Firewall Overview
A firewall (firewall) The word "architecture" was originally used for , The original intention is to protect the building from fire . It has been used for reference in the field of network communication , To protect a local area network or host from network attacks .
A firewall : Working on the edge of the host or network , Check the incoming and outgoing data messages according to the pre-defined rules , monitor , Once the standard is met , We use a set of mechanism components to process actions according to predefined rules ( The Internet )( host ) A firewall
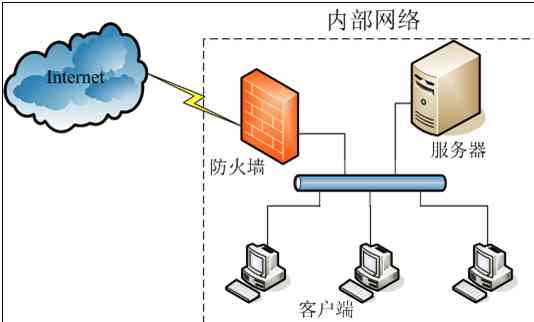
At present, there are some common ones on the market 3,4 Layer firewall , It's called network layer firewall , There are seven layers of firewalls , It's actually the gateway of the proxy layer .
about TCP/IP In terms of the seven layer model , We know that the third layer is the network layer , Three layers of firewall will detect the source address and the target address in this layer , But for the seven layer firewall , Whether you are a source port or a destination port , What is the source address or destination address , Will check everything you have . So for design principles , Seven layer firewall is more secure , But that leads to less efficiency , So the usual firewall solution on the market , It's a combination of the two . And because we all need to access from this port controlled by the firewall , So the efficiency of the firewall becomes the most important control of how much data users can access , Bad configuration may even become the bottleneck of traffic .
It can be divided into many types according to the way of prevention and the different emphasis , But generally speaking, it can be divided into two types: packet filtering firewall and proxy server .
/*
Framework:
The default rules :
to open up : Block up
close : through
The rules : Matching criteria
IP: Source IP, The goal is IP
TCP: SPORT,DPORT
UDP: SPORT,DPORT
ICMP: icmp-type
Data packet filtering :
*/
Firewall classification
Host firewall
Working on the edge of a host , Mainly for in and out of the host
Layered identification of message , It's all implemented at the system kernel level , So the firewall also works in the kernel space of a single host [TCP/IP On the protocol stack ], It can only work on a single host
Network firewall
Firewall devices in the network , It can be divided into three kinds : Proxy firewall 、 Packet filtering firewall 、 State monitoring firewall .
Proxy firewall
Proxy firewall is a device that acts as a host to access the Internet , It could be a router , It can also be a host with two network cards , An intranet 、 A public network , To replace the intranet host to access public network resources , Also known as nat( Network address translation server 、 or nat Fortress server );
working principle
Implement firewall function in application layer , Provide partial transmission related status , It can completely provide application related status and partial transmission information , He can also process and manage information .
Packet filtering firewall
Packet filtering firewall is to detect the packets passing through , The source in the packet can be monitored ip、 Purpose ip、 Source port 、 Destination port 、 Tag bits and other information , According to the communication rules made in advance, whether the data packet is forwarded or not is decided ;
working principle
Select and filter the packets in the network layer , Use access control list (Access control table -ACL) Check the source address of the data stream , Destination address , Source and destination ports ,IP Etc .
netfilter/iptables( Referred to as iptables) form Linux Packet filtering firewall under the platform , With most Linux Like software , This packet filter firewall is free , It can replace expensive commercial firewall solutions , Complete packet filtering , Packet redirection and network address translation (NAT) And so on .

State monitoring firewall
In addition to monitoring the contents of data packets, the state monitoring firewall can monitor the contents of data packets , You can also track every communication from each customer , When there is attack data at the beginning, masquerading as normal access , And then all of a sudden you start to attack , It will be detected and shielded by the state monitoring firewall .
stay Linux In the system , Firewall tools use iptables, Firewall can be implemented by proxy 、 package ( The data packet ) Filter firewall ,nat,mangle And the function of rules , And the state monitoring firewall is generally completed by enterprises purchasing special firewall equipment .
