当前位置:网站首页>Database storage - table partition
Database storage - table partition
2022-07-07 08:43:00 【Blue sky ⊙ white clouds】
With the development of the project , There are more and more single table data in the database , Related operations are getting slower , At this time, how can we improve our relevant operation efficiency ? Many people have heard of Sub database and sub table , But there is another way of partitioning that may be ignored , When the data volume has not reached the level of tens of millions , We may also be able to use partitioning , Let the data of a table be distributed on different files , Of course, we should be clear that our table data is stored on the disk in the form of files , Partition and sub table mean different things , Partitioning refers to distributing the data of a table to different files according to conditions , Before partitioning, it is stored on a file , But it still points to the same table , Just spread the data to different files , But the sub table spreads the data to different tables , Although the structure is the same , But the name of the table has changed . Partitioning helps us reduce the data per operation , To improve performance .
Encounter the problem of such a large amount of data , We can solve it through the following ideas :
1. shunt ( The principle is : Try to reduce the cardinality of data for each operation ):
1.1. With and without 、 Commonly used and infrequently used are separated .
1.2. Data stored in the database : Partition 、 sub-treasury 、 table .
1.3. Data stored in files : Open the file .
1.4. Consider batching .
2. Cache technology : Read more write less cache .
3. Database optimization : Reasonably design the database structure 、 Build index reasonably 、 Database cluster .
4. Processing optimization : Optimize Sql、 Consider using temporary tables 、 In the middle of table .
5. The rational use of NoSql:Mongodb、Redis、HBase etc. .
6. Distributed big data processing scheme :Hadoop、Spark、Storm etc. .
Here we mainly need to know how to partition the table , What are the advantages and disadvantages of partitioning and what are the precautions for partitioning . Here we are mysql Give examples .
Let's first look at the advantages and disadvantages of partitions :
1. advantage :
• Perform logical data segmentation , Split data can have multiple physical file paths
Next, let's look at the partition method :
1.RANGE Partition : Given the column value of a continuous interval .
Create it as follows :
-
CREATE
TABLE tbl_users1 (
-
uuid
INT
NOT
NULL,
-
name
VARCHAR(
20),
-
registerTime
VARCHAR(
100)
-
)
-
PARTITION
BY
RANGE (uuid) (
-
PARTITION p0
VALUES LESS THAN (
5),
-
PARTITION p1
VALUES LESS THAN (
10),
-
PARTITION p2
VALUES LESS THAN (
15),
-
PARTITION p3
VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
-
);
2.LIST Partition :LIST It is the column value that matches a certain value in a discrete value set to select .
Create it as follows :
-
CREATE
TABLE tbl_users2 (
-
uuid
INT
NOT
NULL,
-
name
VARCHAR(
20),
-
registerTime
VARCHAR(
100)
-
)
-
-
PARTITION
BY List (uuid) (
-
PARTITION p0
VALUES
in (
1,
2,
3,
5),
-
PARTITION p1
VALUES
in (
7,
9,
10),
-
PARTITION p2
VALUES
in (
11,
15)
-
);
3.HASH Partition : The return value of user-defined expression hash The partition selected after calculation , The expression evaluates with the column values of the rows to be inserted into the table , This function must produce non negative integer values .
Create it as follows :
-
CREATE
TABLE tbl_users4 (
-
uuid
INT
NOT
NULL,
-
name
VARCHAR(
20),
-
registerTime
VARCHAR(
100)
-
)
-
PARTITION
BY HASH (uuid)
/
/uuid You can add expressions , such as
/
2, perhaps
mod(uuid,
2), Low performance , Each data should be calculated before hash Then insert
-
PARTITIONS
3;
4.KEY Partition : It's like pressing HASH Partition , from MySQL The server provides its own hash function .
