当前位置:网站首页>MySQL function
MySQL function
2022-07-05 12:12:00 【ziyi813】
MySQL function
summary
stay MySQL in , In order to improve code reusability and hide implementation details ,MySQL Many functions are provided , Function can be understood as someone else's closed template code .
stay MySQL in , There are many functions , The main categories are :
- Aggregate functions
- Mathematical functions
- String function
- Date function
- Control flow function
- Window function
Aggregate functions
count , sum, min, max, avg These are aggregate functions .
group_concat
group_concat() Function first according to group by The specified columns are grouped , And separate... With a separator , And connect with the values in the same group , Returns a string .
Format :
group_concat( [distinct] Field name [order by Sort field asc/desc] [separator ' Separator '] )
explain : use distinct You can exclude duplicate values , If you need to sort the values in the results , have access to order by Clause ,separator Is a string , Default to comma .
Example :
use mydb1;
create table emp(
emp_id int primary key auto_increment comment ' Number ',
emp_name char(20) not null default '' comment ' full name ',
salary decimal(10,2) not null default 0 comment ' Wages ',
department char(20) not null default '' comment ' department '
);
insert into emp( emp_name, salary, department)
values (' Zhang Fei ', 5000, ' Shu Kingdom '),
(' zhaoyun ', 8000, ' Shu Kingdom '),
(' Guan Yunchang ', 10000, ' Shu Kingdom '),
(' Liu bei ', 25000, ' Shu Kingdom '),
(' king of Wu in the Three Kingdoms Era ', 25000, ' Wu kingdom '),
(' Sun shangxiang ', 15000, ' Wu kingdom '),
(' Liu chan ', 5000, ' Shu Kingdom '),
(' Sima ', 15000, ' State of Wei '),
(' Cao Cao ', 25000, ' State of Wei '),
(' Cao Pi ', 25000, ' State of Wei '),
(' Lyu3 bu4 ', 35000, ' A group of Heroes ');
-- Merge all names into one line
select group_concat(emp_name) from emp;
-- Zhang Fei , zhaoyun , Guan Yunchang , Liu bei , king of Wu in the Three Kingdoms Era , Sun shangxiang , Liu chan , Sima , Cao Cao , Cao Pi , Lyu3 bu4
select group_concat(emp_name SEPARATOR '、') from emp;
-- Specify sorting method and separator
select department, group_concat(emp_name ) from emp group by department;
select department, group_concat(emp_name order by salary desc) from emp group by department;
Mathematical functions
| Function name | describe | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ABS(x) | return x The absolute value of | SELECT ABS(-1) – return 1 |
| ACOS(x) | seek x The arccosine of ( In radians ),x Is a numerical value | SELECT ACOS(0.25); |
| ASIN(x) | Find the inverse sine ( In radians ),x Is a numerical value | SELECT ASIN(0.25); |
| ATAN(x) | Find the arctangent ( In radians ),x Is a numerical value | SELECT ATAN(2.5); |
| ATAN2(n, m) | Find the arctangent ( In radians ) | SELECT ATAN2(-0.8, 2); |
| AVG(expression) | Returns the average value of an expression ,expression It's a field | return Products In the table Price The average value of the field :SELECT AVG(Price) AS AveragePrice FROM Products; |
| CEIL(x) | Returns greater than or equal to x Minimum integer of | SELECT CEIL(1.5) -- return 2 |
| CEILING(x) | Returns greater than or equal to x Minimum integer of | SELECT CEILING(1.5); -- return 2 |
| COS(x) | Find the cosine ( The parameter is radian ) | SELECT COS(2); |
| COT(x) | Find the cotangent value ( The parameter is radian ) | SELECT COT(6); |
| COUNT(expression) | Returns the total number of records queried ,expression A parameter is a field or * Number | return Products In the table products How many records are there in the field :SELECT COUNT(ProductID) AS NumberOfProducts FROM Products; |
| DEGREES(x) | Convert radians to degrees | SELECT DEGREES(3.1415926535898) -- 180 |
| n DIV m | to be divisible by ,n For divisor ,m Divisor | Calculation 10 Except in 5:SELECT 10 DIV 5; -- 2 |
| EXP(x) | return e Of x Power | Calculation e The third power of :SELECT EXP(3) -- 20.085536923188 |
| FLOOR(x) | Returns less than or equal to x Maximum integer for | Less than or equal to 1.5 The integer of :SELECT FLOOR(1.5) -- return 1 |
