当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of platform device driver architecture in driver development
Detailed explanation of platform device driver architecture in driver development
2022-07-07 05:54:00 【Embedded Yuexiang Garden】
1、 What is? platform Bus
from Linux2.6 Start Linux Added a set of driver management and registration mechanism —platform Bus driven model .platform The bus is a Virtual bus ( There is only one ), This kind of bus There is no corresponding hardware structure .platform_device For the corresponding equipment ,platform_driver For the corresponding drive . With the traditional bus/device/driver Mechanism compared to ,platform Managed by the kernel , It improves the portability and security of the code .
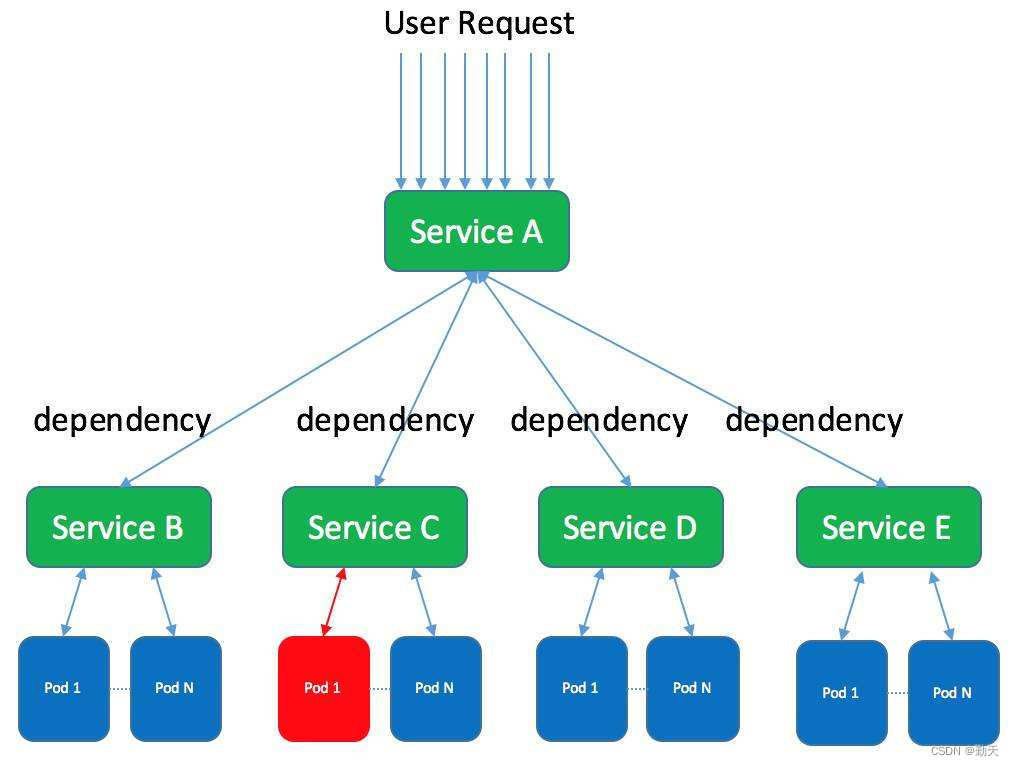
So-called platform_device It's not about character devices 、 The concept of juxtaposition of block devices and network devices , It is Linux An additional means provided by the system .Linux The framework of the bus device driver model is shown in the figure below :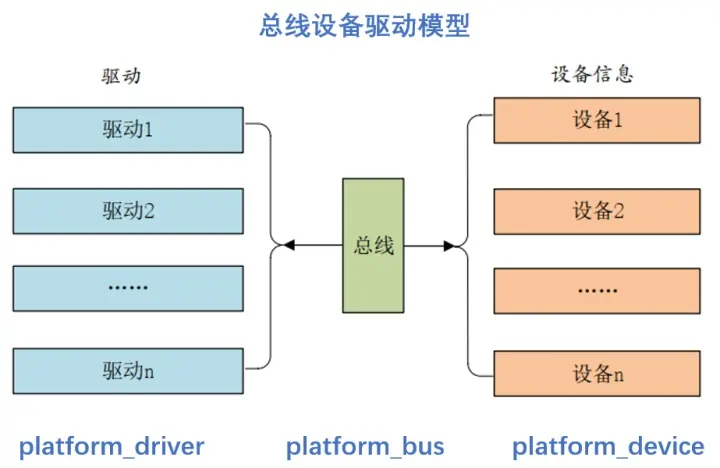
We can see clearly from the picture Linux platform The overall architecture of the bus device driver model . In the bus device driver model , Care about the bus 、 Devices and drives, this 3 Entity , The bus binds the device to the driver .
