当前位置:网站首页>Sentinel源码(六)ParamFlowSlot热点参数限流
Sentinel源码(六)ParamFlowSlot热点参数限流
2022-08-02 14:01:00 【Ethan_199402】
Sentinel源码(三)slot解析中我们还遗留了最后一个slot,ParamFlowSlot没有讲解,本文着重探究sentinel如果做热点参数限流
首先区别于其他的slot,热点参数限流并非在 Sentinel 的 core 模块中实现的,而是在扩展模块中实现的。主要是根据同一资源不同的参数进行限流。
之前的限流策略都是针对资源维度的,热点参数限流则将维度细化到资源的某个参数上
限流类型
热点参数限是流通过对请求的第几个参数以及参数值的流量进行统计,超过阈值触发流控的一种方式
sentinel提供两种限流类型
1.QPS:分为直接限流和匀速限流
- 直接限流:令牌桶原理
- 匀速限流:漏桶原理
2.并发线程
关于令牌桶和漏桶原理可以参考:漏桶算法&令牌桶算法理解及常用的算法
源码
负责热点参数限流的插槽为ParamFlowSlot,当达到设置的阈值时抛出ParamFlowException
void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
//参数为null
if (args == null) {
return;
}
if (!ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {
return;
}
List<ParamFlowRule> rules = ParamFlowRuleManager.getRulesOfResource(resourceWrapper.getName());
for (ParamFlowRule rule : rules) {
// 从 args 中获取本次限流需要使用的 value
applyRealParamIdx(rule, args.length);
// Initialize the parameter metrics.
ParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule);
if (!ParamFlowChecker.passCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, args)) {
String triggeredParam = "";
if (args.length > rule.getParamIdx()) {
Object value = args[rule.getParamIdx()];
triggeredParam = String.valueOf(value);
}
throw new ParamFlowException(resourceWrapper.getName(), triggeredParam, rule);
}
}
}
其中ParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule)初始化各种监控指标
public static void initParamMetricsFor(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, /*@Valid*/ ParamFlowRule rule) {
if (resourceWrapper == null || resourceWrapper.getName() == null) {
return;
}
String resourceName = resourceWrapper.getName();
ParameterMetric metric;
// Assume that the resource is valid.
if ((metric = metricsMap.get(resourceName)) == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
if ((metric = metricsMap.get(resourceName)) == null) {
metric = new ParameterMetric();
metricsMap.put(resourceWrapper.getName(), metric);
RecordLog.info("[ParameterMetricStorage] Creating parameter metric for: " + resourceWrapper.getName());
}
}
}
metric.initialize(rule);
}
先从缓存取,缓存中没有则初始化
public void initialize(ParamFlowRule rule) {
if (!ruleTimeCounters.containsKey(rule)) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (ruleTimeCounters.get(rule) == null) {
long size = Math.min(BASE_PARAM_MAX_CAPACITY * rule.getDurationInSec(), TOTAL_MAX_CAPACITY);
ruleTimeCounters.put(rule, new ConcurrentLinkedHashMapWrapper<Object, AtomicLong>(size));
}
}
}
if (!ruleTokenCounter.containsKey(rule)) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (ruleTokenCounter.get(rule) == null) {
long size = Math.min(BASE_PARAM_MAX_CAPACITY * rule.getDurationInSec(), TOTAL_MAX_CAPACITY);
ruleTokenCounter.put(rule, new ConcurrentLinkedHashMapWrapper<Object, AtomicLong>(size));
}
}
}
if (!threadCountMap.containsKey(rule.getParamIdx())) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (threadCountMap.get(rule.getParamIdx()) == null) {
threadCountMap.put(rule.getParamIdx(),
new ConcurrentLinkedHashMapWrapper<Object, AtomicInteger>(THREAD_COUNT_MAX_CAPACITY));
}
}
}
}
ruleTimeCounters:记录热点参数上次添加令牌的时间,lastAddTokenTime,用于 QPS 限流
ruleTokenCounter:记录热点参数剩余的令牌数,用于 QPS 限流,
threadCountMap:用于线程级别限流,这个其实和令牌桶算法没有关系了,线程限流只是在 Rule 中定义了最大线程数,请求时判断一下当前的线程数是否大于最大线程,具体的应用在 ParamFlowChecker#passSingleValueCheck
接下来ParamFlowChecker.passCheck
public static boolean passCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, /*@Valid*/ ParamFlowRule rule, /*@Valid*/ int count,
Object... args) {
if (args == null) {
return true;
}
int paramIdx = rule.getParamIdx();
if (args.length <= paramIdx) {
return true;
}
// Get parameter value.
