当前位置:网站首页>【Postman】测试(Tests)脚本编写和断言详解
【Postman】测试(Tests)脚本编写和断言详解
2022-07-06 05:59:00 【lichong951】
测试确认您的 API 按预期工作,服务之间的集成运行可靠,并且新开发没有破坏任何现有功能。您可以使用 JavaScript 为 Postman API 请求编写测试脚本。当您的 API 项目出现问题时,您还可以使用测试代码来帮助调试过程。例如,您可以编写一个测试,通过发送包含不完整数据或不正确参数的请求来验证 API 的错误处理。
您可以将测试添加到集合中的单个请求、集合和文件夹。Postman 包含您添加然后修改以适合您的测试逻辑的代码片段。
要将测试添加到请求,请打开请求并在“测试”选项卡中输入您的代码。测试将在请求运行后执行。您将能够在响应数据旁边的“测试结果”选项卡中看到输出。
下图有一个简单的例子
断言定义如下:
//断言返回状态码是200
pm.test("断言返回状态码是200", function () {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
结果如下图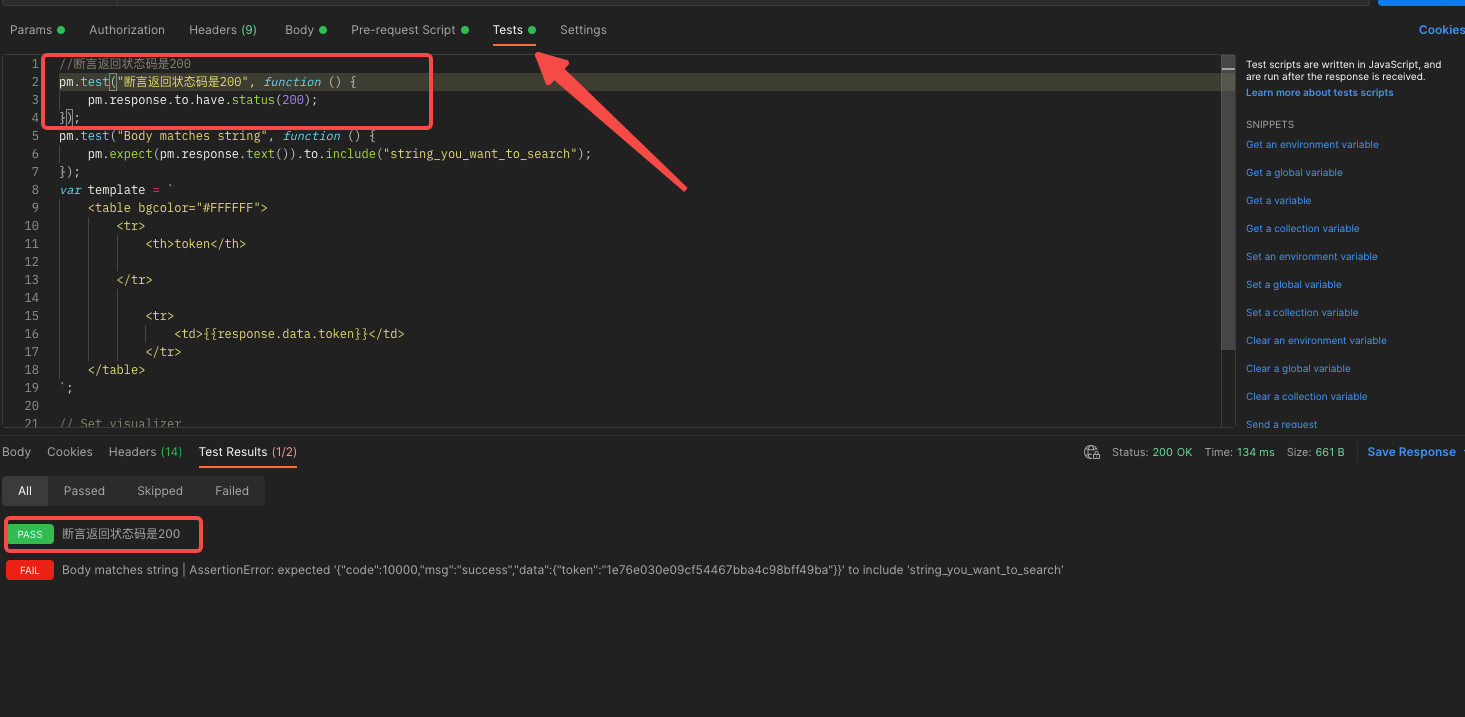
编写断言
测试脚本可以使用动态变量,对响应数据执行测试断言,并在请求之间传递数据。在请求的测试选项卡中,手动输入您的 JavaScript 或使用您将在代码编辑器右侧看到的片段。
收到响应后执行测试。当您选择Send时,Postman 会在响应数据从 API 返回后运行您的测试脚本。
验证响应
要验证请求返回的数据,您可以pm.response在测试中使用该对象。使用该函数定义测试pm.test,提供一个名称和函数,该函数返回一个布尔 (true或false) 值,指示测试是通过还是失败。在你的断言中使用ChaiJS BDD语法pm.expect来测试响应细节。
该.test函数的第一个参数是一个文本字符串,它将出现在测试结果输出中。使用它来识别您的测试,并将测试的目的传达给查看结果的任何人。
例如,在请求的“测试”选项卡中输入以下内容以测试响应状态代码是否为200:
//断言返回状态码是200
pm.test("断言返回状态码是200", function () {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
选择发送以运行您的请求并在响应部分打开测试结果。选项卡标题显示通过了多少测试以及总共运行了多少。您还可以查看Passed、Skipped和Failed测试结果的数量。
如果请求返回200状态码,则测试通过。要查看不同状态代码会发生什么,请更改测试脚本中的预期状态代码并再次运行请求
使用 pm.expect 格式化测试结果消息
使用该pm.expect语法可为您的测试结果消息提供不同的格式。尝试替代方案以实现您认为最有用的输出。
您的代码可以测试请求环境,如下例所示:
pm.test("environment to be production", function () {
pm.expect(pm.environment.get("env")).to.equal("production");
});
您可以使用不同的语法变体以您认为可读且适合您的应用程序和测试逻辑的方式编写测试。
pm.test("response should be okay to process", function () {
pm.response.to.not.be.error;
pm.response.to.have.jsonBody("");
pm.response.to.not.have.jsonBody("error");
});
您的测试可以使用您为响应数据格式定制的语法来确定请求响应的有效性。
pm.test("response must be valid and have a body", function () {
pm.response.to.be.ok;
pm.response.to.be.withBody;
pm.response.to.be.json;
});
您的脚本可以包含您需要的任意数量的测试,并且在您选择Save时将与您的其余请求详细信息一起保存。如果您共享一个集合、发布文档或使用在 Postman 中运行按钮,您的测试代码将包含在任何查看或导入您的模板的人中。
测试集合和文件夹
您可以将测试脚本添加到集合、文件夹或集合中的单个请求。与集合关联的测试脚本将在集合中的每个请求之后运行。与文件夹关联的测试脚本将在文件夹中的每个请求之后运行。这使您能够在每次请求后重用通常执行的测试。每个请求的执行顺序是集合测试,文件夹测试,然后是请求测试。
将脚本添加到集合和文件夹使您能够测试 API 项目中的工作流。这有助于确保您的请求涵盖典型场景,为应用程序用户提供可靠的体验。
更多操作图标 您可以通过选择集合或文件夹名称旁边的查看更多操作图标并选择编辑来更新集合和文件夹脚本 。选择测试选项卡以添加或更新您的脚本。您还可以在首次创建集合时添加集合脚本。
