当前位置:网站首页>Yiwen takes you into [memory leak]
Yiwen takes you into [memory leak]
2022-07-07 01:44:00 【Choice~】
List of articles
0. background
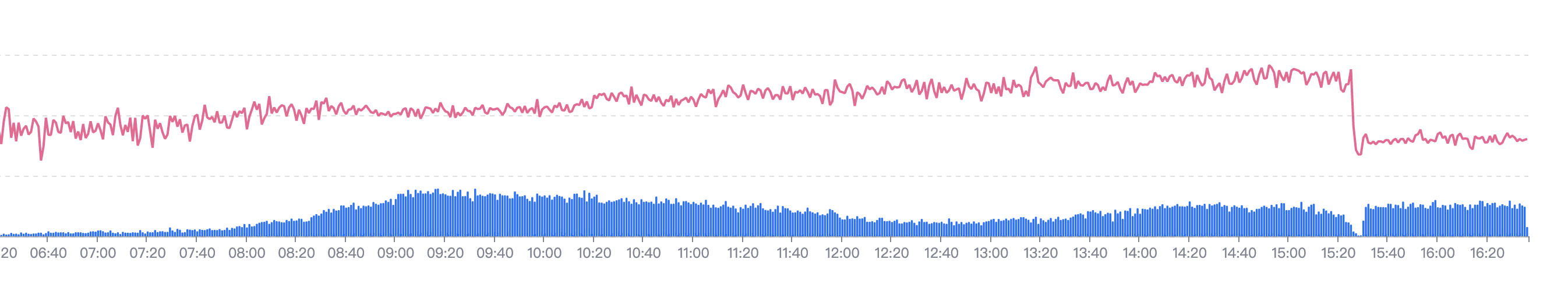
I didn't expect that after the project was put online , As the number of requests increases , But I feel that the speed of the first screen is getting slower and slower , And it keeps slowing down . And after the release ( That is, the container is rebuilt ), The time-consuming has dropped precipitously .
Therefore, it is reasonable to suspect that there is a memory leak . Therefore, STKE Take a look at the monitoring panel , Memory is really a wave like spray .
1. Repetition problem
I know it's a memory leak , We need to find the leak . Because it is not easy to operate the online environment , Online code is also compressed , Therefore, we need to set up a local environment to see if it is convenient for debugging . Here we can start locally Server after , Write a script to initiate a request , To simulate the online environment .( But everyone who has read the last article knows , We also have a skeleton screen mode , You can skip initiating CGI The requested step , Greatly reduce the time-consuming of a single request , Let the result come out in a few seconds )
We can use heapdump Package to write stack information to a local file .heapdump The basic use posture of is like this :
const heapdump = require('heapdump');
heapdump.writeSnapshot('./test.heapsnapshot');
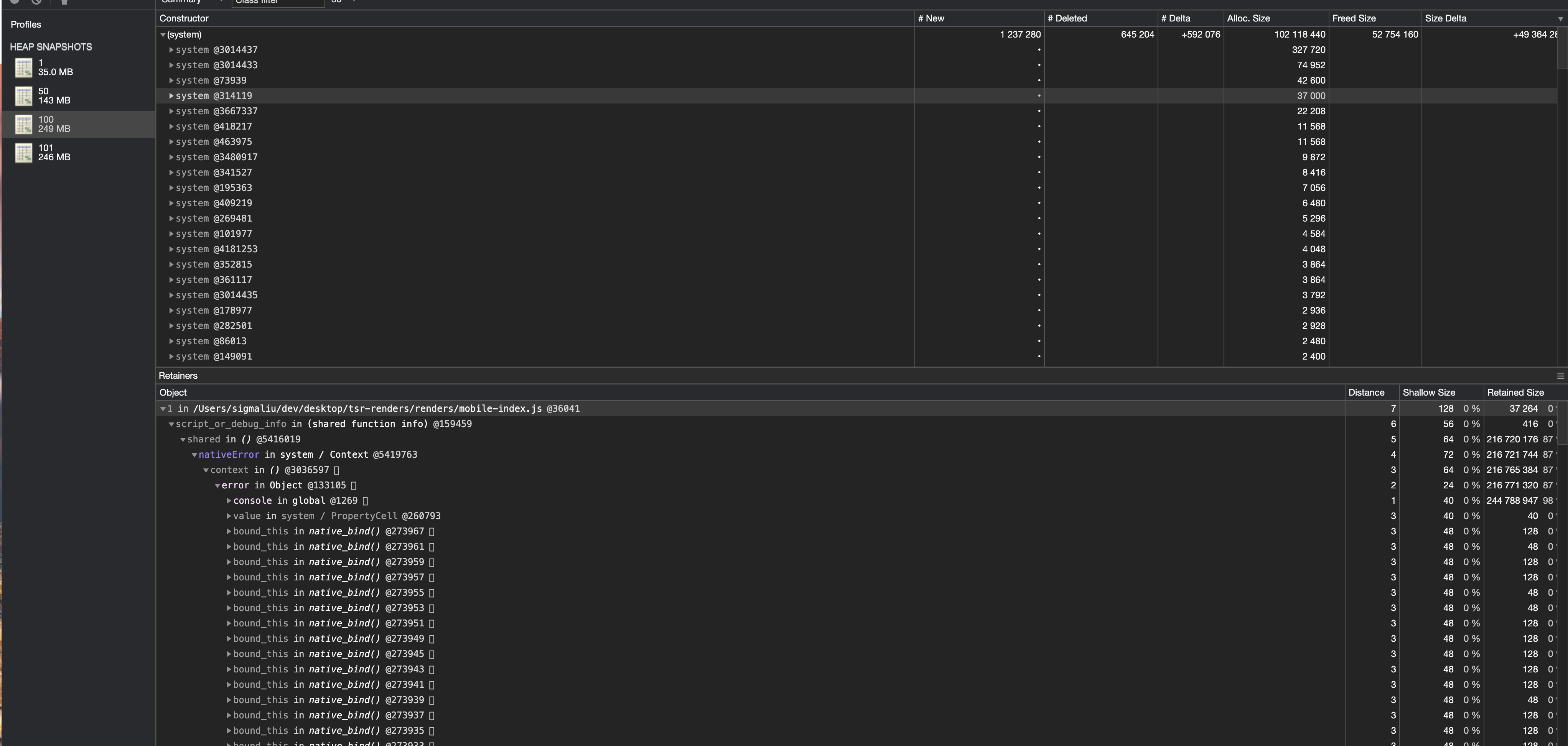
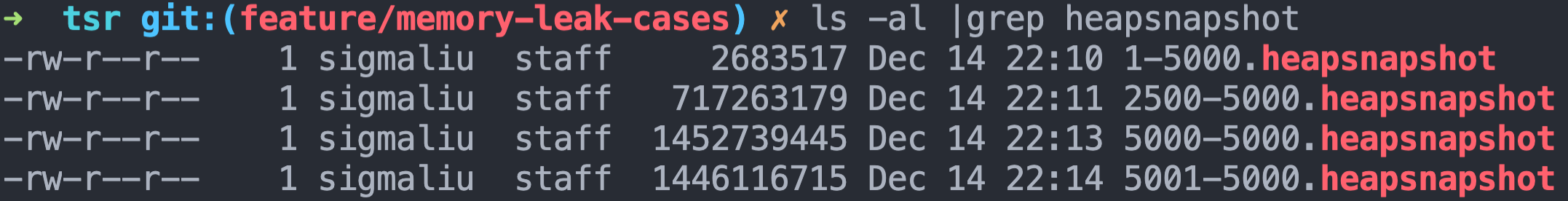
You can then import the stack file into Chrome Developer Tools Memory Column to analyze . Here I have chosen to run separately 1 Time 、50 Time 、100 Time And wait a few seconds for garbage collection before writing 101 Secondary stack information . You can see that the stack file is getting larger and larger , from 35M Increase to 249M.