Object value = args[paramIdx];
// Assign value with the result of paramFlowKey method
if (value instanceof ParamFlowArgument) {
value = ((ParamFlowArgument) value).paramFlowKey();
}
// If value is null, then pass
if (value == null) {
return true;
}
if (rule.isClusterMode() && rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {
return passClusterCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}
return passLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}
注意也已经写的很明白了,重点就是根据 rule 判断是该请求使用集群限流还是本地限流
passClusterCheck
实现原理是=选出一台 Server 来做限流决策,所有客户端的限流请求都咨询 Server,由 Server 来决定,源码相对简单,本文不重点介绍
private static boolean passClusterCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int count,
Object value) {
try {
Collection<Object> params = toCollection(value);
TokenService clusterService = pickClusterService();
if (clusterService == null) {
// No available cluster client or server, fallback to local or
// pass in need.
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(resourceWrapper, rule, count, params);
}
TokenResult result = clusterService.requestParamToken(rule.getClusterConfig().getFlowId(), count, params);
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case TokenResultStatus.OK:
return true;
case TokenResultStatus.BLOCKED:
return false;
default:
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(resourceWrapper, rule, count, params);
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
RecordLog.warn("[ParamFlowChecker] Request cluster token for parameter unexpected failed", ex);
return fallbackToLocalOrPass(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}
}
passLocalCheck
重点看一下passLocalCheck方法
private static boolean passLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int count,
Object value) {
try {
if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(value.getClass())) {
for (Object param : ((Collection)value)) {
if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {
return false;
}
}
} else if (value.getClass().isArray()) {
int length = Array.getLength(value);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object param = Array.get(value, i);
if (!passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, param)) {
return false;
}
}
} else {
return passSingleValueCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, value);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
RecordLog.warn("[ParamFlowChecker] Unexpected error", e);
}
return true;
}
如果 value 是 Collection 或者 Array,Sentinel 认为这一组数据都需要经过热点参数限流校验,所以需要遍历所有值调用热点参数限流校验,查看passSingleValueCheck方法
static boolean passSingleValueCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount,
Object value) {
if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {
//匀速限流
if (rule.getControlBehavior() == RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER) {
return passThrottleLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);
} else {
//直接限流
return passDefaultLocalCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, acquireCount, value);
}
// // 线程级限流逻辑
} else if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD) {
Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();
long threadCount = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper).getThreadCount(rule.getParamIdx(), value);
if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {
int itemThreshold = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);
return ++threadCount <= itemThreshold;
}
long threshold = (long)rule.getCount();
return ++threadCount <= threshold;
}
return true;
}
匀速限流passThrottleLocalCheck
static boolean passThrottleLocalCheck(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, ParamFlowRule rule, int acquireCount,
Object value) {
//获取上文初始化的ParameterMetric
ParameterMetric metric = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper);
//根据rule 获得最后添加令牌的时间记录map
CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> timeRecorderMap = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTimeCounter(rule);
if (timeRecorderMap == null) {
return true;
}
// Calculate max token count (threshold)
Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();
//获取对应热点参数的令牌数
long tokenCount = (long)rule.getCount();
if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {
tokenCount = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);
}
if (tokenCount == 0) {
return false;
}
//根据rule配置的每多少秒可以通过多少请求来计算出一个请求需要多少毫秒
long costTime = Math.round(1.0 * 1000 * acquireCount * rule.getDurationInSec() / tokenCount);
while (true) {
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
//更新timeRecorder为当前时间并返回旧的记录
AtomicLong timeRecorder = timeRecorderMap.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(currentTime));
if (timeRecorder == null) {
return true;
}
//AtomicLong timeRecorder = timeRecorderMap.get(value);
//上次通过请求的时间
long lastPassTime = timeRecorder.get();
//期望的下次请求通过时间
long expectedTime = lastPassTime + costTime;
//期望时间已经过了或者与还需要等待的时间小于配置的排队阈值
if (expectedTime <= currentTime || expectedTime - currentTime < rule.getMaxQueueingTimeMs()) {
AtomicLong lastPastTimeRef = timeRecorderMap.get(value);
//CAS修改lastPastTimeRef时间戳
if (lastPastTimeRef.compareAndSet(lastPassTime, currentTime)) {
long waitTime = expectedTime - currentTime;
//waitTime>0表示还需要排队到期望时间点,否则不用排队直接返回true
if (waitTime > 0) {
lastPastTimeRef.set(expectedTime);
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
RecordLog.warn("passThrottleLocalCheck: wait interrupted", e);
}
}
return true;
} else {
Thread.yield();
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
使用漏桶原理,通过与两次请求的时间间隔以及排队等待的时间比较来决定触发热点参数限流还是放行。
- 获取上文初始化的metric
- 根据rule 从metric获得最后添加令牌的时间记录timeRecorderMap
- 如果排除的热点参数中包含当前 value,则使用热点参数配置的count,否则使用 rule 中定义的 count
- 根据rule配置的每多少秒可以通过多少请求来计算出一个请求需要多少毫秒costTime
- 根据timeRecorderMap获得上次通过请求的时间lastPassTime
- 计算期望的下次请求通过时间
long expectedTime = lastPassTime + costTime;请求放行的条件是期望时间已经过了或者还需要等待的时间小于配置的排队时间阈值 - CAS修改lastPastTimeRef时间戳,如果成功,计算需要等待多久可以放行这个请求;如果失败线程让出cpu资源。
waitTime = expectedTime - currentTime;,waitTime>0表示还需要排队到期望时间点,否则不用排队直接返回true
直接限流passDefaultLocalCheck
直接限流的前半部分如下
//参数统计类metric
ParameterMetric metric = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper);
CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> tokenCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTokenCounter(rule);
CacheMap<Object, AtomicLong> timeCounters = metric == null ? null : metric.getRuleTimeCounter(rule);
if (tokenCounters == null || timeCounters == null) {
return true;
}
// Calculate max token count (threshold)
Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();
//如果排除的热点参数中包含当前 value,则使用热点参数配置的count,否则使用 rule 中定义的 count
long tokenCount = (long)rule.getCount();
if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {
tokenCount = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);
}
if (tokenCount == 0) {
return false;
}
//最大令牌数 = 设置的阈值 + 额外允许的突发流量
long maxCount = tokenCount + rule.getBurstCount();
//请求的令牌数超过最大令牌数直接限流
if (acquireCount > maxCount) {
return false;
}
- 获得参数统计类metric
- 获得热点参数令牌统计器tokenCounters
- 获得热点参数令牌加入时间统计器timeCounters
- 如果热点参数中包含当前 value,则使用热点参数配置的count,否则使用 rule 中定义的 count
- 计算允许的最大令牌数 = 设置的阈值 + 额外允许的突发流量
- 请求的令牌数超过最大令牌数直接限流
再来看while中的代码
while (true) {
long currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
//获得上一次添加令牌的时间,如果为null,令牌统计器
AtomicLong lastAddTokenTime = timeCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(currentTime));
if (lastAddTokenTime == null) {
// Token never added, just replenish the tokens and consume {@code acquireCount} immediately.
tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));
return true;
}
// Calculate the time duration since last token was added.
long passTime = currentTime - lastAddTokenTime.get();
// A simplified token bucket algorithm that will replenish the tokens only when statistic window has passed.