| GREATEST(expr1, expr2, expr3, …) | Returns the maximum value in the list | Returns the maximum value in the following list of numbers :SELECT GREATEST(3, 12, 34, 8, 25); -- 34 Returns the maximum value in the following string list :SELECT GREATEST("Google", "Runoob", "Apple"); -- Runoob |
| LEAST(expr1, expr2, expr3, …) | Returns the minimum value in the list | Returns the minimum value in the following list of numbers :SELECT LEAST(3, 12, 34, 8, 25); -- 3 Returns the minimum value in the following string list :SELECT LEAST("Google", "Runoob", "Apple"); -- Apple |
| LN | Returns the natural logarithm of a number , With e Bottom . | return 2 The natural logarithm of :SELECT LN(2); -- 0.6931471805599453 |
| LOG(x) or LOG(base, x) | Return to the natural logarithm ( With e Log base ), If a base Parameters , be base Specifies the base number for the . | SELECT LOG(20.085536923188) -- 3 SELECT LOG(2, 4); -- 2 |
| LOG10(x) | Return to 10 Log base | SELECT LOG10(100) -- 2 |
| LOG2(x) | Return to 2 Log base | Return to 2 Bottom 6 The logarithmic :SELECT LOG2(6); -- 2.584962500721156 |
| MAX(expression) | Return field expression Maximum of | Return to the data table Products Middle field Price The maximum of :SELECT MAX(Price) AS LargestPrice FROM Products; |
| MIN(expression) | Return field expression Minimum of | Return to the data table Products Middle field Price The minimum value of :SELECT MIN(Price) AS MinPrice FROM Products; |
| MOD(x,y) | return x Divide y The remainder after | 5 Except in 2 The remainder of :SELECT MOD(5,2) -- 1 |
| PI() | Return the PI (3.141593) | SELECT PI() --3.141593 |
| POW(x,y) | return x Of y Power | 2 Of 3 Power :SELECT POW(2,3) -- 8 |
| POWER(x,y) | return x Of y Power | 2 Of 3 Power :SELECT POWER(2,3) -- 8 |
| RADIANS(x) | Convert the Angle to radians | 180 Degrees to radians :SELECT RADIANS(180) -- 3.1415926535898 |
| RAND() | return 0 To 1 The random number | SELECT RAND() --0.93099315644334 |
| ROUND(x) | Return from x The nearest integer | SELECT ROUND(1.23456) --1 |
| SIGN(x) | return x The symbol of ,x It's a negative number 、0、 Positive numbers return respectively -1、0 and 1 | SELECT SIGN(-10) -- (-1) |
| SIN(x) | Find the sine ( The parameter is radian ) | SELECT SIN(RADIANS(30)) -- 0.5 |
| SQRT(x) | return x The square root of | 25 The square root of :SELECT SQRT(25) -- 5 |
| SUM(expression) | Returns the sum of the specified fields | Calculation OrderDetails Fields in the table Quantity The sum of :SELECT SUM(Quantity) AS TotalItemsOrdered FROM OrderDetails; |
| TAN(x) | Find tangent ( The parameter is radian ) | SELECT TAN(1.75); -- -5.52037992250933 |
| TRUNCATE(x,y) | Returns the value x Keep it after the decimal point y The value of a ( And ROUND The biggest difference is that there is no rounding ) | SELECT TRUNCATE(1.23456,3) -- 1.234 |
String function
| function | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| ASCII(s) | Return string s Of the first character of ASCII code . | return CustomerName The first letter of the field ASCII code :SELECT ASCII(CustomerName) AS NumCodeOfFirstChar FROM Customers; |
| CHAR_LENGTH(s) | Return string s The number of characters | Return string RUNOOB The number of characters SELECT CHAR_LENGTH("RUNOOB") AS LengthOfString; |
| CHARACTER_LENGTH(s) | Return string s The number of characters | Return string RUNOOB The number of characters SELECT CHARACTER_LENGTH("RUNOOB") AS LengthOfString; |
| CONCAT(s1,s2…sn) | character string s1,s2 When multiple strings are merged into a single string | Merge multiple strings SELECT CONCAT("SQL ", "Runoob ", "Gooogle ", "Facebook") AS ConcatenatedString; |
| CONCAT_WS(x, s1,s2…sn) | Same as CONCAT(s1,s2,…) function , But add... Between each string x,x It can be a separator | Merge multiple strings , And add a separator :SELECT CONCAT_WS("-", "SQL", "Tutorial", "is", "fun!")AS ConcatenatedString; |
| FIELD(s,s1,s2…) | Returns the first string s In the string list (s1,s2…) Position in | Return string c Position in the list value :SELECT FIELD("c", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e"); |
| FIND_IN_SET(s1,s2) | Return in string s2 China and s1 The location of the matching string | Return string c Position in the specified string :SELECT FIND_IN_SET("c", "a,b,c,d,e"); |