Software firewall
Software logic implementation
Software firewall by working on general purpose computers [ namely x86 series cpu] By calling the underlying general cpu Instruction set implementation ;
Hardware firewall
Hardware and software logic combination to achieve , Design and implement for a particular function , Poor flexibility
Hardware firewall uses professional CPU, Its presence CPU The hardware level of the message can be unpacked ; It can only realize the related functions of firewall data flow control ;
Performance is very good [ Because it's in CPU The instruction level has already realized the relatively complex function , It can complete the corresponding function without complex instruction combination in the logic layer
Data flow
/*
Data packets --> Network card driver --> Kernel memory space --> TCP/IP Protocol stack analysis target IP
--> If it's local ip, Then check the port and submit it to the relevant program
--> If it's not native ip, When the routing and forwarding function is enabled ,
The kernel will look at the local routing table , Send the data packet to the corresponding network interface , As the next jump ;
If there is no routing entry , The message is sent to the default gateway , The default gateway forwards it to the relevant host ;
*/
Linux Kernel communication logic
Communication is between processes , Client and server programs through the establishment of tcp Connect , Data transfer through socket .
Open all ports to all internal hosts , To ensure the normal communication , And the firewall to ensure security , There are restrictions outside of all ports , Only ports allowed by certain regulations can be opened to external hosts for access
Linux The development of firewalls :
/*
1.0 Time --> ipfirewall
2.0 Time --> ipchains
3.0 Time --> iptables
4.0 Time --> nftables
*/
Iptables working principle ( Four tables and five chains )
Five chains
Five hook functions (hook functionns), It's also called the five rules (rules) chain (chains) ( The path of packet propagation )
/*
prerouting Before routing
input Packet stream entry
forward Forwarding network card
output Packet exit
postrouting After routing
*/
This is a NetFilter Five chains of rules , Any packet , Just go through the machine , It must go through one of the five chains
Firewall strategies are generally divided into two types , One is called " through " Strategy , One is called " Block up " Strategy :
/*
General strategy , The default door is closed , We have to define who can get into .
Blocking strategy , The gate is open , But you have to have an identity, you have to authenticate , Or you can't go in .
*/
The concept of table
Let's think about another question , We treat each " chain " There's a bunch of rules on it , But some of these rules are very similar , such as ,A Class rules are all right IP Or port filtering ,B The class rule is to modify messages , So at this point , Can we put together the rules that implement the same function , It has to be .
We call a set of rules with the same function " surface ", So , Rules for different functions , We can manage it in different tables , and iptables It has been defined for us 4 Kind of watch , Each table corresponds to a different function , And none of the rules we define can escape this 4 The range of functions , therefore , Study iptables Before , We must understand each kind of watch first The role of .
iptables It provides us with the classification of the following rules , Or say ,iptables We have the following " surface "
/*
filter surface : Responsible for the filtering function , A firewall ; The kernel module :iptables_filter
nat surface :network address translation, Network address translation function ; The kernel module :iptable_nat
mangle surface : Unwrapping messages , Make changes , And repack The function of ;iptable_mangle
raw surface : close nat The connection tracing mechanism enabled on the table ;iptable_raw
in other words , All our custom rules , It's all the rules of the four categories , Or say , All rules exist here 4 Zhang " surface " in .
*/
Filter
filter Implement packet filtering , Define what is allowed or not allowed [ It can only be done in 3 On the chain : INPUT surface ( In the bag ), FORWORD( Forwarded packets ), OUTPUT( Process locally generated packages ), filter Table can only receive and discard packets .
NAT
nat Network address translation ( It can only be done in 3 On the chain : Prerouting( Modify upcoming packets ), output( Modify packets generated locally before routing ), Postrouting( Modify the outgoing packet )
Mangle
mangle Package refactoring ( modify ), To modify the original data of a message is to modify TTL Of , Can realize the metadata of data package to be disassembled , Mark it inside / Modify the content of . And the firewall flag , In fact, it depends on mangle To achieve . All five chains can be made .
raw
Data tracking processing
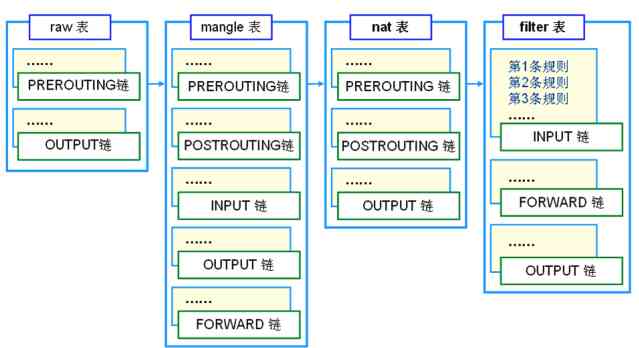
Iptables The process of transmitting packets
1. When a packet enters the network card , He entered first prerouting chain , The kernel according to the packet purpose IP Determine if it's transmitted .