//如果两次请求间隔过了统计时间窗口
if (passTime > rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000) {
AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.putIfAbsent(value, new AtomicLong(maxCount - acquireCount));
if (oldQps == null) {
// Might not be accurate here.
lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
} else {
//剩余令牌数
long restQps = oldQps.get();
//需要补充的令牌数
long toAddCount = (passTime * tokenCount) / (rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000);
//补充后的令牌数
long newQps = toAddCount + restQps > maxCount ? (maxCount - acquireCount)
: (restQps + toAddCount - acquireCount);
//表示acquireCount需要的令牌不足,直接限流
if (newQps < 0) {
return false;
}
//CAS更新剩余令牌数
if (oldQps.compareAndSet(restQps, newQps)) {
lastAddTokenTime.set(currentTime);
return true;
}
Thread.yield();
}
} else {
//不需要补充令牌
AtomicLong oldQps = tokenCounters.get(value);
if (oldQps != null) {
long oldQpsValue = oldQps.get();
//剩余令牌足够并且CAS更新成功则放行,否则限流
if (oldQpsValue - acquireCount >= 0) {
if (oldQps.compareAndSet(oldQpsValue, oldQpsValue - acquireCount)) {
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
Thread.yield();
}
}
热点参数直接限流通过简易令牌桶算法来实现的,请求通过时通过比较剩余令牌的数量。有令牌则放行,无令牌触发热点参数限流抛出ParamFlowException。添加令牌的时机选择在两次请求的时间间隔超过时间窗口大小时,计算出这段时间需要给令牌桶添加多少令牌。热点参数的最大令牌数即用户设置的限流阈值与允许突发流量之和
- 获得上一次添加令牌的时间,如果为null,令牌统计器
- 计算距离上次添加令牌经过的时间passTime
- 如果两次请求间隔过了统计时间窗口,计算需要补充的令牌数
toAddCount = (passTime * tokenCount) / (rule.getDurationInSec() * 1000);,重置tokenCounters为newQps,newQps为restQps+toAddCount,但是不能超过maxCount,CAS更新剩余tokenCounters成功则放行,否则让出cpu时间 - 如果两次请求间隔不大于统计时间窗口,则不需要补充令牌,拿到oldQps即剩余的令牌数,如果大于acquireCount则更新tokenCounters的剩余令牌数,成功则放行,否则拦截
线程级别限流
else if (rule.getGrade() == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD) {
Set<Object> exclusionItems = rule.getParsedHotItems().keySet();
//热词配置的线程阈值
long threadCount = getParameterMetric(resourceWrapper).getThreadCount(rule.getParamIdx(), value);
if (exclusionItems.contains(value)) {
int itemThreshold = rule.getParsedHotItems().get(value);
return ++threadCount <= itemThreshold;
}
long threshold = (long)rule.getCount();
return ++threadCount <= threshold;
}
线程级限流相对简单,从线程计数器中获得获得当前记录的线程数,与用户配置的线程阈值做比较,超过阈值则限流,否则放行
细心的读者应该发现了
1.线程限流的方式并没有去更新计数器的数据是为什么?
因为在StatisticSlot中如果最终所有的插槽链都没有拦截请求,会回调用已经注册的回调函数
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
而ParamFlowStatisticEntryCallback就是其中一个,与ParamFlowStatisticExitCallback对应,一个负责对ParameterMetric中的线程计数器增加,一个负责减少
public void onPass(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count, Object... args) {
// The "hot spot" parameter metric is present only if parameter flow rules for the resource exist.
