当前位置:网站首页>pytorch_ 01 automatic derivation mechanism
pytorch_ 01 automatic derivation mechanism
2022-07-07 05:42:00 【Magnetoelectricity】
One of the most powerful things framework does is : Manually define forward propagation that requires derivation , Calculate all the backward propagation
import torch
# Method 1
x = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)# structure 3 That's ok 4 Columns of the matrix requires_grad=True Indicates that the current X To find the derivative , The default is false
x

# Method 2
x = torch.randn(3,4)#
x.requires_grad=True
x

b = torch.randn(3,4,requires_grad=True)
t = x + b
y = t.sum()
y#y As a loss function , Back propagation is to derive layer by layer from the loss function
y.backward()
b.grad
out:tensor(2.1753, grad_fn=)
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
Although not specified t Of requires_grad But you need it , It will also default
x.requires_grad, b.requires_grad, t.requires_grad
out (True, True, True)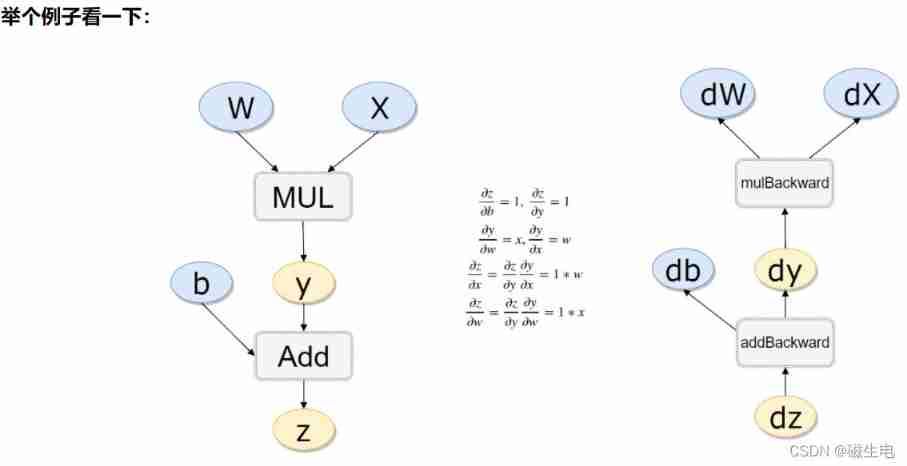
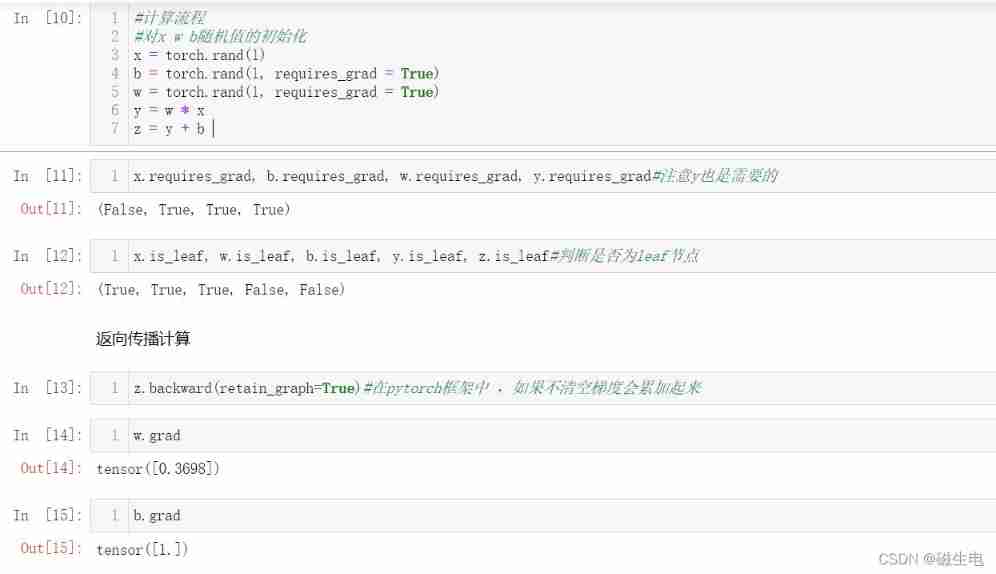
# Calculation process
# Yes x w b Initialization of random values
x = torch.rand(1)
b = torch.rand(1, requires_grad = True)
w = torch.rand(1, requires_grad = True)
y = w * x
z = y + b
# Backward propagation calculation
z.backward(retain_graph=True)# stay pytorch In the frame , If you don't empty the gradient, it will add up
Do a linear regression and try water
Construct a set of input data X And its corresponding label y
import numpy as np
x_values = [i for i in range(11)]
x_train = np.array(x_values, dtype=np.float32)#x Now it is ndarry The format of cannot be input into pytorch Training in To put ndarry Turn into tensor Format
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 1)# In order to prevent subsequent errors, it is converted into matrix format
x_train.shape
y_values = [2*i + 1 for i in x_values]
y_train = np.array(y_values, dtype=np.float32)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
y_train.shape
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
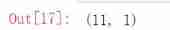
Linear regression model is actually a full connection layer without activation function
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):# No matter how complex the model is built First define the model class Inherit existing nn.Module modular
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):# Write those layers in the constructor
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim) # call nn The full connection layer of , Dimension of incoming input and output layer
def forward(self, x):# Specify the layer to use in forward propagation
out = self.linear(x)
return out
input_dim = 1
output_dim = 1
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim, output_dim)
Specify parameters and loss function for training
epochs = 1000# cycles
learning_rate = 0.01# Learning rate
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)# Define optimizer -SGD ( Parameters to be optimized , Learning rate )
criterion = nn.MSELoss()# Appoint MSE Loss function
Training models
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch += 1
# Pay attention to turning into tensor
inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
labels = torch.from_numpy(y_train)
# The gradient should be cleared every iteration
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Forward propagation results
outputs = model(inputs)
# Calculate the loss
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# Backward propagation
loss.backward()
# Update weight parameters
optimizer.step()
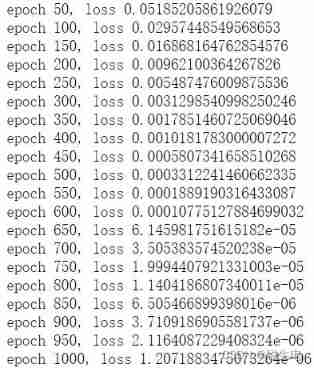
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('epoch {}, loss {}'.format(epoch, loss.item()))