Select two stack files for comparison to analyze , The trick here is to sort by memory size , Then I see that there are many objects of the same size , Then it is likely that it has been cited many times , The leak may be there . Then I found that the problem may be console On the object .
2. To analyze problems
Use... Normally console Object does not cause memory leaks , So I doubt whether it is true console What has been done . Searched the code , Exclude normal calls , Found an operation with assignment , It is similar to the following code :
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
// Omit some operations
nativeError(...argv);
};
This code is actually quite common in front-end development , For example, we need to log Automatically add time in :
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(`[${
(new Date()).toTimeString()}]`, ...argv);
};
console.error('Test');
// [20:58:17 GMT+0800 ( China standard time )] Test
Another more common scenario is , We need to shield most of the... In the production environment log Output , But keep one log Function reference , It is sometimes used to output some key information on the browser terminal , At this time, it will be written like this :
// quote , It is sometimes used to report when necessary
const logger = console.log;
// Must be assigned with a function , A lot of the original use console.log('...') Where there is no error
console.log = () => {};
logger(' Browser terminal AlloyTeam Recruitment information ');
But in our environment , The original client code is compiled and placed in vm Running repeatedly in , What problems will this bring ?
Here is a code , Interested friends can run :
const vm = require('vm');
const heapdump = require('heapdump');
const total = 5000;
const writeSnapshot = (count) => {
heapdump.writeSnapshot(`./${count}-${total}.heapsnapshot`);
};
const code = `
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(argv);
}
`;