Create it as follows :
-
CREATE
TABLE tbl_users5 (
-
uuid
INT
NOT
NULL,
-
name
VARCHAR(
20),
-
registerTime
VARCHAR(
100)
-
)
-
PARTITION
BY LINEAR Key (uuid)
-
PARTITIONS
3;
In a later article, we will specifically introduce partition operations , No more details here . When partitioning, we need to pay attention to the following situations :
1. If... Exists in the table primary key perhaps unique key when , Partitioned columns are part of one of two
边栏推荐
- Opencv learning notes 1 -- several methods of reading images
- 数据分片介绍
- Iptables' state module (FTP service exercise)
- Three series of BOM elements
- Open3d ISS key points
- Merge sort and non comparison sort
- String operation
- [南京大学]-[软件分析]课程学习笔记(一)-introduction
- GOLand idea intellij 无法输入汉字
- Golang compilation constraint / conditional compilation (/ / +build < tags>)
猜你喜欢
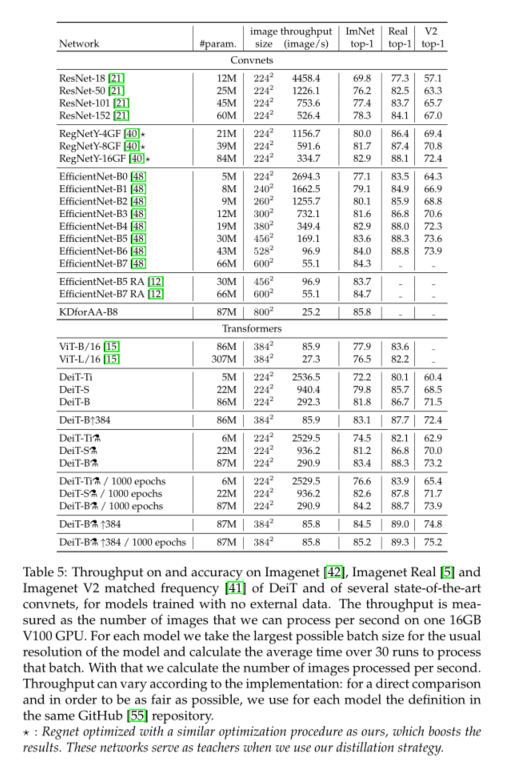
Deit learning notes

oracle一次性说清楚,多种分隔符的一个字段拆分多行,再多行多列多种分隔符拆多行,最终处理超亿亿。。亿级别数据量

Opencv learning notes II - basic image operations
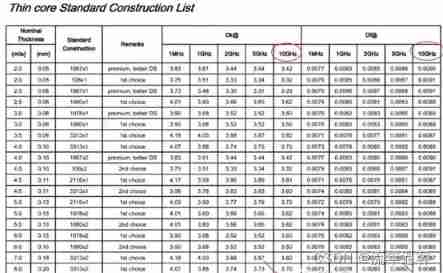
Teach you how to select PCB board by hand (II)
Merge sort and non comparison sort
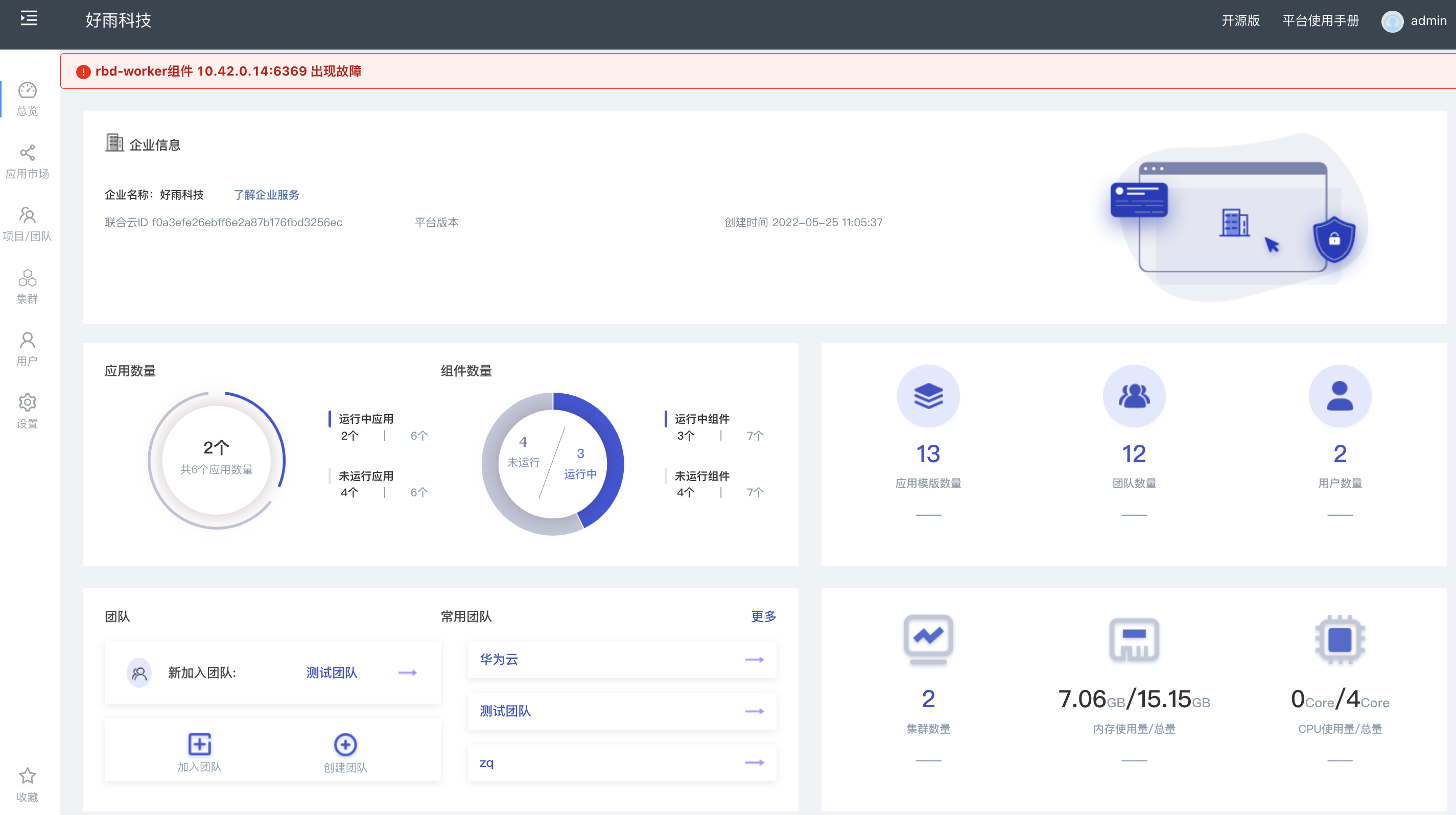
