当前位置:网站首页>Interviewer: is acid fully guaranteed for redis transactions?
Interviewer: is acid fully guaranteed for redis transactions?
2022-07-05 12:17:00 【Xujunsheng】
Redis Transaction mechanism of
The business is The smallest unit of work for database operations , It consists of a limited sequence of database operations . These operations are either all performed , Or none at all , It is an indivisible work unit .
When the transaction is executing , Special attribute guarantee will be provided : Atomicity 、 Uniformity 、 Isolation and persistence , That is to say ACID attribute . These attributes include requirements for execution results , At the same time, there are also requirements for the data state changes of the database before and after the transaction execution .
You may ask , Since transaction is a database specific mechanism , that Redis There is a complete guarantee that ACID Attribute ? If some attributes cannot be guaranteed in some scenarios , It is likely to cause data errors , How should we deal with it ?
Next , Let's start with ACID Start with attributes , Then I'll see Redis How to implement transactions .
Business ACID attribute
- Atomicity (Atomicity): The transaction is executed as a whole , The operations contained in it are either all executed , Either not . This is also the business application transaction , One of the most valued attributes .
- Uniformity (Consistency): It means that the data in the database is consistent before and after the transaction is executed . The most typical example is transfer . No matter how many accounts are transferred between users , How to transfer , After the transaction ends, the total amount of money of the two users remains the same .
- Isolation, (Isolation): Directly related to transaction concurrency , Isolation means that concurrent transactions cannot affect each other . In short , For any two concurrent transactions T1 and T2, In the transaction T1 It seems ,T2 Either in T1 It's over before it starts , Either in T1 It's not until it's over . In this way, each transaction does not feel that other transactions are executing concurrently .
- persistence (Durability): Once the transaction is committed , All modifications to the database data will be permanently saved , Even if the system crashes, the data will not be lost after restart .
I understand ACID After attribute , Let's see Redis How to implement the transaction mechanism .
Redis How to implement transactions ?
Redis Provides MULTI、EXEC、DISCARD and WATCH Commands are the basis for implementing transactions .
Redis The execution of a transaction consists of three steps :
- Open transaction : Client pass
MULTIcommand , Open a transaction explicitly ; - Order to join the team : The client sends a series of instructions to be executed in the transaction to the server , Such as GET、SET etc. . We need to pay attention to , These instructions are only temporarily stored in the command queue , Not immediately executed ;
- Commit transaction , Execute the command submitted in step 2 : The client sends the command to commit the transaction to the server
EXEC, When the server receivesEXECAfter the command , Will actually execute all commands in the command queue .
Use MULTI and EXEC The process of executing a transaction :
# Set up a:stock by 10
127.0.0.1:6379> SET a:stock 10
OK
# Set up b:stock by 20
127.0.0.1:6379> SET b:stock 20
OK
# Open transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
OK
# take a:stock reduce 1
127.0.0.1:6379> DECR a:stock
QUEUED
# take b:stock reduce 1
127.0.0.1:6379> DECR b:stock
QUEUED
# Actually execute the transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> EXEC
1) (integer) 9
2) (integer) 19
We see execution DECR All the people who come back are QUEUED, Indicates that these operations are temporarily stored in the command queue , Not actually implemented yet .
When it's implemented EXEC command , You can see the response data of each instruction .
We see Redis Multiple operations can be performed together , Now let's see Redis What transaction mechanism can support ACID attribute .
Redis Yes ACID Attribute support
Atomicity
Under normal circumstances , No error occurred , Use MULTI and EXEC command , It can ensure the normal execution of multiple operations . however , If an error occurs in transaction execution , Can you still guarantee atomicity ?
There are three situations , Let's take a look at .
- In execution
EXECBefore the command , The operation command sent by the client itself has an error , such as : Grammar mistakes , Used a command that does not exist ; - After execution
EXECAfter the command ,Redis An error occurs when these transaction operations are actually executed , such as : The data types of the command and operation do not match ( Yes String type Of value Yes List The list of operations ) - perform
EXECWhen ordered ,Redis The instance has failed , Cause transaction execution to fail .
EXEC An error is reported before execution
In this case , When ordered to join the team ,Redis Will report an error and record the error .
here , We can still continue to submit commands . Wait until it's done EXEC After the command ,Redis will Refuse to execute all submitted command operations , Return the result of transaction failure .
thus , All commands in the transaction will no longer be executed , It guarantees atomicity .
