当前位置:网站首页>File operation (detailed!)
File operation (detailed!)
2022-07-02 11:48:00 【Less debug every day】
Indexes
file
1, What is a document
Program files : Include source files ( The suffix is .c), Target file (windows Environment suffix is .obj), Executable program (windows Environment suffix is .exe)
Data files : The content of the file is not necessarily a program , It's the data that the program reads and writes when it runs , For example, the file from which the program needs to read data , Or output content file
In the past, input refers to input from the keyboard , Output refers to display on the screen ,
But sometimes we output information to disk , When necessary, read the data from the disk to the memory for use , What we are dealing with here is the files on the disk 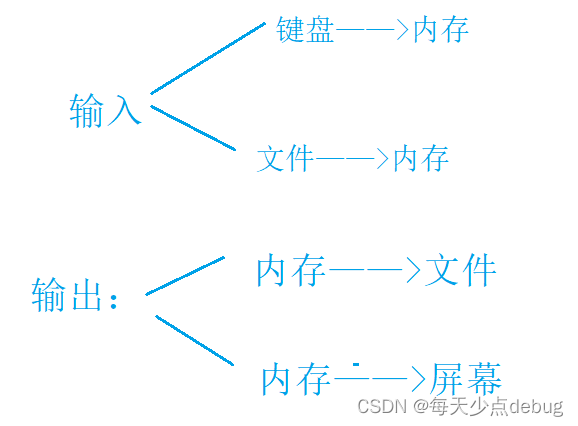
2, The file pointer FILE
seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function : Through the file pointer variable, you can find the file associated with it .
stay vs2013 Yes FILE Have the following statement
struct _iobuf {
char *_ptr;
int _cnt;
char *_base;
int _flag;
int _file;
int _charbuf;
int _bufsiz;
char *_tmpfname;
};
typedef struct _iobuf FILE;
Different compilers for FILE The definition of is different , But it's the same , Every time we open a file , The system will automatically create a FILE Structural variables , And supplement the information , Generally, we use file pointers to perform relevant operations on files .
3, Opening and closing of files
| How files are used meaning If the specified file does not exist | |
| “r”( read-only ) To enter data , Open an existing text file error | |
| “w”( Just write ) To output data , Open a text file Create a new file | |
| “a”( Additional ) Add data to the end of the text file Create a new file | |
| “rb”( read-only ) To enter data , Open a binary file error | |
| “wb”( Just write ) To output data , Open a binary file Create a new file | |
| “ab”( Additional ) Add data to the end of a binary file error | |
| “r+”( Reading and writing ) For reading and writing , Open a text file error | |
| “w+”( Reading and writing ) For reading and writing , Suggest a new file Create a new file | |
| “a+”( Reading and writing ) Open a file , Read and write at the end of the file Create a new file | |
| “rb+”( Reading and writing ) Open a binary file for reading and writing error | |
| “wb+”( Reading and writing ) For reading and writing , Create a new binary file Create a new file | |
| “ab+”( Reading and writing ) Open a binary file , Read and write at the end of the file Create a new file |
// Open file
FILE * fopen ( const char * filename, const char * mode );
The first parameter : Open file name
