当前位置:网站首页>[distributed theory] (II) distributed storage
[distributed theory] (II) distributed storage
2022-07-07 17:38:00 【Lin like】
Distributed storage
Is there distribution or big data first ? This is a question worth thinking about . Because of big data, data is distributed storage , Because a single machine cannot store , So we need distributed storage . however , On the other hand , Our data generation is naturally distributed , But our general idea is centralized storage , Easy to manage .
General idea of distributed storage , Is to slice big data , Store between multiple nodes according to a certain policy , This strategy should ensure that the data is evenly distributed , To ensure the uniform load of nodes ; At the same time, the distribution of data should also have a certain stability , The phenomenon of large-scale data migration cannot be caused by the change of nodes . At the same time, the data should be reliable after dispersion , Adopt redundancy mechanism , Ensure that data will not be abnormally lost . Last , Distributed storage of data , It is necessary to ensure the convenience of data acquisition , And it can be polymerized after being disassembled .
All in all , Problems to be solved in distributed storage : Stability of data distribution , Heterogeneity of data nodes , Availability and reliability of data .
- Stability of data distribution : When a node fails , There will be no large-scale data migration , This means that we need good data distribution algorithms .
- Heterogeneity of data nodes : The performance of data nodes varies , Our data distribution algorithm should consider the bias of data distribution nodes ;
- Availability and reliability of data : It means that our data storage should have certain fault tolerance , For example, replica mechanism 、 Persistence mechanism .
1, Data partitioning mechanism
Stability of data distribution , Depends on our data partitioning strategy , Several common data partitioning algorithms :
- Range based partitioning : For example, according to the age range , Regional scope ;
- List based partitioning : For example, according to the country 、 Provincial and municipal divisions ;
- Loop based partitioning : such as mod A cyclic value ;