Let's take a look at a mistake when ordering to join the team , Examples of transaction failures .
# Open transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
OK
# Send the first operation in the transaction , however Redis The command is not supported , Return error message
127.0.0.1:6379> PUT a:stock 1
(error) ERR unknown command 'PUT'
# Send the second operation in the transaction , This is the right command ,Redis Join the order
127.0.0.1:6379> DECR b:stock
QUEUED
# Actually execute the transaction , But there was an error in the previous command , therefore Redis Refuse to enforce
127.0.0.1:6379> EXEC
(error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.
127.0.0.1:6379>
EXEC Error reported after execution
Unlike in the first case , Error that the data types of command and operation do not match , When the transaction operation is queued, it cannot be checked . Only after the execution EXEC After the order ,Redis When these transaction operations are actually performed , Will report a mistake .
It should be noted that , although Redis An error will be reported for the wrong command , But will still execute the correct command . under these circumstances , The atomicity of transactions cannot be guaranteed .
Example of data type mismatch between command and operation :
# Open transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
OK
# Send the first operation in the transaction ,LPOP The data type of the command operation does not match , No error is reported at this time
127.0.0.1:6379> LPOP a:stock
QUEUED
# Send the second operation in the transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> DECR b:stock
QUEUED
# Actually execute the transaction , The first operation of the transaction reports an error , The second operation is performed normally
127.0.0.1:6379> EXEC
1) (error) WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value
2) (integer) 18
In the above transaction LPOP Command to String Type data to operate , There was no error when joining the team , however , stay EXEC The execution times are wrong . Last ,LPOP The command itself did not execute successfully , But in business DECR The command was successfully executed .
See this , Some students will think , Our database ( such as :MySQL) When doing business , If there is a failure , Then all operations in this transaction will be rolled back . that Redis Is it possible to implement a similar rollback ?
First ,Redis There is no rollback mechanism in ,Redis Provides a DISCARD command , This command You can only voluntarily give up executing transactions , Empty the temporary command queue , No rollback effect .
Use DISCARD Command implementation abandons transactions :
# Read a:stock Value 9
127.0.0.1:6379> GET a:stock
"9"
# Open transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
OK
# The first operation of sending a transaction , Yes a:stock reduce 1
127.0.0.1:6379> DECR a:stock
QUEUED
# perform DISCARD command , Take the initiative to give up the transaction
127.0.0.1:6379> DISCARD
OK
# Read again a:stock Value , The value has not been modified
127.0.0.1:6379> GET a:stock
"8"
EXEC Execution time ,Redis failure
under these circumstances , If Redis Open the AOF journal , that , Some transaction operations will be recorded AOF In the log .
We need to use redis-check-aof Tool check AOF Log files , This tool can remove incomplete transaction operations from AOF Remove from file .
thus , We use AOF After restoring the instance , These transaction operations will no longer be performed , So that atomicity .
If AOF The log is not open , After the instance is restarted , The data can't be recovered , here , There is no atomicity .
below , Let's briefly summarize Redis Assurance of atomicity :
- When you order to join the team, you report an error , Will abandon all transaction execution , Guaranteed atomicity ;
- No error was reported when ordering to join the team , The actual execution times an error , There is no guarantee of atomicity ;
EXECInstance failure during command execution , If it's on AOF journal , You can guarantee atomicity .
Next , Let's keep on learning , Guarantee of consistency .
Uniformity
alike , Let's follow the above three situations one by one , Analysis consistency .
EXEC An error is reported before execution
under these circumstances , The transaction itself will be abandoned , So it can ensure the consistency of the database .
EXEC Error reported after execution
under these circumstances , The order with error was not executed , Just executed the right command . In this case , It can also ensure the consistency of the database .
EXEC Execution time ,Redis failure
In this case , because Redis Instance failure , So there will be a restart , This is related to the way of data recovery .
below , We according to the Redis Whether the instance is on RDB or AOF Let's discuss the situation .
First , We didn't turn it on RDB or AOF, After the instance is restarted , There's no data , At this time, the database is consistent .
