当前位置:网站首页>type_traits metaprogramming library learning
type_traits metaprogramming library learning
2022-07-31 03:32:00 【Wash your feet in Pangong Lake】
type_traitsis part of the metaprogramming library,This library is mainly used to determine the data type,比如,判断类型是否为空,是否为空指针,是否为整型,Whether it is a float or not whether it is an array,Is it an enumeration type,Is it a union,是否为函数,是否为指针,Is it an lvalue reference,Is it an rvalue reference,等等,There are many types of judgments,This article introduces a few basic ones.
Basic type classification | |
(C++11) | 检查类型是否为 void (类模板) |
(C++14) | 检查类型是否为 std::nullptr_t (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is an integer (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is a floating point type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is an array type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is an enumeration type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is a union type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is not a union class type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if it is a function type (类模板) |
(C++11) | Check if the type is a pointer type (类模板) |
(C++11) | 检查类型是否为左值引用 (类模板) |
(C++11) | 检查类型是否为右值引用 (类模板) |
(C++11) | Checks if the type is a pointer to a non-static member object (类模板) |
(C++11) | Checks if the type is a pointer to a non-static member function (类模板) |
1. is_void 检查类型是否为 void
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_void<void>::value==========" << std::is_void<void>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_void<int>::value===========" << std::is_void<int>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2. is_null_pointer 检查类型是否为 std::nullptr_t
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_null_pointer<decltype(nullptr)>::value = " << is_null_pointer<decltype(nullptr)>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_null_pointer<int*>::value = " << is_null_pointer<int*>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

3. is_integral Check if the type is an integer
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {};
enum E: int {};
template <class T>
T fn(T i)
{
static_assert (std::is_integral<T>::value, "Integral required.");
return i;
}
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_integral<A>::value======= " << std::is_integral<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_integral<E>::value======= " << std::is_integral<E>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_integral<float>::value=== " << std::is_integral<float>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_integral<int>::value===== " << std::is_integral<int>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_integral<bool>::value==== " << std::is_integral<bool>::value << endl;
cout << "fn(123)========================== " << fn(123) << endl;
//cout << "fn(123.5)======================== " << fn(123.5) << endl; //编译失败
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

4. is_floating_point Check if the type is a floating point type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {};
int main()
{
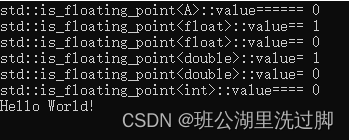
cout << "std::is_floating_point<A>::value====== " << std::is_floating_point<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_floating_point<float>::value== " << std::is_floating_point<float>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_floating_point<float>::value== " << std::is_floating_point<float&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_floating_point<double>::value= " << std::is_floating_point<double>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_floating_point<double>::value= " << std::is_floating_point<double&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_floating_point<int>::value==== " << std::is_floating_point<int>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
5. is_array Check if the type is an array type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {};
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_array<A>::value============ " << std::is_array<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<A[]>::value========== " << std::is_array<A[]>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<A[3]>::value========= " << std::is_array<A[3]>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<float>::value======== " << std::is_array<float>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<int>::value========== " << std::is_array<int>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<int[]>::value======== " << std::is_array<int[]>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<int[3]>::value======= " << std::is_array<int[3]>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_array<array<int,3>>::value= " << std::is_array<array<int,3>>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

6. is_enum Check if the type is an enumeration type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {};
enum E {};
enum class Ec: int {};
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_enum<A>::value====== " << std::is_enum<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_enum<E>::value====== " << std::is_enum<E>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_enum<Ec>::value===== " << std::is_enum<Ec>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_enum<int>::value==== " << std::is_enum<int>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

7. is_union Check if the type is a union type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {};
typedef union {
int a;
float b;
} B;
class C {
B d;
};
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_union<A>::value======== " << std::is_union<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_union<B>::value======== " << std::is_union<B>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_union<C>::value======== " << std::is_union<C>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_union<int>::value====== " << std::is_union<int>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