const script = new vm.Script(code);
for (let i = 1; i <= total; i++) {
script.runInNewContext({
console,
});
console.log(`${i}/${total}`);
switch (i) {
case 1:
case Math.floor(total * 0.5):
case total:
writeSnapshot(i);
}
}
setTimeout(() => {
writeSnapshot(total + 1);
}, 3000);
A small piece of code , function 5000 Times later, the memory was occupied 1G many , And there is no sign of recycling .
Let's first think about vm Under the environment of , The difference is :
- vm There is no console Object's ,vm Inside console Objects are passed in by the host environment , stay vm Li is aimed at console Modification of , It will also be reflected in the host environment console On the object ;
- When the same piece of code is executed multiple times , This means that the execution environment is shared console Object's , In the browser environment , After refreshing the page , The code is executed multiple times , The environment is independent ;
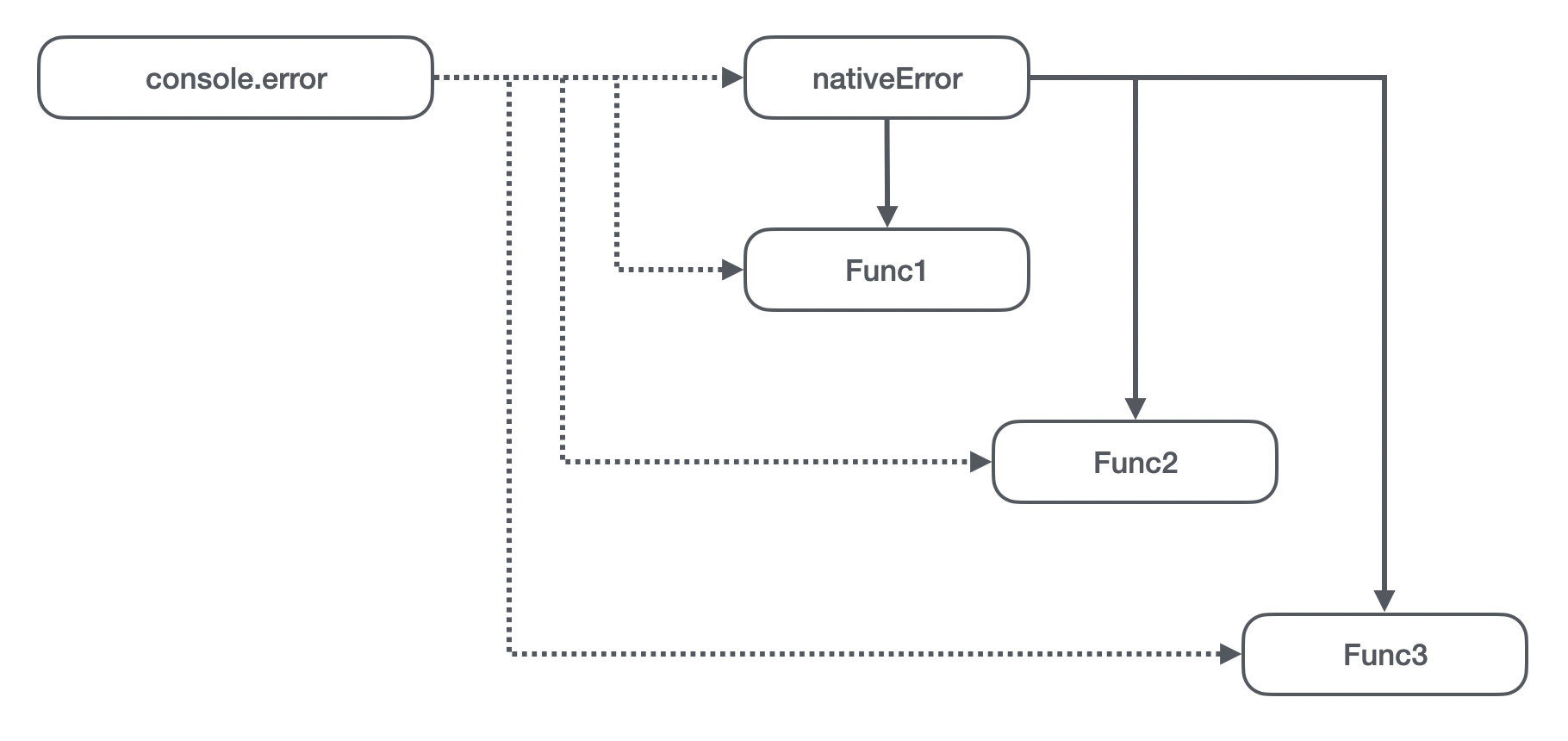
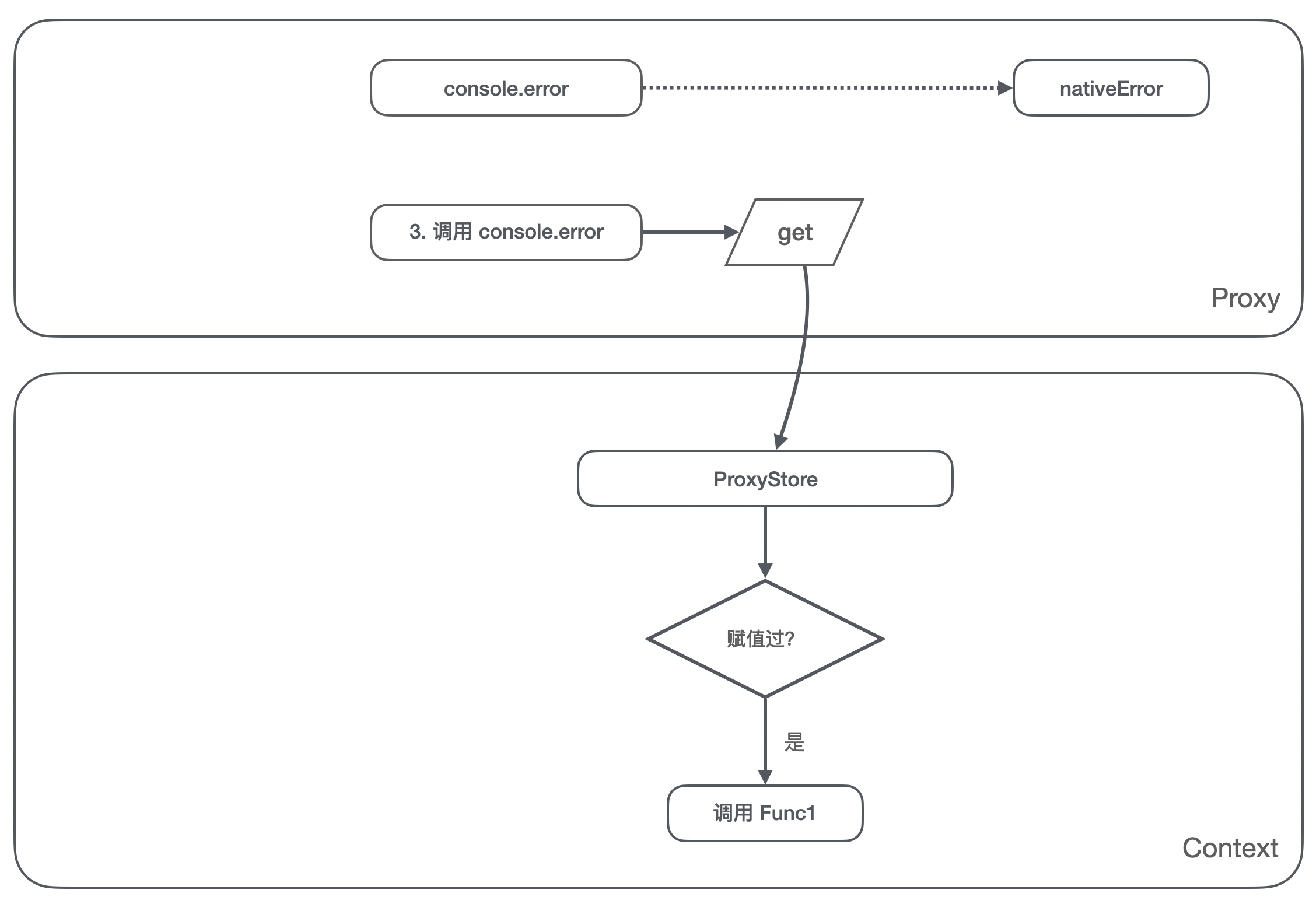
Then our problem will appear as shown in the figure above :
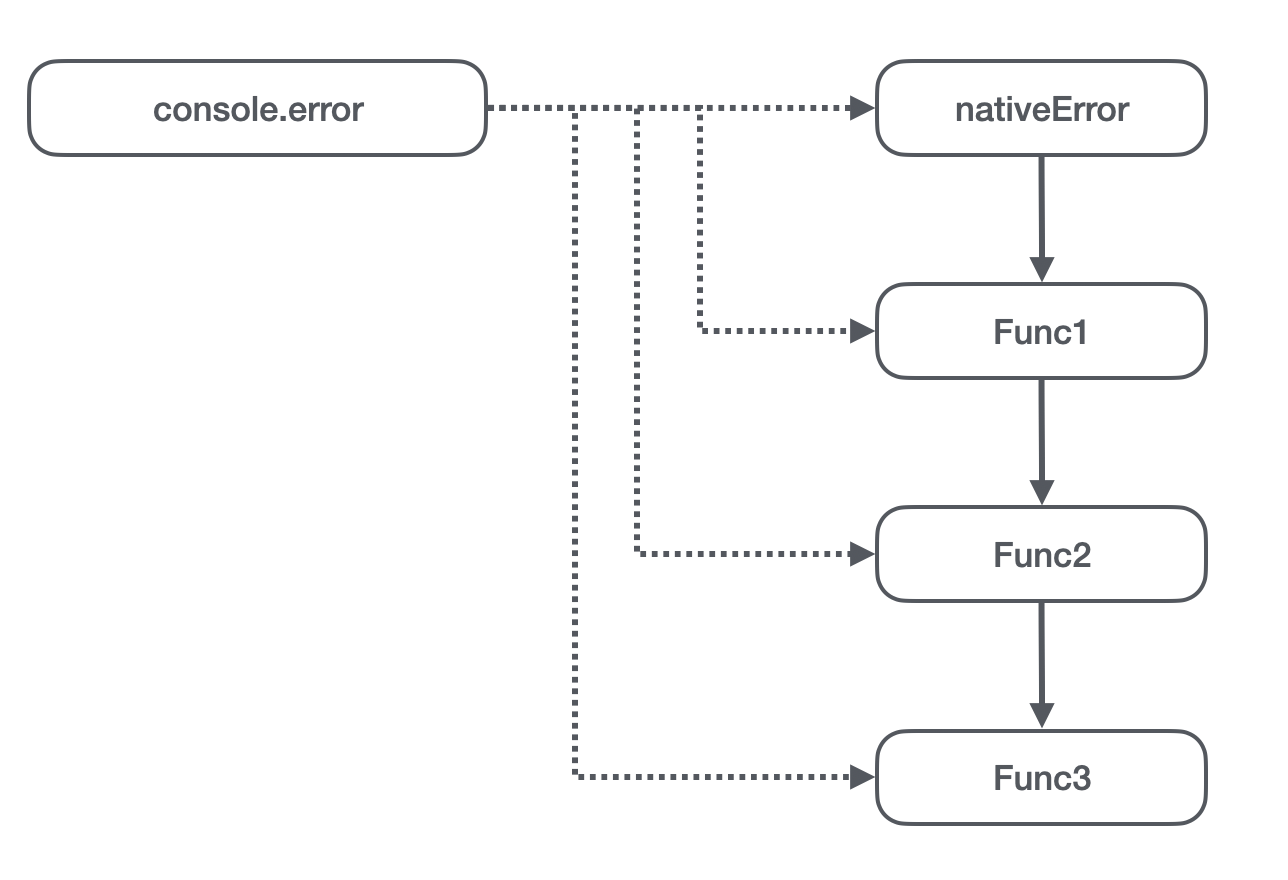
- On the host environment ,
console.errorThe original point is the original error Method ; - stay vm When it was first executed ( Suppose that the function to be assigned to this process is Func1), First, I quoted
console.error, That is, it refers to the native error Method , At the same time, through the assignment operation, theconsole.errorYes Func1; - stay vm The second time it was executed , I also quoted
console.errorMethod , But the reference is already No 2 Step setting Func1, That is to say Func2 Refer to the Func1. At the same time, it will change the host environmentconsole.errorSet up a Func2; - Empathy ,Func3 Refer to the Func2, also
console.errorYes Func3;
So did the smart guys find the problem , This becomes a chained reference . None of the objects in this chain can be recycled , Are tied to death .