The second parameter : Open mode , Must be a double quotation mark , Single quotation marks don't work
// Close file
int fclose ( FILE * stream );
Each time you open a file, you only need to write the corresponding opening method .
eg:
// Open the file as a write
FILE* pf = fopen("text.txt", "w");// To output data , Open a text file
// If the asking price doesn't exist, create a new document
// If the file exists, eliminate the original contents in the file
if (pf == NULL)
{
printf(" fail to open file \n");
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));// Print error messages related to file opening failure
return 0;
}
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;// Be sure to leave the file empty after closing , Otherwise, wild pointers may appear
When you open the same folder, a 
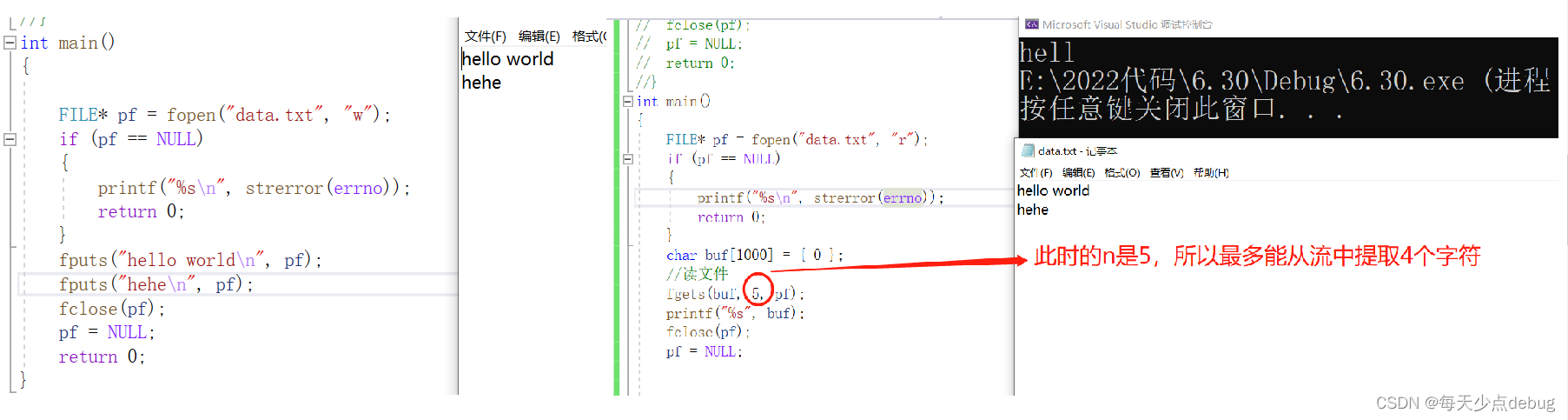
Open file
FILE* pf = fopen("text.txt", "r");// Only existing files can be opened , If it does not exist , Then return to NULL
if (pf == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
fclose(pf);
Other opening methods are similar
4, Sequential reading and writing of files
The reading of file data can be divided into Sequential reading and writing , Random, speaking, reading and writing , Sequential read-write, as the name suggests, is to write and read files in the order we input and output , Random reading and writing is just random reading and writing in a sense , What is it? Let's see below .
| function Function name Apply to | |
| Character input function fgetc All input streams | |
| Character output function fputc All output streams | |
| Text line input function fgets All input streams | |
| Text line output function fputs All output streams | |
| Format input function fscanf All input streams | |
| Format output function fprintf All output streams | |
| Binary input fread file | |
| Binary output fwrite file |
fgetc,fputc
fputc:int fputc( int c, FILE stream ); Output a character to the stream
c: Indicates that the characters entering the stream need to be read
stream: flow
fputc Applicable to all streams ? What does it mean ?
Take the output as an example : At present, what I know about the output is two streams , Does it flow to the screen or to the file .
Flow can be compared to water , Then the screen and file are in two directions , The direction refers to which direction the water flows, so the data is input or output to .
When running a program from a language , Three streams are opened by default :
Standard input stream :stdin
Standard output stream :stdout These three streams The types of FILE
Standard error flow :stderr
for example :
printf: Standard output stream :stdout( Flow to screen )
scanf: Standard output stream :stdout( keyboard )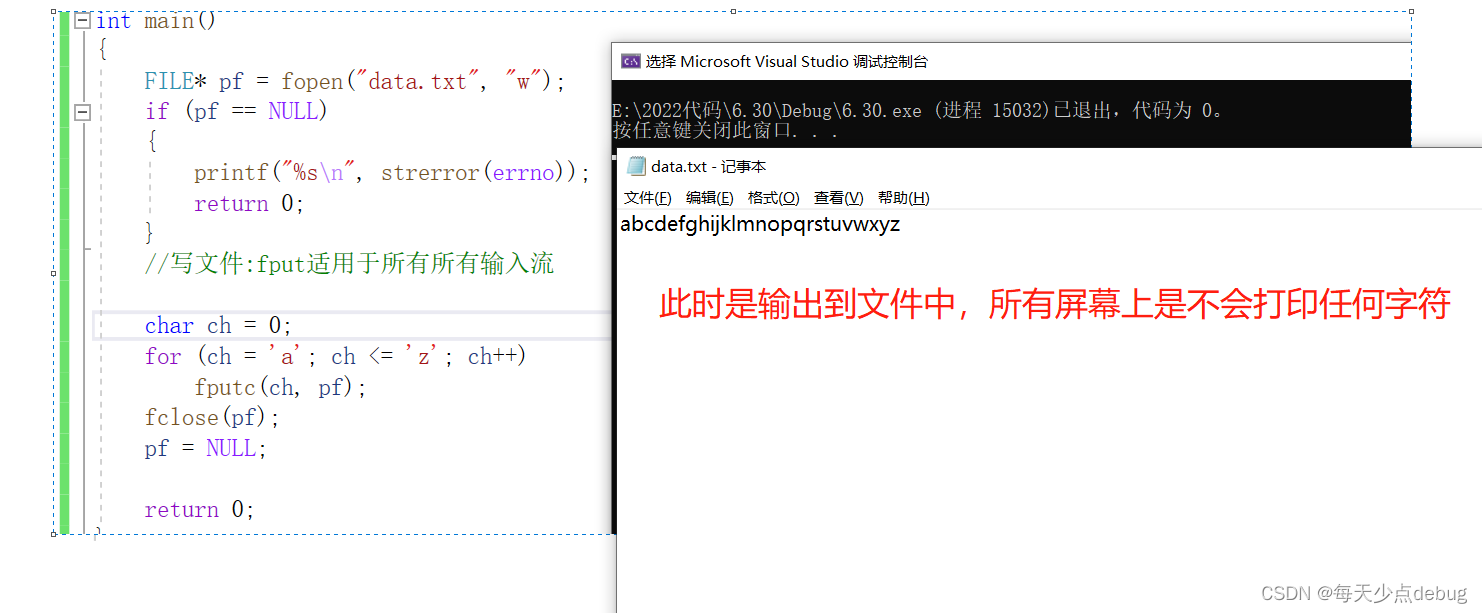

