrix form as :
M
(
R
)
=
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
]
M(R) = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001000010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Reflexive closure : Set the main diagonal value , All changed
1
1
1 , The upper left corner to the lower right corner is the main diagonal ;
M
(
r
(
R
)
)
=
[
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
]
M(r(R)) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}
M(r(R))=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡1100110001100011⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Symmetric closure : Both ends of the main diagonal should be symmetrical , Based on the diagonal , Make the values on both sides of the diagonal symmetrical ;
M
(
s
(
R
)
)
=
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
]
M(s(R)) = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(s(R))=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100101001010010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Pass closures : Find the of the relation matrix second power , third power , fourth power ,
⋯
\cdots
⋯ , Until the value of the same cycle appears ;
Put all the above different Matrix power operation Add logically ( or ) operation , Is the matrix corresponding to its transitive closure , Computer algorithm is suitable for this method , If people calculate , The diagram is more vivid ;
Reference resources : 【 Set theory 】 Relationship means ( The relational matrix | Example of relational matrix | Properties of relation matrix | Relational matrix operation | The diagram | Diagram example | Relationships represent related properties ) Four 、 Relational matrix operation
Pay attention to reverse order synthesis
M
(
R
2
)
=
M
(
R
∘
R
)
=
M
(
R
)
∙
M
(
R
)
=
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
]
∙
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
]
=
[
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
M(R^2) = M(R \circ R) = M(R) \bullet M(R) =\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \bullet \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R2)=M(R∘R)=M(R)∙M(R)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001000010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∙⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001000010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡1000010010000100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
M
(
R
3
)
=
M
(
R
2
∘
R
)
=
M
(
R
)
∙
M
(
R
2
)
=
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
]
∙
[
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
=
[
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
M(R^3) = M(R^2 \circ R) = M(R) \bullet M(R^2) = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \bullet \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R3)=M(R2∘R)=M(R)∙M(R2)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001000010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∙⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡1000010010000100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001001000⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
M
(
R
4
)
=
M
(
R
3
∘
R
)
=
M
(
R
)
∙
M
(
R
3
)
=
[
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
]
∙
[
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
=
[
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
=
M
(
R
2
)
M(R^4) = M(R^3 \circ R) = M(R) \bullet M(R^3) =\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \bullet \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = M(R^2)
M(R4)=M(R3∘R)=M(R)∙M(R3)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001000010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∙⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡0100100001001000⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡1000010010000100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=M(R2)
Therefore, its
R
4
R^4
R4 The subsequent power operation value , Even power relation matrix and
M
(
R
2
)
M(R^2)
M(R2) Same value , Odd power relation matrix and
M
(
R
3
)
M(R^3)
M(R3) Same value ;
M
(
t
(
R
)
)
=
M
(
R
)
∨
M
(
R
2
)
∨
M
(
R
3
)
=
[
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
M(t(R)) = M(R) \lor M(R^2) \lor M(R^3) =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(t(R))=M(R)∨M(R2)∨M(R3)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡1100110011001100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Four 、 Closure operation and relation properties
| reflexivity | symmetry | Transitivity | |
|---|---|---|---|
r ( R ) r(R) r(R) | 1 1 1 ( Nature of itself ) | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 |
r ( R ) r(R) r(R) | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 ( Nature of itself ) | |
r ( R ) r(R) r(R) | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 ( Nature of itself ) |
The median value in the above table is
1
1
1 , It shows that this property originally exists , Find the corresponding introspect / symmetry / Pass on After closure , It still has this property , On the contrary, it does not have this property ;
The meaning of the second row of the table :
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) The corresponding line ;
- reflexivity : If
R
R
R It turned out to be reflexive , that
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) It's also reflexive ;
- symmetry : If
R
R
R It turns out to be symmetrical , that
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) It's also symmetrical ; Find reflexive closure , Just ring the vertex , Does not affect symmetry ;
- Transitivity : If
R
R
R It was transmitted , that
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) It is also transmitted ; Find reflexive closure , Just ring the vertex , Does not affect transmissibility ;
There is only one exception : original
R
R
R It's delivered , If we find symmetric closures , The transitivity of its symmetric closure does not exist ;
Description of the second column of the table ( reflexivity ) : If
R
R
R Relationships are reflexive , So Symmetric closure
s
(
R
)
s(R)
s(R) and Pass closures
t
(
R
)
t(R)
t(R) It's also reflexive ;
R
since
back
⇒
s
(
R
)
and
t
(
R
)
since
back
R introspect \Rightarrow s(R) and t(R) introspect
R since back ⇒s(R) and t(R) since back
The third column of the table explains ( symmetry ) : If
R
R
R The relationship is symmetrical , So Reflexive closure
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) and Pass closures
t
(
R
)
t(R)
t(R) It's also symmetrical ;
R
Yes
call
⇒
r
(
R
)
and
t
(
R
)
Yes
call
R symmetry \Rightarrow r(R) and t(R) symmetry
R Yes call ⇒r(R) and t(R) Yes call
The fourth column of the table explains ( Transitivity ) : If
R
R
R Relationships are transitive , So Reflexive closure
r
(
R
)
r(R)
r(R) It is also transmitted ;
R
Pass on
Deliver
⇒
r
(
R
)
Pass on
Deliver
R Pass on \Rightarrow r(R) Pass on
R Pass on Deliver ⇒r(R) Pass on Deliver
5、 ... and 、 Closure compound operation
R
R
R The relationship is
A
A
A Binary relations on sets ,
R
⊆
A
R \subseteq A
R⊆A , And
A
A
A Set is not empty ,
A
≠
∅
A \not= \varnothing
A=∅
1.
r
s
(
R
)
=
s
r
(
R
)
rs(R) = sr(R)
rs(R)=sr(R) :
- rs( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Relational Reflexive closure , Then find the reflexive closure Symmetric closure
- sr( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Symmetric closure of relation , Then find the reflexive closure of symmetric closure
- The above two closure operations The result is the same
2.
r
t
(
R
)
=
t
r
(
R
)
rt(R) = tr(R)
rt(R)=tr(R)
- rt( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Relational Reflexive closure , Then find the reflexive closure Pass closures
- tr( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Transitive closure of relation , Then find the reflexive closure of transitive closure
- The above two closure operations The result is the same
3.
s
t
(
R
)
⊆
t
s
(
R
)
st(R) \subseteq ts(R)
st(R)⊆ts(R)
- st( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Relational Symmetric closure , Then find the symmetric closure Pass closures
- ts( R ) : First seek
R
R
R Transitive closure of relation , Then find the symmetric closure of transitive closure
- The results of the above two closure operations ,
t
s
(
R
)
ts(R)
ts(R) Relationship contain
s
t
(
R
)
st(R)
st(R) Relationship ;
边栏推荐
- [teacher Zhao Yuqiang] kubernetes' probe
- Bio, NiO, AIO details
- Maximum likelihood estimation, divergence, cross entropy
- Migrate data from Amazon aurora to tidb
- Disruptor learning notes: basic use, core concepts and principles
- Mysql database
- Fluentd is easy to use. Combined with the rainbow plug-in market, log collection is faster
- Cesium entity (entities) entity deletion method
- 项目总结--01(接口的增删改查;多线程的使用)
- Solve the problem that Anaconda environment cannot be accessed in PowerShell
猜你喜欢