| FORMAT(x,n) | The function can change the number to x format “#,###.##”, take x Keep it after the decimal point n position , Round the last one . | Formatting Numbers “#,###.##” form :SELECT FORMAT(250500.5634, 2); -- Output 250,500.56 |
| INSERT(s1,x,len,s2) | character string s2 Replace s1 Of x The starting length of the position is len String | Starting from the first position of the string 6 Replace characters with runoob:SELECT INSERT("google.com", 1, 6, "runoob"); -- Output :runoob.com |
| LOCATE(s1,s) | From a string s In order to get s1 The beginning of | obtain b In string abc Position in :SELECT LOCATE('st','myteststring'); -- 5 Return string abc in b The location of :SELECT LOCATE('b', 'abc') -- 2 |
| LCASE(s) | The string s All of the letters of the are changed into lower case letters | character string RUNOOB Convert to lowercase :SELECT LCASE('RUNOOB') -- runoob |
| LEFT(s,n) | Return string s Before n Characters | Return string runoob The first two characters in :SELECT LEFT('runoob',2) -- ru |
| LOWER(s) | The string s All of the letters of the are changed into lower case letters | character string RUNOOB Convert to lowercase :SELECT LOWER('RUNOOB') -- runoob |
| LPAD(s1,len,s2) | In string s1 Start with a string s2, Make the string length to len | The string xx Fill in abc The beginning of the string :SELECT LPAD('abc',5,'xx') -- xxabc |
| LTRIM(s) | Remove string s The space at the beginning | Remove string RUNOOB The space at the beginning :SELECT LTRIM(" RUNOOB") AS LeftTrimmedString;-- RUNOOB |
| MID(s,n,len) | From a string s Of n The position intercept length is len Substring of , Same as SUBSTRING(s,n,len) | From a string RUNOOB No 2 Location intercepts 3 individual character :SELECT MID("RUNOOB", 2, 3) AS ExtractString; -- UNO |
| POSITION(s1 IN s) | From a string s In order to get s1 The beginning of | Return string abc in b The location of :SELECT POSITION('b' in 'abc') -- 2 |
| REPEAT(s,n) | The string s repeat n Time | The string runoob Repeat three times :SELECT REPEAT('runoob',3) -- runoobrunoobrunoob |
| REPLACE(s,s1,s2) | The string s2 Alternative string s String in s1 | The string abc The characters in a Replace with characters x:SELECT REPLACE('abc','a','x') --xbc |
| REVERSE(s) | The string s In reverse order | The string abc In reverse order :SELECT REVERSE('abc') -- cba |
| RIGHT(s,n) | Return string s After n Characters | Return string runoob The last two characters of :SELECT RIGHT('runoob',2) -- ob |
| RPAD(s1,len,s2) | In string s1 Add a string at the end of s2, Make the length of the string equal to len | The string xx Fill in abc At the end of the string :SELECT RPAD('abc',5,'xx') -- abcxx |
| RTRIM(s) | Remove string s Space at the end | Remove string RUNOOB Space at the end of :SELECT RTRIM("RUNOOB ") AS RightTrimmedString; -- RUNOOB |
| SPACE(n) | return n A space | return 10 A space :SELECT SPACE(10); |
| STRCMP(s1,s2) | Compare strings s1 and s2, If s1 And s2 Equal return 0 , If s1>s2 return 1, If s1<s2 return -1 | Compare strings :SELECT STRCMP("runoob", "runoob"); -- 0 |
| SUBSTR(s, start, length) | From a string s Of start The position intercept length is length Substring of | From a string RUNOOB No 2 Location intercepts 3 individual character :SELECT SUBSTR("RUNOOB", 2, 3) AS ExtractString; -- UNO |
| SUBSTRING(s, start, length) | From a string s Of start The position intercept length is length Substring of | From a string RUNOOB No 2 Location intercepts 3 individual character :SELECT SUBSTRING("RUNOOB", 2, 3) AS ExtractString; -- UNO |
| SUBSTRING_INDEX(s, delimiter, number) | Return from string s Of the number Separators that appear delimiter After the string . If number Positive number , Back to page number The string to the left of characters . If number It's a negative number , Back to page (number The absolute value of ( Count from the right )) The string to the right of characters . | SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('a*b','*',1) -- a SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('a*b','*',-1) -- b SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX('a*b*c*d*e','*',3),'*',-1) -- c |