Rainbow 5.7.1 supports docking with multiple public clouds and clusters for abnormal alarms

Input and output of floating point data (C language)
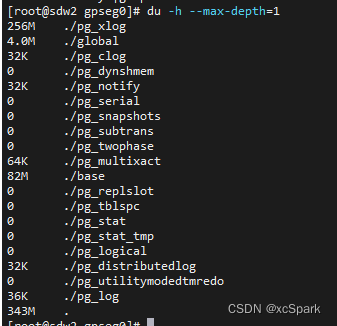
Greenplum6.x常用语句
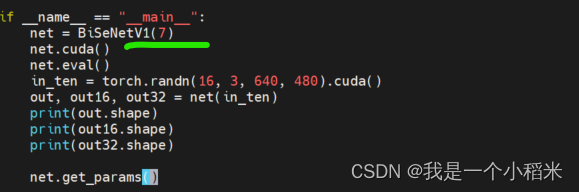
Implement your own dataset using bisenet
Greenplum6.x监控软件搭建
随机推荐
Greenplum6.x搭建_安装
详解华为应用市场2022年逐步减少32位包体上架应用和策略
redis故障处理 “Can‘t save in background: fork: Cannot allocate memory“
PLSQL的安装和配置
Golan idea IntelliJ cannot input Chinese characters
Analysis of using jsonp cross domain vulnerability and XSS vulnerability in honeypot
Sign and authenticate API interface or H5 interface
[hard core science popularization] working principle of dynamic loop monitoring system
【踩坑】nacos注册一直连接localhost:8848,no available server
mysql分区讲解及操作语句
ES6_ Arrow function
Opencv learning note 5 - gradient calculation / edge detection
POJ - 3784 Running Median(对顶堆)
Xcit learning notes
Greenplum6.x常用语句
Redis summary
How to understand distributed architecture and micro service architecture
Go write a program that runs within a certain period of time
How to realize the high temperature alarm of the machine room in the moving ring monitoring system
归并排序和非比较排序