2. If the packet enters the local machine , He would move down the graph , arrive input chain , Here's the packet input After chain , Any process will receive him , Programs running on this machine can send packets , These packets will go through output chain , Then arrive at postrouting Chain output
3. If the packet is to be forwarded , And the kernel allows forwarding , The packet will move to the right as shown in the figure , after Forward chain , Then arrive at Postrouting Chain output
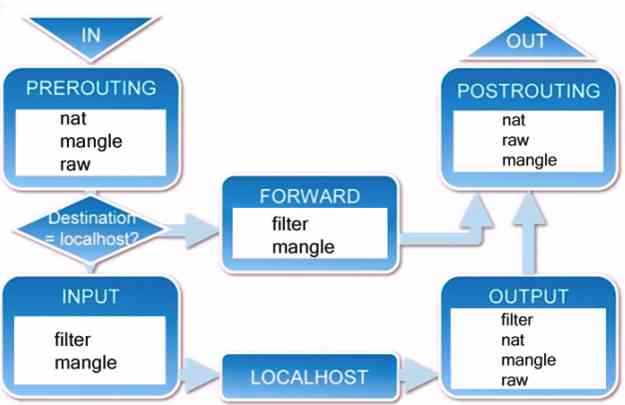
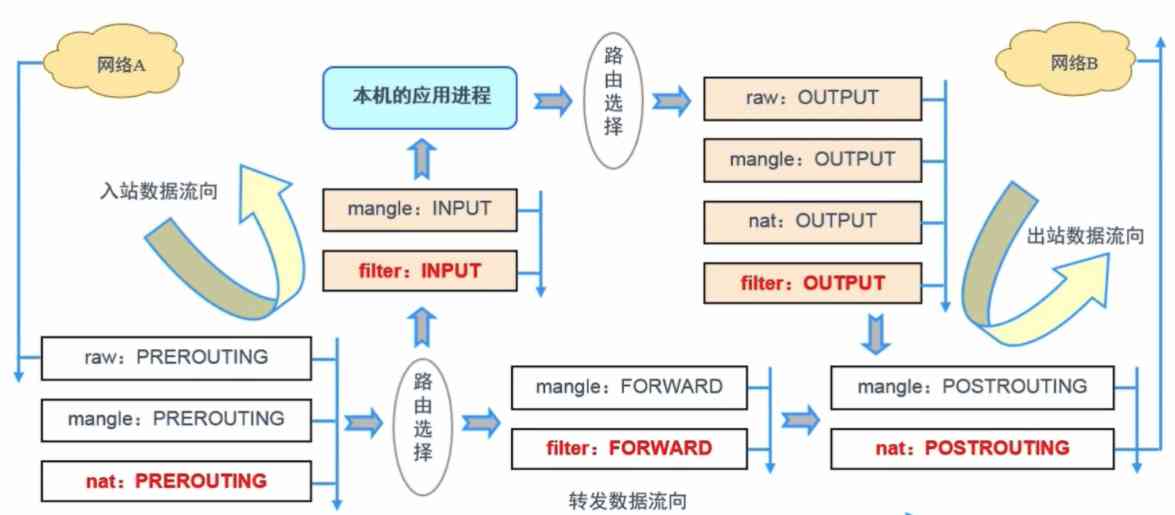
iptables/netfilter( This software ) It works in user space , He can make the rules work , It's not a service in itself , And the rules come into effect immediately , And we iptables Now it's made into a service , It can be started , Stopped , start-up , The rules will take effect directly , stop it , Then the rules are revoked .
Custom chain
iptables Also support your own custom chain , But self defined chain , It has to be associated with a particular chain , Set at a level , Specify that when there is data, go to a specific chain to process , When that chain is finished , Back again , Then continue to check in a particular chain . It works only when it is called , And if there is no custom chain in
Be careful : The order of the rules is crucial , The inspection rules are checked from top to bottom
/*
Users can delete the custom empty chain
Default chain cannot be deleted
Each rule has two built-in counters
The number of matched messages
The sum of the size of the matched packets
*/
Watch chain relationship
But what we need to pay attention to is , some " chain " It is destined not to contain " Some kind of rule ", Like some " checkpoint " It doesn't have some functions by nature , such as ,A" checkpoint " Only responsible for fighting land enemies , No air defense capability ,B" checkpoint " Only in charge of fighting air enemies , No ability to defend infantry ,C" checkpoint " Maybe it's more NB, It's air defense , Can also defend against land enemies ,D" checkpoint " The worst , Both land and sea can prevent .