When registering drivers with the kernel , To be called platform_driver_register Function registers the driver to the bus , And put it into the drv In the list , When registering the driver, it will call the bus match Function to find the matching device on the bus , If a matching device is found, the corresponding probe Function to bind the corresponding device and driver , This matching process is automatically completed by the bus .
Reference resources :Linux Bus 、 equipment 、 Drive model _babyzhaoshu521 The blog of -CSDN Blog _linux Bus driven model
2、Platform Introduce
Platform The role of the platform device driver model is to separate the implementation of the driver from resources , It is a virtual bus platform . There are three members platform_bus,platform_device,platform_driver.platform_device and platform_driver Registration is in no order .
platform_bus: Realized by linked list , Does not correspond to the actual physical bus .
platform_device: Driven resources, such as some I/O port , Interrupt number and so on .
platform_driver: The function realization of the driver, such as Registration drive , Realization file_operations etc.
3、platform_driver Structure
Used to describe the implementation of driver . adopt platform_driver Of name Member matching on device after probe Function will be called , When the device is unplugged, the system will call remove Members do cleaning work .
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); // device and driver Of name After the match is successful, it is called probe function
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *); // Call when the device is removed
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver; // id_table->name When not set , Use driver->name Match
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
};
struct platform_device_id {
char name[PLATFORM_NAME_SIZE]; // For and platform_device->name Match
kernel_ulong_t driver_data;
};
4、platform Main function
/* platform_device Register and uninstall functions . */
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev);
void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *pdev);
/* platform_driver Register and uninstall functions . */
int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv);
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv);
/* obtain platform_device Resources saved in */
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int num);
/* obtain platform_device Interrupt resources for */
int platform_get_irq(struct platform_device *dev, unsigned int num)
/* For batch registration of platform equipment */
int platform_add_devices(struct platform_device **devs, int num)
5、 Take a chestnut
This is a LED Lamp drive , We'll take LED Medium platform_driver Take an example for analysis :
struct platform_driver led_drv = {
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "myled",
.of_match_table = of_match_leds, /* What can be supported from dts Of platform_device */
}
};
probe function , When the driver matches the device successfully probe The function will execute , Very important functions . Generally driven providers will write , If you want to write a new driver , that probe It needs to be realized by itself .
remove function ,platform_driver In structure remove Member variables , When off platform When the device is driven, this function will execute , Before unloading the driver exit What needs to be done in the function is put into this function . such as , Use iounmap Free memory 、 Delete cdev, Log off the equipment number, etc .
driver member , by device_driver Structural variable ,Linux Object oriented thinking is widely used in the kernel ,device_driver Equivalent to base class , Provides the most basic driving framework .plaform_driver Inherited this base class , Then on this basis, some unique member variables are added .
