当前位置:网站首页>Scoring system based on 485 bus
Scoring system based on 485 bus
2022-07-06 15:19:00 【Hu Da jinshengyu】
be based on 485 Bus scoring system
Programming objectives :
Deepen the understanding through this case RS485 communication mode , The main controller of the upper computer communicates with all the lower computers .
Description of program operation effect :
adopt RS232/RS485 The converter will be multiple with 485 The MCU of the lower computer control program of the module is mounted on the bus . Use a single chip microcomputer as the upper computer , Download hex file , Another single-chip microcomputer is used as the lower computer , Download the lower computer program . After the MCU of the lower computer is powered on , The first two digits of the nixie tube display the slave number , The last three digits show the scoring results . First press the center button of the navigation button to enter the setting mode , The selected set decimal point of the nixie tube is lit ; Then by controlling the left and right directions of the navigation keys, the position selection of the nixie tube is realized , The up and down direction realizes the addition and subtraction of the numerical value on the nixie tube , Press the center button again to exit the setting mode . Then press KEY2、KEY3 Press the key to mark the completion of slave number and scoring setting , The first 1 Position and number 8 position LED The light is on ; Finally, by controlling the slave detection and multi machine scoring buttons of the master controller of the upper computer , Get the slave number and score set by the MCU , So as to realize the communication between the upper computer and the lower computer .
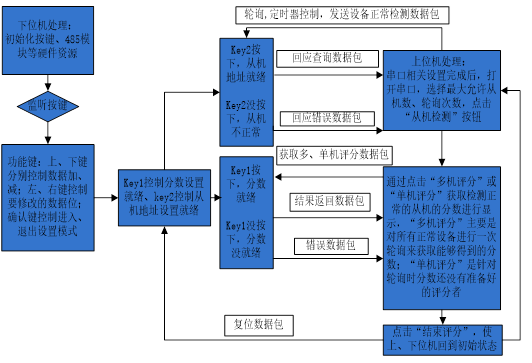
Program related circuit and working principle description
This case is simulated Modbus agreement , Adopt master 、 From a technical , The main controller of the upper computer can communicate with all the lower computers , It can also communicate with a designated lower computer alone . simulation Modbus Agreement , The data packets of the upper and lower computers only contain 5 Bytes , Its basic format is : Data packet head (0x5A)+ Address code ( Broadcast address / Slave address )+ Function code + Carrying data ( A byte )+ Check code bytes , The carrying data part can be expanded by multiple bytes , It can be modified according to the situation . The specific definition of data package is as follows :( Check bytes in the Protocol , This scoring system adopts accumulation and coding .)
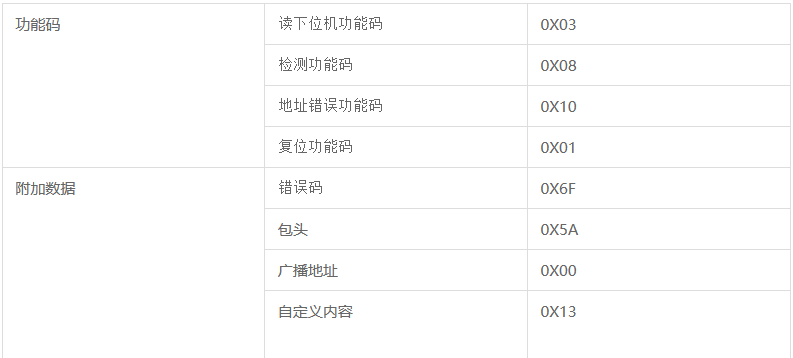
(1) The host detects whether the slave is normal and related data packets :( The host communicates with a single slave device ):
(1) The host detects whether the slave is normal and related data packets :( The host communicates with a single slave device )
A、 The device detects packets normally :
Direction : Upper computer -----> Lower machine
Packet messages : Data packet head + Slave address + Detect function code (Fun_CheckSlave)+ Custom content (Check_Content)+ Check byte
function : Check whether the lower computer is normal . normal , The lower computer sends a response query packet ; Is not normal , Then the lower computer will not respond ; An error occurred during data transmission , The lower computer sends a response error packet , The upper computer can re detect whether the device is normal by setting multiple polling ;
B. Respond to query packets :
Direction : Lower machine —–> Upper computer
Packet messages : Data packet head + Slave address + Detect function code (Fun_CheckSlave)+ Custom content ( Received from host Check_Content)+ Check byte
C. Respond to error packets :
Direction : Lower machine —–> Upper computer
Packet messages : Data packet head + Slave address + Detect function code (Fun_CheckSlave)+ Error code (ErrorInfo)+ Check byte
(2) The host gets the data package related to the score of the slave :( The host communicates with a single slave device ):
D. Get more 、 Stand alone scoring data package :
Direction : Upper computer —–> Lower machine
Packet messages : Data packet head + Detect the normal slave address (0x00)+ Read the function code of the lower computer (Fun_ReadInfo)+ Slave address + Check byte
function : Check the normal equipment , Make a poll , Get the score of the slave machine for which the score is ready . For single machine direct communication , No polling .