| TRIM(s) | Remove string s The spaces at the beginning and the end | Remove string RUNOOB The leading and trailing spaces of :SELECT TRIM(' RUNOOB ') AS TrimmedString; |
| UCASE(s) | Convert strings to uppercase | The string runoob Convert to uppercase :SELECT UCASE("runoob"); -- RUNOOB |
| UPPER(s) | Convert strings to uppercase | The string runoob Convert to uppercase :SELECT UPPER("runoob"); -- RUNOOB |
Date function
| function | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| ADDDATE(d,n) | Calculate start date d add n The date of day | SELECT ADDDATE("2017-06-15", INTERVAL 10 DAY); ->2017-06-25 |
| ADDTIME(t,n) | n It's a time expression , Time t Add the time expression n | Add 5 second :SELECT ADDTIME('2011-11-11 11:11:11', 5); ->2011-11-11 11:11:16 ( second ) add to 2 Hours , 10 minute , 5 second :SELECT ADDTIME("2020-06-15 09:34:21", "2:10:5"); -> 2020-06-15 11:44:26 |
| CURDATE() | Return current date | SELECT CURDATE(); -> 2018-09-19 |
| CURRENT_DATE() | Return current date | SELECT CURRENT_DATE(); -> 2018-09-19 |
| CURRENT_TIME | Return current time | SELECT CURRENT_TIME(); -> 19:59:02 |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() -> 2018-09-19 20:57:43 |
| CURTIME() | Return current time | SELECT CURTIME(); -> 19:59:02 |
| DATE() | Extract a date value from a date or datetime expression | SELECT DATE("2017-06-15"); -> 2017-06-15 |
| DATEDIFF(d1,d2) | Calculate the date d1->d2 The days between | SELECT DATEDIFF('2001-01-01','2001-02-02') -> -32 |
| DATE_ADD(d,INTERVAL expr type) | Calculate start date d Add the date after a period of time | SELECT DATE_ADD("2017-06-15", INTERVAL 10 DAY); -> 2017-06-25 SELECT DATE_ADD("2017-06-15 09:34:21", INTERVAL 15 MINUTE); -> 2017-06-15 09:49:21 SELECT DATE_ADD("2017-06-15 09:34:21", INTERVAL -3 HOUR); ->2017-06-15 06:34:21 SELECT DATE_ADD("2017-06-15 09:34:21", INTERVAL -3 MONTH); ->2017-04-15 |
| DATE_FORMAT(d,f) | By expression f To display the date d | SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2011-11-11 11:11:11','%Y-%m-%d %r') -> 2011-11-11 11:11:11 AM |
| DATE_SUB(date,INTERVAL expr type) | Function to subtract a specified time interval from a date . | Orders In the table OrderDate Field subtraction 2 God :SELECT OrderId,DATE_SUB(OrderDate,INTERVAL 2 DAY) AS OrderPayDate FROM Orders |
| DAY(d) | Returns the date value d The date part of | SELECT DAY("2017-06-15"); -> 15 |
| DAYNAME(d) | Return date d What day is , Such as Monday,Tuesday | SELECT DAYNAME('2011-11-11 11:11:11') ->Friday |
| DAYOFMONTH(d) | Calculate the date d It's the day of the month | SELECT DAYOFMONTH('2011-11-11 11:11:11') ->11 |
| DAYOFWEEK(d) | date d What day is today ,1 Sunday ,2 Monday , And so on | SELECT DAYOFWEEK('2011-11-11 11:11:11') ->6 |
| DAYOFYEAR(d) | Calculate the date d It's the day of the year | SELECT DAYOFYEAR('2011-11-11 11:11:11') ->315 |
| EXTRACT(type FROM d) | From the date d Get the specified value from the ,type Specifies the value to be returned . t | SELECT EXTRACT(MINUTE FROM '2011-11-11 11:11:11') -> 11 |
| FROM_DAYS(n) | Calculate from 0000 year 1 month 1 The day begins n Days after | SELECT FROM_DAYS(1111) -> 0003-01-16 |
| HOUR(t) | return t The hour value in | SELECT HOUR('1:2:3') -> 1 |
| LAST_DAY(d) | Returns the last day of the month for a given date | SELECT LAST_DAY("2017-06-20"); -> 2017-06-30 |
| LOCALTIME() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT LOCALTIME() -> 2018-09-19 20:57:43 |
| LOCALTIMESTAMP() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT LOCALTIMESTAMP() -> 2018-09-19 20:57:43 |
| MAKEDATE(year, day-of-year) | Based on the given parameter year year And the number of days in the year day-of-year Return a date | SELECT MAKEDATE(2017, 3); -> 2017-01-03 |
| MAKETIME(hour, minute, second) | Combination time , The parameters are hour 、 minute 、 second | SELECT MAKETIME(11, 35, 4); -> 11:35:04 |
| MICROSECOND(date) | Returns the number of microseconds corresponding to the date parameter | SELECT MICROSECOND("2017-06-20 09:34:00.000023"); -> 23 |
| MINUTE(t) | return t Minutes in | SELECT MINUTE('1:2:3') -> 2 |
| MONTHNAME(d) | Returns the name of the month in the date , Such as November | SELECT MONTHNAME('2011-11-11 11:11:11') -> November |