If we use it RDB snapshot , because When a transaction is executed , It's not going to happen RDB Snapshot , therefore , If Redis Instance failure , The command of transaction operation will not be recorded RDB Snapshot , So it's the same as above , After the instance is restarted , The database is consistent .
If we use AOF journal , When the transaction operation has not been recorded AOF When the log , The instance fails , that , Use AOF The database data recovered by log is consistent .
If only part of the operation is recorded AOF journal , We can use redis-check-aof Clear the completed operations in the transaction , The database is also consistent after recovery .
therefore , Sum up ,Redis The transaction mechanism guarantees the consistency property .
Next , Let's continue to analyze isolation .
Isolation,
Isolation of transactions , Will be affected by concurrent operations . When a transaction is executed , Divided into orders to join the team (EXEC Before the order is executed ) And the actual execution of the command (EXEC After the execution of the command ) Two phases .
below , Let's focus on these two stages , So let's analyze that .
EXEC Before the order is executed
A business , stay EXEC Before the order is executed , The command operation of this transaction is temporarily stored in the command queue . here , If there are other concurrent operations , We need to see if the transaction uses WATCH Mechanism .
WATCH The function of the mechanism is , Before the transaction is executed , Monitor the value change of one or more keys .
When a transaction calls EXEC When the order is executed ,WATCH The mechanism will first check whether the monitored key has been modified by other clients .
If it changes , Just give up the transaction execution , Avoid breaking the isolation of transactions . then , The client can execute the transaction again , here , If there are no concurrent operations to modify transaction data , The transaction can be executed normally , Isolation is also guaranteed .
WATCH The mechanism is made up of WATCH Command implementation , Here's the picture :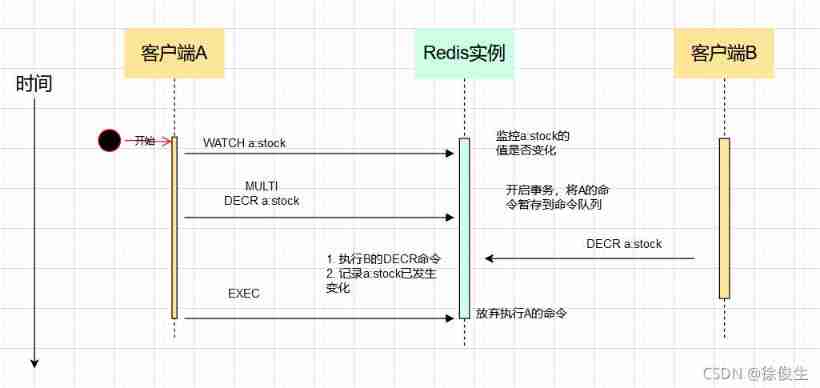 We see because
We see because WATCH Mechanism , Finally, execute EXEC When , Find out a:stock It has been modified , Abandoned the execution of the transaction , This ensures isolation .
If not used WATCH Mechanism , At the end of the execution EXEC When , No matter a:stock Whether it has been modified , Will not give up the execution of the transaction , Isolation is not guaranteed . Here's the picture :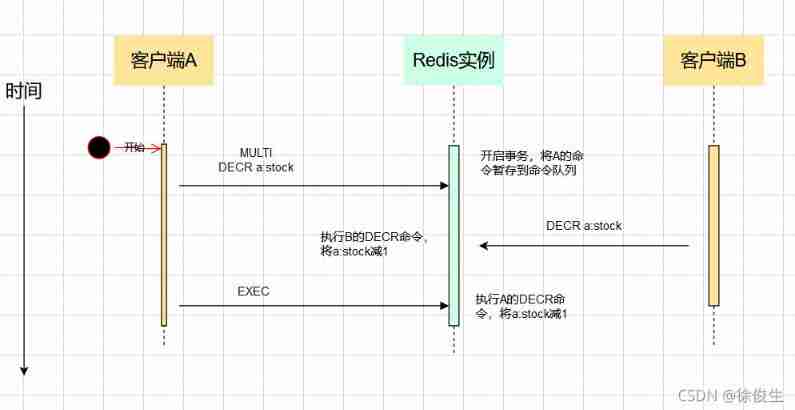
EXEC After the execution of the command
The above is about concurrent operations in EXEC Execution before the command , Let's talk about the second case :
Concurrent operations in EXEC After the command is executed, it is received and executed by the server .
because Redis Is to execute commands with a single thread , and ,EXEC After the execution of the command ,Redis It will ensure that all commands in the command queue are executed first . therefore , under these circumstances , Concurrent operations do not break transaction isolation .
