当前位置:网站首页>Understanding runloop in OC
Understanding runloop in OC
2020-11-09 10:56:00 【osc_7dn4hojn】
understand OC in RunLoop
What is? RunLoop?
It can be simply understood as , One that keeps the program running while loop , This loop listens for various events ( Such as touching events 、performSelector、 Timer NSTimer etc. ), Sleep when there are no events , In order to make effective use of CPU( Use only when there is an event CPU, Sleep when there is no event )
No matter RunLoop How complex is it? , Its essence is the above-mentioned : A cycle , Handle events when there is an event , Sleep when there is no event ( Sleep here refers to switching from user mode to kernel mode , Such a dormant thread is suspended , No more occupation cpu resources ).
RumLoop It has the following relationship with threads :
- There is only one thread RunLoop object
- Main thread RunLoop The default has been created , Child threads need to be created manually .
- RunLoop Create... On first acquisition , Destroy at the end of the thread .
Let's verify , stay main Before the function returns , A print :
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
NSString *appDelegateClassName;
@autoreleasepool {
// Setup code that might create autoreleased objects goes here.
appDelegateClassName = NSStringFromClass([AppDelegate class]);
}
int ret = UIApplicationMain(argc, argv, nil, appDelegateClassName);
NSLog(@"after ret");
return ret;
}
It turns out there's no print , This shows that the main process has entered a RunLoop Lord , The main process doesn't end , You can't jump out RunLoop, You can't print later .
Let's print the main thread's RunLoop try :
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSLog(@"%@", [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]);
}
// Print the results ( Just take the key information ):
// CFRunLoop 0x600001704700
// current mode = kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,
This shows that the main thread is in a RunLoop in , And the current mode of operation is kCFRunLoopDefaultMode
It feels like this RunLoop It's simple , But it's complicated , Because there are many factors to consider , For example, the processing sequence of various events , Timer 、 Multithreading and so on
For a complex problem , One of the solutions is abstraction , Apple to solve the above problem , Abstracted RunLoop object ,RunLoop Contains multiple Mode class , Every mode Class contains several Source,Observer and Timer class , Relations are as follows :
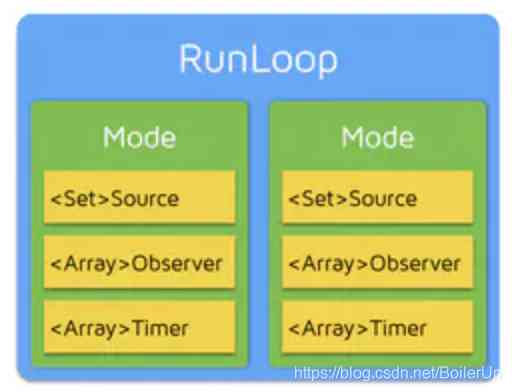
Mode yes RunLoop The mode of operation of , There are five kinds of :
kCFRunLoopDefaultMode //App Default Mode, Usually the main thread is in this Mode Run under
UITrackingRunLoopMode // Interface tracking Mode, be used for ScrollView Track touch slide , Make sure that the interface doesn't slide under any other Mode influence
UIInitializationRunLoopMode // Just started App The first to enter Mode, It will not be used after startup
GSEventReceiveRunLoopMode // Accept the inside of the system event Mode, It's not usually used
kCFRunLoopCommonModes // This is a placeholder Mode, It's not a real Mode, It can be simply understood as kCFRunLoopDefaultMode and UITrackingRunLoopMode The combination of
there Source It's the source of the event , For example, touch events .
Observer Is the observer , Events that listen to the event source , It can be simply understood as thread , For example, the main thread RunLoop Of course Observer It's the main thread .
There are also some rules :
- RunLoop Although there are many Mode, but RunLoop Function execution time , Only one... Can be specified Mode
- If you want to switch Mode, You need to wait for a Loop The loop ends , And let the new Mode Get into
It says a RunLoop only one Mode In execution , Let's do an experiment to see :
@interface ViewController ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextView *textView;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(timerTest) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
}
- (void)timerTest {
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
@end
Here we are ViewControlller It creates a timer, Add him to NSDefaultRunLoopMode in , This ViewControlller There's a scroll UITextView( Inherit UIScrollView,UIScrollView default Mode yes UITrackingRunLoopMode)
When we slide UITextView When ,timer Stop triggering events , explain RunLoop Of Mode from Default Switch to the UITrackingRunLoopMode
The solution is to put timer Put in kCFRunLoopCommonModes in , This Mode It's equivalent to being at the same time kCFRunLoopDefaultMode and UITrackingRunLoopMode:
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
This is a classic example , Can be solved in UIScrollView( Including its subclasses ) There is NSTimer Timing scene .
Inspired by this , We can use RunLoop Solve the stuck problem , There's a kind of stuck problem, which is UITableView There are a lot of big HD images to load in , When you slide the screen, you get stuck .
Let's first analyze the cause of the jam : The most fundamental reason is RunLoop It took too long to make a turn , Because once RunLoop The loop needs to parse a lot of big HD images , The system needs a certain amount of time to render each large high-definition image , This needs to wait until the rendering RunLoop After that , To switch between sliding screens RunLoop Of Mode(UITrackingRunLoopMode), The solution is :
- Create a timer : At regular intervals ( It can be 0.01s) Execute an empty method to wake up RunLoop
- Load the image loading method into block, take block Add a limited number of arrays , When block Exceeding the maximum number limit , Remove the first added block
- monitor RunLoop The awakening of , When you wake up and go back, you execute it once and take one out of the array block Event to perform , The finished event is removed from the array
This design makes RunLoop Only one loading image is executed in each loop block( Reduce RunLoop The time of a single cycle ). Set a maximum limit on the number of arrays , It can prevent too many pictures to be rendered at the same time ( Reduce RunLoop Total time to render images ).
Let's take a look at RunLoop What does it look like :
RunLoop Internal logic
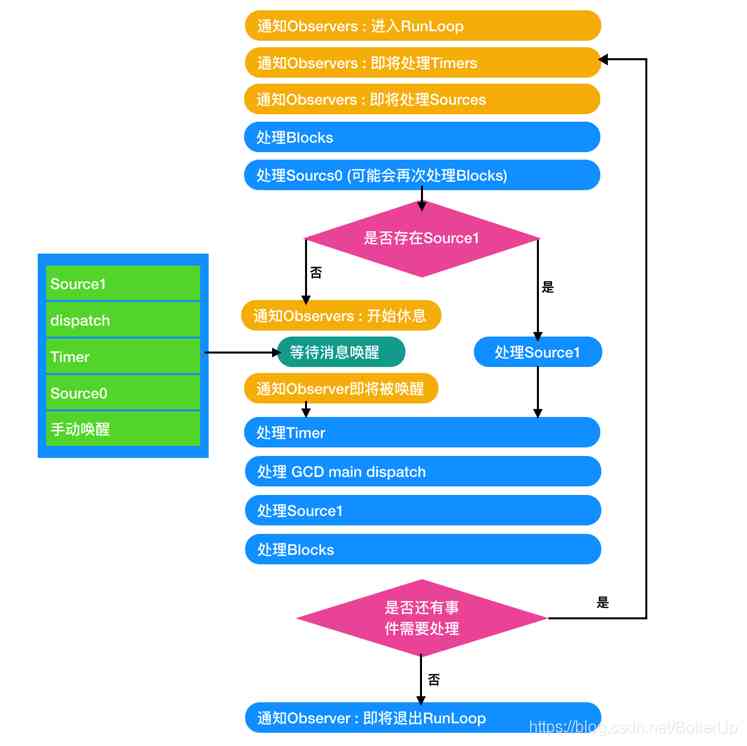
A new concept is introduced here :source0 It's touch events and all execution performSelector Method ,source1 Is based on port Communication between threads of .
