当前位置:网站首页>The use of pytorch: temperature prediction using neural networks
The use of pytorch: temperature prediction using neural networks
2022-08-05 00:59:00 【The romance of cherry blossoms】
1.首先,Let's take a look at what's going on with the data
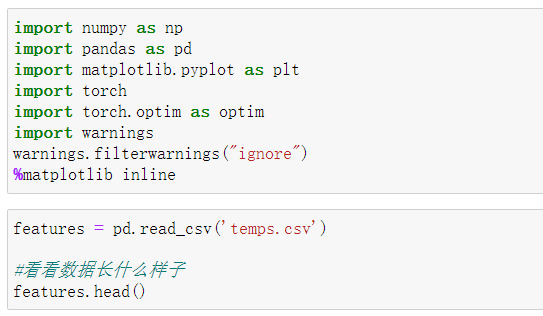
数据表中
- year,moth,day,week分别表示的具体的时间
- temp_2:前天的最高温度值
- temp_1:昨天的最高温度值
- average:在历史中,每年这一天的平均最高温度值
- actual:这就是我们的标签值了,当天的真实最高温度
- friend:这一列可能是凑热闹的,你的朋友猜测的可能值,whatever it is
Year, month and day are all characteristics of time,We convert it to time type data,To facilitate our drawing display
# 处理时间数据
import datetime
# 分别得到年,月,日
years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day']
# datetime格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
We then use the graph to visually display the data:
# 准备画图
# 指定默认风格
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
# 设置布局
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize = (10,10))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation = 45)
# 标签值
ax1.plot(dates, features['actual'])
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax1.set_title('Max Temp')
# 昨天
ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'])
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax2.set_title('Previous Max Temp')
# 前天
ax3.plot(dates, features['temp_2'])
ax3.set_xlabel('Date'); ax3.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax3.set_title('Two Days Prior Max Temp')
# 我的逗逼朋友
ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'])
ax4.set_xlabel('Date'); ax4.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax4.set_title('Friend Estimate')
plt.tight_layout(pad=2) 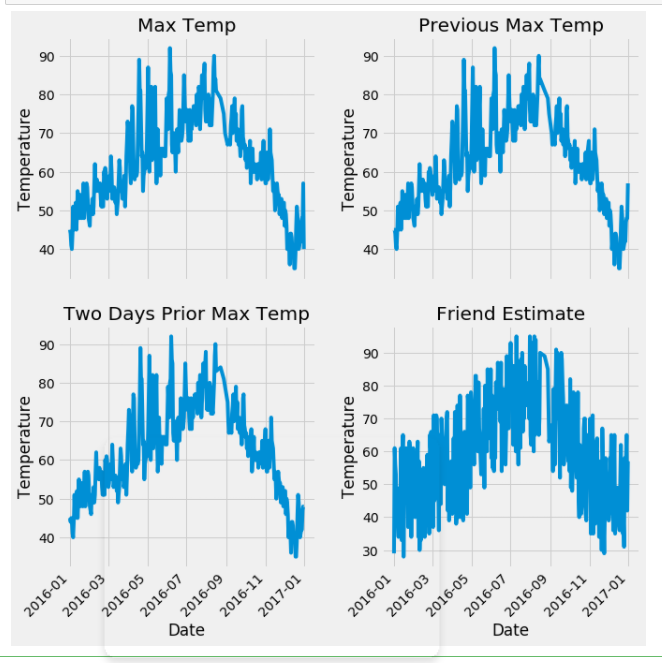
Convert text data to one-hot encoding:
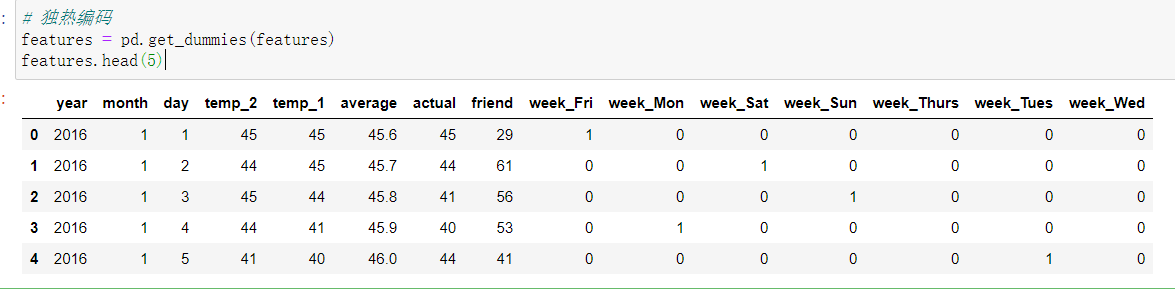
Remove the label column from the feature:
# 标签
labels = np.array(features['actual'])
# 在特征中去掉标签
features= features.drop('actual', axis = 1)
# 名字单独保存一下,以备后患
feature_list = list(features.columns)
# 转换成合适的格式
features = np.array(features)对数据进行标准化处理:
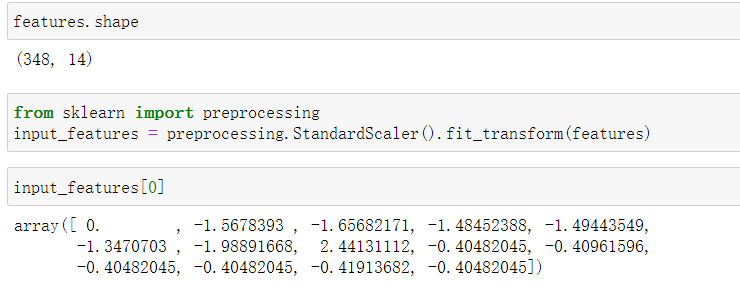
2.构建网络模型
包括:权重参数初始化、计算隐层、加入激活函数、预测结果、计算损失、返向传播计算、更新参数.另外,Remember to clear the gradient every iteration,否则梯度会累加
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = float)
y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype = float)
# 权重参数初始化
weights = torch.randn((14, 128), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases = torch.randn(128, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
weights2 = torch.randn((128, 1), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases2 = torch.randn(1, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
learning_rate = 0.001
losses = []
for i in range(1000):
# 计算隐层
hidden = x.mm(weights) + biases
# 加入激活函数
hidden = torch.relu(hidden)
# 预测结果
predictions = hidden.mm(weights2) + biases2