运行集合时,您将看到集合运行器输出的测试结果。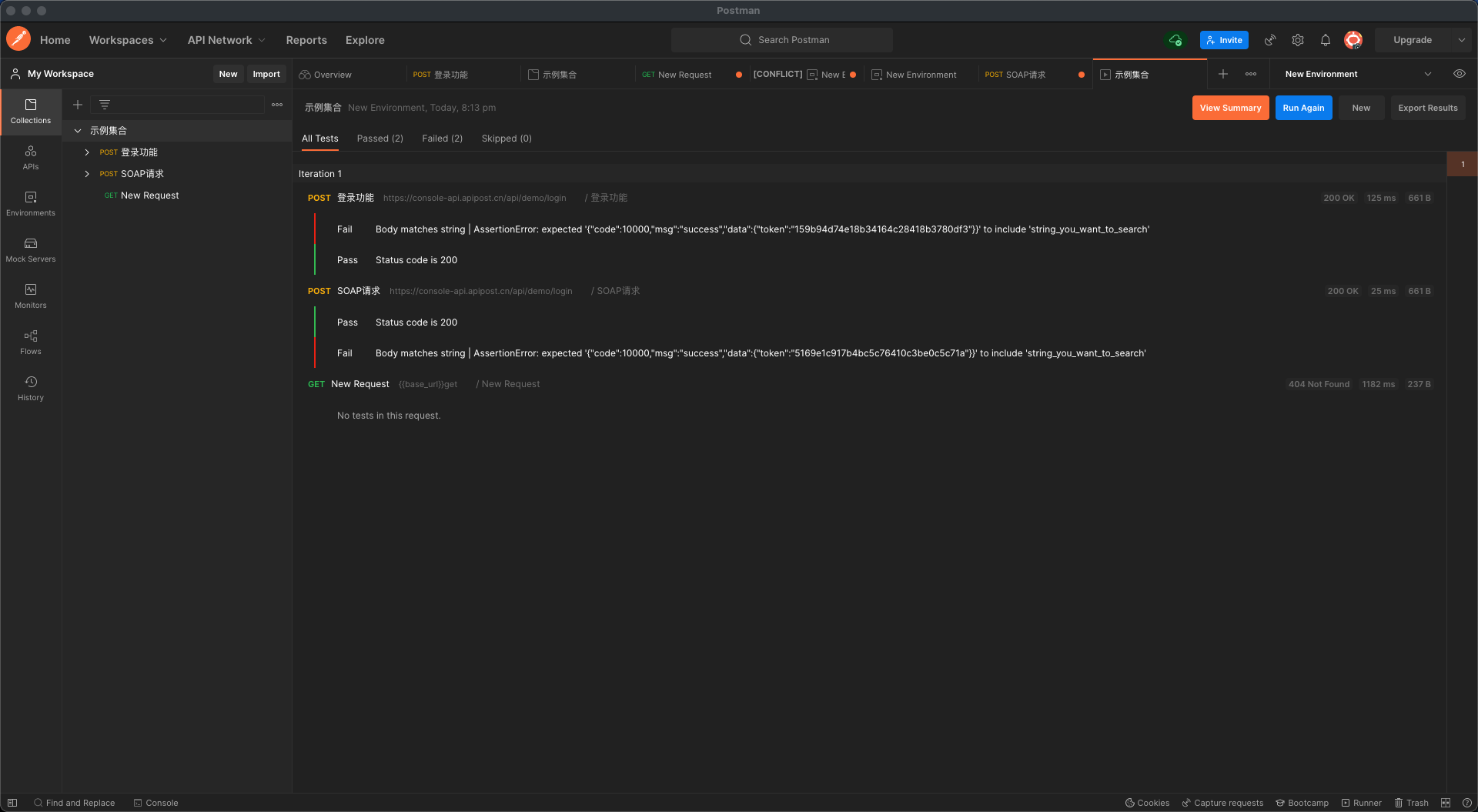
断言测试脚本
使用您的请求、文件夹和集合中的“测试”选项卡来编写测试,这些测试将在 Postman 收到来自您发送请求的 API 的响应时执行。为每个请求添加您需要的许多测试。当您将测试添加到文件夹或集合时,它们将在其中的每个请求之后执行。
使用多个断言
您的测试可以包含多个断言作为单个测试的一部分。使用它来组合相关的断言:
pm.test("The response has all properties", () => {
//parse the response JSON and test three properties
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(responseJson.type).to.eql('vip');
pm.expect(responseJson.name).to.be.a('string');
pm.expect(responseJson.id).to.have.lengthOf(1);
});
如果任何包含的断言失败,则整个测试将失败。所有断言必须成功才能通过测试。
解析响应正文数据
要对您的响应执行断言,您首先需要将数据解析为您的断言可以使用的 JavaScript 对象。
要解析 JSON 数据,请使用以下语法
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
要解析 XML,请使用以下命令:
const responseJson = xml2Json(pm.response.text());
要解析 CSV,请使用CSV 解析实用程序:
const parse = require('csv-parse/lib/sync');
const responseJson = parse(pm.response.text());
要解析 HTML,请使用cheerio
const $ = cheerio.load(pm.response.text());
//output the html for testing
console.log($.html());
处理不解析的响应
如果您无法将响应正文解析为 JavaScript,因为它没有格式化为 JSON、XML、HTML、CSV 或任何其他可解析的数据格式,您仍然可以对数据进行断言。
测试响应正文是否包含字符串:
pm.test("Body contains string",() => {
pm.expect(pm.response.text()).to.include("customer_id");
});
这不会告诉您在哪里遇到字符串,因为它对整个响应正文执行测试。测试响应是否与字符串匹配(通常仅对短响应有效):
pm.test("Body is string", function () {
pm.response.to.have.body("whole-body-text");
});
对 HTTP 响应进行断言
您的测试可以检查请求响应的各个方面,包括正文、状态代码、标头、cookie、响应时间等。
测试响应体
检查响应正文中的特定值:
pm.test("Person is Jane", () => {
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(responseJson.name).to.eql("Jane");
pm.expect(responseJson.age).to.eql(23);
});
测试状态码
测试响应状态码:
pm.test("Status code is 201", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status(201);
});
如果您想测试状态代码是否是一组中的一个,请将它们全部包含在一个数组中并使用oneOf:
pm.test("Successful POST request", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.code).to.be.oneOf([201,202]);
});
检查状态码文本:
pm.test("Status code name has string", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status("Created");
});
测试标头
检查是否存在响应标头:
pm.test("Content-Type header is present", () => {
pm.response.to.have.header("Content-Type");
});
测试具有特定值的响应标头:
pm.test("Content-Type header is application/json", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.headers.get('Content-Type')).to.eql('application/json');