Finally, let's analyze the guarantee of persistence .
persistence
because Redis Is a memory database , therefore , Whether the data is persisted or not depends entirely on Redis Persistence configuration .
If Redis Not used RDB or AOF, Then the persistence property of the transaction cannot be guaranteed .
If Redis Used RDB Pattern , that , After a transaction is executed , Next time RDB Before the snapshot is executed , Instance downtime occurred , In this case , The data modified by transactions cannot be guaranteed to be persistent .
If Redis Adopted AOF Pattern , because AOF Three configuration options for mode no、everysec and always There will be data loss , therefore , The persistence property of transactions is still not guaranteed .
therefore , No matter Redis What persistence pattern to use , The persistence property of transactions is not guaranteed .
Want to know Redis Children's shoes with persistence mechanism can be seen in my last article : Article to read Redis Persistence mechanism
summary
- Redis Atomicity of transaction support part : Atomicity is not guaranteed if the command used in the transaction does not match the data type of the operation ;
- Redis Transactions support consistency
- Redis Transaction support isolation
- Redis There is no guarantee of persistence
If you want to see more quality original articles , Welcome to my official account. 「ShawnBlog」.
边栏推荐
- Reinforcement learning - learning notes 3 | strategic learning
- What is the difference between canvas and SVG?
- MySQL stored procedure
- Multi table operation - sub query
- 一类恒等式的应用(范德蒙德卷积与超几何函数)
- 投资理财适合女生吗?女生可以买哪些理财产品?
- [HDU 2096] 小明A+B
- Matlab boundarymask function (find the boundary of the divided area)
- Matlab superpixels function (2D super pixel over segmentation of image)
- Differences between IPv6 and IPv4 three departments including the office of network information technology promote IPv6 scale deployment
猜你喜欢

What is digital existence? Digital transformation starts with digital existence
Reading notes of growth hacker
Simply solve the problem that the node in the redis cluster cannot read data (error) moved
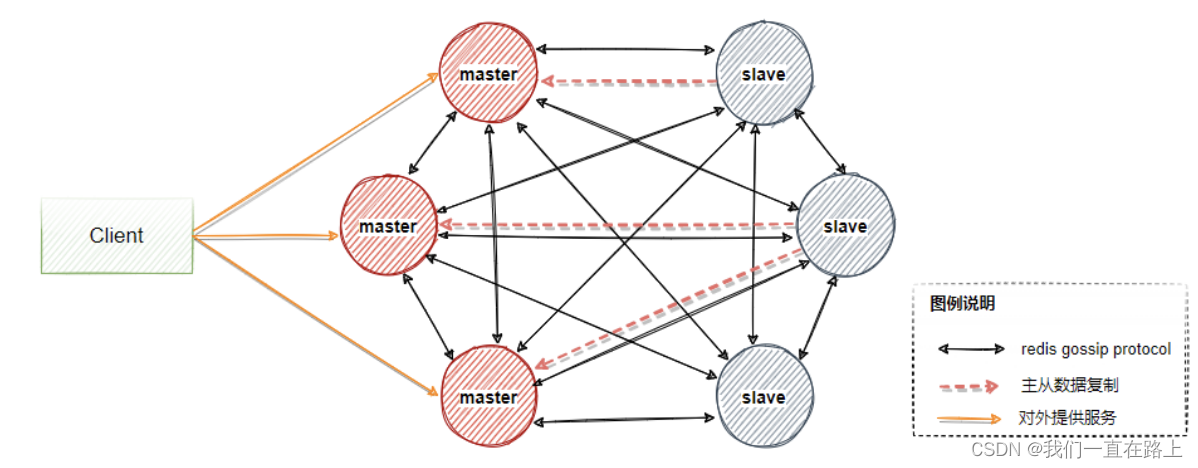
Principle of redis cluster mode
Flutter2 heavy release supports web and desktop applications
![[pytorch modifies the pre training model: there is little difference between the measured loading pre training model and the random initialization of the model]](/img/ad/b96e9319212cf2724e0a640109665d.png)
[pytorch modifies the pre training model: there is little difference between the measured loading pre training model and the random initialization of the model]
Why learn harmonyos and how to get started quickly?
