当前位置:网站首页>Start from the bottom structure to learn the customization and testing of fpga---- FIFO IP
Start from the bottom structure to learn the customization and testing of fpga---- FIFO IP
2022-07-07 01:25:00 【Lonely single knife】
List of articles
2、FIFO IP Instantiation and testing of
2.1、 Exemplify a FIFO IP nucleus
2.3、 Simulation test and test results
Series catalog and portal
《 Start with the underlying structure FPGA》 Directory and portal
Customizing one FIFO IP Before nuclear , It is strongly recommended that you read : Start with the underlying structure FPGA----FIFO IP Introduction to nuclear and its key parameters
In this article , Have been to FIFO IP The key factors of nuclear are explained in detail .
1、FIFO IP The custom of
- After creating a new project , Click on IP Catalog
- It will appear after clicking IP Catalog page , stay IP Search in the search box of the kernel fifo
- According to the screening , Double click to select fifo nucleus “FIFO Generator”
①、 first page
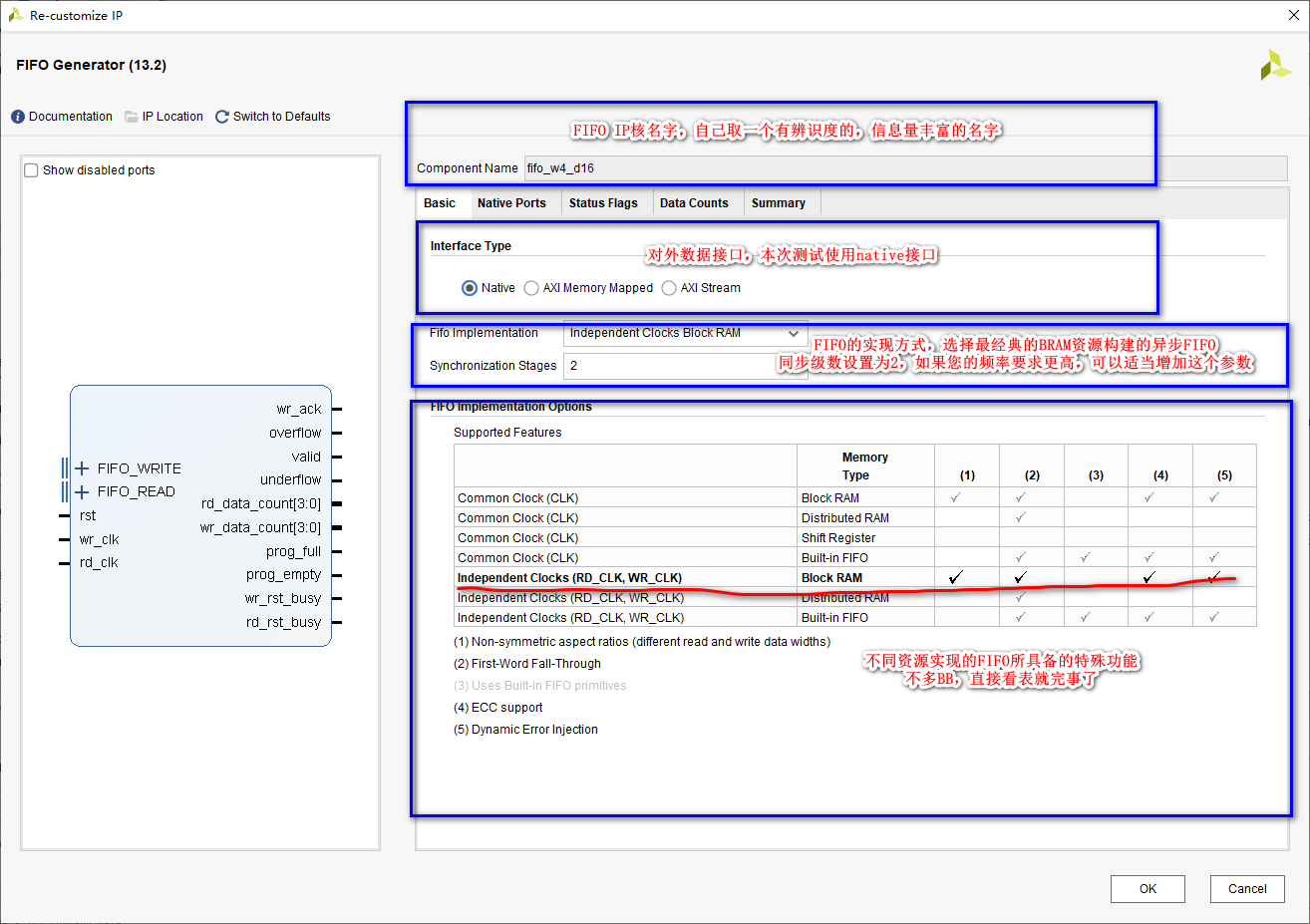
②、 The second page
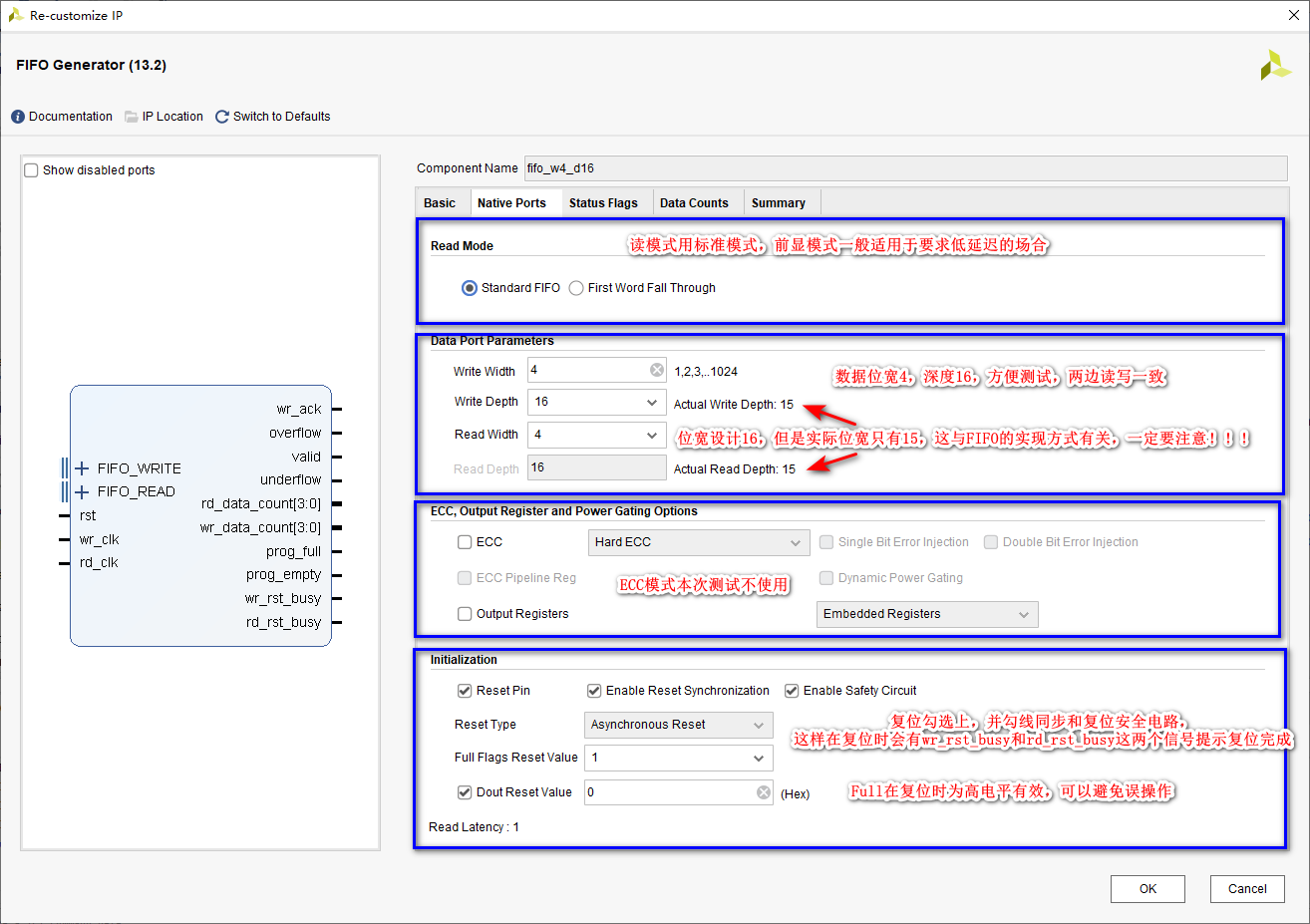
③、 The third page
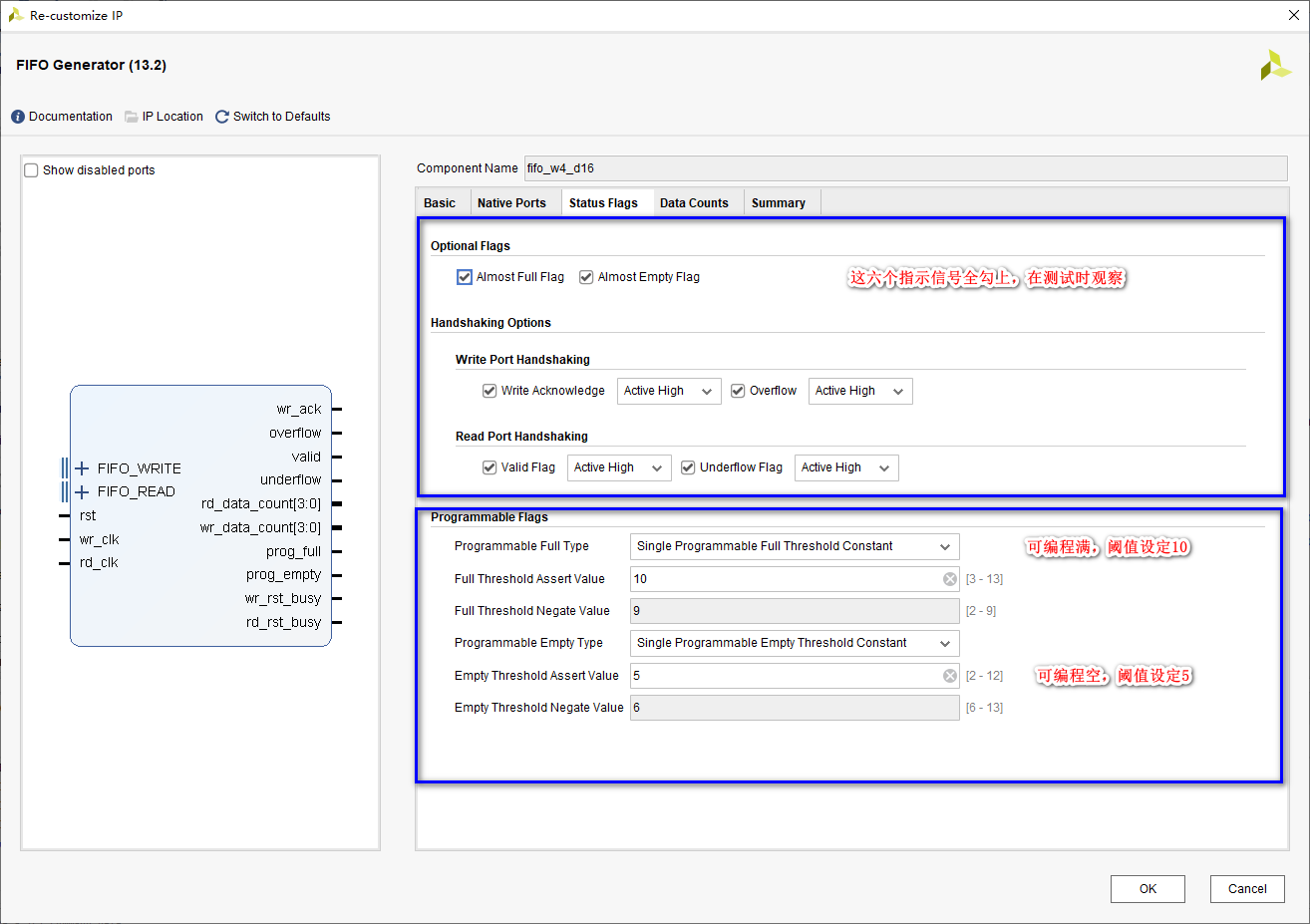
④、 Page four
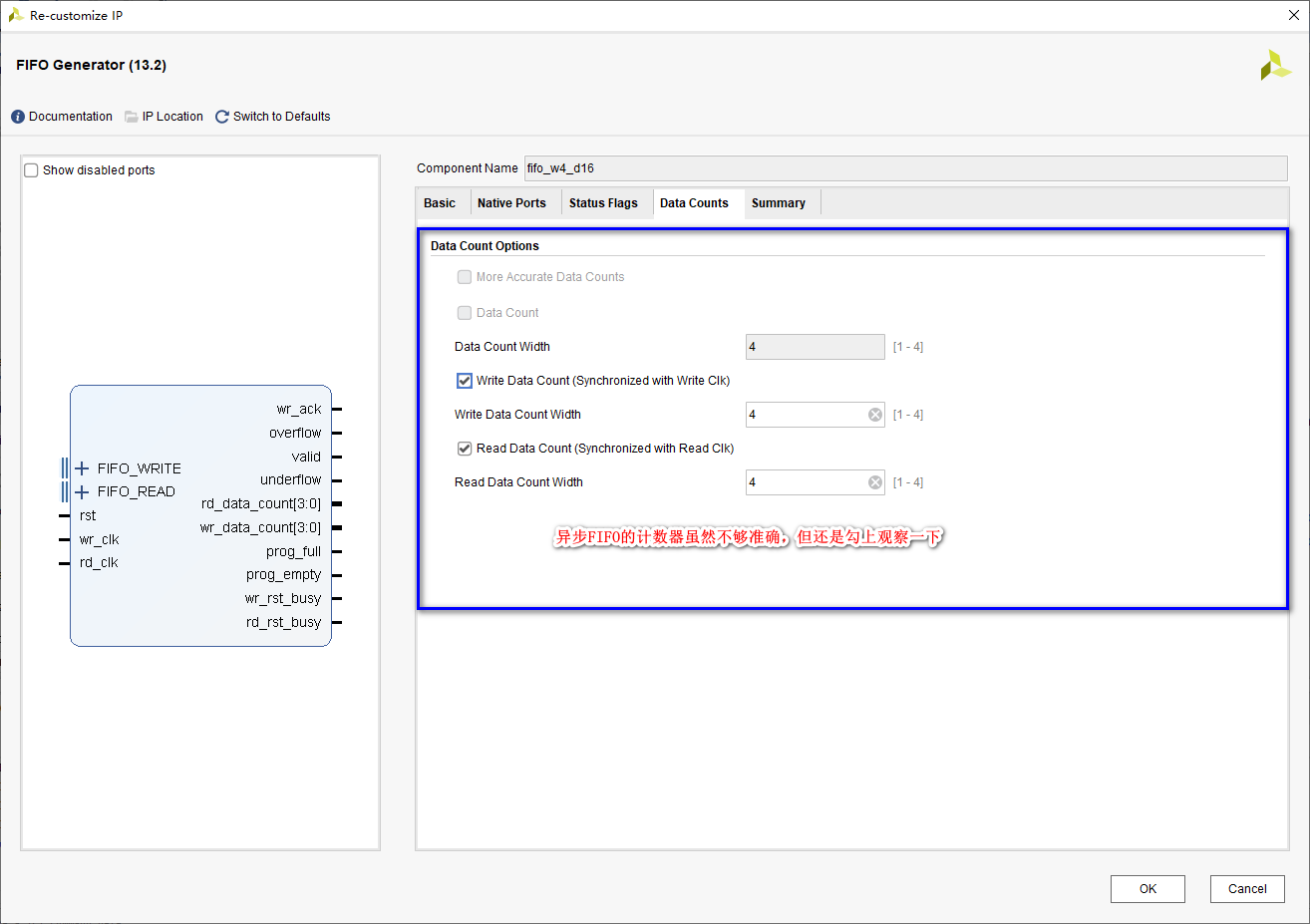
⑤、 Page 5
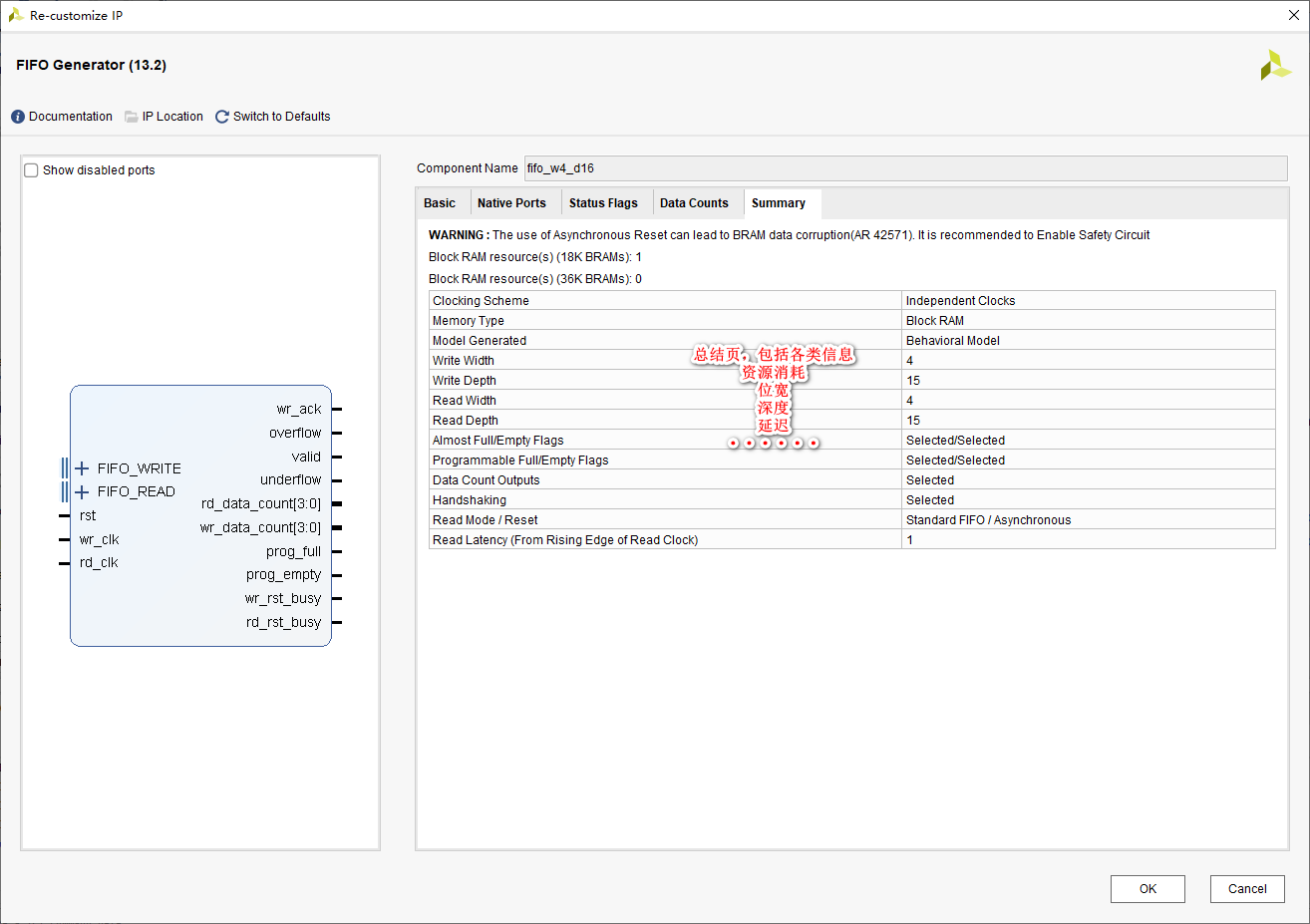
2、FIFO IP Instantiation and testing of
