当前位置:网站首页>Don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
Don't know these four caching modes, dare you say you understand caching?
2022-07-05 13:21:00 【Luo Hanxiang】
I don't know. 4 Cache mode , Dare you understand cache ?

summary
In the system architecture , Caching is one of the easiest ways to provide system performance , Students with a little development experience will inevitably deal with caching , At least I have practiced .
If used properly , Caching can reduce response time 、 Reduce database load and save cost . But if the cache is not used properly , There may be some inexplicable problems .
In different scenarios , The caching strategy used also varies . If in your impression and experience , Caching is just a simple query 、 update operation , Then this article is really worth learning .
ad locum , Explain systematically for everyone 4 Three cache modes and their usage scenarios 、 Process and advantages and disadvantages .
Selection of caching strategy
In essence , Caching strategy depends on data and data access patterns . let me put it another way , How data is written and read .
for example :
Does the system write more and read less ?( for example , Time based logging )
Whether the data is written only once and read many times ?( for example , User profile )
Is the returned data always unique ?( for example , Search for )
Choosing the right caching strategy is the key to improving performance .
There are five common cache strategies :
Cache-Aside Pattern: Bypass caching mode
Read Through Cache Pattern: Read penetration mode
Write Through Cache Pattern: Write through mode
Write Behind Pattern: Also called Write Back, Asynchronous cache write mode
The above cache strategy is divided based on the data reading and writing process , Under some caching strategies, the application only interacts with the cache , Under some caching strategies, applications interact with caches and databases at the same time . Because this is an important dimension of strategy division , Therefore, you need to pay special attention to the following process learning .
Cache Aside
Cache Aside Is the most common caching mode , Applications can talk directly to caches and databases .Cache Aside It can be used for read and write operations .
Read operations Flow chart of :

Cache Aside Pattern
The process of reading operation :
The application receives a data query ( read ) request ;
Whether the data that the application needs to query is in the cache :
If there is (Cache hit), Query the data from the cache , Go straight back to ;
If it doesn't exist (Cache miss), Then retrieve data from the database , And stored in the cache , Return result data ;
Here we need to pay attention to an operation boundary , That is, the database and cache operations are directly operated by the application .
Write operations Flow chart of :

Cache Aside Pattern
The write operation here , Including the creation of 、 Update and delete . When writing operations ,Cache Aside The pattern is to update the database first ( increase 、 Delete 、 Change ), Then delete the cache directly .
Cache Aside Patterns can be said to apply to most scenarios , Usually in order to deal with different types of data , There are also two strategies to load the cache :
Load cache when using : When you need to use cached data , Query from the database , After the first query , Subsequent requests get data from the cache ;
Preload cache : Preload the cache information through the program at or after the project starts , such as ” National Information 、 Currency information 、 User information , News “ Wait for data that is not often changed .
Cache Aside It is suitable for reading more and writing less , For example, user information 、 News reports, etc , Once written to the cache , Almost no modification . The disadvantage of this mode is that the cache and database double write may be inconsistent .
Cache Aside It is also a standard model , image Facebook This mode is adopted .
Read Through
Read-Through and Cache-Aside Very similar , The difference is that the program doesn't need to focus on where to read data ( Cache or database ), It only needs to read data from the cache . Where the data in the cache comes from is determined by the cache .
Cache Aside The caller is responsible for loading the data into the cache , and Read Through The cache service itself will be used to load , So it is transparent to the application side .Read-Through Its advantage is to make the program code more concise .
This involves the application operation boundary problem we mentioned above , Look directly at the flow chart :

Read Through
In the above flow chart , Focus on the operations in the dotted box , This part of the operation is no longer handled by the application , Instead, the cache handles it itself . in other words , When an application queries a piece of data from the cache , If the data does not exist, the cache will load the data , Finally, the cache returns the data results to the application .
Write Through
stay Cache Aside in , The application needs to maintain two data stores : A cache , A database . This is for applications , It's a little cumbersome .
Write-Through In mode , All writes are cached , Every time you write data to the cache , The cache will persist the data to the corresponding database , And these two operations are completed in one transaction . therefore , Only if you succeed in writing twice can you finally succeed . The downside is write latency , The benefit is data consistency .
It can be understood as , Applications think that the back end is a single storage , And storage itself maintains its own Cache.
Because the program only interacts with the cache , Coding will become simpler and cleaner , This becomes especially obvious when the same logic needs to be reused in multiple places .