If we want to solve this problem , What would an ideal reference model look like ?
An ideal reference model should be whatever vm How many times has the code been executed , In our value taking and assignment operations, we should :
- The fetching operation always fetches the native error Method , Because if you get the method of the last run assignment , Then there will be a reference relationship ;
- The assignment operation will not operate on the console object , Because this will affect other batches vm The whole situation in console object ;
- The value taking operation after the assignment operation will need to get the method after the assignment , In this way, the custom logic can be implemented ;
This actually requires us not only to vm The context of , Yes vm The reference objects belonging to the host environment passed by the created context should also be isolated .
3. solve the problem
Is there any simple solution ? Suppose we clearly understand the code execution environment ( Execute multiple times and share the host object ), Then you only need to make a flag bit to prevent multiple executions :
const nativeError = console.error;
if (!nativeError.hasBeenRewrite) {
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(argv);
};
console.error.hasBeenRewrite = true;
}
But in the original code running on the client side, it will be written like this , I feel that I have either experienced this problem , Or we can only say excellent , I had this consciousness from the beginning !
So when we want to build a basic runtime , Can we make sure that we don't need to care about such a detailed problem ? That is, can we isolate the context of the object from the context of the context ? There are several conditions that support us to do so :
- We pass on to vm In fact, the reference objects belonging to the host environment are very limited , So you can isolate these limited objects ;
- What we need to isolate is to follow vm Of the created context ;
So back to the ideal model we mentioned above , The code is attached here first , Let's explain the whole scheme :
const vm = require('vm');
const heapdump = require('heapdump');
const total = 5000;
const writeSnapshot = (count) => {
heapdump.writeSnapshot(`./${count}-${total}.heapsnapshot`);
};
const code = `
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(...argv);
}
`;
const script = new vm.Script(code);
const vmProxy = (context, obj, name) => {
const proxyStore = {};
const proxyObj = new Proxy(obj, {
get: function (target, propKey) {
if (proxyStore[name] && proxyStore[name][propKey]) {
return proxyStore[name][propKey];
}
return target[propKey];
},
set: function (target, propKey, value) {
if (!proxyStore[name]) {
proxyStore[name] = {};
}
const defineObj = proxyStore[name];
if ((typeof value === 'function' || typeof value === 'object') && value !== null) {
defineObj[propKey] = value;
}
},
});
context[name] = proxyObj;
context.proxyStore = proxyStore;
return context;
};
for (let i = 1; i <= total; i++) {
const context = vmProxy({}, console, 'console');
script.runInNewContext(context);
console.log(`${i}/${total}`);
switch (i) {
case 1:
case Math.floor(total * 0.5):
case total:
writeSnapshot(i);
}
}
setTimeout(() => {
writeSnapshot(total + 1);
}, 3000);
Here are some key points :
- use
ProxyMethod , Yes console Properties of get Operate to intercept ; - We will be in vm Set... On the context object