Let's see , Every " checkpoint " What abilities do you have , Or say , Let's look at each one " chain " What are the rules on " surface " in .
Let's take the picture as an example , Have a look first prerouting" chain " Which tables do the rules on exist in .
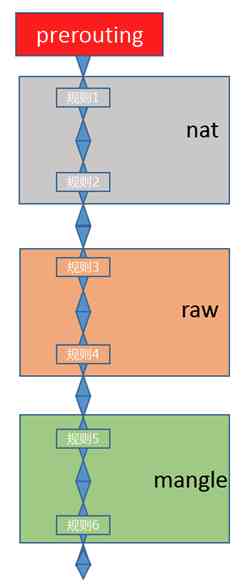
What does this picture mean ? It means to say ,prerouting" chain " Only have nat surface 、raw Table and mangle Functions corresponding to the table , therefore ,prerouting The rules in can only be stored in nat surface 、raw Table and mangle In the table .
Let's summarize , What is the function of each level
/*
PREROUTING The rules of can exist in :raw surface ,mangle surface ,nat surface .
INPUT The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,filter surface ,(centos7 There is also nat surface ,centos6 There is no ).
FORWARD The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,filter surface .
OUTPUT The rules of can exist in :raw surface mangle surface ,nat surface ,filter surface .
POSTROUTING The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,nat surface .
*/
however , We are in actual use , Often through " surface " As an operation entrance , Defining rules , The reason for this is as follows iptables, Because from " checkpoint " It's easier to understand... From the perspective of introduction , But in order to use in practice , Understand them more smoothly , Here we will go to " surface " And " chain " List the relationships of ,
surface ( function ) <--> chain ( hook )
/*
raw The rules in the table can be used by those chains : prerouting,output
mangle The rules in the table can be used by those chains : prerouting, input, forward,output, postrouting
nat The rules in the table can be used by those chains : prerouting, output, postrouting (centos7 There is also input,centos6 There is no )
filter The rules in the table can be used by those chains : input,forward,output
*/
In fact, we need to pay attention to , Because the packet goes through a " chain " When , Will match all the rules of the current chain , But there's always a sequence to match , We should match... One by one , And we said , Rules of the same function type will be gathered in one " surface " in , that , Which? " surface " The rules in will be put in " chain " The first implementation of , There needs to be a priority issue
iptables It defines four tables for us , When they're in the same chain , The priority of execution is as follows
/*
prerouting The rules in the chain are stored in three tables , The execution priorities of the three tables are as follows :
raw --> mangle --> nat
Priority order ( From high to low )
raw --> managle --> nat --> filter
*/
But we said before , Some chains are inherently unable to use rules in some tables , therefore ,4 The rules in the table are in the same chain at present only output chain , It is said that both land and sea can defend .
For more convenient management , We can also create a custom chain in a table , Place the rules set for an application in this custom chain , But custom links can't be used directly , Can only be called by a default chain as an action to work , We can think of it this way , A custom chain is a comparison " short " The chain of , This article " short " The rules on the chain are made for an application , But this short chain can't be used directly , But needs " welding " stay iptables Default definition on Chain , Can be IPtables Use , That's why the default definition is " chain " Need to put " Custom chain " treat as " action " The reason to quote . This is the later story. , Talk later , In actual use, we can understand .
Combine all of the above descriptions , We can summarize the flow of packets through the firewall as follows :
We're writing Iptables When the rules are , Always keep this routing order in mind , Flexible configuration rules .
We will rewrite the frequently used correspondence here , It is convenient to view the corresponding legend .