Understand expectations (mean / estimate) and variances
![[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] use the catalog database of Oracle](/img/0b/73a7d12caf955dff17480a907234ad.jpg)
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] use the catalog database of Oracle
![[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package](/img/cc/5509b62756dddc6e5d4facbc6a7c5f.jpg)
[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package
Merge and migrate data from small data volume, sub database and sub table Mysql to tidb

. Net program configuration file operation (INI, CFG, config)
智牛股项目--05
表达式的动态解析和计算,Flee用起来真香

Kubesphere - Multi tenant management
![[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] RDB persistence of redis](/img/cc/5509b62756dddc6e5d4facbc6a7c5f.jpg)
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] RDB persistence of redis
Synthetic keyword and NBAC mechanism
随机推荐
Simple understanding of ThreadLocal
Solve the problem that Anaconda environment cannot be accessed in PowerShell
88. Merge two ordered arrays
1. 两数之和
Alibaba cloud OOS file upload
The most responsible command line beautification tutorial
Why is the website slow to open?
Cesium Click to obtain the longitude and latitude elevation coordinates (3D coordinates) of the model surface
Convolution operation in convolution neural network CNN
Nacos service installation
Tabbar settings
Get a screenshot of a uiscrollview, including off screen parts
Why should there be a firewall? This time xiaowai has something to say!!!
If function of MySQL
Multithreading and high concurrency (7) -- from reentrantlock to AQS source code (20000 words, one understanding AQS)
Migrate data from Mysql to tidb from a small amount of data
Detailed explanation of findloadedclass
Clickhouse learning notes (2): execution plan, table creation optimization, syntax optimization rules, query optimization, data consistency
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] index in mongodb (Part 1)
Apple submitted the new MAC model to the regulatory database before the spring conference