当前位置:网站首页>Threads and thread pools
Threads and thread pools
2022-07-06 15:10:00 【Hand pluckable Xinchen】
1, Thread concept
At least one process after a program runs , A process can contain multiple threads .
A thread is an execution unit in a process , Responsible for the execution of programs in the current process , At least one thread in a process . There can be multiple threads in a process , This application can also be called a multithreaded program .
2, Thread scheduling
Time sharing scheduling : All threads take turns to get CPU Right to use , Allocate each thread equally CPU Time for .
preemptive scheduling : Threads with high priority use CPU, If the thread priority is the same ,
3, The main thread
java Use java.lang.Thread Class represents thread , All thread objects must be Thread Instances of classes or other subclasses . The function of each thread is to complete certain tasks , In fact, it is to execute a program flow, that is, a piece of sequential code .Java Use thread executor to represent this program flow .
4, How to implement threads
public class xiancehng {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new SubThread();
thread.start();
}
}
// Create child threads
class SubThread extends Thread {
@Override
// rewrite run Method
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
String name = t.getName();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(name + i);
}
}
}
public class xiangcheng2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello word");
}
};
new Thread(runnable).start();
}
}5, Multithreading principle
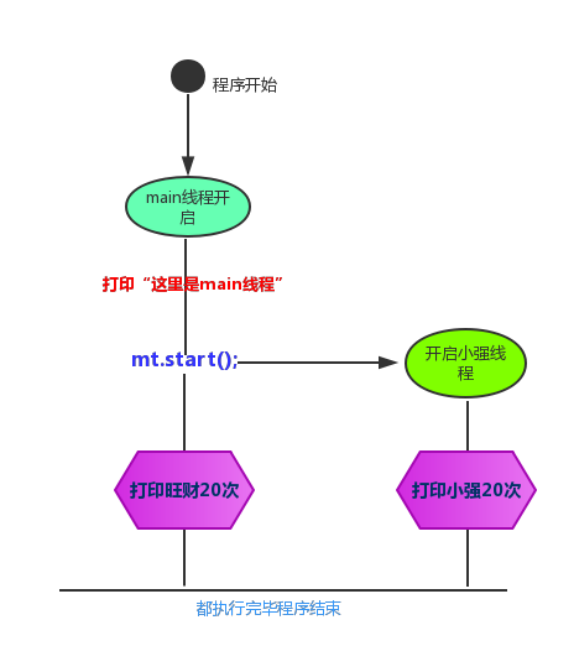
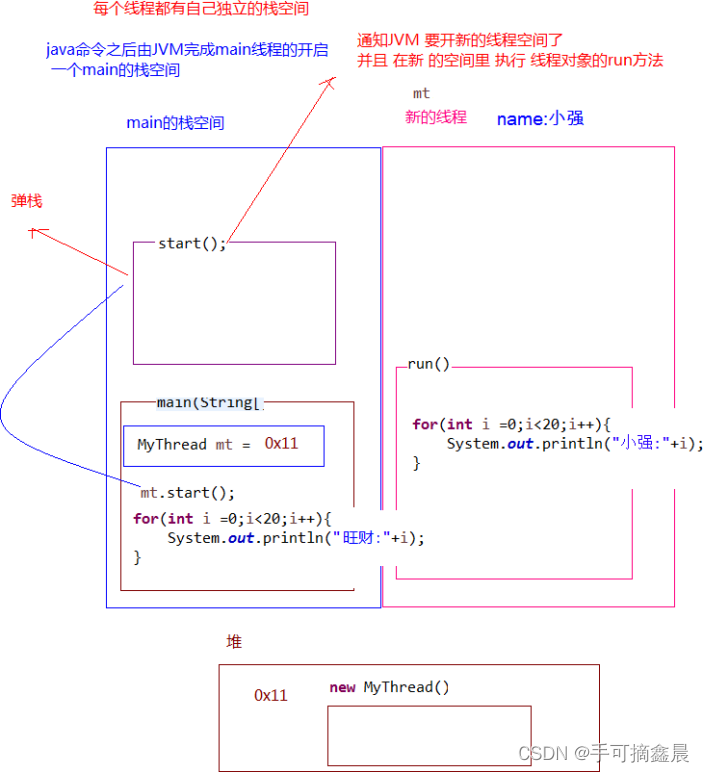
public class duoxiancheng1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" Here is main Threads ");
Thread thread = new ZiThread(" cockroach ");
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(" Wangcai " + i);
}
}
}
class ZiThread extends Thread {
public ZiThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
String name = t.getName();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(name + i);
}
}
}
6,Thread class
Construction method :
public Thread(); Assign a new thread object
public Thread(String name); Assign a new thread object with the specified name
public Thread(Runnable target); Assign a new thread object with a specified target
public Thread(Runnable target,String name); Assign a new thread object with a specified target and specify a name
Member method :
public String getName(); Get the current thread name
public void start(); Call thread execution run Method
public void run(); Tasks executed by threads are defined here
public static void sleep(long millis); The currently executing thread specifies how many milliseconds to pause
public static Thread currentThread(); Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object
7,Thread and Runnable The difference between
Runnable The advantages of :
1, It is suitable for multiple threads to operate the same task object .
