当前位置:网站首页>On binary tree (C language)
On binary tree (C language)
2022-07-04 10:27:00 【Lol only plays Timo】
Binary tree is a very classical non-linear discontinuous data structure in tree data structure , It is widely used because of its excellent time complexity , In this article, we will talk about the generation and traversal of binary trees .
For example, how can we solve the storage problem of binary trees in the figure below ?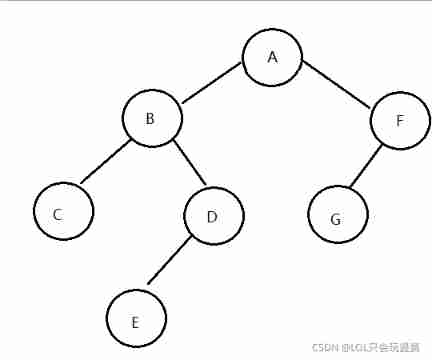
Here we can control the input format when inputting , That is, we can input the left subtree first, set an end flag after the input of the left subtree of a branch, and then continue to input the right subtree , In the figure above, we can input according to the following format :
ABC##DE###FG###
Now let's look at the code directly , There are some recursive ideas in the code , If you don't understand anything, you can track variables , It will also be clearer to see in this way .
void creatB_TREE(B_TREE **root) {
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (B_TREE *) calloc(sizeof(B_TREE), 1);
(*root)->data = ch;
creatB_TREE(&((*root)->leftChild));
creatB_TREE(&((*root)->rightChild));
}
}
After writing this function, let's take a look at the traversal of binary tree , The traversal of binary trees is divided into three types, namely, the first root order , Middle root order , Posterior root order . It looks like three types, but their code is only a little different , We use “ First root order ” For example, let's talk about traversal of binary tree .
The so-called first root order is to access the root node first, take out the data in it, and then treat the left subtree of the root node as the root node, continue to access the data in it, and then access the right subtree after the left subtree is accessed . There are also some recursive ideas , It is suggested that you carry out variable tracking for easy understanding .
void preRootOrder(B_TREE *root) {
if (root) {
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
preRootOrder(root->leftChild);
preRootOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
After understanding the above code, we will directly follow the code of middle root order and post root order , The difference between them is very small , There is only a small difference in when to fetch the data in the root node .
void posteriorRootOrder(B_TREE *root){
if (root) {
posteriorRootOrder(root->leftChild);
posteriorRootOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
}
}
void middleRootOrder(B_TREE *root) {
if (root) {
middleRootOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
middleRootOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
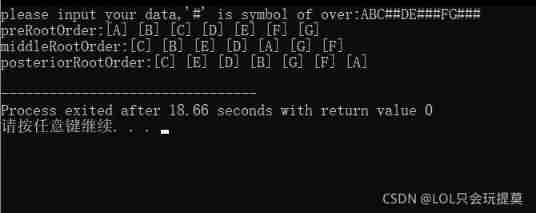
Finally, let's take a look at the complete code and its operation :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef struct B_TREE {
char data;
struct B_TREE *leftChild;
struct B_TREE *rightChild;
}B_TREE;
void creatB_TREE(B_TREE **root);
void preRootOrder(B_TREE *root);
void middleRootOrder(B_TREE *root);
void posteriorRootOrder(B_TREE *root);
void posteriorRootOrder(B_TREE *root){
if (root) {
posteriorRootOrder(root->leftChild);
posteriorRootOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
}
}
void middleRootOrder(B_TREE *root) {
if (root) {
middleRootOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
middleRootOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void preRootOrder(B_TREE *root) {
if (root) {
printf("[%c] ",root->data);
preRootOrder(root->leftChild);
preRootOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void creatB_TREE(B_TREE **root) {
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
if (ch == '#') {
*root = NULL;
} else {
*root = (B_TREE *) calloc(sizeof(B_TREE), 1);
(*root)->data = ch;
creatB_TREE(&((*root)->leftChild));
creatB_TREE(&((*root)->rightChild));
}
}
int main() {
B_TREE *root = NULL;
printf("please input your data,'#' is symbol of over:");
creatB_TREE(&root);
printf("preRootOrder:");
preRootOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("middleRootOrder:");
middleRootOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("posteriorRootOrder:");
posteriorRootOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
If you have any questions, please leave a message below , Thank you for watching .