proxyStoreObject is used to store set Operation set value , ThisproxyStoreWill be recycled as the context is recycled ; - Yes console Of set The operation will not be set to console Reference objects that affect the host environment , But it needs to be stored ;
Step by step :
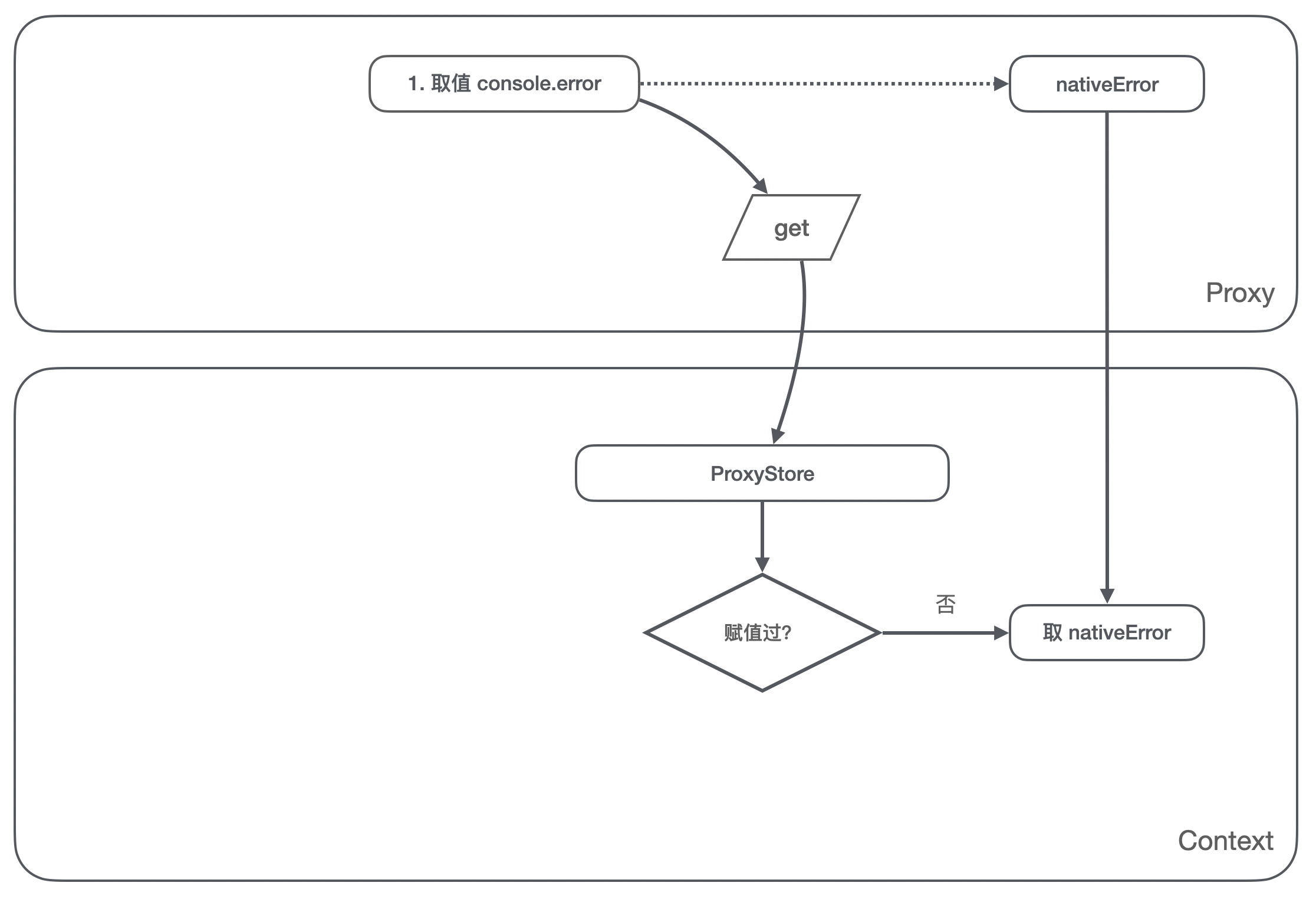
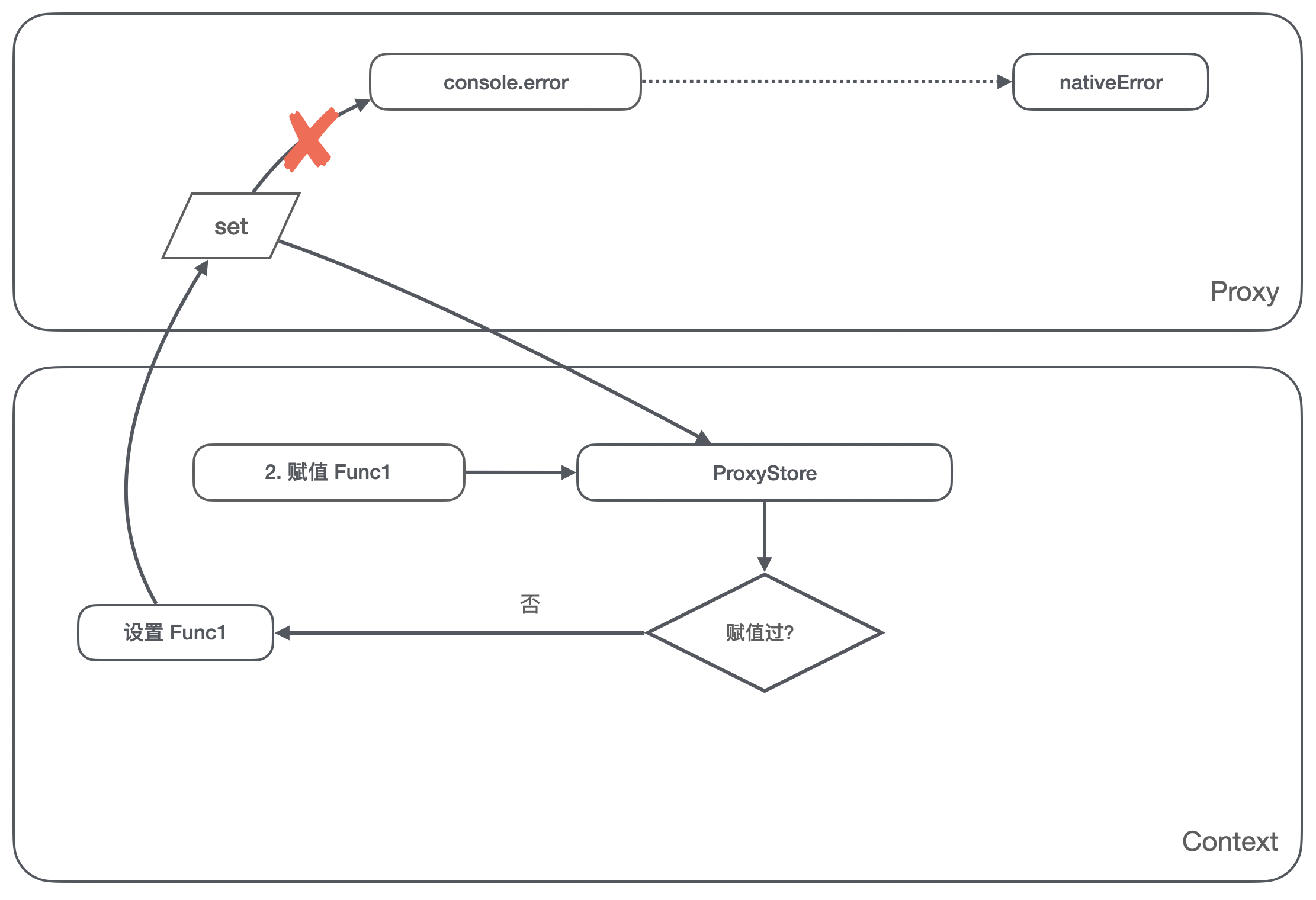
- Yes
console.errorValue operation of , We can judge ProxyStore Whether the current environment has been set in , Not at this time , Then we return the native for the value operation error Method ;
- Yes
console.errorassignment Func1 The operation of , We can judge ProxyStore No assignment to this property is stored in the , It will be Func1 Store in ProxyStore, Note here that we can not Func1 Set toconsole.errorOn ;
- In subsequent calls
console.erroroperation , Will be intercepted by us again get Method , We judged that ProxyStore There are assigned values in Func1, Back at this time Func1, callconsole.errorIt becomes a callFunc1;
Through the above operations , We maintained console.error Always point to native error Method , Each reference is also native to the reference error Method , Instead of the method set last time .
Then we solved the memory leak problem :
4. Avoid problems
This problem was solved in such a clever way , It seems that they all appreciate themselves a little .
But let's think again Proxy What's the problem , Is there a performance problem ?
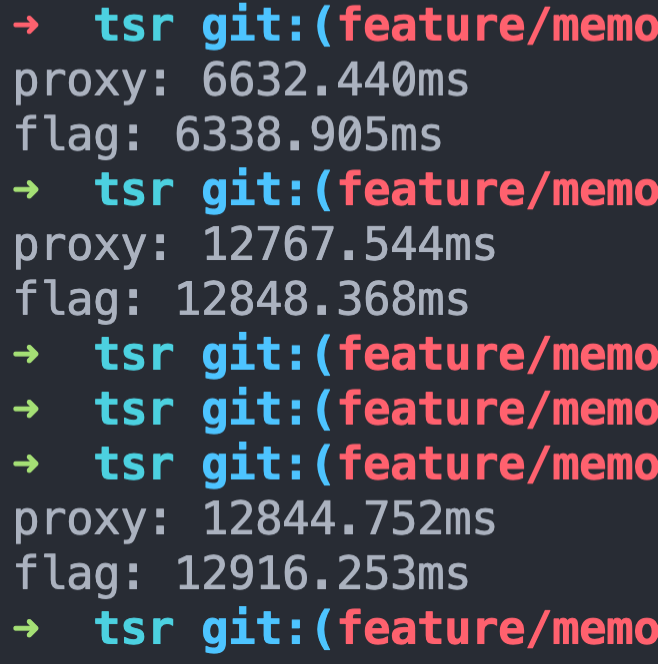
True knowledge comes from practice , We compare the performance differences between the above two solutions :
const vm = require('vm');
const total = 10000;
const vmProxy = (context, obj, name) => {
const proxyStore = {};
const proxyObj = new Proxy(obj, {
get: function (target, propKey) {
if (proxyStore[name] && proxyStore[name][propKey]) {
return proxyStore[name][propKey];
}
return target[propKey];
},
set: function (target, propKey, value) {
if (!proxyStore[name]) {
proxyStore[name] = {};
}
const defineObj = proxyStore[name];
if ((typeof value === 'function' || typeof value === 'object') && value !== null) {
defineObj[propKey] = value;
}
},
});
context[name] = proxyObj;
context.proxyStore = proxyStore;
return context;
};
(() => {
const code = `
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(...argv);
}
`;
const script = new vm.Script(code);
console.time('proxy');
for (let i = 1; i <= total; i++) {
const context = vmProxy({}, console, 'console');
script.runInNewContext(context);
}
console.timeEnd('proxy');
})();
(() => {
let code = `
const nativeError = console.error;
if (!nativeError.hasBeenRewrite) {
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(argv);
};
console.error.hasBeenRewrite = true;
}
`;
let script = new vm.Script(code);
console.time('flag');
for (let i = 1; i <= total; i++) {
script.runInNewContext({
console,
});
}
console.timeEnd('flag');
})();
There seems to be little performance difference
however Proxy There is one this Pointed question , because Proxy Not a transparent proxy , By Proxy Inside the proxy object this Point will point to proxy example , So it's ok if it's such a simple example , But on-line proxy for more complex objects , In my heart, I'm still a little fluffy .( You also need to consider the objects in the object )
Is it possible to find a similar memory leak problem in the development phase , Instead of waiting until it's released online ?