| MONTH(d) | Return date d The month in is worth ,1 To 12 | SELECT MONTH('2011-11-11 11:11:11') ->11 |
| NOW() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT NOW() -> 2018-09-19 20:57:43 |
| PERIOD_ADD(period, number) | by year - month Add a period to the combined date | SELECT PERIOD_ADD(201703, 5); -> 201708 |
| PERIOD_DIFF(period1, period2) | Returns the month difference between two periods | SELECT PERIOD_DIFF(201710, 201703); -> 7 |
| QUARTER(d) | Return date d What season is it , return 1 To 4 | SELECT QUARTER('2011-11-11 11:11:11') -> 4 |
| SECOND(t) | return t The second value in | SELECT SECOND('1:2:3') -> 3 |
| SEC_TO_TIME(s) | Time in seconds s Convert to minutes and seconds | SELECT SEC_TO_TIME(4320) -> 01:12:00 |
| STR_TO_DATE(string, format_mask) | Convert string to date | SELECT STR_TO_DATE("August 10 2017", "%M %d %Y"); -> 2017-08-10 |
| SUBDATE(d,n) | date d subtract n Days after | SELECT SUBDATE('2011-11-11 11:11:11', 1) ->2011-11-10 11:11:11 ( The default is days ) |
| SUBTIME(t,n) | Time t subtract n The second time | SELECT SUBTIME('2011-11-11 11:11:11', 5) ->2011-11-11 11:11:06 ( second ) |
| SYSDATE() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT SYSDATE() -> 2018-09-19 20:57:43 |
| TIME(expression) | Extract the time part of the incoming expression | SELECT TIME("19:30:10"); -> 19:30:10 |
| TIME_FORMAT(t,f) | By expression f The request shows the time t | SELECT TIME_FORMAT('11:11:11','%r') 11:11:11 AM |
| TIME_TO_SEC(t) | Time t Convert to seconds | SELECT TIME_TO_SEC('1:12:00') -> 4320 |
| TIMEDIFF(time1, time2) | Calculate time difference | mysql> SELECT TIMEDIFF("13:10:11", "13:10:10"); -> 00:00:01 mysql> SELECT TIMEDIFF('2000:01:01 00:00:00', -> '2000:01:01 00:00:00.000001'); -> '-00:00:00.000001' mysql> SELECT TIMEDIFF('2008-12-31 23:59:59.000001', -> '2008-12-30 01:01:01.000002'); -> '46:58:57.999999' |
| TIMESTAMP(expression, interval) | When a single parameter , Function returns a date or datetime expression ; Yes 2 When the parameters , Add parameters to | mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMP("2017-07-23", "13:10:11"); -> 2017-07-23 13:10:11 mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMP('2003-12-31'); -> '2003-12-31 00:00:00' mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMP('2003-12-31 12:00:00','12:00:00'); -> '2004-01-01 00:00:00' |
| TIMESTAMPDIFF(unit,datetime_expr1,datetime_expr2) | Calculate the time difference , return datetime_expr2 − datetime_expr1 The time difference | mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(DAY,'2003-02-01','2003-05-01'); // Calculate the number of days between the two times -> 89 mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(MONTH,'2003-02-01','2003-05-01'); // Calculate the number of months between the two times -> 3 mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,'2002-05-01','2001-01-01'); // Calculate the number of years between the two times -> -1 mysql> SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE,'2003-02-01','2003-05-01 12:05:55'); // Calculate the number of minutes between the two times -> 128885 |
| TO_DAYS(d) | Calculate the date d distance 0000 year 1 month 1 Days of the day | SELECT TO_DAYS('0001-01-01 01:01:01') -> 366 |
| WEEK(d) | Calculate the date d It's the first few weeks of the year , The scope is 0 To 53 | SELECT WEEK('2011-11-11 11:11:11') -> 45 |
| WEEKDAY(d) | date d What day is ,0 For Monday ,1 For Tuesday | SELECT WEEKDAY("2017-06-15"); -> 3 |
| WEEKOFYEAR(d) | Calculate the date d It's the first few weeks of the year , The scope is 0 To 53 | SELECT WEEKOFYEAR('2011-11-11 11:11:11') -> 45 |
Demo example :
-- Date function
-- Get the timestamp
select UNIX_TIMESTAMP()
-- Convert a string to a millisecond value
select UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2022-01-19 18:21:00')
-- Converts the time in milliseconds to a date in the specified format
select from_unixtime('1642587660', '%Y-%m-%d %H-%i-%s')\
-- Get the current date
select curdate()
select current_date()
-- Get the current time, minute, second
select current_time()
-- Gets the minutes and seconds of the year, month and day
select current_timestamp()
-- Get the date from the date string
select date('2021-12-11 12:12:12')