Test model prediction results
predicted = model(torch.from_numpy(x_train).requires_grad_()).data.numpy()# Make a forward propagation to predict , Turn the result into ndarry Format , Convenient for drawing and pandas You need to use ndarry Format
predicted

Save and read the model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pkl')# Save in dictionary format Save the weight parameters and offsets
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pkl'))
Use GPU Training
Just pass the data and model into cuda Just inside
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
input_dim = 1
output_dim = 1
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim, output_dim)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")# If GPU Configured for use GPU
model.to(device)# Transfer the model to cuda in
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch += 1
inputs = torch.from_numpy(x_train).to(device)# Transfer training data to cuda in
labels = torch.from_numpy(y_train).to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('epoch {}, loss {}'.format(epoch, loss.item()))


边栏推荐
- sql查询:将下一行减去上一行,并做相应的计算
- 微信小程序蓝牙连接硬件设备并进行通讯,小程序蓝牙因距离异常断开自动重连,js实现crc校验位
- sql优化常用技巧及理解
- Five core elements of architecture design
- Egr-20uscm ground fault relay
- [paper reading] semi supervised left atrium segmentation with mutual consistency training
- 集群、分布式、微服務的區別和介紹
- 2pc of distributed transaction solution
- 消息队列:如何确保消息不会丢失
- 分布式事务解决方案之TCC
猜你喜欢
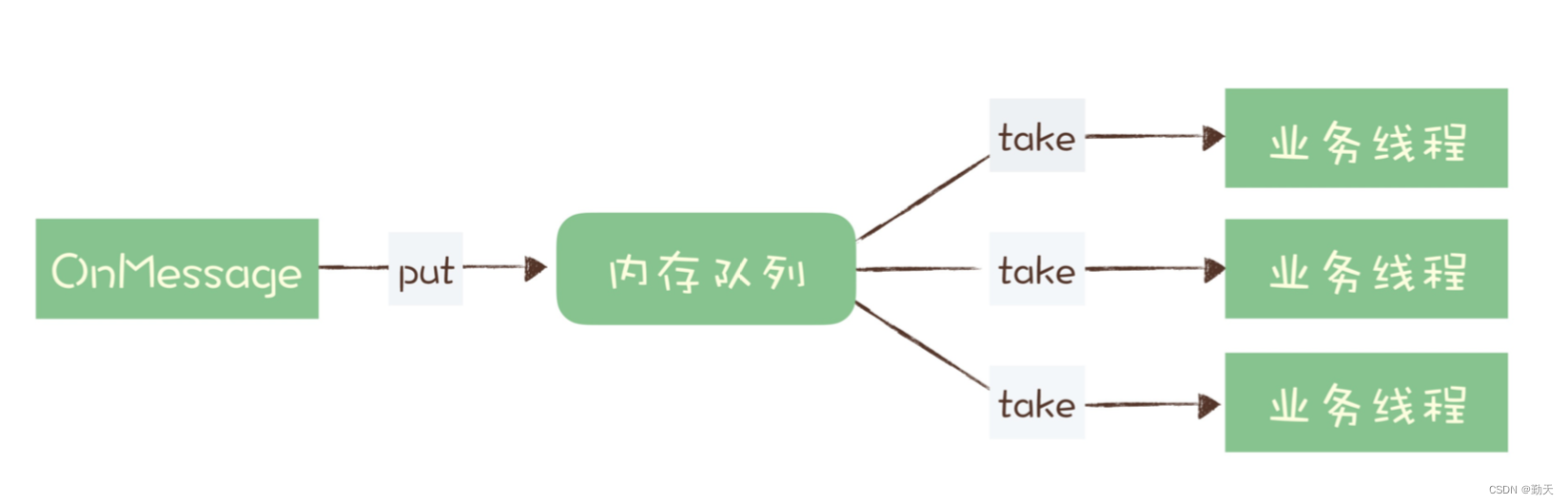
Message queue: how to deal with message backlog?
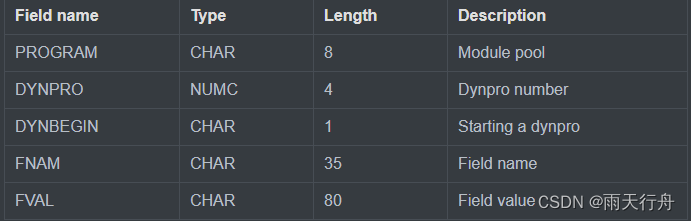
SAP ABAP BDC(批量数据通信)-018
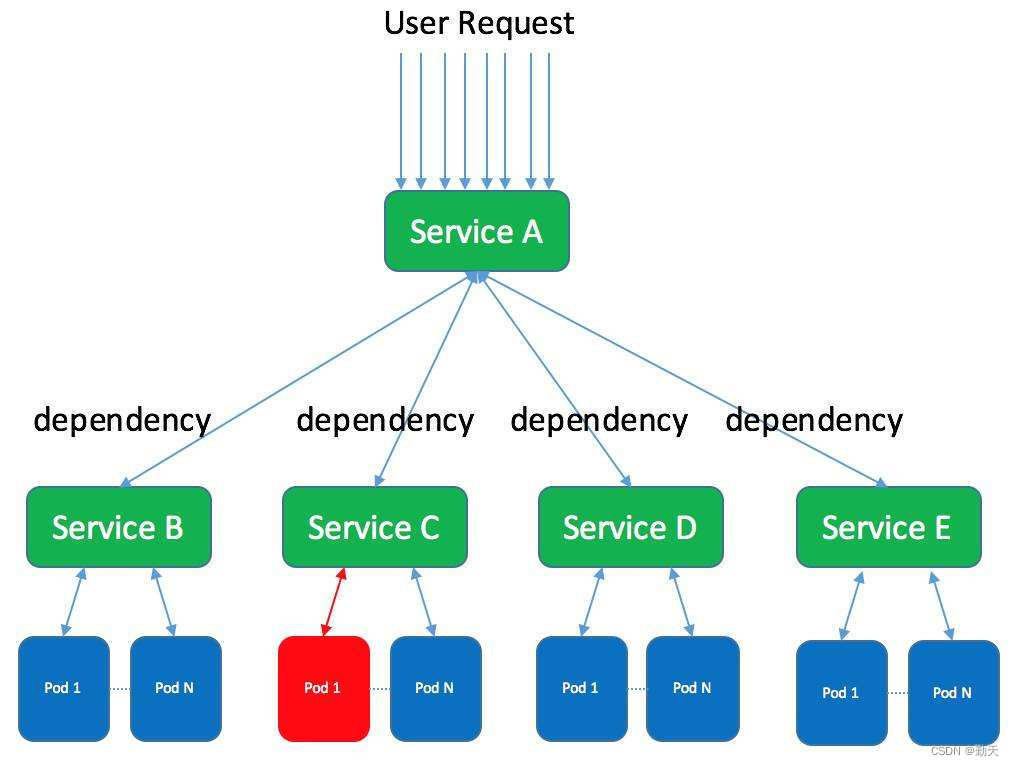
Differences and introduction of cluster, distributed and microservice

