当前位置:网站首页>This time, let's clear up: synchronous, asynchronous, blocking, non blocking
This time, let's clear up: synchronous, asynchronous, blocking, non blocking
2022-07-07 22:53:00 【Yes' level training strategy】
Hello everyone , I am a yes.
Following last article Speak thoroughly I/O Model after , Let's talk about the Internet I/O Several confusing concepts often accompany : Sync 、 asynchronous 、 Blocking 、 Nonblocking differences .
After writing this article, the groundwork is almost done , Then it officially begins Netty In depth analysis of , Coming soon , Hee hee .
Don't talk much , Start !
Sync & asynchronous
Synchronous and asynchronous refer to : Whether the current thread needs to wait for the method call to complete .
For example, you call a method to carry 100 stones :
- Synchronization refers to calling this method , Your thread needs to wait for these 100 stones to be lifted , Then get the result of moving , Then continue to execute the remaining code logic .
// Synchronization mode
result = Lift a hundred stones ();
// You need to wait for the result of moving , To execute the following logic
if(result) {
Pay when the stone is finished ();
}
Calculate the next stone lifting task ();
- Asynchrony refers to calling this method , Immediately return directly , Don't wait for these 100 stones to be moved , You can immediately execute the following code logic , Then use callback or event notification to get the result that the stone has been moved .
// Asynchronous way
Lift a hundred stones ({
// Callback
Pay when the stone is finished ();
});
// Don't wait for the stone to be lifted , Immediately execute the following logic
Calculate the next stone lifting task ();
It can be seen directly , Synchronization and asynchrony are the differences in the calling methods , This makes our coding method different .
The code logic under asynchronous invocation is relatively less intuitive , You need to use callback or event notification , This requires high coding ability in complex logic . Synchronous calls are straightforward , Wait for the execution to finish, then get the result, and then execute the following logic , The requirements for coding ability are low , It's also less likely to make mistakes .
So you will find that there are many methods, which are called asynchronously , But the final use is asynchronous to synchronous .
For example, you submit a task to the thread pool , Get one future, At this time, it is asynchronous , Then you call in the code immediately future.get(), It becomes waiting for the task to be completed , This is called asynchronous to synchronous , image Dubbo RPC Call synchronization to get the return result, which is achieved in this way .
Blocking & Non blocking
Blocking and non blocking refer to : When the current interface data is not ready , Whether the thread is blocked and suspended .
What is blocking pending ? That is, the current thread is still in CPU In the time slice , Blocked method called , Because the data is not ready , Then give up before the time slice CPU.
So blocking and synchronization seem to be waiting , But essentially they are different , I didn't give up when synchronizing CPU.
Non blocking is when the current interface data is not ready , The thread will not be blocked and suspended , You can constantly poll the request interface , See if the data is ready .
So far, we can draw a conclusion :
- Sync & Asynchronous refers to : When the data has not been processed , The logical processing of the code is different .
- Blocking & Non blocking finger : When the data has not been processed ( Not ready ), State of thread .
So synchronization & Asynchrony is actually viewed from the high-level dimension of framework , And jam & Non blocking is often chosen for the underlying system call , In other words, the two are considered from different dimensions .
combining I/O Look at
Premise : There is an operating system between the program and the hardware , And for the sake of safety ,Linux The system is divided into : User mode and kernel mode
Under this premise , Let's be clear I/O The operation has two steps :
- launch I/O request
- actual I/O Reading and writing , That is, data is copied from kernel cache to user space
Blocking I/O And non blocking I/O. As above , It actually refers to whether the user thread is blocked , Here refers to the steps 1( launch I/O request ).
- Blocking I/O, It refers to that the user thread initiates I/O On request , If the data is not ready ( For example, there is no network data reception ), Will block the current thread , Give up CPU.
- Non blocking I/O, It refers to that the user thread initiates I/O On request , If the data is not ready ( For example, there is no network data reception ), It will not block the current thread , You can continue to perform subsequent tasks .
You can find , Blocking and non blocking here actually refer to whether the user thread will be blocked .
Sync I/O And asynchronous I/O. As above , We can know that this is the basis I/O Different response modes .
- Sync I/O, It refers to that the user thread initiates I/O On request , There are data , Then go to step 2( actual I/O Reading and writing , That is, data is copied from kernel cache to user space ), In this process, the user thread waits for the copy to complete .