Here we can roughly see that RunLoop The order in which events are handled in , It can be summarized briefly as follows :
- Let me know first Timer,Sources It's time to deal with the incident
- Handle source0
- See if there's any source1, Sleep if you don't , There is no sleep
- In sleep sources,timer,dispatch, You can wake it up manually
- 3 End or 4 After wake up , I started to deal with all kinds of other events (timer,source1,dispatch)
- If step five deals with at least one event , Then a new round of RunLoop, Otherwise quit RunLoop
The above logic can lead to , stay RunLoop in , As long as there is any one event ,RunLoop Will not quit , Unless it is RunLoop Awakened or forced to stop on sleep timeout , You're going to quit .
Let's use an example to feel RunLoop Logic in :
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self createObserver];
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0 target:self selector:@selector(timerFired) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
}
- (void)timerFired
{
NSLog(@"---- timer fired ----");
}
- (void)createObserver
{
// Create listener
/*
The first parameter CFAllocatorRef allocator: Allocate storage space CFAllocatorGetDefault() Default assignment
The second parameter CFOptionFlags activities: The status to be monitored kCFRunLoopAllActivities Listen to all States
The third parameter Boolean repeats:YES: Continuous monitoring NO: It doesn't last
Fourth parameter CFIndex order: priority , General filling 0 that will do
Fifth parameter : Callback Two parameters observer: monitor activity: Listening events
*/
CFRunLoopObserverRef observer = CFRunLoopObserverCreateWithHandler(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), kCFRunLoopAllActivities, YES, 0, ^(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity) {
switch (activity) {
case kCFRunLoopEntry:
NSLog(@"RunLoop Get into ");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers:
NSLog(@"RunLoop To deal with Timers 了 ");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeSources:
NSLog(@"RunLoop To deal with Sources 了 ");
break;
case kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting:
NSLog(@"RunLoop It's time to rest ");
break;
case kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting:
NSLog(@"RunLoop Wake up ");
break;
case kCFRunLoopExit:
NSLog(@"RunLoop Out of the ");
break;
default:
break;
}
});
CFRunLoopAddObserver(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), observer, kCFRunLoopDefaultMode); // Add monitor , The key !
CFRelease(observer); // Release
}
Here to RunLoop Created an observer , The viewer's callback print RunLoop Logic in , There's another one Timer every other 1.0 Second trigger . give the result as follows :
// 23:26:30 RunLoop Wake up
// 23:26:30 ---- timer fired ----
// 23:26:30 RunLoop To deal with Timers 了
// 23:26:30 RunLoop To deal with Sources 了
// 23:26:30 RunLoop It's time to rest
// 23:26:31 RunLoop Wake up
// 23:26:31 ---- timer fired ----
// 23:26:31 RunLoop To deal with Timers 了
// 23:26:31 RunLoop To deal with Sources 了
// 23:26:31 RunLoop It's time to rest
You can see ,Timer When it comes to triggering , awakened RunLoop,RunLoop Wake up and deal with it Timer, Yes Timer Methods ( Print ---- timer fired ----), then RunLoop Back to the beginning of the loop , Inform the observer to deal with Timers and Sources 了 , It turns out there's nothing to deal with , Then I went to have a rest , So circular ... Basically consistent with the above logic .
Here is an introduction RunLoop Application :
Create a resident thread
First, we create an inheritance from NSThread Class BZThread, Used to print information about destruction , And then in viewDidLoad Create a thread :
@interface BZThread : NSThread
@end
@implementation BZThread
- (void)dealloc {
NSLog(@"BZThread is dealloced");
}
@end
@interface ViewController ()
@property NSThread *thread;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSThread *thread = [[BZThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(threadTest) object:nil];
self.thread = thread;
[self.thread start];
}
- (void)threadTest {
NSLog(@"thread is created");
}
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {
[self performSelector:@selector(doSomethingInThread) onThread:self.thread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO];
}
- (void)doSomethingInThread {
NSLog(@"doSomethingInThread is fired");
}
@end
// BZThread is created
We found that , Threads are created , Also by ViewControlelr Hold on to ( Not immediately destroyed ), But there is no response when we execute methods in this thread , This shows that the thread has RunLoop It doesn't work .
The solution is in this thread method , For this thread RunLoop Create a Mode:
- (void)threadTest {
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addPort:[NSPort port] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run];
NSLog(@"thread is created");
}
Click on the screen , We will execute the thread method :
// doSomethingInThread is fired
This is because , Although a thread corresponds to a RunLoop, But a RunLoop At least one is needed Mode, To run , By default, the main thread has Mode 了 , New threads require us to create new ones manually Mode.
Finally, I'd like to introduce a RunLoop Application :
Test for carton :
If RunLoop The thread of , The execution time of the method before entering sleep is too long to enter sleep , Or when the thread wakes up, it takes too long to receive messages and cannot go to the next step , The thread is blocked . If this thread is the main thread , What it shows is that there is a carton .
How to check for stuck ? You need to create a persistent child thread to monitor the main thread's RunLoop state . Once you find that before you go to sleep state , Or wake up state , There has been no change within the set time threshold , It can be judged as stuck . Next , We can dump Information out of the stack , Which method is too long to carry out .
版权声明
本文为[osc_7dn4hojn]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- Principle analysis and performance tuning of elasticsearch
- Chrome浏览器引擎 Blink & V8
- 如何保证消息不被重复消费?(如何保证消息消费的幂等性)
- A solution to the problem that color picker (palette) cannot use shortcut keys in sublime Text3 plug-in
- Unemployment log, November 5
- 十五年后,重构一个“在线的腾讯”
- Start learning discrete mathematics again
- Deng Junhui's notes on data structure and algorithm learning - Chapter 9
- Commodity management system -- integrate warehouse services and obtain warehouse list
- 抢球鞋?预测股市走势?淘宝秒杀?Python表示要啥有啥
猜你喜欢

