当前位置:网站首页>Memory and stack related concepts
Memory and stack related concepts
2022-07-06 05:46:00 【qq_ twenty-nine million five hundred and sixty-six thousand six】
Memory
The smallest storage unit in a computer is bytes , Memory is no exception , Each byte acts as a storage unit . In this way, the memory is divided into hundreds of millions of memory units , To facilitate the management of these units , The computer has chosen to number each memory unit , When you want to use a memory unit , Just specify the memory unit number ( Memory address ) that will do . In order to number as many addresses as possible , The computer uses a 4 Number of bytes to address memory , This is good for 2^32 Block memory for addressing , Each block is 1byte,2^32 byte = 4Gb, The memory size that can be addressed is 4G size .
Stack
When the program runs, it will not immediately allocate all memory for the program , Will initialize a certain size of memory area to the program , Memory blocks in this memory space can be used by programs , Used to store data in the program . This space is used from memory blocks with large addresses , To see which address memory unit is used by the current stack , stay ESP The current memory location used is recorded in the register , If you add a data , Will be added at this location , then ESP Continue to move forward one position . therefore ESP The current position of the register record , Is the position of the next data insertion . This pointer is called the stack top pointer , The pointer is added with the data (push) And take out (pop) Move . alike ,EBP The address of the beginning of a stack is recorded in , Become a pointer at the bottom of the stack , The address usually does not change , Only in opening up a new stack space , For example, when executing a function call , When you need to re record a new function space for a function , Will change the position of the bottom of the stack . But when changing the pointer at the bottom of the stack , The original position at the bottom of the stack will be put on the stack and saved , It is convenient to restore to the original bottom of the stack in the future .
Stack elevation
We know , In advanced languages , When we execute a function call , Will open up a new stack space , At this point, stack lifting is required , You need to change ESP and EBP Bottom of stack and bottom of stack pointer recorded in register , In this way, the value generated in the function will not affect the original stack space ( The yellow part ) The data of . The right figure shows the result of stack elevation , here push The data will come from 1005 Start adding ,pop Only to 1005 The data of this address , Can't go down any further pop, This will not affect the contents of the metastack .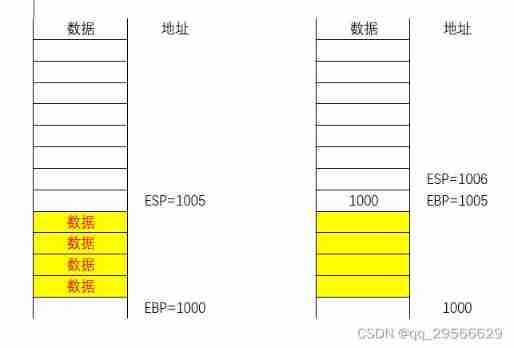
Stack balance
Stack balancing is actually restoring stack contents , For example, when performing a function operation , Stack up , Open up new space for functions , When function execution ends , The bottom and top pointers should be restored to their original positions .
The brief process is
1. take ESP Value in register , Change to EBP Value , In this way, the top of the stack is at the current bottom of the stack .ESP=1005
2. take EBP Get the value in the memory address pointed to by the register , namely 1000, take EBP The value of the register is changed to this value 1000. such EBP Back to 1000 The location of .
Thus, the stack recovery is completed , Stack balance is achieved
Data width
There are three data widths in assembly language , Respectively
BYTE: One byte wide , Occupy 8 position
WORD: word , Two bytes wide , Occupy 16 position
DOUBLEWORD: Two words , Four byte width , Occupy 32 position .
Large and small end mode
Memory is addressed from small to large , When storing a multi byte data , If the small address of memory stores the high order of multi byte data , It's the big end model . in other words , First get the high bit of the data for storage , Then take the low order storage . For example, a string "abcd",a Is the high order of the data ,d It's low , The memory will take out four consecutive memory spaces to store this string . If this continuous memory is stored in a small address a And then in turn bcd, It's the big end model . If the low order data is stored in the small address , Small end mode .
It is up to the compiler to store the data in big end or small end mode .
add , All registers contain addresses
边栏推荐
- 自建DNS服务器,客户端打开网页慢,解决办法
- Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 73_ Webmin
- 【华为机试真题详解】统计射击比赛成绩
- Station B Liu Erden - linear regression and gradient descent
- The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
- 【经验】win11上安装visio
- Closure, decorator
- The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
- Remember an error in MySQL: the user specified as a definer ('mysql.infoschema '@' localhost ') does not exist
- 网络协议模型
猜你喜欢

什么是独立IP,独立IP主机怎么样?
【torch】|torch. nn. utils. clip_ grad_ norm_

授予渔,从0开始搭建一个自己想要的网页
华为BFD的配置规范
类和对象(一)this指针详解
ArcGIS应用基础4 专题图的制作
03. 开发博客项目之登录

What impact will frequent job hopping have on your career?

The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower

大型网站如何选择比较好的云主机服务商?
随机推荐
华为路由器如何配置静态路由
Pytorch代码注意的细节,容易敲错的地方
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
改善Jpopup以实现动态控制disable
[experience] install Visio on win11
大型网站如何选择比较好的云主机服务商?
Anti shake and throttling are easy to understand
Auto. JS learning notes 17: basic listening events and UI simple click event operations
【SQL server速成之路】——身份验证及建立和管理用户账户
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
Jushan database appears again in the gold fair to jointly build a new era of digital economy
【华为机试真题详解】检查是否存在满足条件的数字组合
[Jiudu OJ 08] simple search x
通讯录管理系统链表实现
[force buckle]43 String multiplication
28io stream, byte output stream writes multiple bytes
Rustdesk builds its own remote desktop relay server
Practice sharing: how to safely and quickly migrate from CentOS to openeuler
P2802 回家
Garbage collector with serial, throughput priority and response time priority