# 通计算损失
loss = torch.mean((predictions - y) ** 2)
losses.append(loss.data.numpy())
# 打印损失值
if i % 100 == 0:
print('loss:', loss)
#返向传播计算
loss.backward()
#更新参数
weights.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights.grad.data)
biases.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases.grad.data)
weights2.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights2.grad.data)
biases2.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases2.grad.data)
# 每次迭代都得记得清空
weights.grad.data.zero_()
biases.grad.data.zero_()
weights2.grad.data.zero_()
biases2.grad.data.zero_()
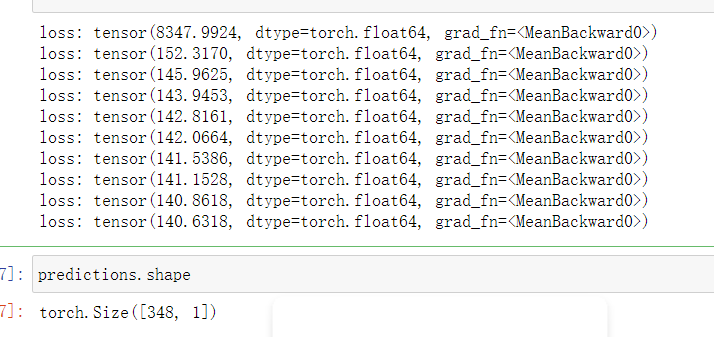
3.Simpler network model
直接使用nn.Model
input_size = input_features.shape[1]
hidden_size = 128
output_size = 1
batch_size = 16
my_nn = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size),
torch.nn.Sigmoid(),
torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size),
)
cost = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(my_nn.parameters(), lr = 0.001)训练网络:
# 训练网络
losses = []
for i in range(1000):
batch_loss = []
# MINI-Batch方法来进行训练
for start in range(0, len(input_features), batch_size):
end = start + batch_size if start + batch_size < len(input_features) else len(input_features)
xx = torch.tensor(input_features[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
yy = torch.tensor(labels[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
prediction = my_nn(xx)
loss = cost(prediction, yy)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer.step()
batch_loss.append(loss.data.numpy())
# 打印损失
if i % 100==0:
losses.append(np.mean(batch_loss))
print(i, np.mean(batch_loss))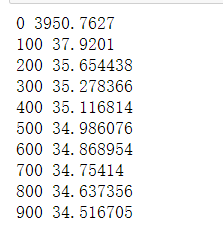
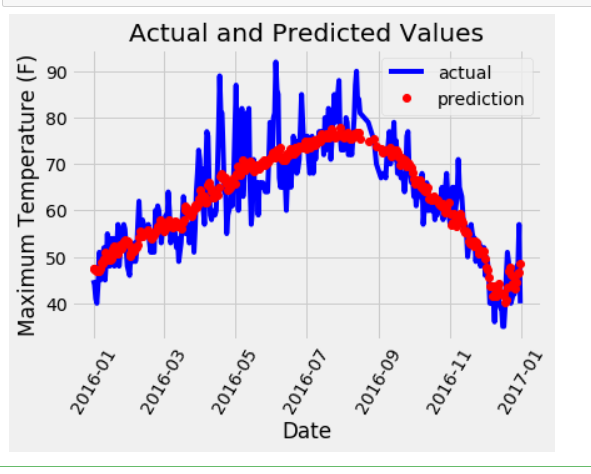
4.预训练结果
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = torch.float)
predict = my_nn(x).data.numpy() 转换日期格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
# 创建一个表格来存日期和其对应的标签数值
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': dates, 'actual': labels})
# 同理,再创建一个来存日期和其对应的模型预测值
months = features[:, feature_list.index('month')]
days = features[:, feature_list.index('day')]
years = features[:, feature_list.index('year')]
test_dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
test_dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in test_dates]
predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': test_dates, 'prediction': predict.reshape(-1)}) # 真实值
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label = 'actual')
# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label = 'prediction')
plt.xticks(rotation = '60');
plt.legend()
# 图名
plt.xlabel('Date'); plt.ylabel('Maximum Temperature (F)'); plt.title('Actual and Predicted Values');
边栏推荐
- Redis visual management software Redis Desktop Manager2022
- 面试汇总:为何大厂面试官总问 Framework 的底层原理?