});
测试 cookie
测试响应中是否存在 cookie:
pm.test("Cookie JSESSIONID is present", () => {
pm.expect(pm.cookies.has('JSESSIONID')).to.be.true;
});
测试特定的 cookie 值:
pm.test("Cookie isLoggedIn has value 1", () => {
pm.expect(pm.cookies.get('isLoggedIn')).to.eql('1');
});
测试响应时间
测试响应时间是否在指定范围内:
pm.test("Response time is less than 200ms", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.responseTime).to.be.below(200);
});
断言示例
针对变量断言响应值
检查响应属性是否与变量(在本例中为环境变量)具有相同的值:
pm.test("Response property matches environment variable", function () {
pm.expect(pm.response.json().name).to.eql(pm.environment.get("name"));
});
断言值类型
测试响应的任何部分的类型:
/* response has this structure: { "name": "Jane", "age": 29, "hobbies": [ "skating", "painting" ], "email": null } */
const jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.test("Test data type of the response", () => {
pm.expect(jsonData).to.be.an("object");
pm.expect(jsonData.name).to.be.a("string");
pm.expect(jsonData.age).to.be.a("number");
pm.expect(jsonData.hobbies).to.be.an("array");
pm.expect(jsonData.website).to.be.undefined;
pm.expect(jsonData.email).to.be.null;
});
断言数组属性
检查数组是否为空,以及它是否包含特定项:
/* response has this structure: { "errors": [], "areas": [ "goods", "services" ], "settings": [ { "type": "notification", "detail": [ "email", "sms" ] }, { "type": "visual", "detail": [ "light", "large" ] } ] } */
const jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.test("Test array properties", () => {
//errors array is empty
pm.expect(jsonData.errors).to.be.empty;
//areas includes "goods"
pm.expect(jsonData.areas).to.include("goods");
//get the notification settings object
const notificationSettings = jsonData.settings.find
(m => m.type === "notification");
pm.expect(notificationSettings)
.to.be.an("object", "Could not find the setting");
//detail array must include "sms"
pm.expect(notificationSettings.detail).to.include("sms");
//detail array must include all listed
pm.expect(notificationSettings.detail)
.to.have.members(["email", "sms"]);
});
断言对象属性
断言一个对象包含键或属性:
pm.expect({
a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.all.keys('a', 'b');
pm.expect({
a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.any.keys('a', 'b');