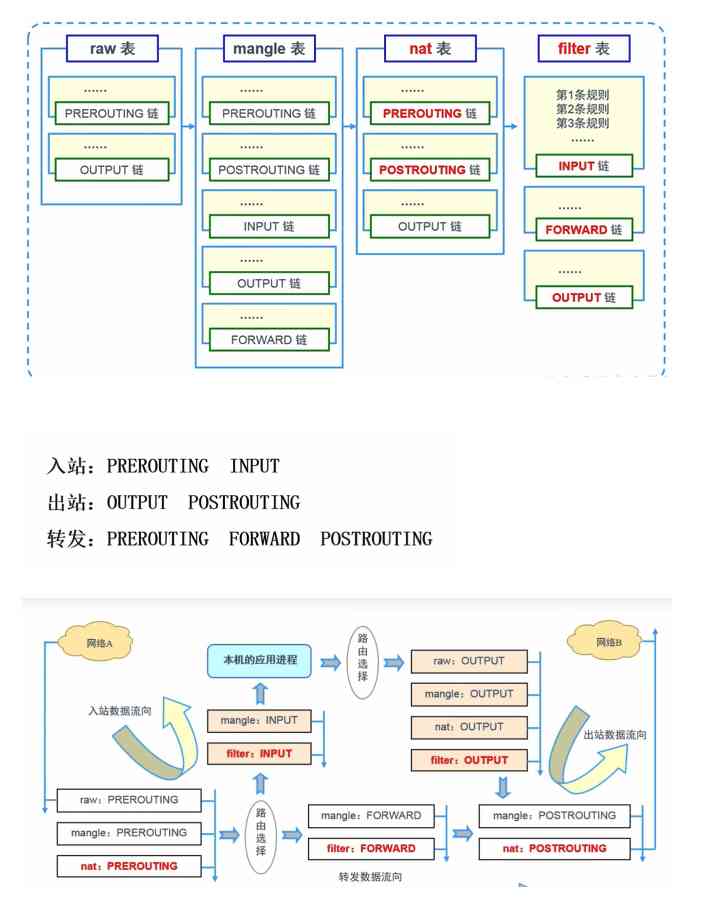
The rules of the chain are stored in which tables ( The correspondence from chain to table ):
/*
PREROUTING The rules of can exist in :raw surface ,mangle surface ,nat surface .
INPUT The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,filter surface ,(centos7 There is also nat surface ,centos6 There is no ).
FORWARD The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,filter surface .
OUTPUT The rules of can exist in :raw surface mangle surface ,nat surface ,filter surface .
POSTROUTING The rules of can exist in :mangle surface ,nat surface .
Which chains can the rules in the table be used by ( From table to chain ):
raw Which chains can the rules in the table be used by :PREROUTING,OUTPUT
mangle Which chains can the rules in the table be used by :PREROUTING,INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING
nat Which chains can the rules in the table be used by :PREROUTING,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING(centos7 There is also INPUT,centos6 There is no )
filter Which chains can the rules in the table be used by :INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT
*/
iptables Rule writing
The concept of rules
The rules
According to the specified matching conditions, try to match each message flowing through here , Once the match is successful , It is processed by the processing action specified after the rule ;
So let's explain what is iptables The rules of , I made an analogy before , Every one of them " chain " It's all one " checkpoint ", Each through this " checkpoint " All messages must match the rules on this level , If the match , The message is processed accordingly , for instance , You and I are like two at the moment " message ", You and I are both going to enter at the moment , But the city Lord has a life , Only those who have a high reputation can enter the pass , Those who do not meet the conditions cannot enter the customs , So the guards made it according to the city Lord " The rules ", Start to look at you and me , Final , You have successfully entered the customs , And I've been turned away , Because you fit in with " one's deportment is dignified " Standards for , So put you " release " 了 , And I'm not up to the standard , So it wasn't released , Actually ," one's deportment is dignified " It's a kind of " Matching condition "," release " It's a kind of " action "," Matching condition " And " action " Make up the rules .
Rules consist of matching conditions and processing actions
Matching condition
/*
The basic matching conditions are divided into matching conditions and extension conditions
Basic matching conditions :
source address Source IP, Destination address DestinationIP.
Extend match criteria :
It is divided into
1. Implicit extension : It's not necessary to specify the extensions made by that module , Because it's time to use -p {tcp|udp|icmp}
Removing the above conditions can be used to match , There are other conditions that can be used to match , These conditions are generally called extension conditions .
These extension conditions are actually netfilter Part of , It's just in the form of modules , If you want to use these conditions , You need to rely on the corresponding extension module .
Source port Source Port, Target port Destination Port
2. Explicitly extend : The extension made by that module must be specified , stay iptables Use in -m Options can be used to complete the function .
*/
Handling actions
Processing action in iptables Known as target( That's not true , Let's call it that for the time being ), Actions can also be divided into basic actions and extended actions .
/*
ACCEPT: Allow packets to pass .
DROP: Discard packets directly , Don't give any response , At this time, the client will feel that its request is in the sea , After the timeout, there will be a response .
REJECT: Reject packet pass , If necessary, a response message will be sent to the data sender , The client will receive the rejection message as soon as it requests .
SNAT: Source address translation , Solve the problem that intranet users use the same public address to access the Internet .