2.1、 Exemplify a FIFO IP nucleus
Follow the above steps to generate IP after , Copy IP The instantiation template provided by the core .
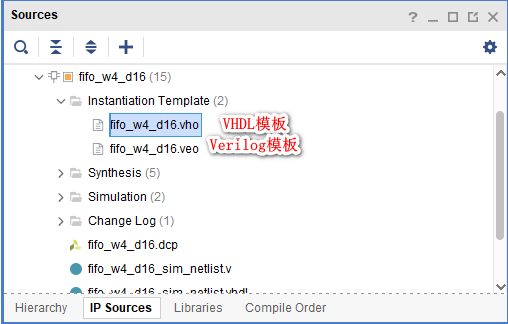
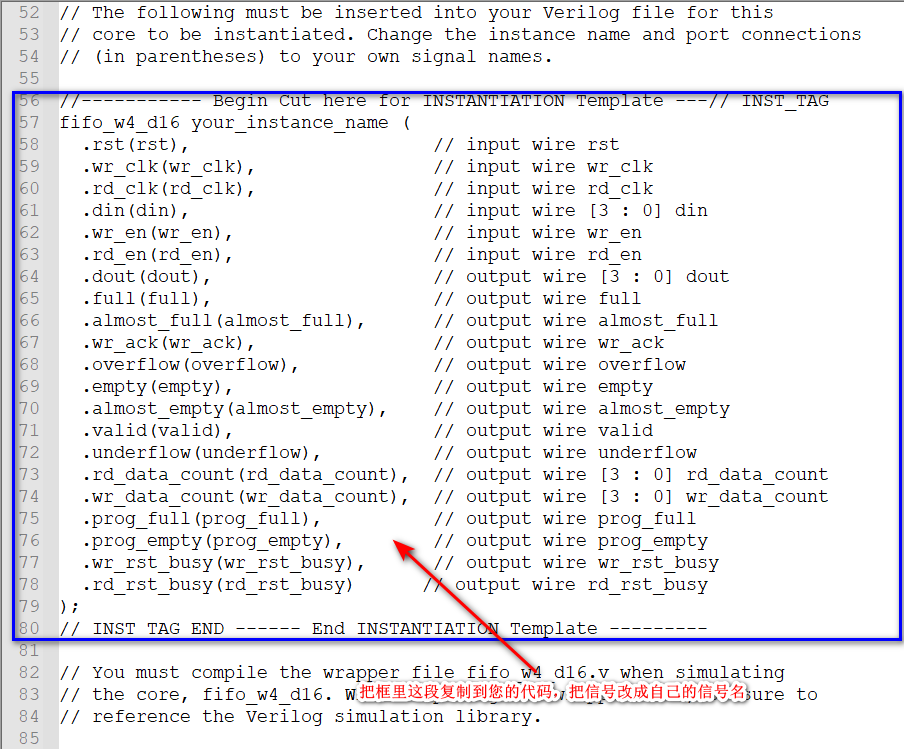
2.2、RTL
Let's write a RTL Code to verify this FIFO IP, And learn its temporal logic .
Because it's asynchronous FIFO, So there is also an example PLL The afterlife becomes a writing clock 50M, Read the clock 75M.RTL The code uses a simple state machine , To realize the following logic :
- wait for PLL Stable
- PLL After stabilization, right FIFO Reset , Duration 10 More than one cycle
- FIFO After reset , Write data until it is full , The written data are 0,1,2···14, common 15 Data
- After writing the data , from FIFO Read data from , Observe whether the read data is consistent with the written data
module fifot_test(
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *) input sys_clk,
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *) input sys_rst_n
);
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg fifo_rst ; // Make yourself a FIFO Reset signal of
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg [3:0] din ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg [3:0] rst_cnt ; // Reset counter
