当前位置:网站首页>Interviewer: please introduce cache penetration, cache null value, cache avalanche and cache breakdown, which are easy to understand
Interviewer: please introduce cache penetration, cache null value, cache avalanche and cache breakdown, which are easy to understand
2022-06-27 06:50:00 【xy29981】
An avalanche Is a professional term in back-end services , To understand it , Let's introduce... Step by step . Avalanches are cumulative problems , Under the avalanche , No snowflake is innocent .
today , To have a chat Cache penetration 、 Cache breakdown 、 cache An avalanche Related issues . I believe you will have a clearer understanding of these concepts .
For Internet developers , You will be familiar with the concept of avalanche , It seems that I feel a little pale when talking about Tiger . If the backend service avalanches , It would be GG 了 .
The topic written today , It's actually very basic , But there are several scenarios that are very important for high concurrency , I can't get around it , It is estimated that during the interview , Often .
Articles on this topic , There are a lot of them on the Internet , But I feel there is no suitable , Or the article is not refined enough , Or it's too lean , So I'd better write one by myself .
Although the content is basic , But I still stick to my previous writing style , After referring to many excellent blogs , I'm going to write an article that can be easily understood , Without losing a comprehensive article .
Preface
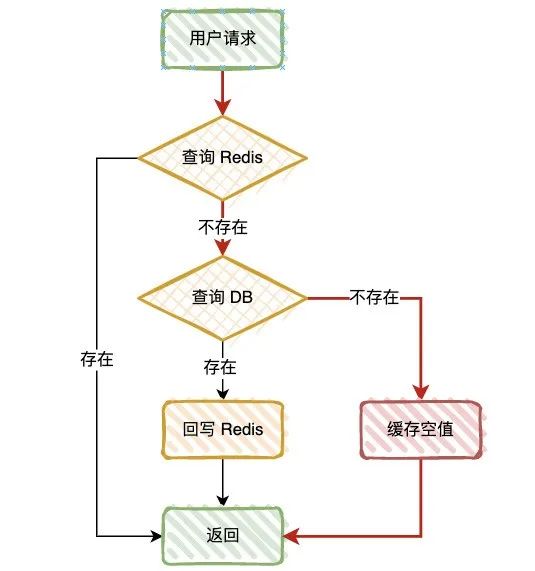
Let's first look at the normal query process :
First query Redis, If the query is successful , Go straight back to , Query does not exist , Go to query DB;
If DB The query is successful , Data write back Redis, Query does not exist , Go straight back to .

Cache penetration
Definition : When there is no data in the query database and cache , Because the database query has no data , For fault tolerance , The results will not be saved to the cache , therefore Every request will query the database , This is called cache penetration .

Red lines , This is the scene of cache penetration , When inquired Key In cache and DB When none of them exist , This will happen .
You can imagine , For example, there is an interface that needs to query product information , If a malicious user impersonates a non-existent product ID Initiate request , Instantaneous concurrency is very high , Estimate your DB I'll just hang up .
Maybe your first reaction is to perform regular verification on the input parameters , Filter out invalid requests , Yes ! The true , Is there any other better plan ?
Cache null
When we find a null value from the database , We can return a null value to the cache , In order to avoid the cache being occupied for a long time , You need to add a shorter expiration time to this null value , for example 3~5 minute .
But there's a problem with this plan , When a large number of invalid requests penetrate , There will be a large number of null value caches in the cache , If the cache space is full , It will also eliminate some user information that has been cached , Instead, it will reduce the cache hit rate , So this program , Need to evaluate cache capacity .
If a cache null value is not desirable , At this time, you can consider using Bloom filter .
The bloon filter
The bloom filter is made up of a variable length N A binary array with a variable number M The hash function of , Be simple and rough , It's just one. Hash Map.
The principle is quite simple : Such as element key=#3, If through Hash The algorithm gets a value of 9 Value , There is this Hash Map Of the 9 Bit element , By marking 1 Indicates that there is already data in this bit , As shown in the figure below ,0 No data ,1 Yes, there are data .

