当前位置:网站首页>Time complexity and space complexity
Time complexity and space complexity
2022-07-04 10:25:00 【sqjddb】
* The efficiency of the algorithm
After the algorithm is written into an executable program , Runtime needs Waste time, resources and space ( Memory ) resources . So measure the quality of an algorithm , Usually from Time and Space Measured in two dimensions , That is, time complexity and space complexity .
Time complexity mainly measures the performance of an algorithm Running fast or slow , The spatial complexity mainly measures the time required for the operation of an algorithm Extra space . In the early days of computer development , The storage capacity of the computer is very small . So I care about space complexity . But after the rapid development of the computer industry , The storage capacity of the computer has reached a high level . So now we don't need to pay special attention to the spatial complexity of an algorithm
* Time complexity
The time that an algorithm takes to execute , In theory , It can't be worked out , Only you put your program on the machine and run , To know . That's why we have the time complexity analysis . The time taken by an algorithm is proportional to the number of statements executed . In the algorithm Basic operation Number of executions , Time complexity of the algorithm , namely : Find a basic statement and the scale of the problem N Mathematical expressions between , Is to calculate the time complexity of the algorithm .
* Big O Asymptotic representation of
In practice, when we calculate the time complexity , We don't really have to calculate the exact number of execution , And it only takes about the number of times , Here we use Big O Asymptotic representation of .
Derivation is great O Order method :
1、 With constant 1 Replace all the addition constants in runtime .
2、 In the modified run times function , Only the highest order terms .
3、 If the highest order term exists and is not 1, The constant multiplied by this item is removed . The result is big O rank .
Big O The progressive representation of Remove those items that have little impact on the results , Simple and clear Indicates the number of executions
In addition, some algorithms have the best time complexity 、 Average and worst case :
The worst : Maximum number of runs of any input size ( upper bound )
On average : Expected number of runs of any input size
The best situation : Minimum number of runs of any input size ( Lower bound )
for example : At a length of N Search for a data in the array x
The best situation :1 Times found
The worst :N Times found
On average :N/2 Times found
In practice, the general concern is the worst-case operation of the algorithm , Therefore, the time complexity of searching data in the array is O(N)
* Time complexity of calculation
Here is a well written article that is very helpful to understand the calculation of complexity
example 1:
// Calculation BubbleSort Time complexity of ?
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
for (size_t end = n; end > 0; --end)
{
int exchange = 0;
for (size_t i = 1; i < end; ++i)
{
if (a[i-1] > a[i])
{
Swap(&a[i-1], &a[i]);
exchange = 1;
}
}
if (exchange == 0)
break;
}
}
example 5 Basic operations perform best N Time , At worst, it's executed (N*(N+1)/2 Time , By deducing the big O Order method + Time complexity is generally the worst , The time complexity is O(N^2)
example 2:
// Compute factorial recursion Fac Time complexity of ?
long long Fac(size_t N)
{
if(0 == N)
return 1;
return Fac(N-1)*N;
}
Through calculation and analysis, it is found that the basic operation is recursive N Time , The time complexity is O(N)
example 3:
// Compute Fibonacci recursion Fib Time complexity of ?
long long Fib(size_t N)
{
if(N < 3)
return 1;
return Fib(N-1) + Fib(N-2);
}