-- Calculate the time interval
select datediff('2021-01-11', '2022-12-12');
-- Calculate time difference
select timediff('2021-12-11 12:12:12', '2021-2-11 12:12:12');
select timediff('12:12:12', '11:12:12');
-- Convert string to date
select STR_TO_DATE('2021-12-11 12:12:12','%Y-%m-%D %H:%i:%s');
-- Subtract the date , The date jumps forward
select date_sub('2021-3-01', interval 2 day);
select date_sub('2021-3-2', interval 2 month);
-- Add the date , The date jumps to the right
select date_add('2021-02-1' ,interval 2 month);
select date_add('2021-02-1', interval 2 day);
-- Get the time from the date [ hour, month, day, hour]
select extract(hour from '2021-01-22 12:01:00');
select extract(year from '2021-01-22 12:01:00');
select extract(month from '2021-01-22 12:01:00');
-- Get the last day of a given date
select last_day('2021-12-01'); -- 2021-12-31
-- Gets the date of the year and the specified number of days
select makedate('2022', 53); -- 2022 In the first 53 God
-- Obtain the time, minute and second of month, day and year according to the date
select year('2021-01-22 12:01:00')
select month('2021-01-22 12:01:00')
select day('2021-01-22 12:01:00')
select minute('2021-01-22 12:01:00')
select QUARTER('2021-01-22 12:01:00') -- quarter
-- Get information based on date
select DAYOFMONTH('2022-01-18 18:13:00') -- The day of the month
select DAYOFWEEK('2022-01-18 18:13:00') -- What day
select DAYOFYEAR('2022-01-18 18:13:00') -- Get the day of the year
-- week
select WEEK('2022-01-18') -- The first few weeks of the year
select WEEKDAY('2022-01-18') -- The acquisition date is the day of the week ,0 For weeks 1,1 For weeks 2
select WEEKOFYEAR('2022-01-18') -- The calculation date is the week ordinal of the year ,0-53
select YEARWEEK('2022-01-18') -- Return year and week 202203,2022 In the first 3 Zhou
select NOW() -- Returns the current date and time
MySQL Advanced functions
| function | describe | example |
|---|---|---|
| BIN(x) | return x Binary code of | 15 Of 2 Hexadecimal code :SELECT BIN(15); -- 1111 |
| BINARY(s) | The string s Convert to binary string | SELECT BINARY "RUNOOB"; -> RUNOOB |
CASE expression WHEN condition1 THEN result1 WHEN condition2 THEN result2 ... WHEN conditionN THEN resultN ELSE result END | CASE Represents the beginning of a function ,END End of function . If condition1 establish , Then return to result1, If condition2 establish , Then return to result2, When all fail, return to result, And when one is established , The latter will not be implemented . | SELECT CASE WHEN 1 > 0 THEN '1 > 0' WHEN 2 > 0 THEN '2 > 0' ELSE '3 > 0' END ->1 > 0 |
| CAST(x AS type) | Convert data type | Convert string date to date :SELECT CAST("2017-08-29" AS DATE); -> 2017-08-29 |
| COALESCE(expr1, expr2, …, expr_n) | Returns the first non empty expression in the parameter ( From left to right ) | SELECT COALESCE(NULL, NULL, NULL, 'runoob.com', NULL, 'google.com'); -> runoob.com |
| CONNECTION_ID() | Returns a unique connection ID | SELECT CONNECTION_ID(); -> 4292835 |
| CONV(x,f1,f2) | return f1 The base number becomes f2 Hexadecimal number | SELECT CONV(15, 10, 2); -> 1111 |
| CONVERT(s USING cs) | Function to string s The character set of becomes cs | SELECT CHARSET('ABC') ->utf-8 SELECT CHARSET(CONVERT('ABC' USING gbk)) ->gbk |
| CURRENT_USER() | Return to current user | SELECT CURRENT_USER(); -> [email protected]% |
| DATABASE() | Returns the current database name | SELECT DATABASE(); -> runoob |
| LAST_INSERT_ID() | Returns the most recently generated AUTO_INCREMENT value | SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID(); ->6 |
| NULLIF(expr1, expr2) | Compare two strings , If the string expr1 And expr2 equal return NULL, Otherwise return to expr1 | SELECT NULLIF(25, 25); -> |
| SESSION_USER() | Return to current user | SELECT SESSION_USER(); -> [email protected]% |
| SYSTEM_USER() | Return to current user | SELECT SYSTEM_USER(); -> [email protected]% |
| USER() | Return to current user | SELECT USER(); -> [email protected]% |
| VERSION() | Return the version number of the database | SELECT VERSION() -> 5.6.34 |
Control flow function
IF control
| function | describe | Example |
|---|---|---|