pm.expect({
a: 1, b: 2}).to.not.have.any.keys('c', 'd');
pm.expect({
a: 1}).to.have.property('a');
pm.expect({
a: 1, b: 2}).to.be.an('object')
.that.has.all.keys('a', 'b');
目标可以是object、set或。如果在没有or的情况下运行,则表达式默认为。由于行为因目标而异,建议在使用前检查with 。arraymap.keys.all.any.all.keystypetype.keys.a
断言一个值在一个集合中
根据有效选项列表检查响应值:
pm.test("Value is in valid list", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.json().type)
.to.be.oneOf(["Subscriber", "Customer", "User"]);
});
断言包含一个对象
检查对象是否是父对象的一部分:
/* response has the following structure: { "id": "d8893057-3e91-4cdd-a36f-a0af460b6373", "created": true, "errors": [] } */
pm.test("Object is contained", () => {
const expectedObject = {
"created": true,
"errors": []
};
pm.expect(pm.response.json()).to.deep.include(expectedObject);
});
Using.deep导致链中所有.equal, .include, .members, .keys, 和.property断言使用深度相等(松散相等)而不是严格 ( ===) 相等。虽然.eql也比较松散,但.deep.equal导致深度相等比较也可用于链中的任何其他断言,而.eql不会。
断言当前环境
检查 Postman 中的活动(当前选择的)环境:
pm.test("Check the active environment", () => {
pm.expect(pm.environment.name).to.eql("Production");
});
排除常见测试错误
当您在测试脚本中遇到错误或意外行为时,Postman控制台可以帮助您识别来源。通过将console.log()、和debug 语句与您的测试断言相结合console.info(),您可以检查 HTTP 请求和响应的内容,以及诸如变量之类的 Postman 数据项。从 Postman 页脚中选择 控制台以将其打开。console.warn()console.error()
记录变量或响应属性的值:
console.log(pm.collectionVariables.get("name"));
console.log(pm.response.json().name);
记录变量或响应属性的类型:
console.log(typeof pm.response.json().id);
使用控制台日志来标记代码执行,有时称为“跟踪语句”:
if (pm.response.json().id) {
console.log("id was found!");
// do something
} else {
console.log("no id ...");
//do something else
}
断言深度相等错误
你可能会遇到AssertionError: expected to deeply equal ‘’. 例如,这将出现在以下代码中:
pm.expect(1).to.eql("1");
发生这种情况是因为测试将数字与字符串值进行比较。只有当类型和值都相等时,测试才会返回 true。
JSON 未定义错误
你可能会遇到这个ReferenceError: jsonData is not defined问题。当您尝试引用尚未声明或超出测试代码范围的 JSON 对象时,通常会发生这种情况。
pm.test("Test 1", () => {
const jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.name).to.eql("John");
});
pm.test("Test 2", () => {
pm.expect(jsonData.age).to.eql(29); // jsonData is not defined
});
确保所有测试代码都可以访问将响应数据设置为变量的任何代码,例如在这种情况下const jsonData = pm.response.json();,在第一个代码之前移动pm.test会使它对两个测试函数都可用。
断言未定义的错误
你可能会遇到这个AssertionError: expected undefined to deeply equal…问题。当您引用不存在或超出范围的属性时,通常会发生这种情况。