- Hash based partitioning : The most common partition , such as hash;
- Composition based partitioning : Combination of the above methods .
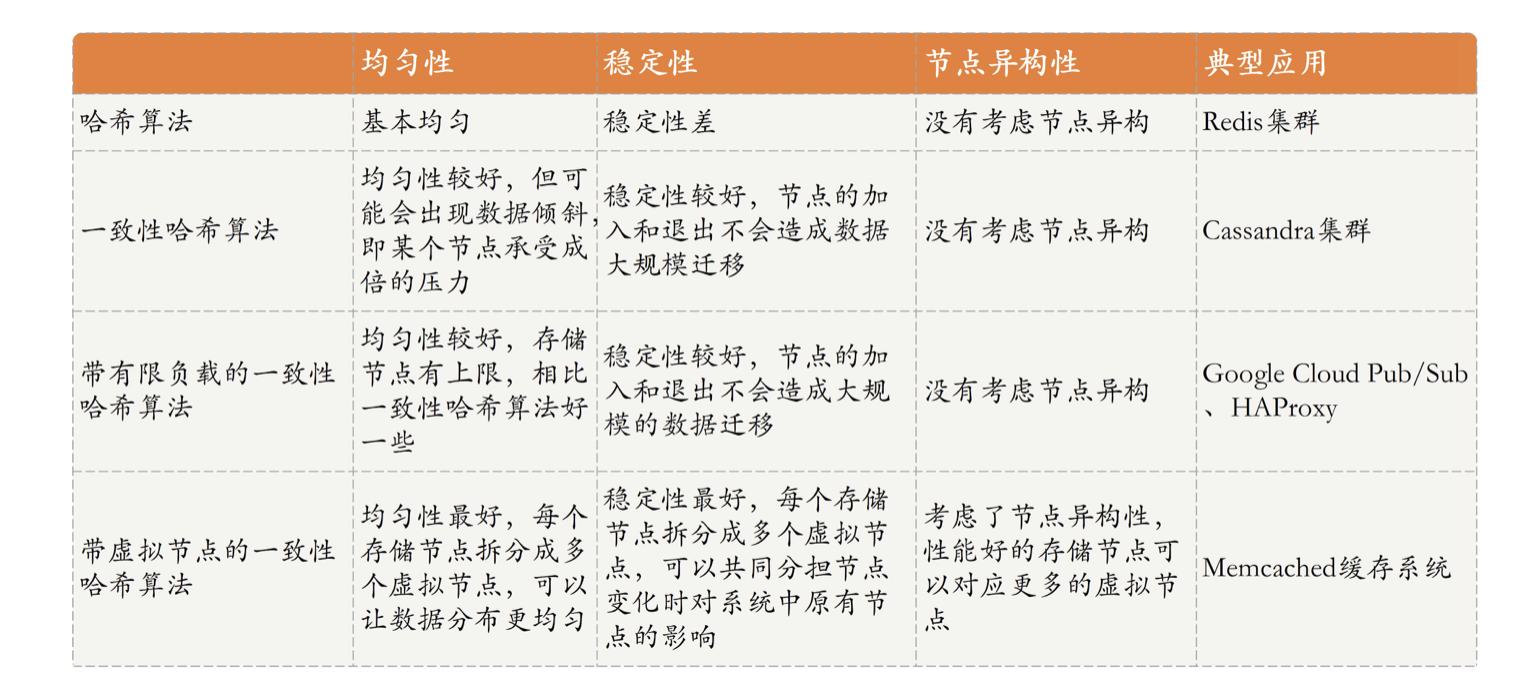
Hash based partitioning , It is the most common partition strategy in large-scale distributed systems , So here we mainly discuss several implementation forms of the algorithm :
1, Ordinary hashes , For example, hash according to a certain field of data , And then partition ; But there are node changes , Large scale data migration rehash The phenomenon ;
2, Consistent Hashing , That is, the data is stored in clockwise order hash Ring , When the node changes , Just migrate the data of adjacent nodes . One detail is , Uniformity hash When doing data query, you need to maintain an index table in the node , To locate the actual storage location of the data inside the node . But this way , This will cause some nodes to undertake more data storage tasks , The data load of nodes is high .
3, Consistency with limited load hash, That is, each node has a fixed storage limit , When the upper limit is reached, it will continue to traverse the next node clockwise , Store the data ; However, this approach does not take into account the differences in storage performance caused by heterogeneous nodes ;
4, Consistency with virtual head nodes hash, Virtual nodes are virtual nodes allocated according to node performance differences , That is, nodes with good performance , There will be more virtual nodes , The data will be stored in this node as much as possible . Relatively stable performance .
2, Data replication mechanism
In the distributed environment , How to realize the consistency of data replication ? Let's take a look at several data replication strategies :
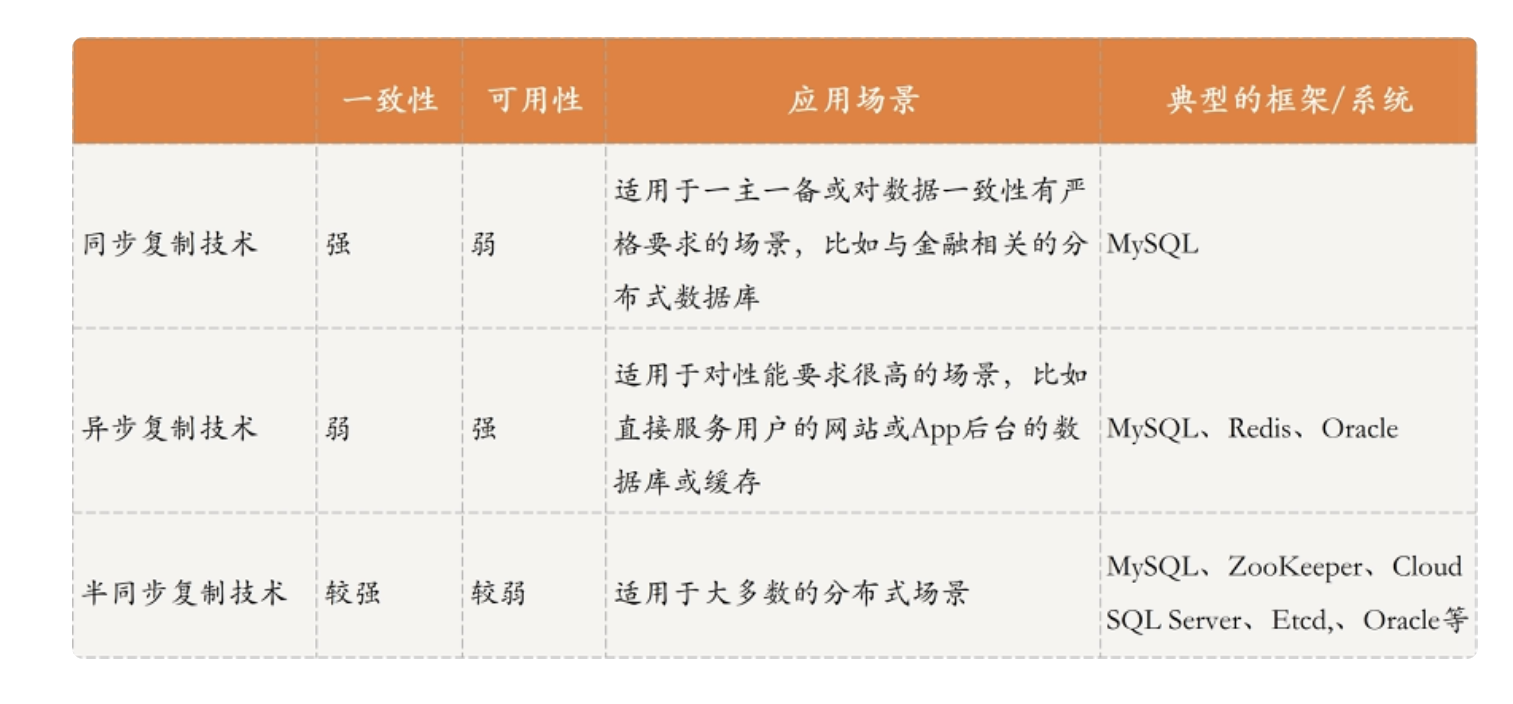
Synchronous replication : The client is writing a message to the master node , Then the master node synchronizes with other slave nodes , Will return the operation success message to the client . Such a mechanism ensures the strong consistency of data , But if there are many slave nodes , The delay of synchronous replication is long , It will inevitably affect the availability . In some financial situations , Applicable to trading occasions . Like our mysql Active and standby cluster solutions , Including our kafka Copy of the cluster ack Mechanisms adopt similar ideas .