E. The result returns a packet :
Direction : Lower machine —–> Upper computer
Packet messages : Data packet head + Slave address + Read the function code of the lower computer (Fun_ReadInfo)+ The score returned by the slave + Check byte ( The score is >100: Indicates that the above mentioned is not ready , Respond to error packets )
(3) This round of scoring ends with relevant data packets :
F. Reset packet :( The master communicates with all slaves )
Direction : Upper computer —–> Lower machine
Packet messages : Data packet head + Broadcast address + Reset function code (Fun_Reset)+ The score returned by the slave (0x00)+ Check byte
function : Instruct all normally connected slaves to reset , Prepare for the next round of scoring .
Implementation process :
- Through the DuPont line 51 SCM and RS232/RS485 Converter connection , Re pass USB turn RS232/RS485 Serial communication line and PC Machine connection , download hex file , And power on the MCU ;
- If you directly use a single chip microcomputer as the host , The MCU needs to download the contact software in the upper computer program instead of the lower computer software ;
- The initial phenomenon after downloading from the lower computer is : The leftmost two nixie tubes show 00 Indicates the slave number , Far right 3 A digital tube display 000 Indicates the score ;
- Press the center button of the navigation key to enter the setting mode , Press the center key again to exit the setting mode after setting the slave number and scoring , Then press the KEY1,KEY2, Flag setting is complete ;
- Control the upper computer to detect the slave computer and obtain the number of the lower computer , And get its score , The data is displayed on the main controller of the upper computer , Finally, finish scoring , Single chip microcomputer LED The light goes out .
The specific idea is shown in the figure above .
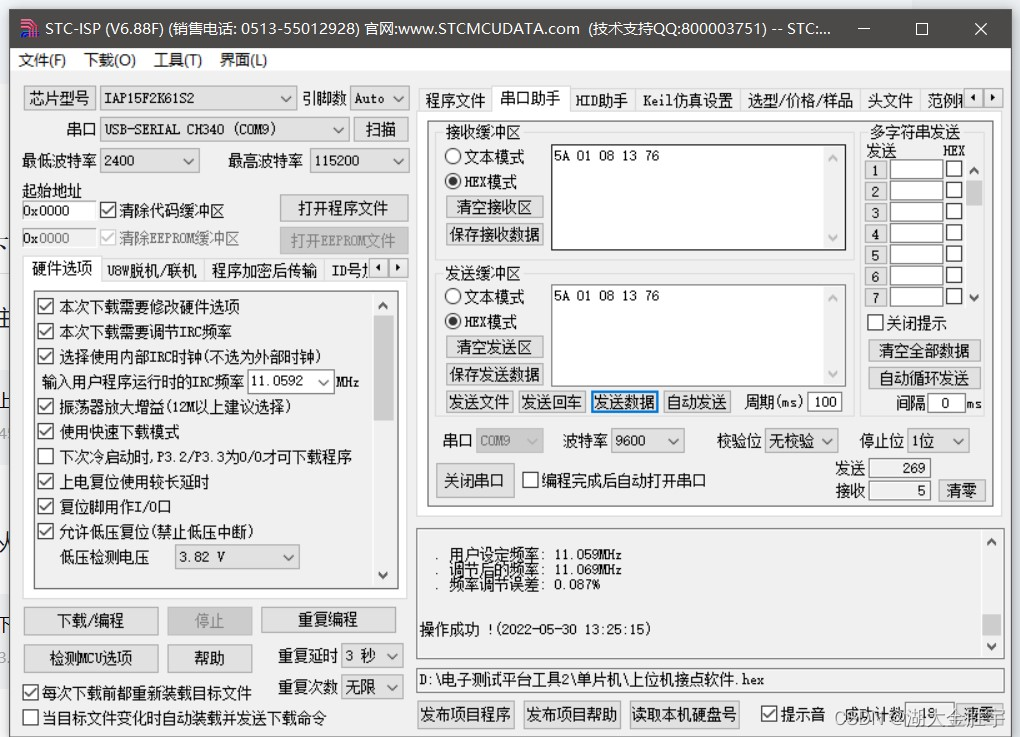
First , We can understand the specific function of this program through the serial port assistant , You can use the above A、D、F Let's get a general idea of what we need to do .A The function of is to query whether the lower computer is normal . normal , The lower computer sends a response query packet ; Is not normal , Then the lower computer will not respond ; An error occurred during data transmission , The lower computer sends a response error packet , The upper computer can re detect whether the device is normal by setting multiple polling . therefore , You only need to see the following output on the serial port assistant, which is correct :
D、F The situation is similar , You can also get the following output :
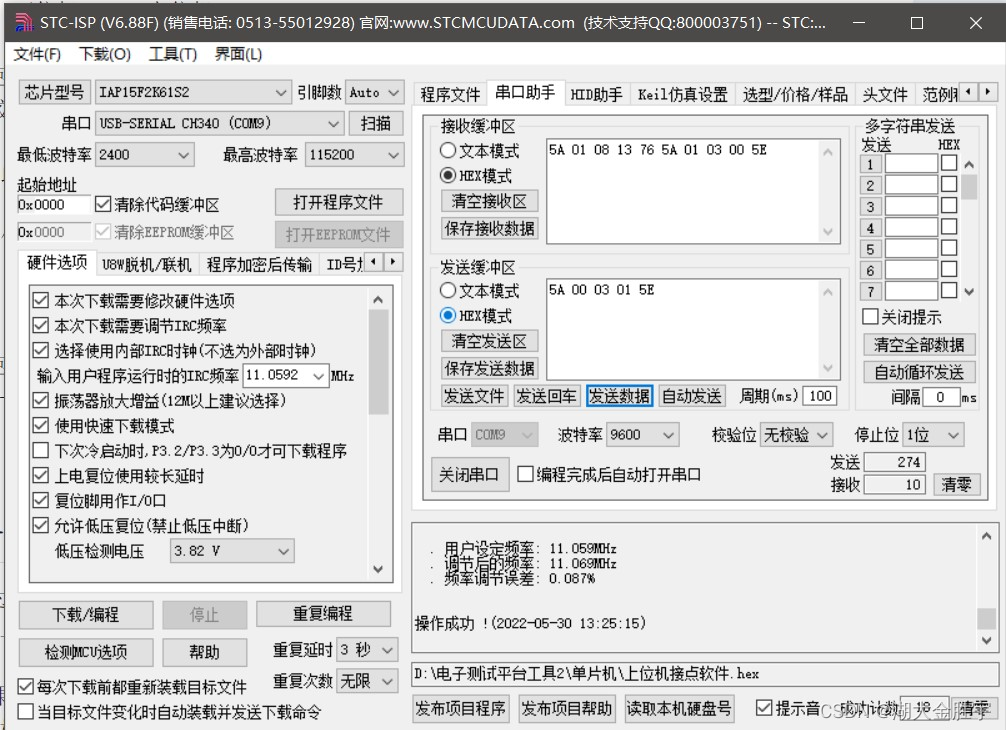
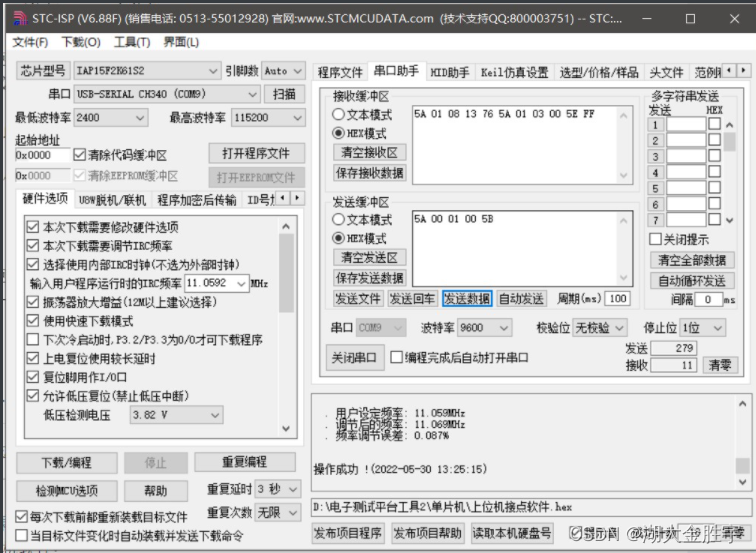
Define the functional requirements of dual computer communication through the serial port assistant .