So through this method , There will be a conclusion : stay Hash Map in , Tagged data , Not necessarily , But unmarked data , There must be no .
Why? “ Tagged data , Not necessarily ” Well ? because Hash Conflict !
such as Hash Map The length of is 100, But you have 101 A request , If you're lucky enough to explode , this 100 Requests are typed evenly with a length of 100 Of Hash Map in , Your Hash Map All have been marked as 1.
When the first 101 When a request comes , Just 100% appear Hash Conflict , Although I didn't ask , But the mark is 1, The bloom filter did not intercept .
If you need to reduce miscalculation , Can increase Hash Map The length of , And choose a higher grade Hash function , For example, many times to key Conduct hash.
except Hash Conflict , The bloom filter can actually cause a fatal problem : Bloom filter update failed .
For example, there is a commodity ID First request , When DB When in , Need to be in Hash Map Mark in , But because of the Internet , Cause the tag to fail , So next time this product ID When the request is reissued , The request will be intercepted by the bloom filter , For example, this is a double 11 Stock of popular goods , There is clearly 10W Commodity , But you suggest that the inventory does not exist , Leaders may say “ You don't have to come tomorrow ”.
So if you use a bloom filter , In the face of Hash Map When updating data , It needs to be ensured that this data can 100% The update is successful , It can be done asynchronously 、 How to retry , Therefore, this scheme has certain implementation cost and risk .
Cache breakdown
Definition : A hotspot cache just fails at a certain time , Then there happens to be a large number of concurrent requests , At this point, these requests will put great pressure on the database , This is called cache breakdown .
This is actually the same as “ Cache penetration ” The flow chart is the same , But the starting point of this is “ A hotspot cache just fails at a certain time ”, For example, a very popular popular product , Cache suddenly fails , All the traffic directly reaches DB, This will cause excessive database requests at a certain time , More emphasis on instantaneity .
The main ways to solve the problem are 2 Kind of :
Distributed lock : Only the first thread that gets the lock requests the database , Then insert the cache , Of course, every time you get the lock, you have to check whether the cache has , In high concurrency scenarios , I don't recommend using distributed locks , It will affect the query efficiency ;
Settings never expire : For some hotspot caches , We can set it to never expire , This ensures the stability of the cache , But it should be noted that after the data changes , To update this hotspot cache in time , Otherwise, it will cause the error of query results , For example, popular goods , Preheat to the database first , Then go offline .
There are also “ Cache renewal ” The way , Such as caching 30 Minutes out , You can do a regular task , Every time 20 Run every minute , It feels like this way is neither fish nor fowl , For your reference only .
Cache avalanche
Definition : A large number of caches expire at the same time in a short time , Resulting in a large number of requests to query the database directly , This has caused great pressure on the database , In severe cases, the situation that may lead to database downtime is called cache avalanche .
if “ Cache breakdown ” It's individual resistance , that “ Cache avalanche ” It's a collective uprising , Then what happens to cache avalanche ?
A large number of caches expire at the same time in a short time ;
Cache service down , Cause a large-scale cache failure at a certain time .
So what are the solutions ?
Add random time to cache : Random time can be added when setting the cache , such as 0~60s, This can greatly avoid a large number of cache failures at the same time ;
Distributed lock : Add a distributed lock , The first request is to persist the data to the cache , Only other requests can enter ;
Current limiting and degradation : Through current limiting and degradation strategies , Reduce requested traffic ;
Cluster deployment :Redis Deploy through cluster 、 Master-slave strategy , After the primary node goes down , Will switch to the slave node , Guarantee the availability of services .
Example of adding random time to cache :
// Cache original expiration time
int exTime = 10 * 60;
// Random number generating class
Random random = new Random();
// Cache Settings
jedis.setex(cacheKey, exTime + random.nextInt(1000) , value);
In this way , It's much simpler . I'm sure you're right Cache penetration 、 Cache breakdown 、 cache An avalanche There must be a new understanding .
Please look forward to my next article , thank you .
more java Advanced information , Interview information , Official account
边栏推荐
- 可扩展哈希
- Crawler learning 5--- anti crawling identification picture verification code (ddddocr and pyteseract measured effect)
- 2018年数学建模竞赛-高温作业专用服装设计
- matlab GUI界面仿真直流电机和交流电机转速仿真
- 2022 CISP-PTE(一)文件包含
- 研究生数学建模竞赛-无人机在抢险救灾中的优化应用
- Winow10 installation nexus nexus-3.20.1-01
- Redis 缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓存雪崩
- Basic SQL operations in tidb
- Inter thread wait and wake-up mechanism, singleton mode, blocking queue, timer
猜你喜欢

thrift

快速实现Thread Mesh组网详解

The fourth question of the 299th weekly match 6103 Minimum fraction of edges removed from the tree

Quick realization of Bluetooth ibeacn function

MPC control of aircraft wingtip acceleration and control surface
高斯分布Gaussian distribution、線性回歸、邏輯回歸logistics regression
浅谈GPU:历史发展,架构

AHB2APB桥接器设计(2)——同步桥设计的介绍

Distribution gaussienne, régression linéaire, régression logistique

【OpenAirInterface5g】RRC NR解析之RrcSetupComplete
随机推荐
LeetCode 0086. Separate linked list
写一个 goroutine 实例, 同时练习一下 chan
multiprocessing.pool详解
Get the query parameter in the address URL specify the parameter method
Force buckle 179, max
[getting started] regular expression Basics
Ahb2apb bridge design (2) -- Introduction to synchronous bridge design
YOLOv6又快又准的目标检测框架 已开源
SQL 注入绕过(一)
浅谈GPU:历史发展,架构
HTAP 快速上手指南
高斯分布Gaussian distribution、線性回歸、邏輯回歸logistics regression
SQL injection bypass (I)
JVM common instructions
【LeetCode】Day90-二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
Us camera cloud service scheme: designed for lightweight video production scenes
Unrecognized VM option ‘‘
Matlab GUI interface simulation DC motor and AC motor speed simulation
日期 数据库日期 字符串 之间互相转换
高薪程序员&面试题精讲系列116之Redis缓存如何实现?怎么发现热key?缓存时可能存在哪些问题?