fgetc:int fgetc( FILE *stream ); Read characters from the stream into memory , And return the read characters
FILE* pf = fopen("data.txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
int ch = 0;
//while ((ch = fgetc(stdin)) != EOF)// When the error or the end of the file is returned EOF
while ((ch = fgetc(pf)) != EOF)// When the error or the end of the file is returned EOF
{
printf("%c ", ch);
}
fputs,fgets
fputs:int fputs( const char *string, FILE *stream );
string: The string to be read
streat: The stream to which the string should flow
Return value : If executed successfully , These functions will return a non negative value . When something goes wrong ,fputs return EOF
fgets:char *fgets( char *string, int n, FILE *stream );
string: The data extracted from the stream is roughly stored in the string
n:fgets Read characters from the current position of the stream , Including the first line break , Read to the end of the stream , Or until the number of characters read is equal to n - 1, Stored at the end of the character will automatically add a ’\0’
stream: Which stream to extract data from
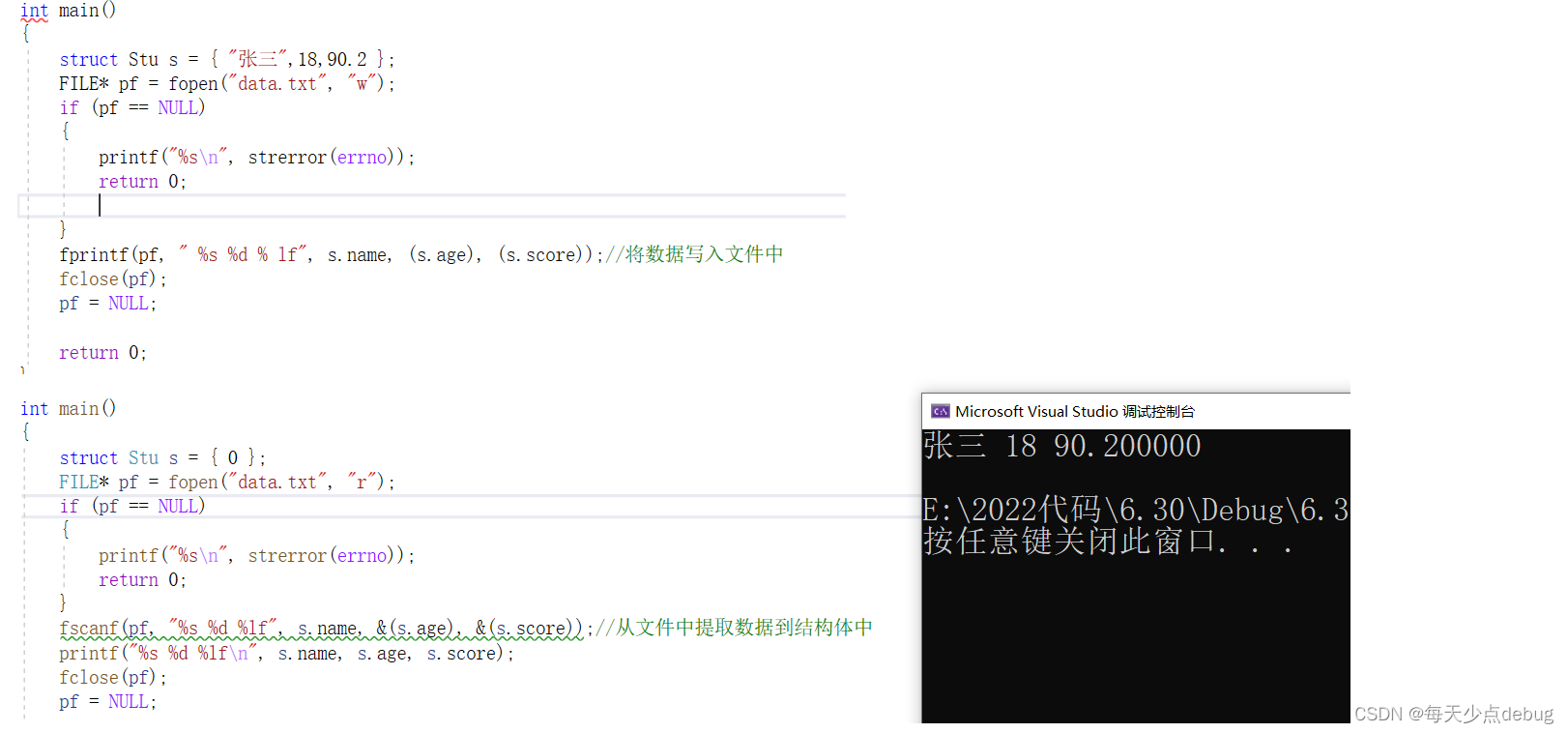
fscanf ,fprint