商品管理系统——整合仓库服务以及获取仓库列表
Dynamo: a typical distributed system analysis

2. Introduction to computer hardware

BIOS of operating system

From the practice, this paper discusses the problems caused by the inconsistent design of ruby syntax.

嘉宾专访|2020 PostgreSQL亚洲大会阿里云数据库专场:樊文凯

彩虹排序 | 荷兰旗问题

20201108 programming exercise exercise 3
VisualStudio(Mac)安装过程笔记

重新开始学习离散数学
随机推荐
nodejs学习笔记(慕课网nodejs从零开发web Server博客项目)
商品管理系统——SPU检索功能
商品管理系统——整合仓库服务以及获取仓库列表
1450. Number of students doing homework at a given time
《内网安全攻防》配套视频 之 利用PS查询域内信息
How to query by page after 10 billion level data is divided into tables?
[Python from zero to one] 5. Detailed explanation of beautiful soup basic syntax of web crawler
解决python调用 ffmpeg时 ‘ffmpeg‘ 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序
The whole process of building a fully distributed cluster
Ten year itch of programmer
Commodity management system -- implementation of local preservation of new commodities
Dynamo: a typical distributed system analysis
一个简单的能力,决定你是否会学习!
Principle analysis and performance tuning of elasticsearch
Rainbow sorting | Dutch flag problem
2020,Android开发者打破寒冬的利器是什么?
【QT】子类化QThread实现多线程
从实践谈 Ruby 语法上的几个设计不一致带来的问题。
Android 复选框 以及回显
Several rolling captions based on LabVIEW