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg wr_en ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg rd_en ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)reg [2:0] state ;
reg [2:0] state_rd1 ;
reg [2:0] state_rd2 ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire locked ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire rst_n ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire rd_clk ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire wr_clk ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire [3 : 0] dout ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire full ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire almost_full ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire wr_ack ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire overflow ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire empty ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire almost_empty ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire valid ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire underflow ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire [3 : 0] rd_data_count ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire [3 : 0] wr_data_count ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire prog_full ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire prog_empty ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire wr_rst_busy ;
(* MARK_DEBUG="true" *)wire rd_rst_busy ;
assign rst_n = sys_rst_n && locked; // stay locked Reset until pulled high
//PLL After outputting the waveform , Start counting until 1111
always @(posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
rst_cnt <= 1'b0;
else if(&rst_cnt) //rst_cnt == 1111
rst_cnt <= rst_cnt;
else
rst_cnt <= rst_cnt + 1;
end
always @(posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
fifo_rst <= 1'b1;
else if(&rst_cnt)
fifo_rst <= 1'b0;
else
fifo_rst <= 1'b1;
end
always @(posedge sys_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
state <= 3'd0;
else begin
case(state)
3'd0:begin
if(~fifo_rst)
state <= 3'd1;
else
state <= state;
end
3'd1:begin
if(~wr_rst_busy && ~full)
state <= 3'd2;
else
state <= state;
end
3'd2:begin
if(almost_full)
state <= 3'd3;
else
state <= state;
end
3'd3:begin
if(~rd_rst_busy && ~empty)
state <= 3'd4;
else
state <= state;
end
3'd4:begin
if(almost_empty)
state <= 3'd5;
else
state <= state;
end
3'd5:begin
state <= state;
end
default:state <= 3'd0;
endcase
end
end
// Write enable
always @(posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
wr_en <= 1'b0;
else if(state == 3'd2)