6、platform Drive frame
platform The drive frame is shown below :
/* Equipment structure */
struct xxx_dev{
struct cdev cdev;
/* Other specific contents of equipment structure */
};
struct xxx_dev xxxdev; /* Define a device structure variable */
static int xxx_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
/* Function details */
return 0;
}
static ssize_t xxx_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
/* Function details */
return 0;
}
/* * Character device driver operation set */
static struct file_operations xxx_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = xxx_open,
.write = xxx_write,
};
/* * platform Driven probe function * After the driver matches the device successfully, this function will execute */
static int xxx_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
......
cdev_init(&xxxdev.cdev, &xxx_fops); /* Register character device driver */
/* Function details */
return 0;
}
static int xxx_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
......
cdev_del(&xxxdev.cdev);/* Delete cdev */
/* Function details */
return 0;
}
/* Match list */
static const struct of_device_id xxx_of_match[] = {
{
.compatible = "xxx-gpio" },
{
/* Sentinel */ }
};
/* * platform Platform driven structure */
static struct platform_driver xxx_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "xxx",
.of_match_table = xxx_of_match,
},
.probe = xxx_probe,
.remove = xxx_remove,
};
/* Driver module loading */
static int __init xxxdriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&xxx_driver);
}
/* Driver module unloading */
static void __exit xxxdriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&xxx_driver);
}
module_init(xxxdriver_init);
module_exit(xxxdriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("jamesbin");
The first 1~27 That's ok , Traditional character device driver , So-called platform The driver is not independent of the character device driver 、 Drivers other than block device drivers and network device drivers .platform It is just a framework proposed to drive separation and layering , The specific implementation of its driver still needs character device driver 、 Block device driver or network device driver .
The first 33~39 That's ok ,xxx_probe function , When the driver and device match successfully, this function will execute , Used to drive the entrance init All the character device drivers written in the function are put here probe In the function . For example, register character device drivers 、 add to cdev、 Create classes and so on .
The first 41~47 That's ok ,xxx_remove function ,platform_driver In structure remove Member variables , When off platform When the device is driven, this function will execute , Before unloading the driver exit What needs to be done in the function is put into this function . such as , Use iounmap Free memory 、 Delete cdev, Log off the equipment number, etc .
The first 50~53 That's ok ,xxx_of_match Match table , If the device tree is used, the driver and device will be matched through this matching table . The first 51 Line sets a match , Of this match compatible The value is “xxx-gpio”, Therefore, when the device node in the device tree compatible The property value is “xxx-gpio” The device will match with the driver when the .
The first 52 The line is a marker ,of_device_id The last match in the table must be empty .
The first 58 ~ 65 That's ok , Define a platform_driver Structural variable xxx_driver, Express platform drive , The first 59~62 Line set up paltform_driver Medium device_driver Of member variables name and of_match_table These two properties . among name Property is used for traditional driver and device matching , That is, check the drive and equipment name Are the fields the same .of_match_table Attribute is used for driver and device inspection under the device tree . For a complete driver , There must be two matching methods: device tree and no device tree .
The first 63 and 64 These two lines set probe and remove These two member variables .
The first 68~71 That's ok , Drive entry function , call platform_driver_register Functional direction Linux The kernel registers a platform drive , That is what is defined above xxx_driver Structural variable .
The first 74~77 That's ok , Driving the exit function , call platform_driver_unregister Function to uninstall the previously registered platform drive .
7、platform summary
1) Define a platform_driver Structural variable .
2) Realization probe function .
3) Realization remove function .
4) Realization of_match_table.
5) call platform_driver_register Functional direction Linux The kernel registers a platform drive .
6) call platform_driver_unregister Function unload platform drive .
8、platform_device Registration process
platform_device The registration process can be simplified as follows :
struct platform_device *pdev; // Define a platform device and initialize
platform_device_register(pdev) // register
->>platform_device_add(pdev)
->>device_add(&pdev->dev)
->>bus_probe_device(&pdev->dev)
->>device_attach(&pdev->dev)
->>bus_for_each_drv(&(pdev->dev)->bus, NULL, &pdev->dev, __device_attach)
->>__device_attach(drv, &pdev->dev)
->>driver_probe_device(drv, &pdev->dev)
->>really_probe(&pdev->dev, drv)
->>&pdev->dev->bus->probe(dev) or drv->probe(dev)
Here we are Linux The bus device driver model of the kernel is analyzed . As can be seen from the above analysis process , So-called platform_device It's not about character devices 、 The concept of juxtaposition of block devices and network devices , It is Linux An additional means provided by the system .