- asynchronous I/O, It refers to that the user thread initiates I/O On request , There are data , Then go to step 2( actual I/O Reading and writing , That is, data is copied from kernel cache to user space ), There is no need for user threads to wait in the process of copying , User threads can execute other logic , Wait until the kernel copies the data from kernel space to user space , The user thread will get a “ notice ”.
Think again , stay I/O In this scenario, synchronization and asynchrony are actually the implementation of the kernel , Because the executor of the copy is the kernel , One is to synchronously copy data to user space , User threads need to wait . One is through asynchronous way , User threads don't have to wait , After copying , The kernel will call the specified callback function .
If you don't understand the above , Just remember :
- Sync I/O: It means that the user thread will need to wait for the step 2 completion of enforcement .
- asynchronous I/O: It means that the user thread does not need to wait for the step 2 perform .
Okay , If you have understood the above concepts , So what we call synchronization blocking in ordinary days I/O, Synchronous nonblocking I/O Wait is actually to combine the above two steps , It shouldn't be hard to understand .
Let me briefly summarize , About I/O The block 、 Non blocking 、 Sync 、 asynchronous :
- Blocking and non blocking refer to initiating I/O After the request , Different user thread states , Blocking I/O The current user thread will be blocked when the data is not ready , Instead of blocking I/O Will immediately return an error , Does not block the current user thread .
- Synchronous and asynchronous refer to , Kernel I/O Copy implementation , When the data is ready , You need to copy kernel space data to user space , If it's synchronization I/O Then the user thread will wait for the copy to complete , The asynchronous I/O Then the user thread of this copy process can do whatever it should do , When the kernel is copied, it will “ notice ” User threads .
Last
it is to be noted that , The same noun may have different meanings in different scenes . My article about synchronization 、 asynchronous 、 Blocking 、 The concepts of non blocking are based on I/O In the scene .
Limited personal ability , I don't know if I have made it clear , If you have any questions, you can leave a message in the message area .
Okay , About Netty The series is almost ready , The next chapter begins to deepen Netty On a journey !