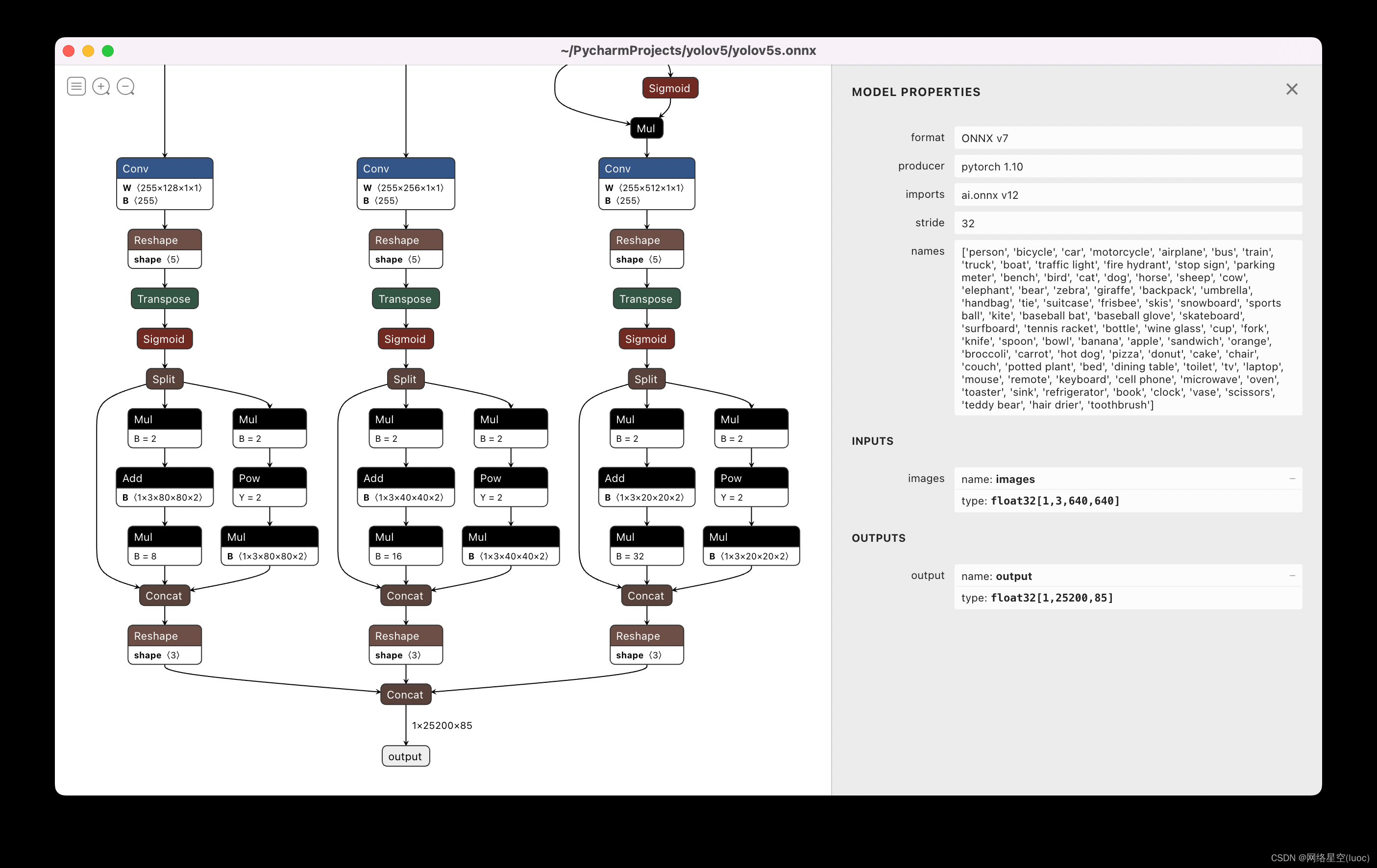
【TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export】
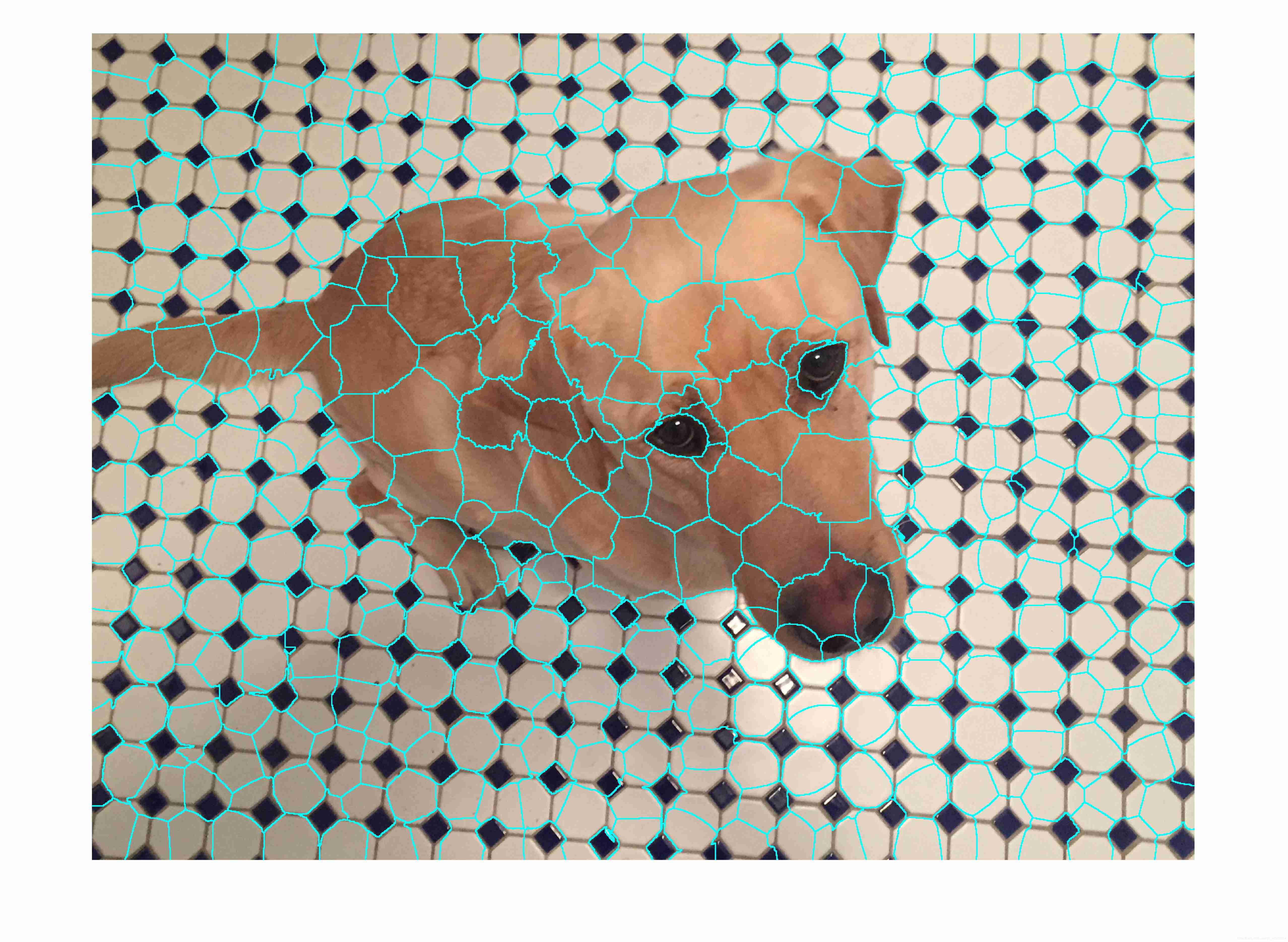
Matlab superpixels function (2D super pixel over segmentation of image)
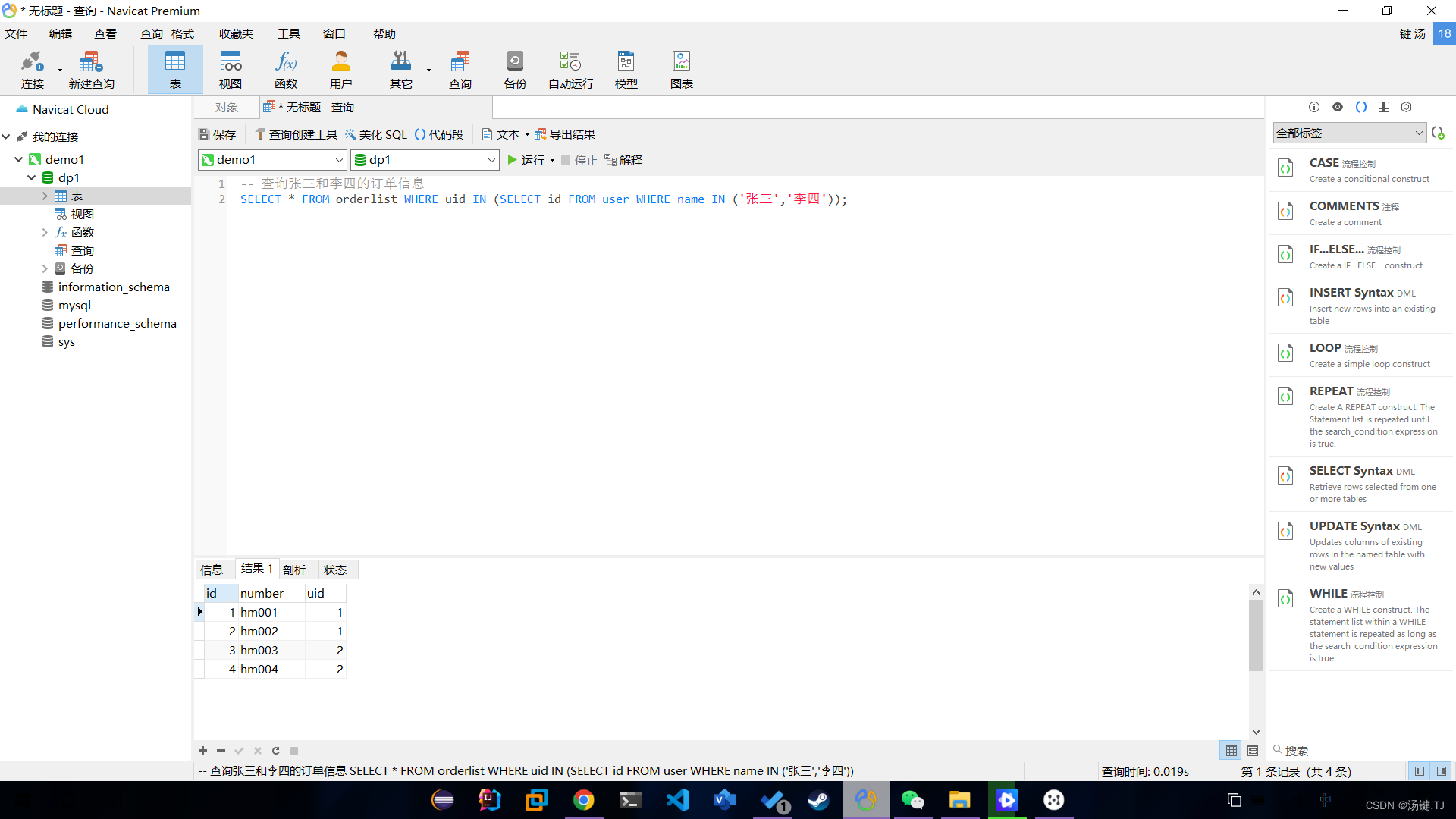
多表操作-子查询
随机推荐
Simple production of wechat applet cloud development authorization login
Application of a class of identities (vandermond convolution and hypergeometric functions)
Course design of compilation principle --- formula calculator (a simple calculator with interface developed based on QT)
MySQL view
[yolov5.yaml parsing]
POJ-2499 Binary Tree
Use and install RkNN toolkit Lite2 on itop-3568 development board NPU
你做自动化测试为什么总是失败?
Reading notes of growth hacker
PXE startup configuration and principle
II. Data type
手机 CPU 架构类型了解
MySQL multi table operation
多表操作-自关联查询
Read and understand the rendering mechanism and principle of flutter's three trees
Uniapp + unicloud + Unipay realize wechat applet payment function
Flutter2 heavy release supports web and desktop applications
Tabbar configuration at the bottom of wechat applet
Automated test lifecycle
Seven polymorphisms