Of course, I said it when I thought of a way , I thought about it all afternoon before , It's too complicated , So I tried many methods but didn't come up with it . Let's clarify one thing first , This is because the stored... Is called in the function to be assigned nativeError Do you ? In fact, it is irrelevant , Even if you will nativeError(...argv) Comment out , There will still be memory leaks .
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = (...argv) => {
nativeError(...argv);
}
The reason here is that there is only one vm The same reference object in the virtual machine to the host environment key Do it at the same time get and set operation , Then there will be a memory leak . Let's consider whether there will be memory leaks in the following three cases :
same key:
const nativeError = console.undefined;
console.undefined = (...argv) => {
nativeError(argv);
}
Different key:
const nativeError = console.undefined;
console.notExist = (...argv) => {
nativeError(argv);
}
The setting is not a reference object :
const nativeError = console.error;
console.error = 'AlloyTeam';
The answer is that there will be a memory leak first , The second and third will not . Curious friends can run with the above example code .
We simplify the problem , Let's look at the detection scheme , Code first as usual :
const { workerData, Worker, isMainThread } = require('worker_threads');
const vm = require('vm');
const log = console.log;
const memoryCheckStore = {};
const isReferenced = value => !!(value && typeof value === 'object' || typeof value === 'function');
const vmProxy = (context, obj, name) => {
const proxyObj = new Proxy(obj, {
get: function (target, propKey) {
const propValue = target[propKey];
if (!memoryCheckStore[obj]) {
memoryCheckStore[obj] = {};
}
// todo: You need to deal with arrays and iterated child objects
if (!memoryCheckStore[obj][propKey]) {
memoryCheckStore[obj][propKey] = 1;
}
return propValue;
},
set: function (target, propKey, value) {
if (isReferenced(value) && memoryCheckStore[obj][propKey]) {