边栏推荐
- View CSDN personal resource download details
- system design
- Batch distribution of SSH keys and batch execution of ansible
- PHP code audit 3 - system reload vulnerability
- Native div has editing ability
- Collection of practical string functions
- 入职中国平安三周年的一些总结
- Uniapp--- initial use of websocket (long link implementation)
- Kotlin set operation summary
- DML statement of MySQL Foundation
猜你喜欢
用数据告诉你高考最难的省份是哪里!

OSPF summary
When I forget how to write SQL, I
![[200 opencv routines] 218 Multi line italic text watermark](/img/3e/537476405f02f0ebd6496067e81af1.png)
[200 opencv routines] 218 Multi line italic text watermark
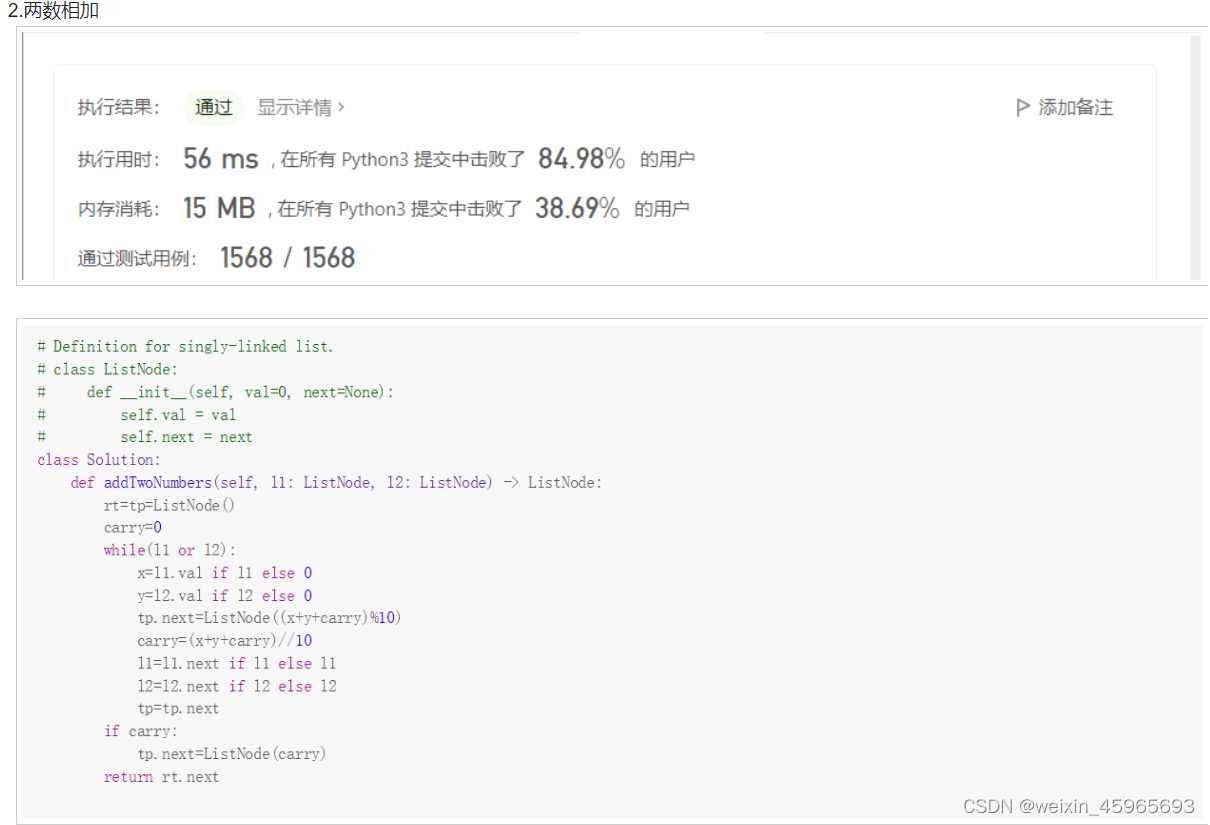
leetcode1-3
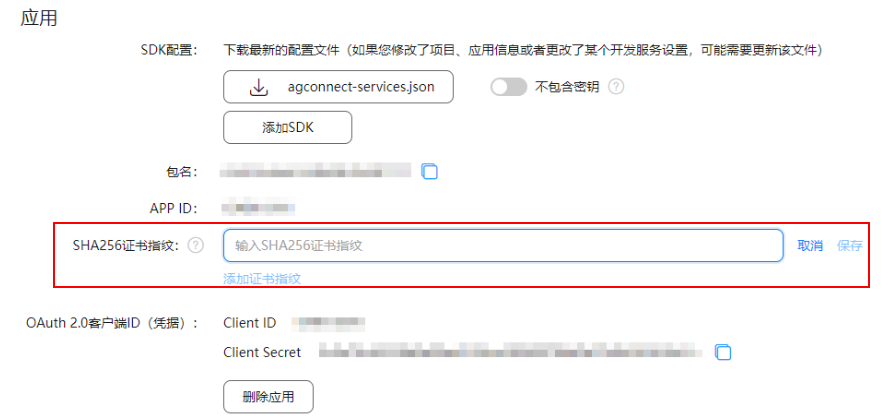
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法

Basic principle of servlet and application of common API methods
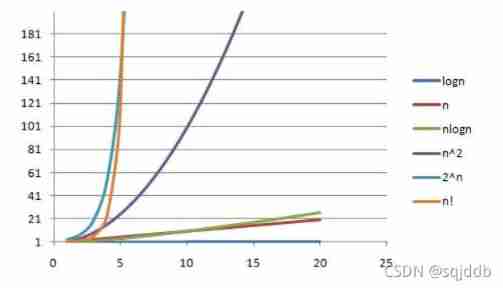
Time complexity and space complexity
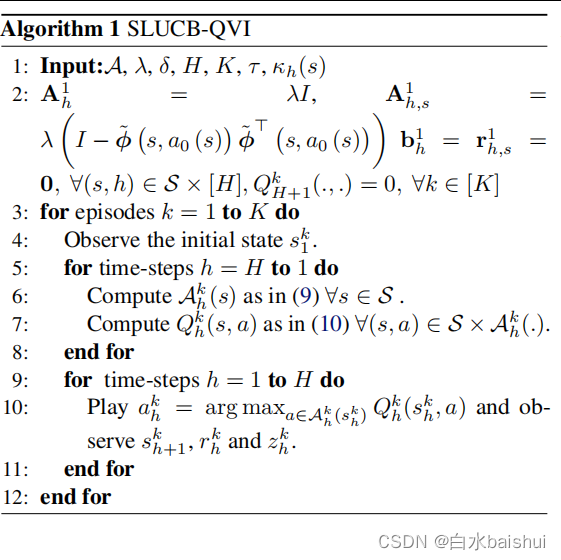
基于线性函数近似的安全强化学习 Safe RL with Linear Function Approximation 翻译 1

The bamboo shadow sweeps the steps, the dust does not move, and the moon passes through the marsh without trace -- in-depth understanding of the pointer
随机推荐
Summary of several job scheduling problems
Press the button wizard to learn how to fight monsters - identify the map, run the map, enter the gang and identify NPC
2. Data type
MongoDB数据日期显示相差8小时 原因和解决方案
Rhcsa day 10 operation
Knapsack problem and 0-1 knapsack problem
Sword finger offer 31 Stack push in and pop-up sequence
Safety reinforcement learning based on linear function approximation safe RL with linear function approximation translation 2
Evolution from monomer architecture to microservice architecture
【FAQ】华为帐号服务报错 907135701的常见原因总结和解决方法
Static comprehensive experiment ---hcip1
Software sharing: the best PDF document conversion tool and PDF Suite Enterprise version sharing | with sharing
Advanced technology management - how to design and follow up the performance of students at different levels
Deep learning 500 questions
Laravel文档阅读笔记-How to use @auth and @guest directives in Laravel
Exercise 9-3 plane vector addition (15 points)
A little feeling
Service developers publish services based on EDAs
Two way process republication + routing policy
If the uniapp is less than 1000, it will be displayed according to the original number. If the number exceeds 1000, it will be converted into 10w+ 1.3k+ display