当前位置:网站首页>Data Lake (IX): Iceberg features and data types
Data Lake (IX): Iceberg features and data types
2022-07-07 14:31:00 【51CTO】
Iceberg Feature details and data types
One 、Iceberg Feature details
1、Iceberg Partition and hidden partition (Hidden Partition)
Iceberg Support partition to speed up data query . stay Iceberg After setting partition in , Similar rows can be grouped when writing data , Speed up query when querying .Iceberg Can be in accordance with the year 、 month 、 Day and hour granularity time stamp organization partition .
stay Hive Partition is also supported in , But if you want to make partitions faster , Need to write SQL Specify the corresponding partition conditions to filter the data , stay Iceberg Write in SQL There is no need to query SQL Partition filtering conditions are specially specified in ,Iceberg Will automatically partition , Filter out unwanted data .
stay Iceberg Partition information in can be hidden ,Iceberg The partition field of can be calculated by one field , After creating tables or modifying partition policies , The new data will automatically calculate the partition to which it belongs , When querying, you also don't need to care about what fields the table partition is , Just focus on the business logic ,Iceberg Automatic data partitioning is not required .
It is because of Iceberg The partition information and table data storage directory are independent , bring Iceberg Table partitions can be modified , And it won't involve data migration .
2、Iceberg Performative (Table Evolution)
stay Hive In the partition table , If you change a table divided by days to divided by hours , Then there is no way to modify the original table , You need to create a table partitioned by hours , Then load the data into this table .
Iceberg Support the evolution of the earth's surface , Can pass SQL Table level schema evolution , for example : Change table partition layout .Iceberg When doing the above , The price is very low , There is no time-consuming and laborious operation of reading data, rewriting or migrating data .
3、 Pattern evolution (Schema Evolution)
Iceberg The following are supported Schema Evolution of :
- ADD: Add new columns to a table or nested structure .
- Drop: Remove columns from a table or nested structure .
- Rename: Rename a column in a table or nested structure .
- Update: Complex structures (Struct、Map<Key,Value>,list) The length of the basic type extension type in , such as :tinyint Modified into int.
- Reorder: Change the order of columns , You can also change the sort order of the fields in the nested structure .
Be careful :
Iceberg Schema The change is just the operation change of metadata , It doesn't involve rewriting data files .Map Structure type does not support Add and Drop Field .
Iceberg Guarantee Schema Evolution is an independent operation without side effects , It doesn't involve rewriting data files , As follows :
- Adding a column does not read existing data from another column
- When deleting a field in a column or nested structure , Does not change the value of any other column .
- When updating a field in a column or nested structure , Does not change the value of any other column .
- When changing the order of fields in a column or nested structure , Does not change the associated value .
Iceberg For the above reasons, use the only id To track every column in the table , When adding a column , New... Will be assigned ID, Therefore, the data corresponding to the column will not be misused .
4、 Partition evolution (partition Evolution)
Iceberg Partitions can be updated in existing tables , because Iceberg The query process is not directly related to the partition information .
When we change the partition policy of a table , The data before modifying the partition will not change , The old partition strategy will still be adopted , New data will adopt a new partition strategy , In other words, the same table will have two partition strategies , The old data adopts the old partition policy , The new data adopts the new partition strategy , In metadata, the two partition policies are independent of each other , Not coincident .
therefore , Before we write SQL When making data query , If there is a cross partition policy , It will be resolved into two different execution plans , Such as Iceberg The official website provides... As shown in the figure :
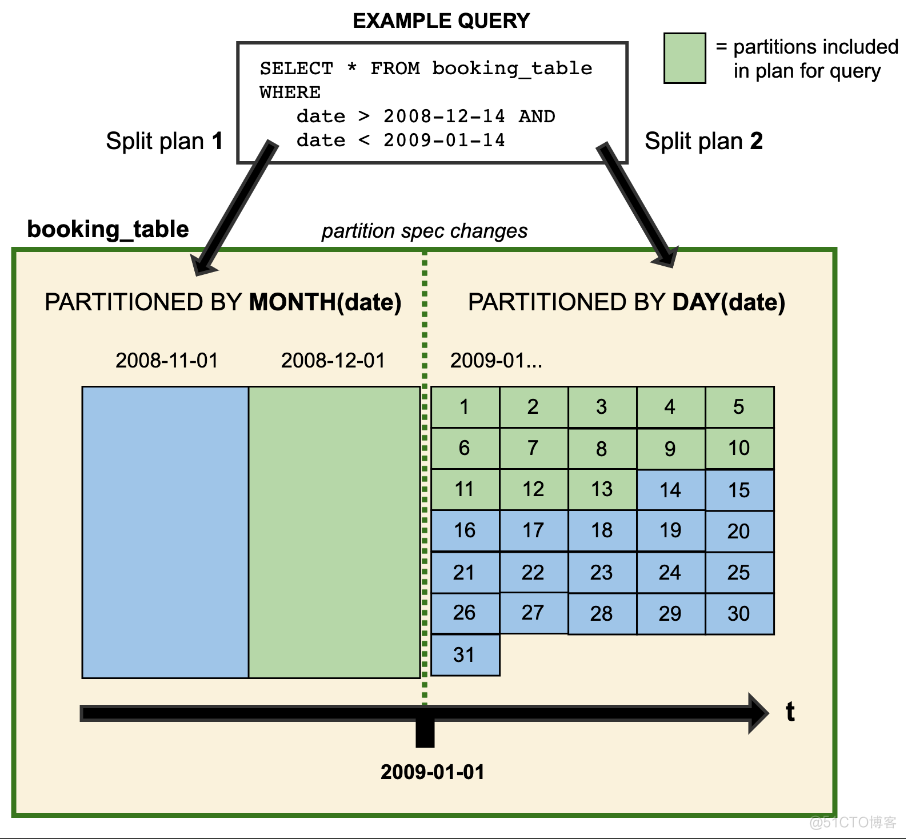