wr_en <= 1'b1;
else
wr_en <= 1'b0;
end
// Writing data
always @(posedge wr_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
din <= 4'd0;
else if(wr_en)
din <= din + 1;
end
// Put state state Sync to read clock field
always @(posedge rd_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)begin
state_rd1 <= 3'd0;
state_rd2 <= 3'd0;
end
else begin
state_rd1 <= state;
state_rd2 <= state_rd1;
end
end
// Reading enable
always @(posedge rd_clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(~rst_n)
rd_en <= 1'b0;
else if(state_rd2 == 3'd4)
rd_en <= 1'b1;
else
rd_en <= 1'b0;
end
clk_wiz_0 clk_wiz_0_inst
(
.clk_in1 (sys_clk ),
.clk_out1 (wr_clk ), //50M
.clk_out2 (rd_clk ), //75M
.resetn (sys_rst_n ),
.locked (locked )
);
// Exemplification FIFO
fifo_w4_d16 fifo_w4_d16_inst(
.rst (fifo_rst),
.wr_clk (wr_clk),
.din (din),
.wr_en (wr_en),
.wr_rst_busy (wr_rst_busy),
.wr_data_count (wr_data_count),
.prog_full (prog_full),
.full (full),
.almost_full (almost_full),
.wr_ack (wr_ack),
.overflow (overflow),
.rd_clk (rd_clk),
.rd_en (rd_en),
.empty (empty),
.almost_empty (almost_empty),
.valid (valid),
.rd_data_count (rd_data_count),
.dout (dout),
.underflow (underflow),
.prog_empty (prog_empty),
.rd_rst_busy (rd_rst_busy)
);
endmodule2.3、 Simulation test and test results
