1. Create set
Creating a collection is a two-step process ,- It's about setting rules for sets , The second is to create a collection , establish mongoose.Schema An instance of the constructor creates a collection .
// mongoose.Schema() It's a constructor , want new An instance object
//2、 Set set rules
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
author: String ,
isPub1ished: Boolean
});
//3、 Use rules to create collections The collection created here is also a constructor
const Course = mongoose.model ('Course', courseSchema); // The first parameter is the collection name , The second is set rules . The actual set generated in the database is named courses
1. create documents
Creating a document is actually Insert data into the collection .
Method 1
Divided into two steps : ① Create a collection instance .
② Call the instance object save Method to save the data to the database .
//4、 create documents insert data
// Create a collection instance object
const course = new Course({
name: 'node.js',
author: 'xc-dh',
isPublished: true
});
// Call the instance object save Method to save the data to the database .
course.save();
Method 2
All operations related to the database are asynchronous
create documents insert data
Course.create({
name: 'JavaScript',
author: ' Stars and sea ',
isPublished: false
}, (err, result) => {
console.log(err);
console.log(result);
});
// have access to promise Methods
Course.create({
name: 'JavaScript12',
author: ' Stars and sea ',
isPublished: false
}).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(err => console.log(err));
3.mongoDB Database import data
find mongodb Database installation directory , Will install under the directory bin The directory is placed in the environment variable .
Enter the following command in the project root directory to import
mongoimport -d Database name -c Collection name --file Data file to import
4. Query the document
find() Method
Return a set of documents
// Search for documents based on criteria ( If the condition is empty, all documents will be searched )
Course.find().then(result => console.log(result))
// Return to document collection ( Array form )
[{
_id: 5c0917ed37ec9b03c07cf95f,
name: 'node.js Basics ',
author: 'xc-dh‘
},{
_id: 5c09dea28acfb814980ff827,
name: 'Javascript',
author: 'xc-dh‘
}]
findOne() Method
Return a document
// Search for documents based on criteria
Course.findOne({name: 'node.js Basics '}).then(result => console.log(result))
// Return to document Just return one , Default return to the first item
{
_id: 5c0917ed37ec9b03c07cf95f,
name: 'node.js Basics ',
author: 'xc-dh‘
}
// Match greater than , Less than
// User.find({
// age: {
// $gt: 20, // Greater than
// $lt: 40 // Less than
// }
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// Matching inclusion Return to favorite documents that contain Typing Code
// User.find({
// hobbies: {
// $in: [' Knock on the code ']
// }
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// Select the field to query Add... Before the field - This field is not queried
// User.find().select('name age -_id').then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// Sort by age field in ascending order
// User.find().sort('age').then(result => {
// console.log(result)
// })
// Descending order , Add a negative sign to it
// User.find().sort('-age').then(result => {
// console.log(result)
// })
// skip How many data to skip limit Limit the number of queries
User.find().skip(2).limit(3).then(result => {
console.log(result)
})
5. Delete the document
// Delete a single document If the condition contains more than one document , By default, the first document that meets the criteria is deleted Return the deleted document
User.findOneAndDelete({
_id: '5c09f1e5aeb04b22f8460965'
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
});
// To delete multiple If the condition is empty , All documents are deleted by default Return an object ,n Represents the number of documents deleted ,OK Indicates whether the deletion was successful
User.deleteMany({}).then(result => console.log(result)) //{ n: 4, ok: 1, deletedCount: 4 }
6. Update the document
// Update single
User.updateOne({ Query criteria }, { Value to modify }).then(result => console.log(result))
// Update multiple
User.updateMany({ Query criteria }, { The value to change }).then(result => console.log(result))
// Update a single document If the condition satisfies multiple documents , By default, only the first one is updated
User.updateOne({
name: ' Li Si '
}, {
name: ' Li goudan '
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
});
// Update multiple documents {} If it is blank, all documents will be selected by default
User.updateMany({}, {
age: 45
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
7. mongoose verification
When creating a set rule , You can set the validation rules for the current field , If the verification fails, the insertion fails .