English grammar_ Noun possessive

Différenciation et introduction des services groupés, distribués et microservices

Use Zhiyun reader to translate statistical genetics books
Cve-2021-3156 vulnerability recurrence notes
Message queuing: how to ensure that messages are not lost
![Paper reading [MM21 pre training for video understanding challenge:video captioning with pre training techniqu]](/img/9c/1f031400f0e201df47bd51547ff73f.png)
Paper reading [MM21 pre training for video understanding challenge:video captioning with pre training techniqu]
![Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]](/img/db/feb719e2715c7b9c669957995e1d83.png)
Reading the paper [sensor enlarged egocentric video captioning with dynamic modal attention]
随机推荐
[paper reading] semi supervised left atrium segmentation with mutual consistency training
Flinksql 读写pgsql
Nodejs get client IP
Paper reading [MM21 pre training for video understanding challenge:video captioning with pre training techniqu]
Web Authentication API兼容版本信息
Zhang Ping'an: accelerate cloud digital innovation and jointly build an industrial smart ecosystem
“多模态”概念
淘宝店铺发布API接口(新),淘宝oAuth2.0店铺商品API接口,淘宝商品发布API接口,淘宝商品上架API接口,一整套发布上架店铺接口对接分享
分布式事务解决方案之2PC
京东商品详情页API接口、京东商品销量API接口、京东商品列表API接口、京东APP详情API接口、京东详情API接口,京东SKU信息接口
分布式事务介绍
随机生成session_id
【oracle】简单的日期时间的格式化与排序问题
Simple case of SSM framework
删除文件时提示‘源文件名长度大于系统支持的长度’无法删除解决办法
[论文阅读] A Multi-branch Hybrid Transformer Network for Corneal Endothelial Cell Segmentation
淘宝商品详情页API接口、淘宝商品列表API接口,淘宝商品销量API接口,淘宝APP详情API接口,淘宝详情API接口
async / await
Paper reading [semantic tag enlarged xlnv model for video captioning]
Make web content editable