Asynchronous replication : The client is writing a message to the master node , The master node immediately returns the information of successful operation , Then asynchronously copy the data to other slave nodes . You can see , This mechanism ensures availability , But at the expense of consistency , The data queried by the client on the master node and the slave node are inconsistent . This scheme is applicable to the situation with low data requirements , our mysql This scheme is adopted by default in the active / standby mode . And our redis colony , This scheme is also adopted to ensure high performance .
Semi-synchronous replication : That is to balance the above two methods , Both consistency and availability . Semi synchronous replication includes two , One is to receive a response from the slave node, which means that the synchronization is successful , One is that half of the slave nodes respond and are considered successful . This scheme involves data inconsistency after synchronization , That is, our data synchronization should be based on which node . One idea is , With leader The data of the node shall prevail , Match according to index records , The data after the inconsistent position will start from the node data , Force synchronization with leader Agreement .
our mysql Cluster solution , Three replication methods can be supported through configuration .
Reference link :
Geek time 《 Distributed principle and algorithm analysis 》
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
[Huang ah code] Why do I suggest you choose go instead of PHP?
本周小贴士#134:make_unique与私有构造函数
本周小贴士#140:常量:安全习语
Lex & yacc of Pisa proxy SQL parsing
notification是显示在手机状态栏的通知
跟奥巴马一起画方块(Lua)
专精特新软件开发类企业实力指数发布,麒麟信安荣誉登榜
【网络攻防原理与技术】第5章:拒绝服务攻击
L1-019 谁先倒(Lua)
阿富汗临时政府安全部队对极端组织“伊斯兰国”一处藏匿点展开军事行动
LeetCode1051(C#)
【网络攻防原理与技术】第1章:绪论
Notes on installing MySQL in centos7
calendarview日历视图组件的功能和用法
99% of users often make mistakes in power Bi cloud reports
Devops' operational and commercial benefits Guide
Matplotlib绘图界面设置
字符串 - string(Lua)
[fan Tan] after the arrival of Web3.0, where should testers go? (ten predictions and suggestions)
到底有多二(Lua)