fread/fwrite
size_t fread( void *buffer, size_t size, size_t count, FILE *stream );
Return value : Returns the number of completed entries actually read
buffer: The entries read from the stream are stored in buffer in
size: The overall size of each read ( In bytes )
count: The maximum number of entries read
stream: Read the source of the entry , It's from the standard input stream ( keyboard ) Or file input
size_t fwrite( const void *buffer, size_t size, size_t count, FILE *stream );
Return value : Returns the number of complete entries successfully written to the stream
size: The size of each entry written
count: Maximum number of entries written
stream: Same as fread
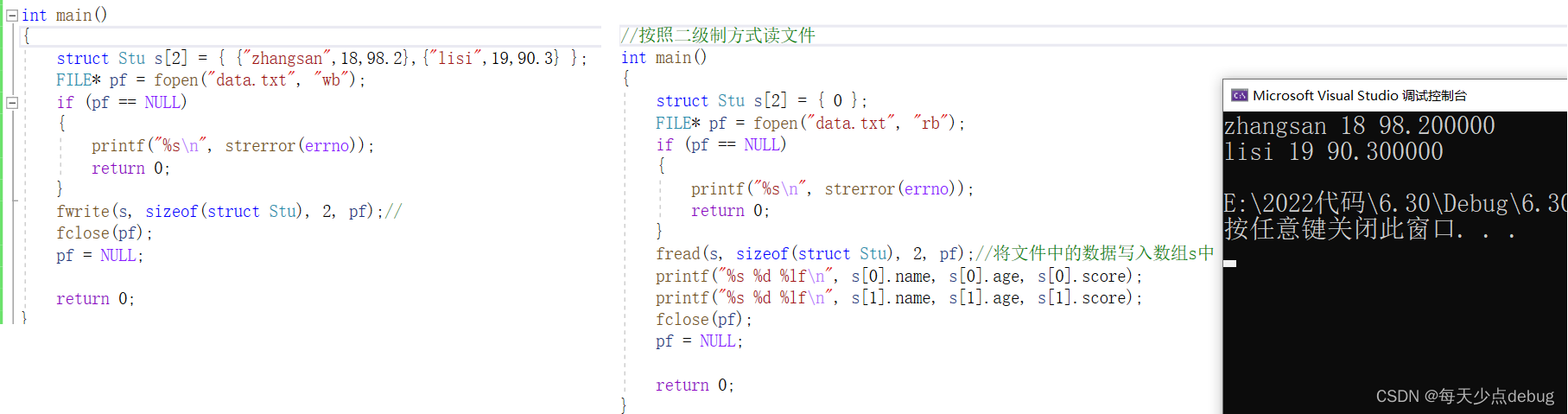
feof/ferror
int main()
{
FILE* pf = fopen("data,txt", "r");
if (pf == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
int ch = 0;
//fgetc When reading fails or the end of the file is encountered , Will return to EOF
while ((ch = fgetc(pf)) != EOF);// Label read file operation cycle
// Judge what caused it
if (ferror(pf))// If there is no error on the stream ,ferror return 0. otherwise , It returns a non-zero value .
puts("I/O error when reading");
else if (feof(pf))//eof Function returns a non-zero value after the first read operation attempts to read to the end of the file .
// If the current location is not at the end of the file , Then return to 0.
puts("End of file reached successfully");
fclose(pf);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- K-Means Clustering Visualization in R: Step By Step Guide
- ren域名有价值吗?值不值得投资?ren域名的应用范围有哪些?
- A sharp tool for exposing data inconsistencies -- a real-time verification system
- mysql链表数据存储查询排序问题
- VS2019代码中包含中文内容导致的编译错误和打印输出乱码问题
- What week is a date obtained by QT
- [multithreading] the main thread waits for the sub thread to finish executing, and records the way to execute and obtain the execution result (with annotated code and no pit)
- PHP query distance according to longitude and latitude
- 基于Hardhat和Openzeppelin开发可升级合约(一)
- 微信小程序利用百度api达成植物识别
猜你喜欢