Next, let's implement the code :
following , Give priority to the code ( It uses C++)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include "serial.h"
#include <setjmp.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned char uchar;
/* be based on RS485 Bus scoring system - Host program - Double machine scoring */
string format(const vector<uchar> &data); // Data is processed into strings
int check(serial &pipe, int addr); // Equipment inspection
int get_score(serial &pipe, int addr); // Get points
void reset(serial &pipe); // Slave reset
int main() {
serial pipe("/dev/ttyUSB0", B9600);
int addr, check_ret, score;
while(1){
cout<<" Enter description :\n Enter the legal slave address to query the score \n Input -2 Reset the slave \n Input -1 Exit procedure \n If the program does not work correctly , Cannot receive slave response , Please restart and try again \n Please enter the command :";
cin>>addr;
if(addr == -1) break;
if(addr == -2) {
reset(pipe);
continue;
}
check_ret = check(pipe, addr);
if(check_ret == 1){
cout<<"Equipment test normal"<<endl;
sleep(1);
if(!(score = get_score(pipe, addr)))
cout<<"Failed to get score"<<endl;
else
cout<<"score:"<<score<<endl;
}
else if(check_ret == 0){
cout<<"The address is incorrect. Please enter the address and try again"<<endl;
continue;
}
else{
cout<<"Data transfer error, please restart slave machine"<<endl;
}
//reset(pipe);
cout<<"The slave machine is reset. Enter -1 to exit"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*****************************************************
Process data into strings
******************************************************/
string format(const vector<uchar> &data) {
std::string str(2 * data.size() + 1, '\x00');
for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {
sprintf(&str[i * 2], "%02X", data[i]);
}
return str;
}
/*****************************************************
Slave address detection :
Parameters :serial A serial port , Slave address
The host sends data for detection :5a + Slave address + Detect function code 08 + 13 + Check code
Return value :1( The address is correct );0( Wrong address );-1( Data error )
******************************************************/
int check(serial &pipe,int addr){
int check_code = 117 + addr, ret; // The check code is cumulative sum
vector<uchar> code = {0x5a, 0x08, 0x13};
vector<uchar> rec;
code.insert(code.begin()+1, (uchar)addr); // Insert slave address
code.push_back((uchar)check_code); // Insert the check code
//cout << format(code) << endl;
/* Write and receive response packets */
pipe.myWrite(code);
sleep(1);
rec = pipe.myRead(5);
if(format(rec) == format(code)) // Check whether the received packet is the same as the sent one , If it is the same, the slave address is correct
ret = 1;
else{
if(rec[3] == 0x6f) ret = 0;
else ret = -1;
}
return ret;
}
/*****************************************************
Get slave scores :
Parameters :serial A serial port , Slave address
The host sends for score acquisition :5a + 00 + Read function code 03 + Slave address + Check code
Return value : fraction ( The data is correct );-1( The slave is not ready );-2( Data error )
******************************************************/
int get_score(serial &pipe, int addr){
int check_code = 93 + addr, ret; // The check code is cumulative sum
vector<uchar> code = {0x5a, 0x00, 0x03};
vector<uchar> rec;
code.insert(code.begin()+3, (uchar)addr); // Insert slave address
code.push_back((uchar)check_code); // Insert the check code
//cout << format(data) << endl;
/* Write and receive response packets */
pipe.myWrite(code);
sleep(1);
rec = pipe.myRead(5);
if(rec[3] == 0x6f) ret = -1; // Check for errors
else {
ret = (int)rec[3]; // Turn to numbers
if(ret < 0 || ret > 100) ret =-2; // Check whether the number is legal
}
return ret;
}
/*****************************************************
Slave reset :
Parameters :serial A serial port , Slave score
Master sends for slave reset :5a + Broadcast address 00 + Reset function code 01 + 00 + Check byte
******************************************************/
void reset(serial &pipe){
vector<uchar> code = {0x5a, 0x00, 0x01,0x00,0x5b};
//cout <<"reset:"<< format(code) << endl;
/* Send packet */
for(int i=0;i<600;i++) {
pipe.myWrite(code);
}
return;
}
Ideas as follows :
- First , Judge whether the input lower computer number exists , Address exists and returns 1, Address error returned 0, Data error return -1.