log(new Error('[ Warning ] There may be a memory leak '));
}
target[propKey] = value;
},
});
context[name] = proxyObj;
return context;
};
const code1 = `
const nativeError = console.undefined;
// leak
console.undefined = (...argv) => {}
`;
const code2 = `
const nativeError = console.undefined;
// It won't leak
console.notExist = (...argv) => {}
`;
const code3 = `
const nativeError = console.undefined;
// It won't leak
console.error = 'AlloyTeam';
`;
const code4 = `
const nativeError = console.error;
// leak
console.error = (...argv) => {}
`;
if (isMainThread) {
for (let i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Worker(__filename, {
workerData: {
code: eval(`code${i}`),
flag: i,
},
});
}
} else {
const { code, flag } = workerData;
const script = new vm.Script(code, {
filename: `code${flag}`,
});
const context = vmProxy({}, console, 'console');
script.runInNewContext(context);
}
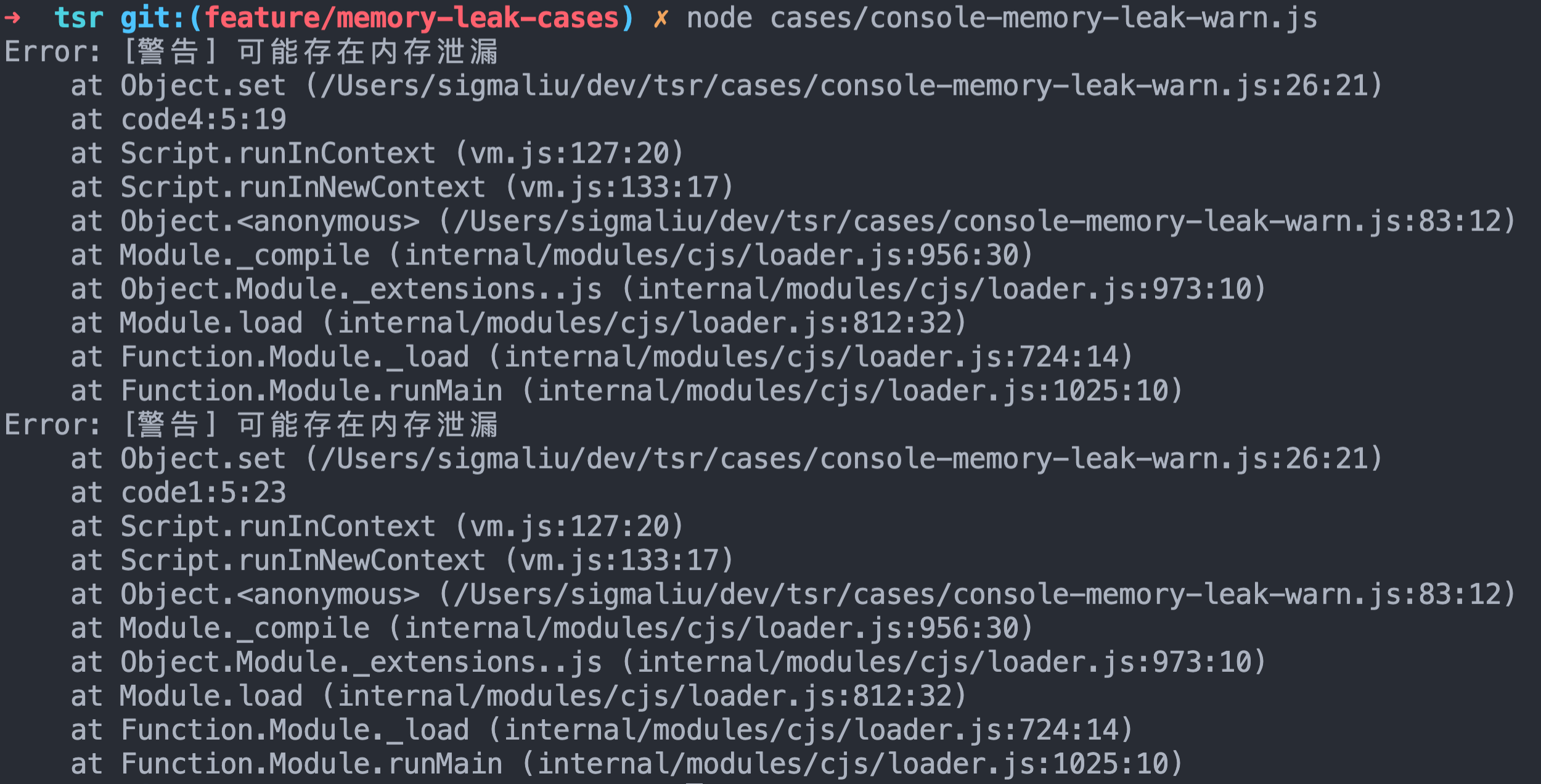
Run only once , You know code1、code4 There may be a memory leak :
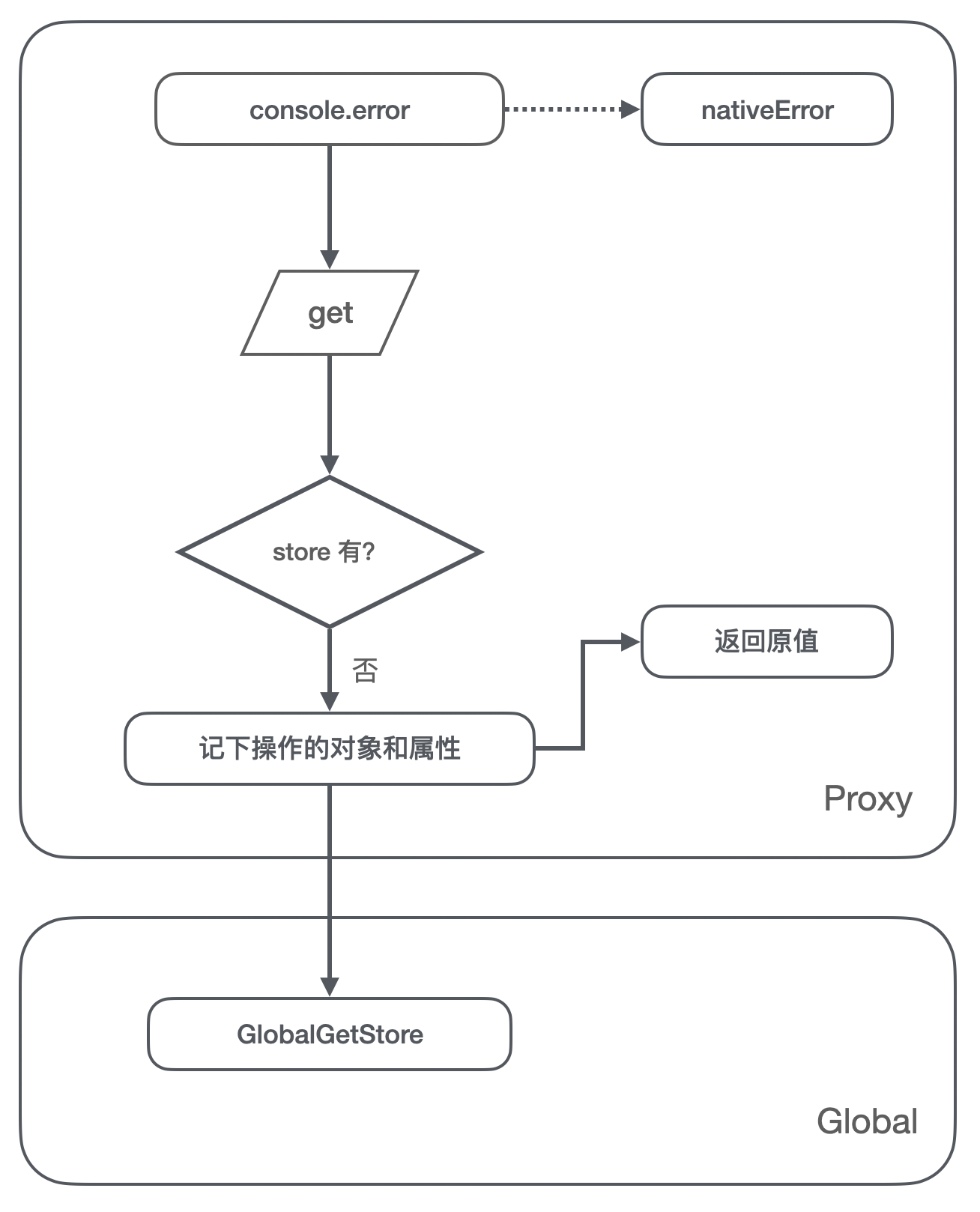
Scheme diagram 1,get Stage :
- In limine
console.errorPoint to the original error Method ; - We set up a global GlobalGetStore object , Used to record the referenced object and the referenced attribute name ;
- First run , Intercepted get Judgment in method store There is no such object in the , Record the object to store, Also record the quoted key value ;
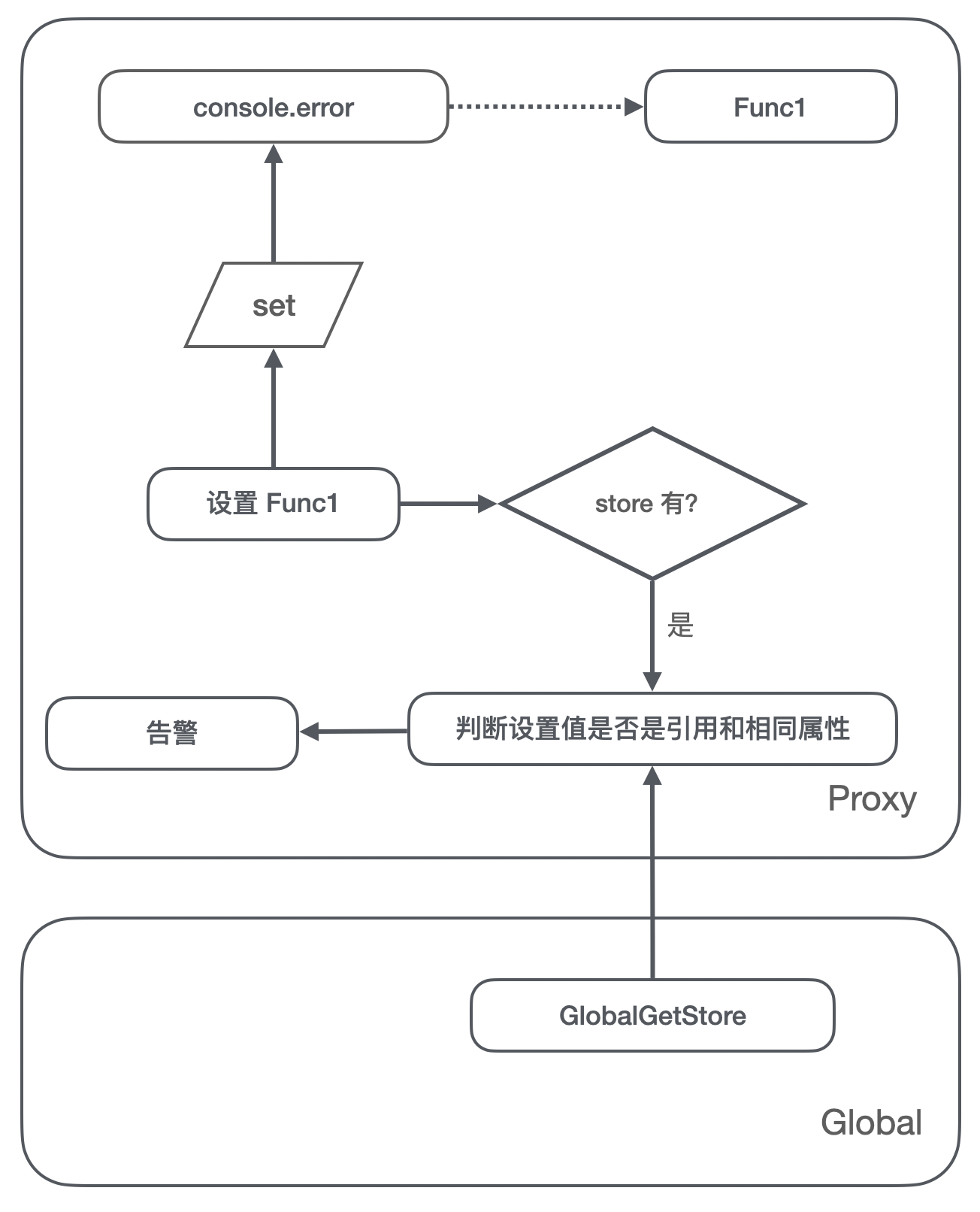
Scheme diagram 2,set Stage :
- Intercepted set In the method store There are already referenced objects stored in the , At the same time, the current operation key Values have also been referenced , Therefore, it is determined that vm In such a multi execution environment , There may be a memory leak , Print out the alarm information ;
In this way, we can deploy such memory detection code in the development phase (demo The code still needs to deal with cases where arrays and object properties are reference types ), Remove or invalidate from the production environment .