8. is_class Check if the type is not a union class type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
struct A { };
class B { } ;
enum class C { };
int main()
{
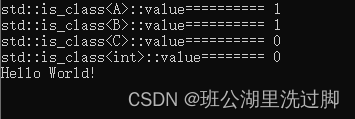
cout << "std::is_class<A>::value========== " << std::is_class<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_class<B>::value========== " << std::is_class<B>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_class<C>::value========== " << std::is_class<C>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_class<int>::value======== " << std::is_class<int>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:
9. is_function Check if it is a function type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
struct A {
int fun() const &;
};
template<typename>
struct PM_traits { };
template<class T, class U>
struct PM_traits<U T::*> {
using member_type = U;
};
int f();
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_function<A>::value================= " << std::is_function<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_function<int(int)>::value========== " << std::is_function<int(int)>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_function<decltype(f)>::value======= " << std::is_function<decltype(f)>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_function<int>::value=============== " << std::is_function<int>::value << endl;
using T = PM_traits<decltype(&A::fun)>::member_type; //T为int() const&
cout << "std::is_function<T>::value================= " << std::is_function<T>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

10. is_pointer Check if the type is a pointer type
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
struct A {
int fun() const &;
};
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_pointer<A>::value ================= " << is_pointer<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<A *>::value =============== " << is_pointer<A *>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<A &>::value =============== " << is_pointer<A &>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<int>::value =============== " << is_pointer<int>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<int *>::value ============= " << is_pointer<int *>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<int **>::value ============ " << is_pointer<int **>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<int[10]>::value =========== " << is_pointer<int[10]>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<nullptr_t>::value ========= " << is_pointer<nullptr_t>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_pointer<decltype(nullptr)>::value = " << is_pointer<decltype(nullptr)>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

11. is_lvalue_reference Checks if the type is an lvalue reference
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A { };
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<A>::value====== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<A&>::value===== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<A&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<A&&>::value==== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<A&&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<int>::value==== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<int>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<int&>::value=== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<int&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_lvalue_reference<int&&>::value== " << std::is_lvalue_reference<int&&>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

12. is_rvalue_reference Checks if the type is an rvalue reference
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A { };
int main()
{
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<A>::value====== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<A>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<A&>::value===== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<A&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<A&&>::value==== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<A&&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<int>::value==== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<int>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<int&>::value=== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<int&>::value << endl;
cout << "std::is_rvalue_reference<int&&>::value== " << std::is_rvalue_reference<int&&>::value << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

13. is_member_object_pointer Checks if the type is a pointer to a non-static member object
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
class cls {};
std::cout << (std::is_member_object_pointer<int(cls::*)>::value
? "T is member object pointer"
: "T is not a member object pointer") << endl;
std::cout << (std::is_member_object_pointer<int(cls::*)()>::value
? "T is member object pointer"
: "T is not a member object pointer") << endl;
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

14. is_member_function_pointer Checks if the type is a pointer to a non-static member function
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
void member() { }
};
int main()
{
// 若 A::member is a data member not a function,fails at compile time
static_assert(std::is_member_function_pointer<decltype(&A::member)>::value,
"A::member is not a member function.");
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}
参考:
边栏推荐
- TCP详解(一)
- Daily practice of LeetCode - 138. Copy a linked list with random pointers
- 【编译原理】递归下降语法分析设计原理与实现
- 进程间通信
- Mysql 45 study notes (twenty-four) MYSQL master-slave consistency
- Implementation of a sequence table
- TCP和UDP详解
- (线段树) 基础线段树常见问题总结
- 【异常】The field file exceeds its maximum permitted size of 1048576 bytes.
- [C language] General method of expression evaluation
猜你喜欢

A brief introduction to the showDatePicker method of the basic components of Flutter

No qualifying bean of type 问题
The application and practice of mid-to-platform brand advertising platform

【编译原理】递归下降语法分析设计原理与实现

SIP协议标准和实现机制

Database implements distributed locks

大小端模式

浅识Flutter 基本组件之CheckboxListTile组件
识Flutter 基本组件之showTimePicker 方法
postgresql 15源码浅析(5)—— pg_control
随机推荐
CloudCompare & PCL calculate the degree of overlap between two point clouds
Use of QML
【C语言】预处理操作
C primer plus study notes - 8, structure
7年经验,功能测试工程师该如何一步步提升自己的能力呢?
下载jar包的好地方
C# remote debugging
Pytest电商项目实战(上)
BUG definition of SonarQube
识Flutter 基本组件之showTimePicker 方法
TCP详解(一)
Know the showTimePicker method of the basic components of Flutter
$parent/$children 与 ref
立足本土,链接全球 | 施耐德电气“工业SI同盟”携手伙伴共赴未来工业
CloudCompare&PCL 计算两个点云之间的重叠度
endian mode
LeetCode simple problem to find the subsequence of length K with the largest sum
Good place to download jar packages
C语言从入门到如土——数据的存储
安全20220722