- After judging that the lower computer number exists , Next, you need to get the score of the lower computer ( Here, only the dual computer program is implemented ). Output the obtained scores .
- Next, we need to implement , Exit and reset , Exit input -1, Reset input -2 that will do .
The contents of the header file are as follows :
#ifndef SERIAL_H
#define SERIAL_H
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <sys/termios.h>
class serial {
private:
int board = -1, epfd = -1;
public:
serial(const char *board_path, speed_t baud_rate);
~serial();
std::vector<unsigned char> myRead(size_t n) const;
void myWrite(const std::vector<unsigned char> &data) const;
};
#endif //SERIAL_H
The functions defined in the header file are as follows :
#include "serial.h"
#include <cerrno>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <sys/termios.h>
#include <sys/unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define err_check(code) if ((code) < 0) {
\ printf("Error: %s\n", strerror(errno)); \ _exit(1); \ }
serial::serial(const char *board_path, speed_t baud_rate) {
/** * O_RDWR Means in read-write mode (myRead & myWrite) Open file * Reference resources :https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/open.3p.html */
err_check(board = open(board_path, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY ))
termios attrs {
};
tcgetattr(board, &attrs);
// set baud rate
err_check(cfsetispeed(&attrs, baud_rate))
err_check(cfsetospeed(&attrs, baud_rate))
attrs.c_iflag &= ~( BRKINT | ICRNL | INPCK | ISTRIP | IXON | IXOFF );
attrs.c_oflag &= ~( OPOST | ONLCR | OCRNL );
attrs.c_lflag &= ~( ECHO | ICANON | IEXTEN | ISIG );
attrs.c_cflag &= ~( CSIZE | PARENB );
attrs.c_cflag |= CS8;
attrs.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
attrs.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
// Set terminal parameters , All changes take effect immediately
err_check(tcsetattr(board, TCSANOW, &attrs))
// Reopen the device file to apply the new terminal parameters
close(board);
err_check(board = open(board_path, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY))
// Create a new epoll example , And return a file descriptor for control
err_check(epfd = epoll_create(1))
epoll_event event {
.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET, // An event is triggered when the opposite end becomes readable
.data = {
.fd = board
}
};
// Add this event to epoll In the listening list
err_check(epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, board, &event))
}
serial::~serial() {
(~board) && close(board);
(~epfd) && close(epfd);
}
std::vector<unsigned char> serial::myRead(size_t n) const {
size_t count = 0;
std::vector<unsigned char> buffer(n);
while (count < n)
{
epoll_event event {
};
// Wait for data from the opposite end of the serial port
epoll_wait(epfd, &event, 1, 5000); // Specify the timeout value , Avoid indefinite blocking waiting
// Reading data , Then decide whether to continue reading according to the amount of data read