Write Through
When using Write-Through when , Generally, it is used together Read-Through To use .Write-Through The potential use scenario for is the banking system .
Write-Through Applicable cases are :
You need to read the same data frequently
Can't stand data loss ( relative Write-Behind for ) Inconsistent with the data
In the use of Write-Through Special attention should be paid to the effectiveness management of cache , Otherwise, a large amount of cache will occupy memory resources . Even valid cache data is cleared by invalid cache data .
Write-Behind
Write-Behind and Write-Through stay ” The program only interacts with the cache and can only write data through the cache “ This aspect is very similar . The difference is Write-Through The data will be written into the database immediately , and Write-Behind After a while ( Or triggered by other ways ) Write the data together into the database , This asynchronous write operation is Write-Behind The biggest feature .
Database write operations can be done in different ways , One way is to collect all write operations and at a certain point in time ( For example, when the database load is low ) Batch write . Another way is to merge several write operations into a small batch operation , Then the cache collects write operations and writes them in batches .
Asynchronous write operations greatly reduce request latency and reduce the burden on the database . At the same time, it also magnifies the inconsistency of data . For example, someone directly queries data from the database at this time , But the updated data has not been written to the database , At this time, the queried data is not the latest data .
Summary
Different caching modes have different considerations and characteristics , According to the different scenarios of application requirements , You need to choose the appropriate cache mode flexibly . In the process of practice, it is often a combination of multiple modes .
边栏推荐
- MATLAB论文图表标准格式输出(干货)
- Rocky基础知识1
- 【每日一题】1200. 最小绝对差
- Lb10s-asemi rectifier bridge lb10s
- 国际自动机工程师学会(SAE International)战略投资几何伙伴
- mysql econnreset_Nodejs 套接字报错处理 Error: read ECONNRESET
- Apicloud studio3 API management and debugging tutorial
- 碎片化知识管理工具Memos
- SAE international strategic investment geometry partner
- 一网打尽异步神器CompletableFuture
猜你喜欢

百度杯”CTF比赛 2017 二月场,Web:爆破-2
Pycharm installation third party library diagram
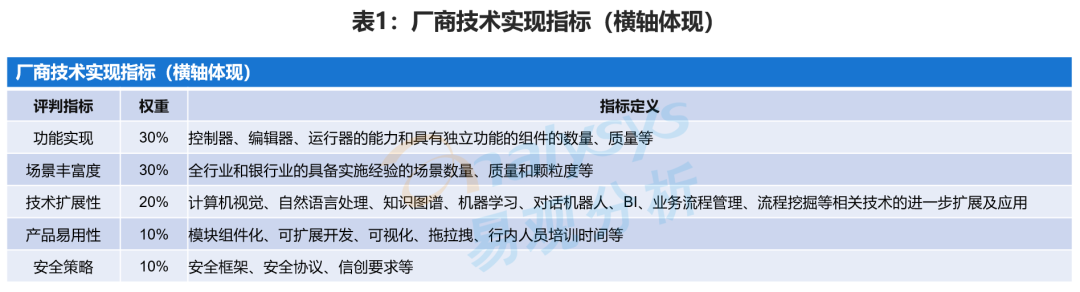
《2022年中國銀行業RPA供應商實力矩陣分析》研究報告正式啟動
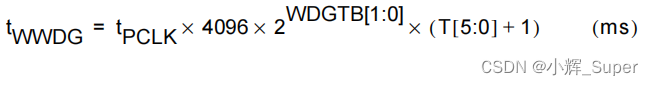
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(HAL 库)—— 实验7 窗口看门狗实验(学习笔记)

Shu tianmeng map × Weiyan technology - Dream map database circle of friends + 1

DataPipeline双料入选中国信通院2022数智化图谱、数据库发展报告
MSTP and eth trunk
Fragmented knowledge management tool memos
What is a network port
Word document injection (tracking word documents) incomplete
随机推荐
Laravel document reading notes -mews/captcha use (verification code function)
The Research Report "2022 RPA supplier strength matrix analysis of China's banking industry" was officially launched
Datapipeline was selected into the 2022 digital intelligence atlas and database development report of China Academy of communications and communications
"Baidu Cup" CTF competition in September, web:sql
[notes of in-depth study paper]uctransnet: rethink the jumping connection in u-net from the perspective of transformer channel
“百度杯”CTF比赛 九月场,Web:SQL
Fragmented knowledge management tool memos
C object storage
南理工在线交流群
CloudCompare——点云切片
How to choose note taking software? Comparison and evaluation of notion, flowus and WOLAI
Difference between avc1 and H264
精彩速递|腾讯云数据库6月刊
【MySQL 使用秘籍】一网打尽 MySQL 时间和日期类型与相关操作函数(三)
Talking about fake demand from takeout order
[deep learning paper notes] hnf-netv2 for segmentation of brain tumors using multimodal MR imaging
ASEMI整流桥HD06参数,HD06图片,HD06应用
Talk about seven ways to realize asynchronous programming
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(HAL 库)—— 实验7 窗口看门狗实验(学习笔记)
LB10S-ASEMI整流桥LB10S