ParameterMetric parameterMetric = ParameterMetricStorage.getParamMetric(resourceWrapper);
if (parameterMetric != null) {
parameterMetric.addThreadCount(args);
}
}
public void onExit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
if (context.getCurEntry().getBlockError() == null) {
ParameterMetric parameterMetric = ParameterMetricStorage.getParamMetric(resourceWrapper);
if (parameterMetric != null) {
parameterMetric.decreaseThreadCount(args);
}
}
}
2.另外一个问题:为什么线程计数器读出来的threadCount还要先加一再比较?
return ++threadCount <= threshold;
回顾一下这篇文章Sentinel源码(三)slot解析插槽链的执行顺序如下: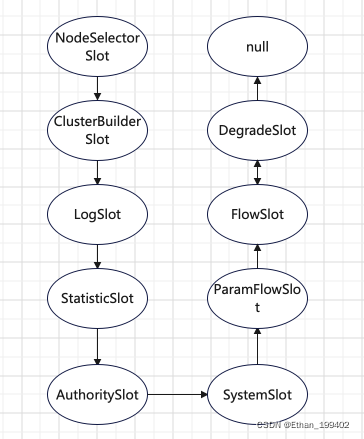
在StatisticSlot中,还没有进行回调的时候,首先就fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);来执行后面的插槽链,所以ParamFlowSlot拿到的线程数是没有加1的线程数,所以要加1再比较,返回true以后,才会在StatisticSlot中进行回调对线程计数器加一
边栏推荐
- static修饰的函数有什么特点(static可以修饰所有的变量吗)
- 玉溪卷烟厂通过正确选择时序数据库 轻松应对超万亿行数据
- stack && queue
- 乐心湖‘s Blog——MySQL入门到精通 —— 囊括 MySQL 入门 以及 SQL 语句优化 —— 索引原理 —— 性能分析 —— 存储引擎特点以及选择 —— 面试题
- els strip collision deformation judgment
- 第二届中国Rust开发者大会(RustChinaConf 2021~2022)线上大会正式开启报名
- 世界上最大的开源基金会 Apache 是如何运作的?
- WiFi Association & Omnipeek Packet Capture Analysis
- SQL函数 UPPER
- 二分查找 && 树
猜你喜欢

How to do short video food from the media?5 steps to teach you to get started quickly
网络安全第二次作业
【C语言】手撕循环结构 —— for语句
苏州大学:从 PostgreSQL 到 TDengine

栈 && 队列
![[C language] Explicit array solution (1)](/img/d2/26e3e64bb07578a6348747c00abb64.png)
[C language] Explicit array solution (1)
FreeBSD bnxt以太网驱动源码阅读记录三:

数据机构---第六章图---图的遍历---选择题
【C语言】手撕循环结构 —— while语句
【Tensorflow】AttributeError: '_TfDeviceCaptureOp' object has no attribute '_set_device_from_string'
随机推荐
Image retrieval method based on deep learning!
Awesome!Alibaba interview reference guide (Songshan version) open source sharing, programmer interview must brush
els long block deformation conditions, boundary collision judgment
C# using 使用方法
目前想通过提取本地excel文件创建数据表,在sql语句这出了一些问题
你真的懂单例模式么
Fabric.js 动态设置字号大小
ORACLE expdp/impdp详解
【Tensorflow】AttributeError: module ‘keras.backend‘ has no attribute ‘tf‘
SQL函数 UCASE
音频处理:浮点型数据流转PCM文件
[C language] Analysis of function recursion (3)
Detailed explanation of ORACLE expdp/impdp
【C语言】细品分支结构——switch语句
【C语言】手撕循环结构 —— for语句
CSDN(成长一夏竞赛)- 最大数
els strip collision deformation judgment
Audio processing: floating point data stream to PCM file
不精确微分/不完全微分(Inexact differential/Imperfect differential)
[C language] Explicit array solution (1)