count += ::read(board, &buffer[count], n);
}
//tcflush(board,TCIOFLUSH);
return buffer;
}
void serial::myWrite(const std::vector<unsigned char> &data) const {
size_t count = 0;
//tcflush(board,TCOFLUSH);
while (count < data.size()) {
// Write data to serial port
count += ::write(board, &data[count], data.size() - count);
}
}
The operation results are as follows :
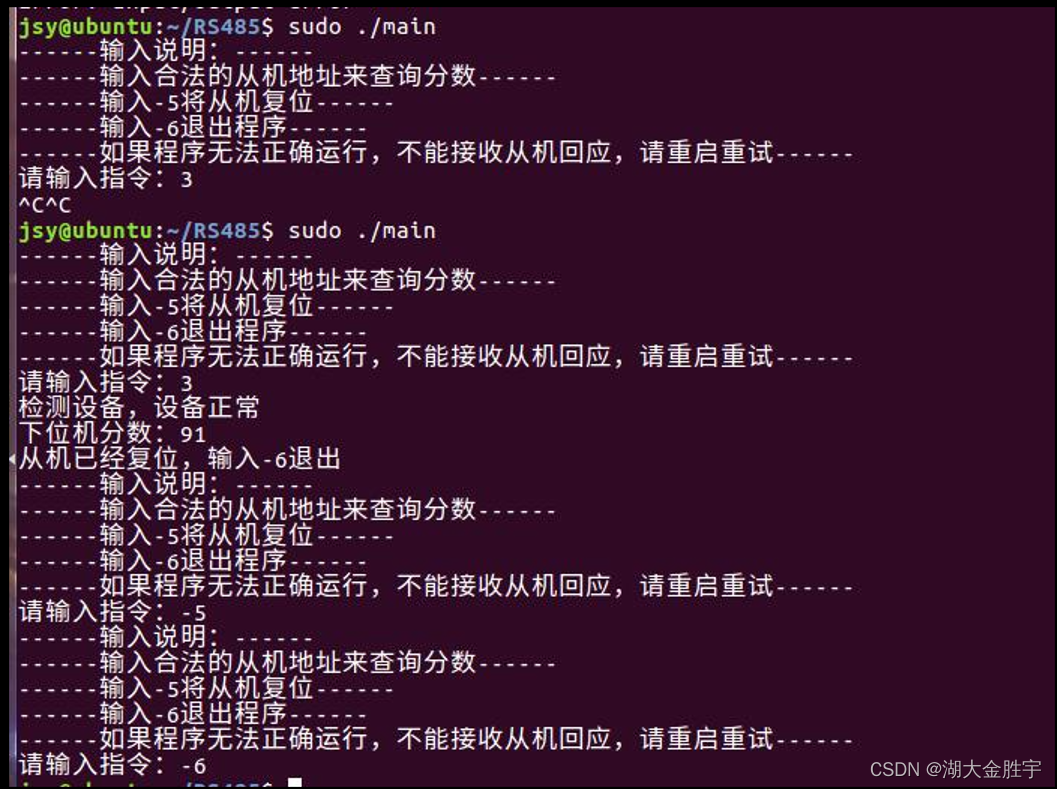
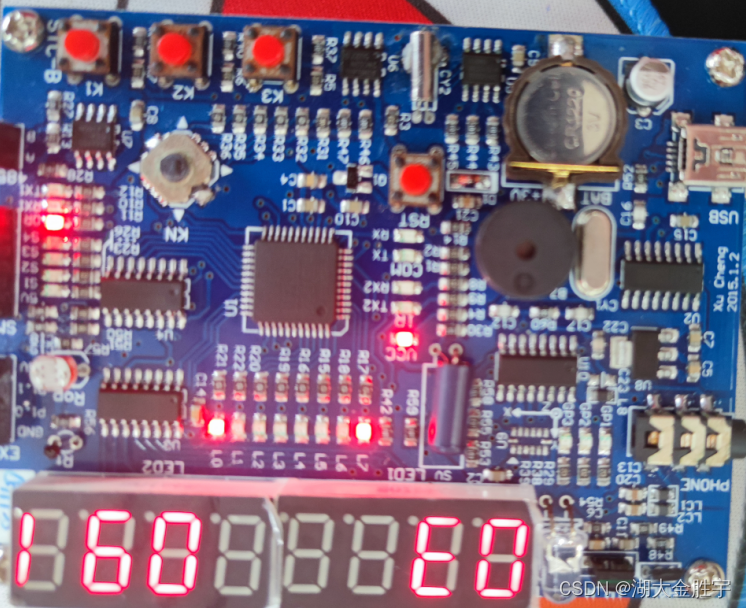
( Here is just a change in the number of judgments .)
So far, the experiment , Complete .
Experience :
After several experiments , Not only honed my will , Strengthened my faith , I believe we can also gain a lot in future experiments .
ad locum , The procedure for running on multiple machines is as follows :
import binascii
import serial.tools.list_ports
# init
plist = list(serial.tools.list_ports.comports()) # Get port list
ser = serial.Serial(list(plist[0])[0], 9600, timeout=0.05) # Import pyserial modular
def read_times():
while 1:
dic = []
reading = ser.read(5) # Read serial data
if reading != b'':
a = str(hex(int(binascii.hexlify(reading), 16)))
b = a.replace("0x", "")
for index in range(0, len(b), 2):
dic.append(b[index] + b[index + 1])
return dic
devices = list(map(int, input(" Please input the lower computer of the device , In the middle to ' ' separate :").split())) # List of storage devices
print(devices)
# part 1: Verify the lower computer equipment
for device in devices:
data = [0x5A, device, 0x08, 0x13]
data.append(sum(data))
print("{}\n Slave equipment number : {:2d} The verification information is : {}\n Trying to verify ...".format('-'*50, device, data))
flag = True
for _ in range(100):
ser.write(data)
retdata = read_times()
if retdata:
print(retdata)
retdata = [int(i,16) for i in retdata]
if retdata == data:
print(" The returned verification information is : {}, The slave is normal .".format(retdata))
else:
print(" The slave transmission result is abnormal ")
flag = False
break
if flag:
print(" There is no return from the slave ")
print('-'*50)
print(' Read the scores from the machine :')
for device in devices:
data = [0x5A, 0x00, 0x03, device]
data.append(sum(data))
print("{}\n Slave equipment number : {:2d} The message sent is : {}\n Try to score ...".format('-'*50, device, data))
flag = True
for _ in range(100):
ser.write(data)
retdata = read_times()
if retdata:
print(retdata)
retdata = [int(i,16) for i in retdata]
print(retdata)
if retdata[1] == device and retdata[4] == sum(retdata[:4]):
print(" The slave score is : {}, The slave is normal .".format(retdata[3]))
elif retdata[3] == 0x6F:
print(" The slave score is greater than 100, error ")
else:
print(" The slave transmission result is abnormal ")
flag = False
break
if flag:
print(" There is no return from the slave ")
print('-'*50)
print(' Slave reset operation :')
data = [0x5A, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x5B]
ser.write(data)
print(" The slave has been reset , You can start the next round of scoring .")