边栏推荐
- Paper reading [open book video captioning with retrieve copy generate network]
- Question 102: sequence traversal of binary tree
- 得物客服一站式工作台卡顿优化之路
- Classic questions about data storage
- Senior programmers must know and master. This article explains in detail the principle of MySQL master-slave synchronization, and recommends collecting
- EMMC print cqhci: timeout for tag 10 prompt analysis and solution
- Polynomial locus of order 5
- C nullable type
- Hcip seventh operation
- [shell] clean up nohup Out file
猜你喜欢
Mac version PHP installed Xdebug environment (M1 version)
Modes of optical fiber - single mode and multimode
bat 批示处理详解
pytorch_ 01 automatic derivation mechanism
C#可空类型
AI face editor makes Lena smile
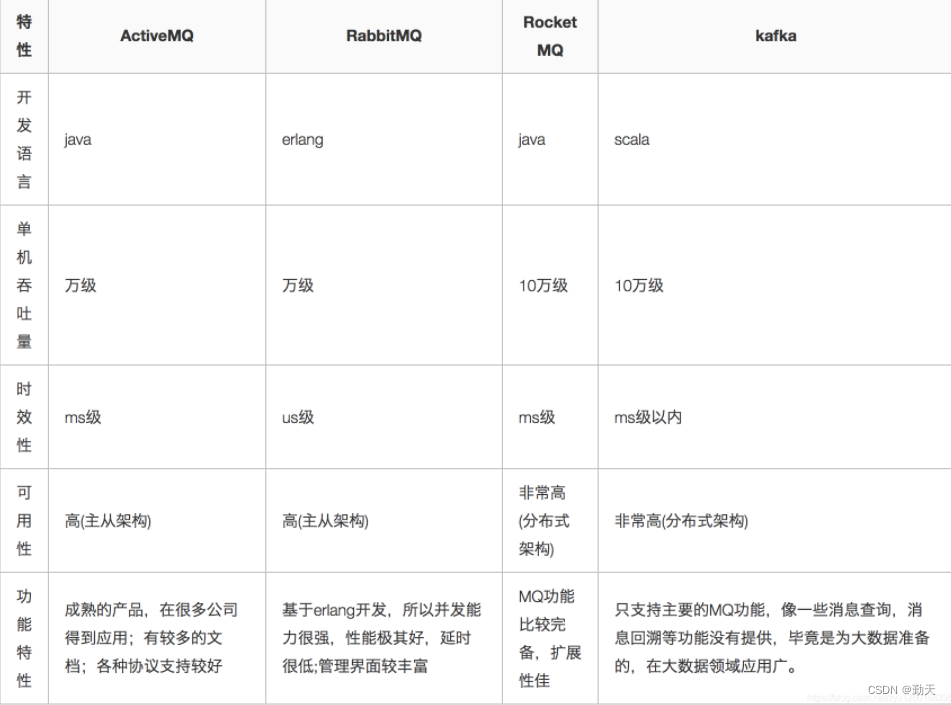
What are the common message queues?
集群、分布式、微服务的区别和介绍

集群、分布式、微服務的區別和介紹
Get the way to optimize the one-stop worktable of customer service
随机推荐
Ten stages of becoming a Senior IC Design Engineer. What stage are you in now?
PowerPivot——DAX(函数)
Différenciation et introduction des services groupés, distribués et microservices
Flinksql read / write PgSQL
Unity keeps the camera behind and above the player
Flink SQL realizes reading and writing redis and dynamically generates hset key
980. 不同路径 III DFS
搞懂fastjson 对泛型的反序列化原理
Loss function and positive and negative sample allocation in target detection: retinanet and focal loss
话说SQLyog欺骗了我!
Go 语言的 Context 详解
Win configuration PM2 boot auto start node project
English grammar_ Noun possessive
Message queue: how to handle repeated messages?
[shell] clean up nohup Out file
力扣102题:二叉树的层序遍历
随机生成session_id
What are the common message queues?
Flask 1.1.4 werkzeug1.0.1 analyse du code source: processus de démarrage
Dynamic memory management