pm.expect(jsonData.name).to.eql("John");
在上面的示例中,如果您看到AssertionError: expected undefined to deeply equal ‘John’,这表明该name属性未在jsonData对象中定义。
测试没有失败
在某些情况下,您可能希望测试失败,但事实并非如此。
//test function not properly defined - missing second parameter
pm.test("Not failing", function () {
pm.expect(true).to.eql(false);
});
确保您的测试代码在语法上正确并再次发送您的请求。
验证响应结构
使用 Tiny Validator V4 (tv4) 执行 JSON 模式验证:
const schema = {
"items": {
"type": "boolean"
}
};
const data1 = [true, false];
const data2 = [true, 123];
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data1, schema)).to.be.true;
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data2, schema)).to.be.true;
});
使用 Ajv JSON 模式验证器验证 JSON 模式:
const schema = {
"properties": {
"alpha": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
};
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.response.to.have.jsonSchema(schema);
});
发送异步请求
从您的测试代码发送请求并记录响应。
pm.sendRequest("https://postman-echo.com/get", function (err, response) {
console.log(response.json());
});
边栏推荐
- Novice entry SCM must understand those things
- Yygh-11-timing statistics
- 【论文阅读】NFlowJS:基于鲁棒学习的合成负数据密集异常检测
- Embedded point test of app
- 假设检验学习笔记
- Configuring OSPF GR features for Huawei devices
- Download, install and use NVM of node, and related use of node and NRM
- 华为路由器如何配置静态路由
- 【课程笔记】编译原理
- Testing and debugging of multithreaded applications
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
P2802 go home
Bit operation rules
假设检验学习笔记
Demander le Code de texte standard correspondant à un centre de travail dans l'ordre de production
CoDeSys note 2: set coil and reset coil
实践分享:如何安全快速地从 Centos迁移到openEuler
Station B Liu Erden softmx classifier and MNIST implementation -structure 9
GTSAM中李群的運用
Eigen稀疏矩阵操作
Detailed explanation of BF and KMP
Practice sharing: how to safely and quickly migrate from CentOS to openeuler
Embedded point test of app
Grant Yu, build a web page you want from 0
First knowledge database
Classes and objects (I) detailed explanation of this pointer
Interface test: what are the components of the URL in fiddler
【C语言】qsort函数
公司視頻加速播放
Usage of test macro of GTEST
About PHP startup, mongodb cannot find the specified module