Links to the first two foreshadowing articles are as follows :
Why the Internet I/O Will be blocked
Let us , From a to Z , Be transparent I/O Model
I am a yes, From a little bit to a billion , See you next time !
边栏推荐
- Debezium series: introducing support for the final operator
- VTOL in Px4_ att_ Control source code analysis [supplement]
- GBU1510-ASEMI电源专用15A整流桥GBU1510
- Yarn cannot view the historical task log of yarn after enabling ACL user authentication. Solution
- XMIND mind mapping software sharing
- Firefox browser installation impression notes clipping
- How to judge whether the input content is "number"
- 行测-图形推理-9-线条问题类
- 软件测评中心▏自动化测试有哪些基本流程和注意事项?
- Write in front -- Talking about program development
猜你喜欢
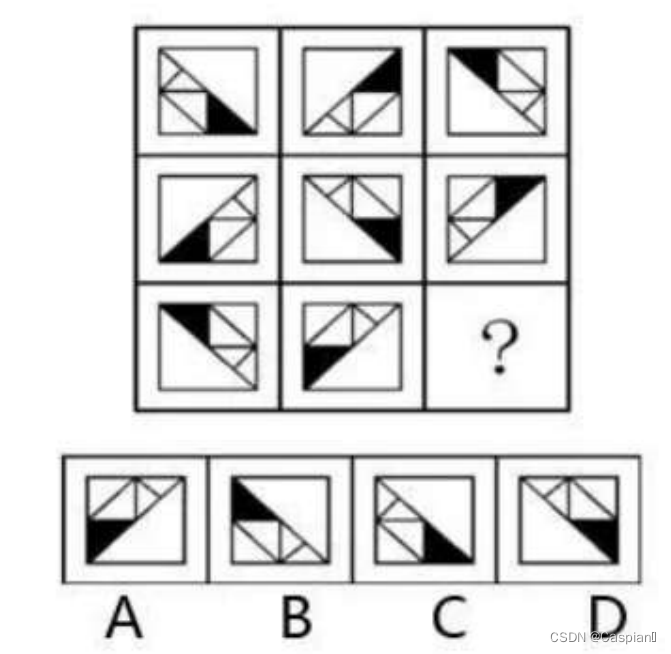
行测-图形推理-6-相似图形类
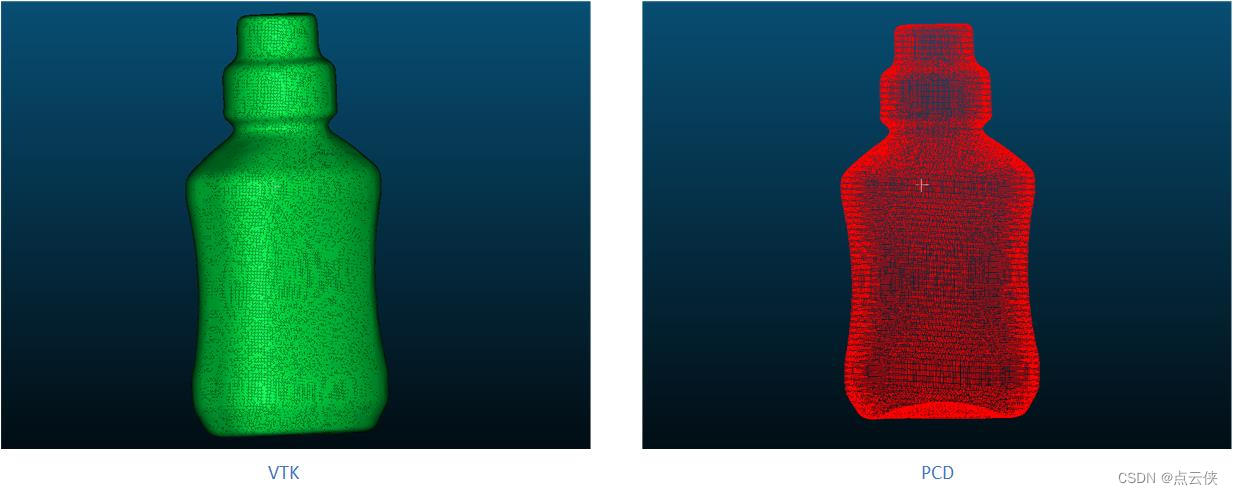
PCL .vtk文件与.pcd的相互转换
![LeetCode206. Reverse linked list [double pointer and recursion]](/img/3c/84351e771ac9763c1e5f7b4921c099.jpg)
LeetCode206. Reverse linked list [double pointer and recursion]
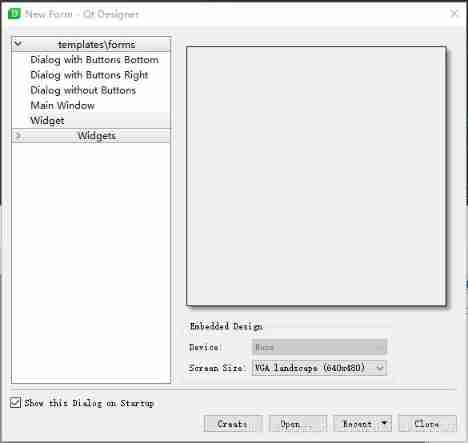
Visual design form QT designer design gui single form program

0-5vac to 4-20mA AC current isolated transmitter / conversion module

Robot autonomous exploration series papers environment code
Firefox browser installation impression notes clipping
C # realizes the communication between Modbus protocol and PLC
![[problem] pytorch installation](/img/9f/1419c471838e3af8ea2158266254a5.jpg)
[problem] pytorch installation
Apple further entered the financial sector through the 'virtual card' security function in IOS 16
随机推荐
. Net automapper use
Common verification rules of form components -2 (continuously updating ~)
JS number is insufficient, and 0 is added
IP网络主动测评系统——X-Vision
OpenGL configure assimp
Apple further entered the financial sector through the 'virtual card' security function in IOS 16
面试百问:如何测试App性能?
Line test - graphic reasoning -5- one stroke class
Aspose. Word operation word document (I)
0-5vac to 4-20mA AC current isolated transmitter / conversion module
Aspose. Word operation word document (II)
微服務遠程Debug,Nocalhost + Rainbond微服務開發第二彈
Write in front -- Talking about program development
De la famille debezium: SET ROLE statements supportant mysql8
[azure microservice service fabric] start the performance monitor in the SF node and set the method of capturing the process
Pyqt GUI interface and logic separation
Visual design form QT designer design gui single form program
Gazebo import the mapping model created by blender
Quick sort (diagram +c code)
Redis cluster installation