Because the test logic is RTL Implemented in the , therefore testbench It's simpler , Just instantiate the tested module and realize clock and reset .
`timescale 1 ns / 1 ns
module tb_fifo_test();
reg sys_clk;
reg sys_rst_n;
initial begin
sys_clk = 0;
sys_rst_n = 0;
#60
sys_rst_n = 1;
#6000
$finish; // Stop simulation
end
always #10 sys_clk = ~ sys_clk;
fifot_test fifot_test_inst(
.sys_clk (sys_clk ),
.sys_rst_n (sys_rst_n )
);
endmoduleUse vivado Built in simulation tools simulator Run the simulation , The simulation results are as follows :
(1) whole

(2)PLL From unstable to stable
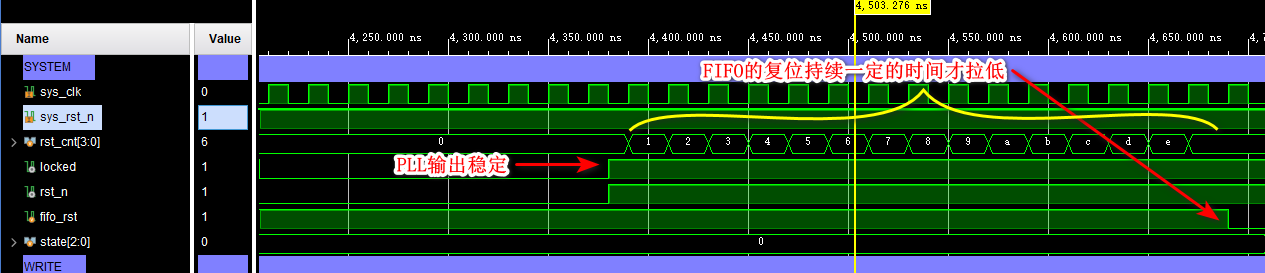
(3)FIFO It takes some time to operate after reset
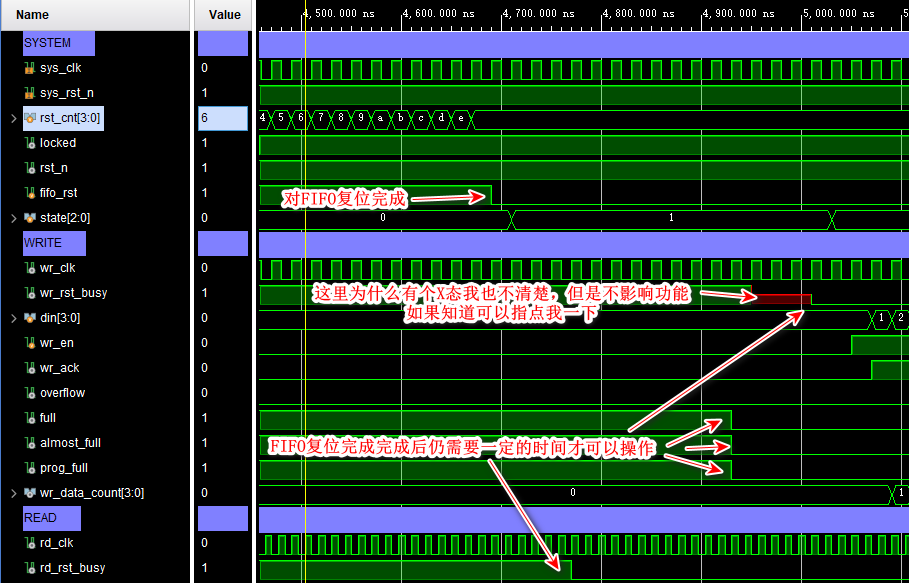
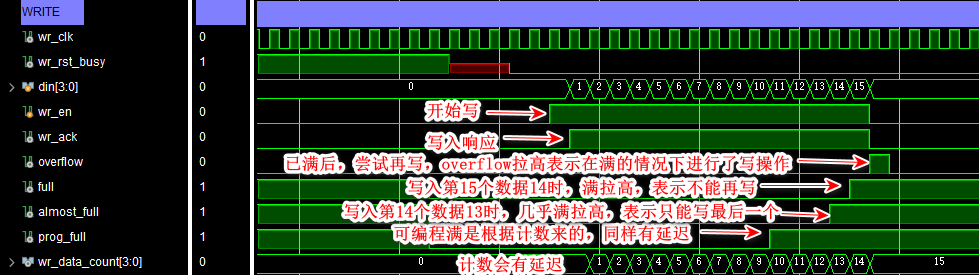
(4) Write FIFO operation
(5) read FIFO operation

Write data 0-14 common 15 Data , Reading data is also 0-14 common 15 Data . Write 、 Read consistent , Function verification is correct .
2.4、 Lower plate measurement
Download the code to the development board , use ILA Observe , The observation results are consistent with the simulation results , Don't go into , Just put a few pictures :
(1)PLL Stable and FIFO Reset

(2) Write FIFO operation , Write data 0-14

(3) read FIFO operation , Reading data 0-14