由粒子加速器产生的反中子形成的白洞

HOW TO ADD P-VALUES ONTO A GROUPED GGPLOT USING THE GGPUBR R PACKAGE
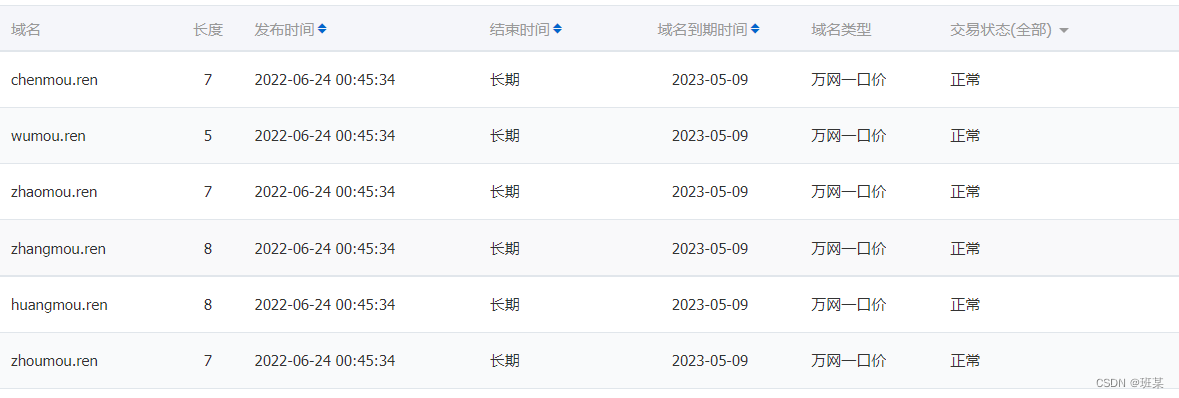
Is the Ren domain name valuable? Is it worth investing? What is the application scope of Ren domain name?

Summary of data export methods in powerbi

GGPUBR: HOW TO ADD ADJUSTED P-VALUES TO A MULTI-PANEL GGPLOT
Wechat applet uses Baidu API to achieve plant recognition

CTF record

Basic usage of MySQL in centos8

ESP32存储配网信息+LED显示配网状态+按键清除配网信息(附源码)
GGHIGHLIGHT: EASY WAY TO HIGHLIGHT A GGPLOT IN R
随机推荐
GGPUBR: HOW TO ADD ADJUSTED P-VALUES TO A MULTI-PANEL GGPLOT
to_bytes与from_bytes简单示例
Compilation errors and printout garbled problems caused by Chinese content in vs2019 code
对毕业季即将踏入职场的年轻人的一点建议
HOW TO ADD P-VALUES ONTO A GROUPED GGPLOT USING THE GGPUBR R PACKAGE
easyExcel和lombok注解以及swagger常用注解
Digital transformation takes the lead to resume production and work, and online and offline full integration rebuilds business logic
PLC-Recorder快速监控多个PLC位的技巧
【多线程】主线程等待子线程执行完毕在执行并获取执行结果的方式记录(有注解代码无坑)
How to Add P-Values onto Horizontal GGPLOTS
ESP32存储配网信息+LED显示配网状态+按键清除配网信息(附源码)
Tdsql | difficult employment? Tencent cloud database micro authentication to help you
deepTools对ChIP-seq数据可视化
TDSQL|就业难?腾讯云数据库微认证来帮你
Webauthn - official development document
BEAUTIFUL GGPLOT VENN DIAGRAM WITH R
念念不忘,必有回响 | 悬镜诚邀您参与OpenSCA用户有奖调研
[visual studio 2019] create and import cmake project
Astparser parsing class files with enum enumeration methods
mysql 基本语句