2, You can avoid java The limitations of single inheritance in .
3, Increase the robustness of the program , Decouple operation , Code can be shared by multiple threads , Code and thread are independent .
4, Thread pool can only be put into implementation Runable or Callable Class thread , Can't put inheritance directly Thread Class . You can avoid java The limitations of single inheritance in .
8, Anonymous inner class way to create threads
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i);
}
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
}9, Thread safety
Case study : The cinema sells tickets , We simulate the ticket selling process in the cinema . Suppose the movie to be shown is “ My country and I ”, There are... Seats in this movie 100 individual ( This movie can only be sold 100 Tickets ).
Let's simulate the ticket window in the cinema , Realize the simultaneous sale of multiple windows “ Peppa Pig ” Tickets for the film ( Multiple windows sell this together 100 Tickets ) Window required , Use thread objects to simulate ; Need a ticket ,Runnable Interface subclass to simulate .
public class xcanq {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
new Thread(ticket, " window 1").start();
new Thread(ticket, " window 2").start();
new Thread(ticket, " window 3").start();
}
}
class Ticket implements Runnable {
private int ticket = 100;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " It's on sale " + ticket + " Tickets ");
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
}
10,Lock lock
Usage method :
public void lock();
public void unlock();
11, Thread state
| NEW | New state | After a thread is created , Before starting , In that state . |
| TERMINATED | Die state | After the thread has executed the task , In this state . |
| RUNNABLE | Operational state | Thread is integer task , In that state . |
| BLOCKED | Blocked state | obtain synchronized Lock object failed , In this state . |
| WAITING | Infinite waiting state | obtain Lock Lock object failed , In that state . |
| TIMED_WAITING | Time waiting state | perform sleep Method , In that state . |
12,sleep and wait The difference between

13,wait and notify Method
(1)wait Method
Thread is no longer active , No longer participate in scheduling , Get into wait set in , So there's no waste CPU resources , I'm not going to compete for locks , The thread state is WAITING.
It has to wait for another thread to perform a special action , That is to say “ notice (notify)” The thread waiting on this object from wait set Let it go , Re enter the scheduling queue (ready queue) in .
(2)notify Method
Then select the wait set One of the threads in release ; for example , When the restaurant has a free seat , The customers who wait the longest for dinner are the first Take a seat .
(3)notifyAll Method
Release the of the notified object wait set All threads on .
Be careful :
(1)wait Methods and notify Method must be called by the same lock object . because : The corresponding lock object can be notify Wake up using the same lock pair Like calling wait Thread after method .
(2)wait Methods and notify The method belongs to Object Class . because : The lock object can be any object , The class of any object is the following Yes Object Class .
(3)wait Methods and notify Methods must be used in synchronization blocks or synchronization functions . because : This must be called through the lock object 2 Individual Law .
14, Thread communication
Case study :
Baozi shop thread production baozi , Food thread consumes steamed stuffed bun . When there is no steamed stuffed bun ( Steamed stuffed bun status is false), Eating thread waiting , Baozi shop thread production baozi ( That is, the steamed stuffed bun status is true), And notify the eating thread ( Release the waiting state of eating goods ), Because there are already steamed buns , Then the Baozipu thread enters the waiting state .
Next , Whether the feeding thread can execute further depends on the acquisition of the lock . If you get
Take out the lock , Then perform the action of eating steamed stuffed bun , After eating the steamed stuffed bun ( Steamed stuffed bun status is false), And notify the baozi shop thread ( Release the waiting state of the steamed stuffed bun shop ), The eating thread enters wait . Whether the package shop thread can execute further depends on the acquisition of the lock .