| IF(expr,v1,v2) | If the expression expr establish , Return results v1; otherwise , Return results v2. | SELECT IF(1 > 0,' correct ',' error ') -> correct |
| IFNULL(v1,v2) | If v1 The value of the NULL, Then return to v1, Otherwise return to v2. | SELECT IFNULL(null,'Hello Word') ->Hello Word |
| ISNULL(expression) | Determine whether the expression is NULL | SELECT ISNULL(NULL); ->1 |
Sample code :
-- IF Sentence judgment
select *, if(salary >=25000, ' The Lord ', ' Senior general ') from emp;
case when end function
Format :
CASE case_value
WHEN when_value THEN
statement_list
ELSE
statement_list
END;
The operation sample :
-- Create order form
create table orders(
oid int primary key,
price double,
payType int -- 1 Wechat payment 2 Alipay 3 other
);
use mydb1;
insert into orders values(1, 1200, 1);
insert into orders values(2, 1100, 2);
insert into orders values(3, 800, 3);
insert into orders values(4, 5200, 1);
insert into orders values(5, 100, 2);
-- Output payment method
select
*,
CASE payType
WHEN 1 THEN ' Wechat payment '
WHEN 2 THEN ' Alipay '
ELSE ' Other payments '
END as payIntf
from orders;
Window function
Ordinal function
ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), DENSE_RANK() Group sorting can be realized , And add serial number .
Format :
row_number() | rank() | dense_rank() over(
partition by ...
order by ...
)
The operation sample :
create table employee(
dname varchar(20), -- Department name
eid varchar(20),
ename varchar(20),
hiredate date, -- Entry time
salary double -- Salary
);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1001', ' Liu bei ', '2021-11-01', 15000);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1002', ' Guan yu ', '2021-11-02', 5000);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1003', ' Zhang Fei ', '2021-11-03', 5000);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1004', ' zhaoyun ', '2021-11-04', 7000);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1005', ' d ', '2021-11-05', 4000);
insert into employee values(' Shu Kingdom ', '1006', ' Huang Zhong ', '2021-11-06', 4000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1007', ' Cao Cao ', '2021-11-01', 15000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1008', ' Xu Zhen ', '2021-11-01', 3000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1009', ' Dianwei ', '2021-11-01', 3000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1010', ' Zhang liao ', '2021-11-01', 5000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1011', ' Summer ', '2021-11-01', 5000);
insert into employee values(' State of Wei ', '1012', ' Sima ', '2021-11-01', 8000);
-- Sort the employees of each department according to their salary , And output the ranking
select
dname, ename, salary,
row_number() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn
from employee;
-- Three sorting functions
select
dname, ename, salary,
row_number() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn,
rank() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn2,
dense_rank() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn3
from employee;
Windowed aggregate function
Windowed aggregate function :SUM(), avg(), max(), min(), count()
The operation sample :
select
dname, ename, salary,
sum(salary) over (partition by dname order by hiredate) as pv1,
count(salary) over (partition by dname order by hiredate) as pv2
from employee;
-- Start with the third line and count down
-- hiredate rows between 3 preceding and current row
select
dname, ename, salary,
sum(salary) over (partition by dname order by hiredate rows between 3 preceding and current row ) as pv1
from employee;
Distribution function
Distribution function :CUME_DIST() and PERCENT_RANK()
CUME_DIST()
purpose : Less than... In the group 、 Equal to current rank The number of rows for the value / The total number of rows in the group
Example :
select
dname, ename, salary,
cume_dist() over( order by salary) as rn1,
cume_dist() over(partition by dname order by salary) as rn2
from employee;
PERCENT_RANK()
purpose : Each line follows the formula (rank-1) / row(rows-1) Calculate , among ,rank by RNAK() The sequence number generated by the function ,rows Record the total number of rows for the current window .