After running the program, enter the number you set on your board , If multiple machines are running, the numbers of each machine are separated by spaces , Then return and wait .
边栏推荐
- A method and implementation of using VSTO to prohibit excel cell editing
- The minimum sum of the last four digits of the split digit of leetcode simple problem
- Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (II)
- Maximum nesting depth of parentheses in leetcode simple questions
- CSAPP Shell Lab 实验报告
- 安全测试入门介绍
- ArrayList set
- [200 opencv routines] 98 Statistical sorting filter
- 软件测试面试要问的性能测试术语你知道吗?
- CSAPP家庭作业答案7 8 9章
猜你喜欢
Stc-b learning board buzzer plays music

How to become a good software tester? A secret that most people don't know
What are the software testing methods? Show you something different
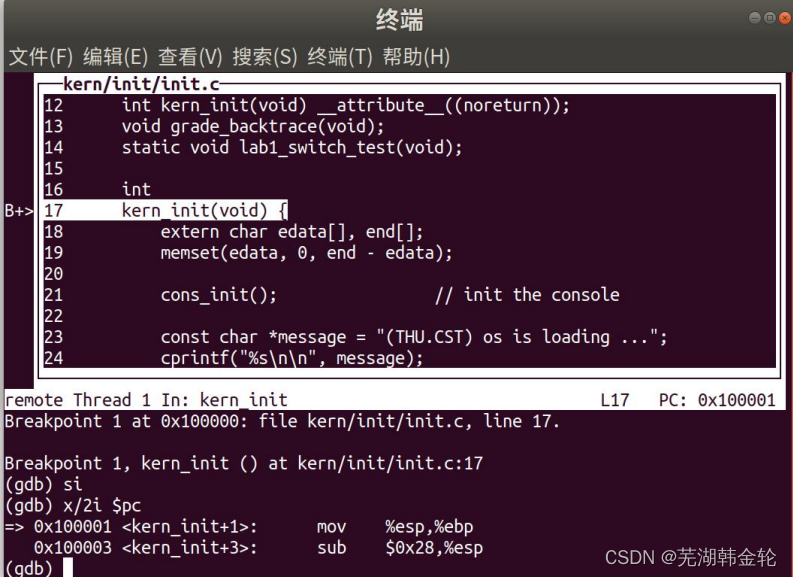
ucore lab1 系统软件启动过程 实验报告
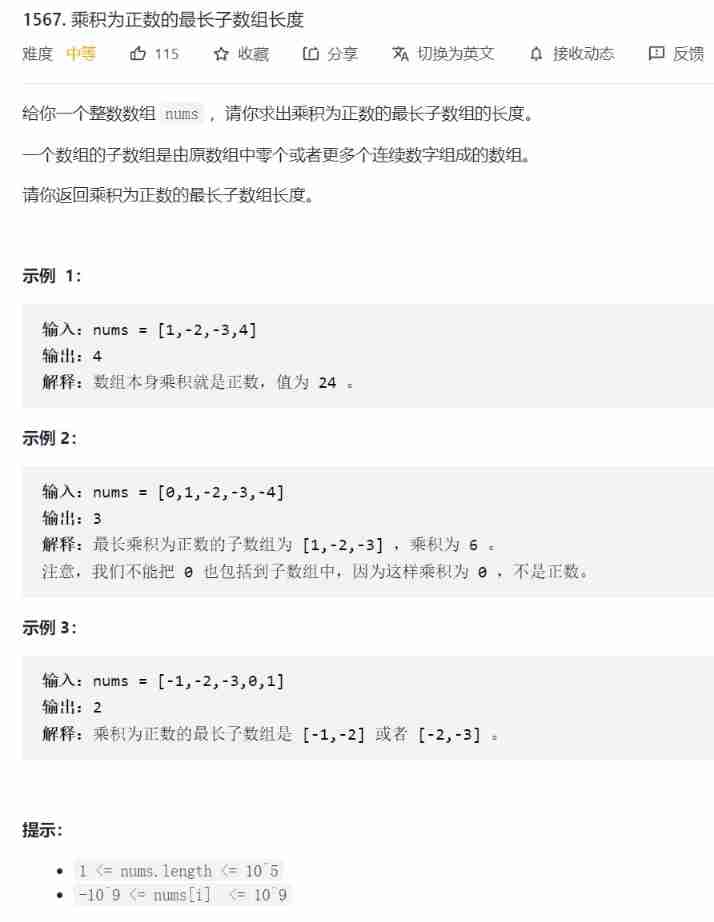
Leetcode notes - dynamic planning -day6

软件测试有哪些常用的SQL语句?