Define package subclasses :
public class Baozi {
String pier;
String xianer;
boolean flag = false;
}Define the feeding thread :
public class Chihuo extends Thread {
private Baozi bz;
public Chihuo(String name, Baozi bz) {
super(name);
this.bz = bz;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (bz) {
if (bz.flag == true) {
System.out.println(" The food is being eaten "+bz.pier+bz.xianer+" Steamed stuffed bun ");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
bz.flag = false;
bz.notify();
} else {
try {
bz.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}Define the thread of the package store :
public class BaoZiPu extends Thread {
private Baozi bz;
public BaoZiPu(String name, Baozi bz) {
super(name);
this.bz = bz;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 0;
while (true) {
synchronized (bz) {
if (bz.flag == true) {
try {
bz.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(" The steamed stuffed bun shop began to make steamed stuffed buns ");
if (count % 2 == 0) {
bz.pier = " Ice skin ";
bz.xianer = " Wuren ";
} else {
bz.pier = " Thin skin ";
bz.xianer = " Beef and scallions ";
}
count++;
bz.flag = true;
System.out.println(" The steamed stuffed bun is ready :" + bz.pier + bz.xianer);
System.out.println(" Eat, eat ");
bz.notify();
}
}
}
}
}
Test thread :
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Baozi bz = new Baozi();
Chihuo ch = new Chihuo(" version ", bz);
BaoZiPu bzp = new BaoZiPu(" Steamed bun shop ",bz);
bzp.start();
ch.start();
}
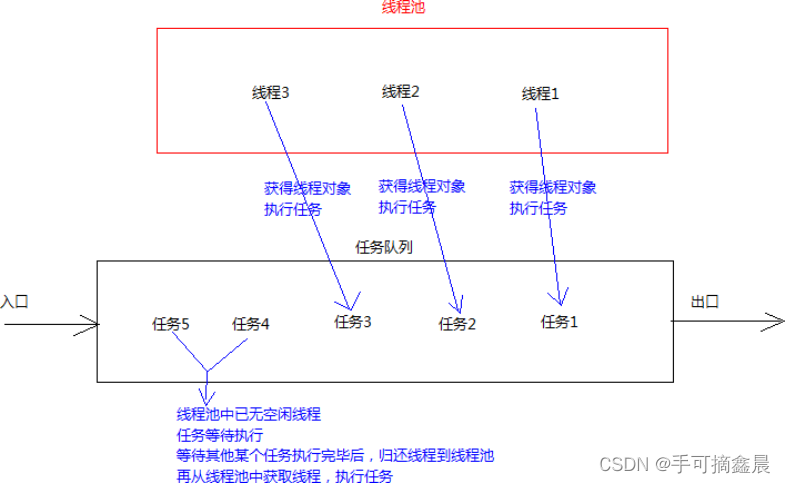
}15, Thread pool concept
In fact, it's a container that holds multiple threads , The threads can be reused , Eliminating the frequent creation of Thread objects , No need to create threads repeatedly and consume too much resources .
16, Benefits of thread pools
(1) Reduce resource consumption . Reduces the number of threads created and destroyed , Every worker thread can be reused , Can perform multiple tasks .
(2) Improve response time . When the mission arrives , Tasks can be executed without waiting for thread creation .
(3) Improve the manageability of threads . According to the system's bearing capacity , Adjust the number of worker threads in the thread pool , Prevent excessive internal consumption save , And get the server down ( Each thread requires about 1MB Memory , More threads open , The more memory you consume , The final crash ).
17, The use of thread pools
Creating a thread pool :public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
Use thread pool objects :public Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class xcc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
MyRunnable r = new MyRunnable();
service.submit(r);
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" I want a coach ");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(" Here comes the coach : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(" Teach me how to swim , After you hand it in , The coach went back to the pool ");
}
}
边栏推荐
- {1,2,3,2,5} duplicate checking problem
- Transplant hummingbird e203 core to Da Vinci pro35t [Jichuang xinlai risc-v Cup] (I)
- Zhejiang University Edition "C language programming experiment and exercise guide (3rd Edition)" topic set
- Pointer -- eliminate all numbers in the string
- Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 1 after class exercises and answers summary
- Programmers, how to avoid invalid meetings?
- 软件测试工作太忙没时间学习怎么办?
- Summary of thread implementation
- 线程及线程池
- [Ogg III] daily operation and maintenance: clean up archive logs, register Ogg process services, and regularly back up databases
猜你喜欢
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (II)
Fundamentals of digital circuits (II) logic algebra
Vysor uses WiFi wireless connection for screen projection_ Operate the mobile phone on the computer_ Wireless debugging -- uniapp native development 008

Summary of thread implementation

软件测试有哪些常用的SQL语句?
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (I)
What level do 18K test engineers want? Take a look at the interview experience of a 26 year old test engineer
软件测试面试要问的性能测试术语你知道吗?
MySQL数据库(一)
“Hello IC World”
随机推荐
[issue 18] share a Netease go experience
JDBC介绍
UCORE lab7 synchronous mutual exclusion experiment report
MySQL数据库(三)高级数据查询语句
Don't you even look at such a detailed and comprehensive written software test question?
[oiclass] maximum formula
"If life is just like the first sight" -- risc-v
Stc-b learning board buzzer plays music 2.0
Thinking about three cups of tea
ucore lab8 文件系统 实验报告
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (II)
Capitalize the title of leetcode simple question
[pointer] delete all spaces in the string s
ucore lab5用户进程管理 实验报告
Global and Chinese markets of MPV ACC ECU 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
王爽汇编语言学习详细笔记一:基础知识
If the position is absolute, touchablehighlight cannot be clicked - touchablehighlight not clickable if position absolute
The four connection methods of JDBC are directly coded
MySQL development - advanced query - take a good look at how it suits you
Global and Chinese markets of cobalt 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