-
required: true Required fields
-
minlength: 3 Minimum string length
-
maxlength: 20 Maximum string length
-
min: 2 The minimum value is 2
-
max: 100 The maximum value is 100
-
enum: ['html', 'css', "javascript, 'nodejs]
-
trim: true Remove the spaces on both sides of the string
-
validate: Custom validator
-
default: The default value is
-
Get error messages :error.errors[' Field name '].message
// Validation rules can be followed by two parameters , The second parameter represents a custom error message
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
// Required fields , If you don't spread it, you will report an error
required: [true, ' Please pass in the title of the article '],
minlength: 2,
maxlength: [6, ' The title length cannot be greater than 6 Characters '],
trim: true // Remove the space around the string
},
age: {
type: Number,
min: 24, // Minimum value
max: 80 // Maximum value
},
publishDate: {
type: Date,
// The default value is , Default display value when no information is inserted
default: Date.now
},
category: {
type: String,
// enumeration , Lists the values that the current field can have
enum: ['HTML', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js']
},
author: {
type: String,
// Custom validator
validate: {
validator: v => {
// Returns a Boolean value
// true Verify success
// false Validation failed
// v The value to verify
return v && v.length > 4;
},
// Custom error message
message: ' The value you entered does not match the validation rules '
}
}
});
// Use rules to create collections
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
// create Method insert data
Post.create({
title: 'aaa',
age: 68,
category: 'javascript',
author: 'db'
}).then(result => console.log(result))
// Get error message
.catch((error) => {
// Get error message object
const err = error.errors;
// Loop error message object
for (var k in err) {
// console.log(err[k].message);
// Print error messages
console.log(err[k]['message']);
}
})
8. Set Association
Usually there is a relationship between different sets of data , For example, article information and user information are stored in different collections , But the article was published by a user To query all information about the article, including the publishing user , We need to use set association .
-
Use id Associate sets
-
Use populate Method to query the association set
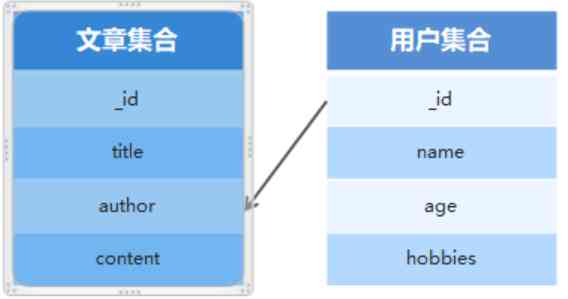
// Collection of related
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// Connect to database
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', {
useUnifiedTopology: true,
useNewUrlParser: true
}).then(() => {
console.log(' Database connection successful ');
}).catch((error) => {
console.log(error, ' Database connection failed ');
});
// Create set rules
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String
}
});
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String
},
// 1、 Use ID Associate a collection of articles with a collection of authors
author: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'User'
}
});
// Create set
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
// Insert document data
// User.create({
// name: 'xc'
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// Post.create({
// title: 'html',
// author: '5f9668bb20347221d49d0254'
// }).then((result => {
// console.log(result);
// }));
// 2、 The joint query
Post.find().populate('author').then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
// The results are as follows [ { _id: 5f966a51c70ba932880c36d3, title: 'html', author: { _id: 5f9668bb20347221d49d0254, name: 'xc', v: 0 },v: 0 } ]
9. Case study : Add, delete, modify and search user information
-
Build a web server , Realize the communication between client and server
-
Connect to database , Create user collections , Insert a document into the collection
-
When users access /list when , Look up all the user information
-
Put user information and forms HTML And splice the results back to the client
-
When users access /add when , Render the form page , And realize the function of adding user information
-
When users access /modify when , Render modification page , And realize the function of modifying user information
-
When users access /delete when , Realize the user delete function