MASQUERADE: yes SNAT A special form of , For dynamic 、 It will change temporarily ip On .
DNAT: Target address translation .
REDIRECT: Do port mapping on this machine .
LOG: stay /var/log/messages Log information in the file , Then pass the packet to the next rule , That is to say, there is no operation other than recording the data package , Still let the next rule match .
*/
Grammatical structure
/*
iptables [-t Table name ] Options [ Chain name ] [ Conditions ] [-j Type of control ]
matters needing attention
1. When the table name is not specified , Default finger filter surface .
2. When the chain name is not specified , By default, all chains in the table .
3. Unless you set the default policy for the chain , Otherwise, you must specify the matching condition .
4. Options , Chain name , Control types use uppercase letters , The rest are in small letters
*/
Look at the rules
/*
iptables -L INPUT --line-numbers
-L: List all rule entries
-n: Show the address in digital form , Port and other information
-v: Display rule information in a more detailed way
--line-numbers: When looking at the rules , Display the sequence number of the rule
*/
Management rules
/*
Add new rules :
-A: Add a rule to the end of the chain
-I: At the beginning of the chain ( Or specify the serial number ) Insert a rule
-s: --src: Specify the source address
-d: --dst: Specify the destination address
-p: {tcp|udp|icmp}: Designated agreement
-i(INTERFACE): Specifies the interface to which the datagram flows PREROUINT.
-o(INTERFACE): Specify the interface that the data message flows out of .
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT -p udp -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT 2 -p icmp -j ACCEPT
Replacement rules
-R CHAIN [num]: Replace the specified rule
Delete , Clear rules
-D: Delete the specified sequence number in the chain ( Or content ) One of the rules of .
-F: Clear all the rule chains
iptables -D INPUT 3
iptables -n -L INPUT
Set the default rules for the specified chain
*/
Type of control
/*
1. ACCEPT: Allowed to pass through
2. DROP: Direct discarding , No response
3. REJECT: Refuse to pass , Give tips when necessary .
4. LOG: Logging information , Then pass on to the next rule to continue matching
5. SNAT: Modify the packet source address
6. REDIRECT: Redirect
*/
iptables Forbid sth IP visit
stay CentOS Next stop IP, There are blocking segments and blocking individual IP Two forms . Generally speaking , Today's attackers will not use a segment of IP To attack ( It's too ostentatious ),IP It's usually hash . So here is a detailed description of the killing of individual IP The order of , And unseal single IP The order of .
stay CentOS Next , Use ipteables To maintain the IP Rule table . To stop or unseal IP, In fact, in the IP Add rules to the inbound part of the rules table .
We're going to ban one IP, Use this command :
iptables -I INPUT -s ***.***.***.*** -j DROP
To unseal one IP, Use this command
iptables -D INPUT -s ***.***.***.*** -j DROP
Parameters -I Is said Insert( add to ),-D Express Delete( Delete ). It's followed by the rules ,INPUT Indicates inbound ,... Means to stop IP,DROP Means to give up the connection .
Besides , You can also use the following command to view the current IP Rule table :
iptables --list
For example, now we have to 123.44.55.66 This IP kill , enter :
iptables -I INPUT -s 123.44.55.66 -j DROP
To unseal would be -I Switch to -D that will do , Premise is iptables There's already a record . If you want to empty the sealed IP Address , You can enter :
iptables --flush
You want to add IP Segment to block list , Use the following command :
iptables -I INPUT -s 121.0.0.0/8 -j DROP
In fact, that is to say, a single IP Closed IP Part of it was replaced by Linux Of IP Segment expression . About IP There are many detailed explanations on the Internet , I won't mention it here .
I believe there is iptables With the help of the , Solve the small DDoS There's no such thing as an attack !
Other common commands
edit iptables file
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
close / Turn on / service iptables restart
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
#stop close
#start Turn on
#restart restart
Verify that the rules are in effect :
iptables -L
Save and restart iptables
/etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables save
service iptables restart
Or by host.allow Limit specific IP Visit
# It takes effect immediately , But for those that have been opened shell Invalid , So keep it on one side shell Set up , Open it again shell
tail -1 /etc/hosts.allow
sshd:39.108.140.0:allow # Allow this IP land
tail -1 /etc/hosts.deny
sshd:all # All machines are not allowed to log in
tail -1 /etc/ssh/sshd_config
allowusers root@ip # Allow someone to IP What account to log in with , Otherwise, we can't land
cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config |grep 10086
Port 10086