select
dname, ename, salary,
rank() over( partition by dname order by salary) as rn1,
percent_rank() over(partition by dname order by salary) as rn2
from employee;
/* first line : (1-1) / (6-1) = 0 row2: (1-1) / (6-1) = 0 row3: (3-1) / (6-1) = 0.4 */
Before and after function LAG and LEAD
Returns the line that precedes the current line n That's ok (lag(expr, n )) Or after n That's ok (LEAD(EXPR, N) ) Of expr value
-- Before and after function LAG and LEAD
select
dname, ename, salary, hiredate,
lag(hiredate, 1, '2000-01-01') over( partition by dname order by hiredate ) as time1,
lag(hiredate, 2) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as time2
from employee;
Head tail function FIRST_VALUE() and lAST_VALUE
Introduce :
purpose : Return to the first (first_value(expr) Or the last one ( last_value(expr) ) expr Value
Application scenarios : As of now , Query by date 1 The salary of the first and last employee
The operation sample :
-- Head tail function FIRST_VALUE() and lAST_VALUE
select
dname, ename, salary, hiredate,
first_value(salary) over( partition by dname order by hiredate ) as first,
last_value(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last
from employee;
Other functions
NTH_VALUE(expr, n)
purpose : Return to... In the window N individual Expr Value ,EXPR It could be an expression , It can also be listed
Application scenarios : As of the current salary , Displays the salary ranking of each employee 2 Or 3 Pay for
The operation sample :
select
dname, ename, salary, hiredate,
nth_value(salary, 2) over( partition by dname order by salary ) as two,
nth_value(salary, 3) over(partition by dname order by salary) as three
from employee;
-- Take out the first group of employees in each department
select * from (
select
dname, ename, hiredate, salary,
ntile(3) over(partition by dname order by hiredate ) as rn
from employee
) t
where t.rn = 1;
边栏推荐
- 【L1、L2、smooth L1三类损失函数】
- Video networkstate property
- 【PyTorch预训练模型修改、增删特定层】
- A guide to threaded and asynchronous UI development in the "quick start fluent Development Series tutorials"
- Pytorch MLP
- 想问问,如何选择券商?在线开户是很安全么?
- 【ijkplayer】when i compile file “compile-ffmpeg.sh“ ,it show error “No such file or directory“.
- Time tools
- Thoughts and suggestions on the construction of intelligent management and control system platform for safe production in petrochemical enterprises
- ABAP table lookup program
猜你喜欢
调查显示传统数据安全工具在60%情况下无法抵御勒索软件攻击
Uniapp + unicloud + Unipay realize wechat applet payment function
Pytorch softmax regression
![[singleshotmultiboxdetector (SSD, single step multi frame target detection)]](/img/c7/8ad64582e09683818171b625769f37.png)
[singleshotmultiboxdetector (SSD, single step multi frame target detection)]

July Huaqing learning-1
How can beginners learn flutter efficiently?
1 plug-in to handle advertisements in web pages

The most comprehensive new database in the whole network, multidimensional table platform inventory note, flowus, airtable, seatable, Vig table Vika, flying Book Multidimensional table, heipayun, Zhix
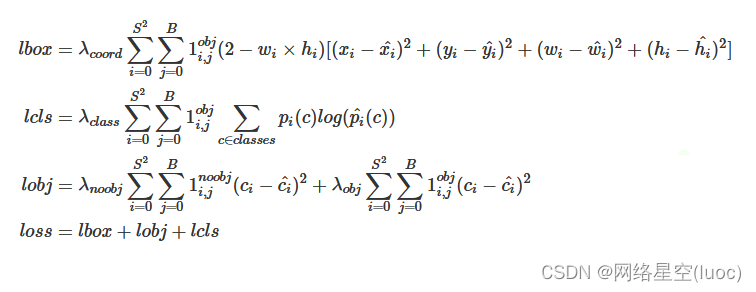
【 YOLOv3中Loss部分计算】
多表操作-子查询
随机推荐
你做自动化测试为什么总是失败?
Seven polymorphisms
Image hyperspectral experiment: srcnn/fsrcnn
Redis cluster (master-slave) brain crack and solution
Splunk configuration 163 mailbox alarm
Matlab boundarymask function (find the boundary of the divided area)
codeforces每日5题(均1700)-第五天
【上采样方式-OpenCV插值】
一款新型的智能家居WiFi选择方案——SimpleWiFi在无线智能家居中的应用
Simply solve the problem that the node in the redis cluster cannot read data (error) moved
Redirection of redis cluster
Linux Installation and deployment lamp (apache+mysql+php)
Uniapp + unicloud + Unipay realize wechat applet payment function
Four operations and derivative operations of MATLAB polynomials
Check the debug port information in rancher and do idea remote JVM debug
[deploy pytoch project through onnx using tensorrt]
1 plug-in to handle advertisements in web pages
What is the difference between canvas and SVG?
Matlab label2idx function (convert the label matrix into a cell array with linear index)
July Huaqing learning-1