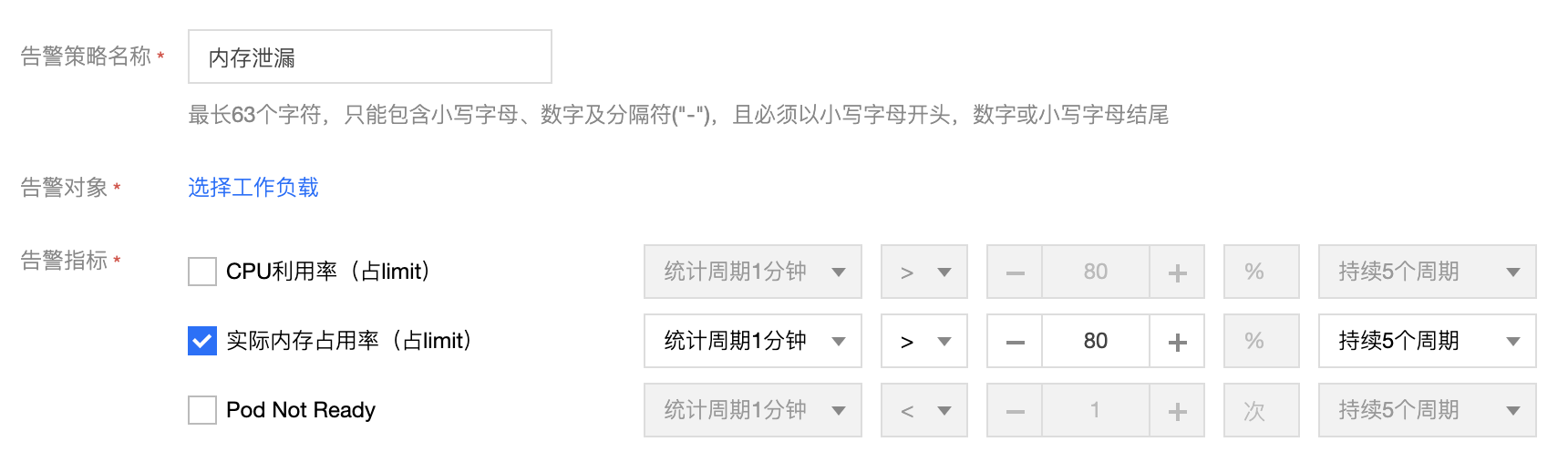
Yes, of course , An excellent project , There are still two related things to do before and after the launch :
- automated testing , Initiate multiple user requests through simulation , Detect memory changes , Possible memory leak detected before going online ;
- Set alarm strategy , Alarm when memory exceeds limit , View memory changes , Confirm whether there is leakage ;
5. Postscript
Meet such a problem , It's actually quite interesting , Although it is a little bit , But it has combed a relatively complete thinking process , I hope it can bring reference and ideas to the partners to solve relevant problems .
边栏推荐
- Go zero micro service practical series (IX. ultimate optimization of seckill performance)
- 盒子拉伸拉扯(左右模式)
- Image watermarking, scaling and conversion of an input stream
- 使用nodejs完成判断哪些项目打包+发版
- 刨析《C语言》【进阶】付费知识【完结】
- AcWing 1142. 繁忙的都市 题解(最小生成树)
- [signal and system]
- 糊涂工具类(hutool)post请求设置body参数为json数据
- C language - array
- AcWing 1148. Secret milk transportation problem solution (minimum spanning tree)
猜你喜欢
Basic introduction and use of dvajs
Go zero micro service practical series (IX. ultimate optimization of seckill performance)
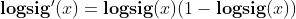
tansig和logsig的差异,为什么BP喜欢用tansig
修改px4飞控的系统时间
Baidu flying general BMN timing action positioning framework | data preparation and training guide (Part 2)
制作带照明的DIY焊接排烟器

百度飞将BMN时序动作定位框架 | 数据准备与训练指南 (下)
LeetCode:1175. 质数排列
Start from the bottom structure to learn the customization and testing of fpga---- FIFO IP
Instructions for using the domain analysis tool bloodhound
随机推荐
The cradle of eternity
长按按钮执行函数
场景实践:基于函数计算快速搭建Wordpress博客系统
Dark horse notes - exception handling
JVM 内存模型
LeetCode:1175. Prime permutation
What does front-end processor mean? What is the main function? What is the difference with fortress machine?
百度飞将BMN时序动作定位框架 | 数据准备与训练指南 (上)
Add the applet "lazycodeloading": "requiredcomponents" in taro,
Amway wave C2 tools
AcWing 1148. Secret milk transportation problem solution (minimum spanning tree)
Baidu flying general BMN timing action positioning framework | data preparation and training guide (Part 2)
js如何快速创建一个长度为 n 的数组
How to manage distributed teams?
图片打水印 缩放 和一个输入流的转换
Make Jar, Not War
AcWing 1140. Shortest network (minimum spanning tree)
HDU 4661 message passing (wood DP & amp; Combinatorics)
AcWing 1141. 局域网 题解(kruskalkruskal 求最小生成树)
Taro2.* applet configuration sharing wechat circle of friends