The time complexity can be approximated as 2^N
But strictly speaking In this way
* Spatial complexity
Space complexity is a measure of the amount of storage space temporarily occupied by an algorithm during operation . Space complexity is not how much the program takes up bytes Space , Because it doesn't make much sense either , So the space complexity is the number of open spaces .
The calculation rules of spatial complexity are basically similar to that of time complexity , Also use large O Asymptotic representation .
Be careful : Stack space required for function runtime ( Store parameters 、 local variable 、 Some register information, etc ) It has been determined during compilation , Therefore, the spatial complexity is mainly determined by the additional space explicitly requested by the function at run time .
* Computational space complexity
example 1:
// Calculation BubbleSort Spatial complexity of ?
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
for (size_t end = n; end > 0; --end)
{
int exchange = 0;
for (size_t i = 1; i < end; ++i)
{
if (a[i-1] > a[i])
{
Swap(&a[i-1], &a[i]);
exchange = 1;
}
}
if (exchange == 0)
break;
}
}
We've used an extra space , So the space complexity is zero O(1)
example 2:
// Calculation Fibonacci Spatial complexity of ?
// Returns the first of the Fibonacci sequence n term
long long* Fibonacci(size_t n)
{
if(n==0)
return NULL;
long long * fibArray = (long long *)malloc((n+1) * sizeof(long long));
fibArray[0] = 0;
fibArray[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n ; ++i)
{
fibArray[i] = fibArray[i - 1] + fibArray [i - 2];
}
return fibArray;
}
Dynamic opens up N Space , The space complexity is O(N)
example 3:
// Compute factorial recursion Fac Spatial complexity of ?
long long Fac(size_t N)
{
if(N == 0)
return 1;
return Fac(N-1)*N;
}
example 3 Recursively called N Time , Opens the N Stack frame , Each stack frame uses a constant space . The space complexity is O(N)
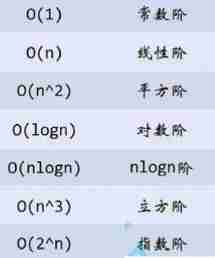
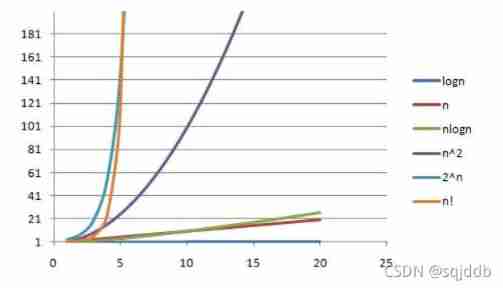
* Complexity comparison
边栏推荐
- Latex arranges single column table pictures in double column format articles
- Latex error: missing delimiter (. Inserted) {\xi \left( {p,{p_q}} \right)} \right|}}
- Kotlin set operation summary
- 5g/4g wireless networking scheme for brand chain stores
- Leetcode48. Rotate image
- Reasons and solutions for the 8-hour difference in mongodb data date display
- Three schemes of ZK double machine room
- What is devsecops? Definitions, processes, frameworks and best practices for 2022
- Dynamic memory management
- Intelligent gateway helps improve industrial data acquisition and utilization
猜你喜欢
基于线性函数近似的安全强化学习 Safe RL with Linear Function Approximation 翻译 1
Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)

Intelligent gateway helps improve industrial data acquisition and utilization

Development guidance document of CMDB

DDL statement of MySQL Foundation
What is an excellent architect in my heart?
Histogram equalization
El Table Radio select and hide the select all box

Safety reinforcement learning based on linear function approximation safe RL with linear function approximation translation 1
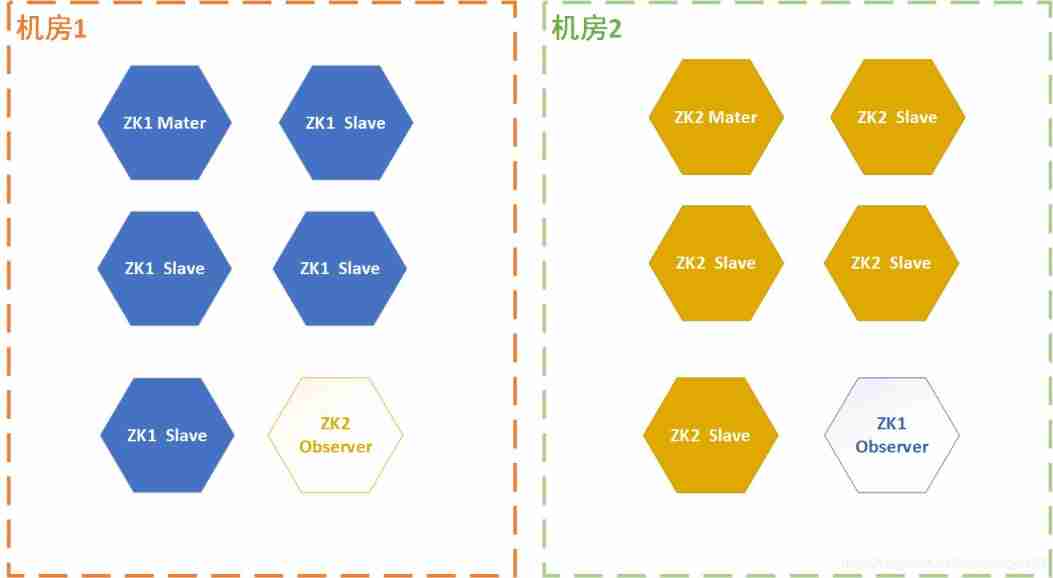
Three schemes of ZK double machine room
随机推荐
Talk about scalability
Intelligent gateway helps improve industrial data acquisition and utilization
Use the data to tell you where is the most difficult province for the college entrance examination!
What are the advantages of automation?
2. Data type
The future education examination system cannot answer questions, and there is no response after clicking on the options, and the answers will not be recorded
Exercise 9-5 address book sorting (20 points)
View CSDN personal resource download details
Two way process republication + routing policy
Container cloud notes
用数据告诉你高考最难的省份是哪里!
leetcode729. My schedule 1
Use C to extract all text in PDF files (support.Net core)
BGP ---- border gateway routing protocol ----- basic experiment
Ruby time format conversion strftime MS matching format
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
MPLS: multi protocol label switching
MongoDB数据日期显示相差8小时 原因和解决方案
Ruby时间格式转换strftime毫秒匹配格式
Differences among opencv versions