In the figure booking_table surface 2008 The year is divided by month , Get into 2009 Years later, it will be divided into districts by day , These two partition policies coexist in the table . Thanks to the Iceberg Hidden partitions (Hidden Partition), For SQL Inquire about , Don't need to SQL Partition filtering conditions are specially specified in ( By month or by day ), Iceberg Will automatically partition , Filter out unwanted data .
5、 Column order evolution (Sort Order Evolution)
Iceberg You can modify the sorting policy on an existing table . After modifying the sorting policy , The old data still adopts the old sorting strategy . Go to Iceberg The computing engine that writes the data will always choose the latest sorting strategy , But when sorting is extremely expensive , No sorting .
Two 、Iceberg data type
Iceberg Table supports the following data types :
type | describe | Be careful |
boolean | Boolean type ,true perhaps false | |
int | 32 Bit signed shaping | It can be converted into long type |
long | 64 Bit signed shaping | |
float | Single precision floating point | It can be converted into double type |
double | Double precision floating point | |
decimal(P,S) | decimal(P,S) | P Represents precision , Determine the total number of digits ,S On behalf of scale , Determine the number of decimal places .P Must be less than or equal to 38. |
date | date , Time and time zone are not included | |
time | Time , Excluding date and time zone | Store in microseconds ,1000 Microsecond = 1 millisecond |
timestamp | Without time zone timestamp | Store in microseconds ,1000 Microsecond = 1 millisecond |
timestamptz | With time zone timestamp | Store in microseconds ,1000 Microsecond = 1 millisecond |
string | Any length string type | UTF-8 code |
fixed(L) | The length is L Fixed length byte array of | |
binary | An array of bytes of any length | |
struct<...> | A structured field consisting of any data type | |
list<E> | Any data type List | |
map<K,V> | Of any type K,V Of Map |
边栏推荐
- Multi merchant mall system function disassembly lecture 01 - Product Architecture
- bashrc与profile
- Attribute keywords ondelete, private, readonly, required
- MRS离线数据分析:通过Flink作业处理OBS数据
- UML sequence diagram (sequence diagram)
- 昇腾体验官第五期随手记I
- 潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(HAL 库)—— 实验12 RTC实时时钟实验(学习笔记)
- UML 顺序图(时序图)
- [network security] SQL injection syntax summary
- electron remote 报错
猜你喜欢
Horizontal of libsgm_ path_ Interpretation of aggregation program

The longest ascending subsequence model acwing 1014 Mountaineering

数据湖(九):Iceberg特点详述和数据类型
多商户商城系统功能拆解01讲-产品架构
设备故障预测机床故障提前预警机械设备振动监测机床故障预警CNC震动无线监控设备异常提前预警

libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读

Vscode configuration uses pylint syntax checker
PERT图(工程网络图)
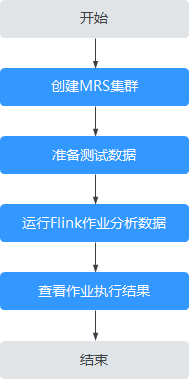
MRS离线数据分析:通过Flink作业处理OBS数据
全球首款 RISC-V 笔记本电脑开启预售,专为元宇宙而生!
随机推荐
多商户商城系统功能拆解01讲-产品架构
Vscode configuration uses pylint syntax checker
ES日志报错赏析-maximum shards open
2022云顾问技术系列之高可用专场分享会
WPF DataGrid realizes the UI interface to respond to a data change in a single line
大厂做开源的五大痛点
Million data document access of course design
Cvpr2022 | backdoor attack based on frequency injection in medical image analysis
Introduction to sakt method
electron remote 报错
Equipment failure prediction machine failure early warning mechanical equipment vibration monitoring machine failure early warning CNC vibration wireless monitoring equipment abnormal early warning
libSGM的horizontal_path_aggregation程序解读
oracle 触发器实现级联更新
PyTorch模型训练实战技巧,突破速度瓶颈
C # use TCP protocol to establish connection
The world's first risc-v notebook computer is on pre-sale, which is designed for the meta universe!
Leetcode——344. 反转字符串/541. 反转字符串 II/151. 颠倒字符串中的单词/剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
多商戶商城系統功能拆解01講-產品架構
Leetcode——剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
Leetcode——236. The nearest common ancestor of binary tree