- 5.PCIe官方示例
- 2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi-School Training Session 3 1009 Package Delivery
- VOC格式数据集转COCO格式数据集
- 4. PCIe interface timing
- 软件基础的理论
- If capturable=False, state_steps should not be CUDA tensors
- Software test interview questions: BIOS, Fat, IDE, Sata, SCSI, Ntfs windows NT?
- MBps与Mbps区别
猜你喜欢

测试工作这么难找吗?今年32,失业2个月,大龄测试工程师接下来该拿什么养家?
面试汇总:为何大厂面试官总问 Framework 的底层原理?

ORA-01105 ORA-03175
Helm Chart
pytorch的使用:卷积神经网络模块
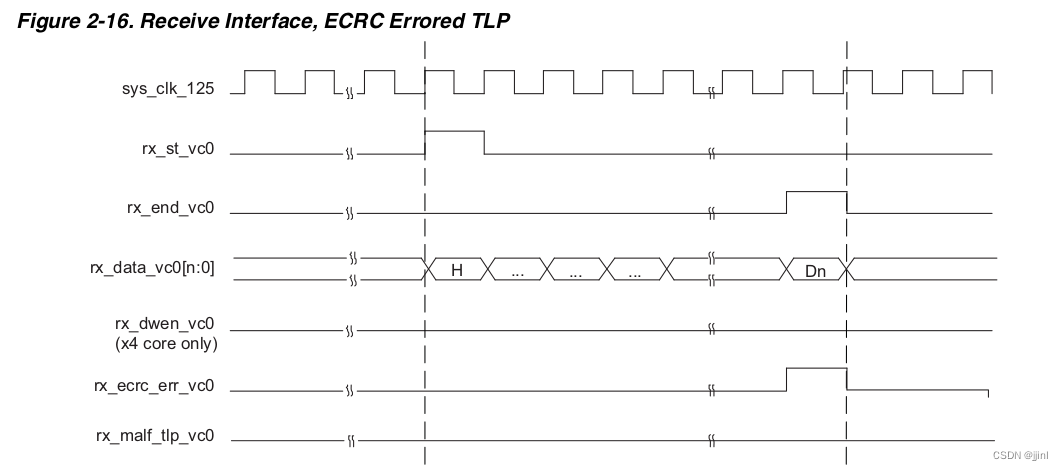
4. PCIe 接口时序
![[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy](/img/33/3177b4c3de34d4920d741fed7526ee.png)
[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy

Interview summary: Why do interviewers in large factories always ask about the underlying principles of Framework?

创意代码表白
Inter-process communication and inter-thread communication
随机推荐
tiup status
FSAWS 的全球基础设施和网络
Pytorch使用和技巧
The method of freely controlling concurrency in the sync package in GO
LiveVideoStackCon 2022 Shanghai Station opens tomorrow!
Dynamic Programming/Knapsack Problem Summary/Summary - 01 Knapsack, Complete Knapsack
5. PCIe official example
软件测试技术之最有效的七大性能测试技术
After the staged testing is complete, have you performed defect analysis?
接口自动化测试框架postman tests常用方法
pytorch的使用:使用神经网络进行气温预测
gorm joint table query - actual combat
DHCP的工作过程
matlab 采用描点法进行数据模拟和仿真
MongoDB搭建及基础操作
Helm Chart
(十七)51单片机——AD/DA转换
E - Many Operations (bitwise consideration + dp thought to record the result after the operation
深度学习训练前快速批量修改数据集中的图片名
Bit rate vs. resolution, which one is more important?