软件测试需求分析之什么是“试纸测试”
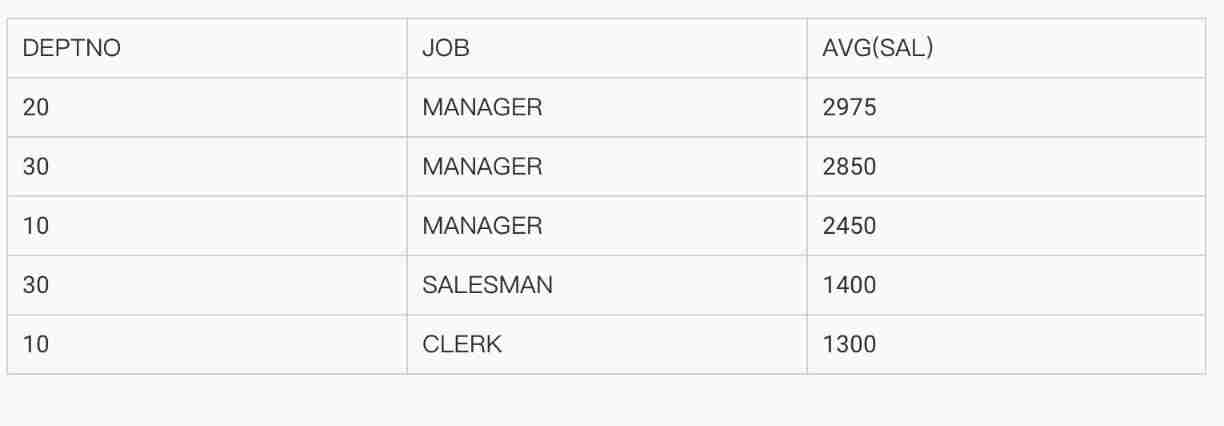
MySQL development - advanced query - take a good look at how it suits you

Rearrange spaces between words in leetcode simple questions
![[pytorch] simple use of interpolate](/img/16/87aa8a49e60801404822fe644e70c8.jpg)
[pytorch] simple use of interpolate
随机推荐
Public key box
Investment operation steps
Global and Chinese market of pinhole glossmeter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese markets of electronic grade hexafluorobutadiene (C4F6) 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
CSAPP家庭作业答案7 8 9章
In Oracle, start with connect by prior recursive query is used to query multi-level subordinate employees.
Description of Vos storage space, bandwidth occupation and PPS requirements
How to change XML attribute - how to change XML attribute
UCORE LaB6 scheduler experiment report
软件测试方法有哪些?带你看点不一样的东西
[200 opencv routines] 98 Statistical sorting filter
想跳槽?面试软件测试需要掌握的7个技能你知道吗
转行软件测试必需要知道的知识
China's county life record: go upstairs to the Internet, go downstairs' code the Great Wall '
Brief introduction to libevent
Soft exam information system project manager_ Project set project portfolio management --- Senior Information System Project Manager of soft exam 025
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) global and Chinese markets 2022-2028: technology, participants, trends, market size and share Research Report
[Ogg III] daily operation and maintenance: clean up archive logs, register Ogg process services, and regularly back up databases
How to solve the poor sound quality of Vos?
Oracle foundation and system table