3、 Summary and reference
- FIFO Pay attention to the actual depth when using
- FIFO Reset before use , The reset time should be long enough , And it takes some time to use after reset FIFO
- Sync FIFO It will be simpler to use , Because it is not asynchronous FIFO The delay caused by the required synchronization clock domain
- Implemented by different resources FIFO There will be subtle differences in various functional features , Be sure to test carefully before using , Summarize the sequence
- asynchronous FIFO The counter of is not accurate , It can only be used as a general reference , To achieve, for example, half empty and half full 、1/4 Empty and full wait for judgment
- The implementation of programmable empty full is counter dependent , Its value is also not accurate
Reference material 1:pg057-fifo-generator
- Blog home page :wuzhikai.blog.csdn.net
- This paper is written by Lonely single blade original , First appeared in CSDN platform
- The article is still being updated , Do you have any questions , You can communicate with me in the comment area !
- It's not easy to create , Your support is the biggest driving force for me to continuously update ! If this article helps you , Please give me more praise 、 Reviews and collections !
边栏推荐
- 微信公众号发送模板消息
- Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
- Case development of landlord fighting game
- What are the differences between Oracle Linux and CentOS?
- Spark TPCDS Data Gen
- Dark horse notes - create immutable sets and streams
- 免费白嫖的图床对比
- How to evaluate load balancing performance parameters?
- Taro applet enables wxml code compression
- Dynamic planning idea "from getting started to giving up"
猜你喜欢
云呐|工单管理软件,工单管理软件APP

ClickHouse字段分组聚合、按照任意时间段粒度查询SQL
域分析工具BloodHound的使用说明
Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
1123. 最深叶节点的最近公共祖先

云呐|工单管理办法,如何开展工单管理

How to manage distributed teams?

ARM裸板调试之JTAG调试体验

LLDP兼容CDP功能配置
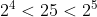
Typical problems of subnet division and super network construction
随机推荐
How to manage distributed teams?
Dark horse notes - exception handling
pyflink的安装和测试
The difference between spin and sleep
交叉验证如何防止过拟合
THREE.AxesHelper is not a constructor
资产安全问题或制约加密行业发展 风控+合规成为平台破局关键
Atomic in golang, and cas Operations
Openjudge noi 1.7 10: simple password
taro3.*中使用 dva 入门级别的哦
从底层结构开始学习FPGA----FIFO IP的定制与测试
Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
Metauniverse urban legend 02: metaphor of the number one player
实现mysql与ES的增量数据同步
MySQL script batch queries all tables containing specified field types in the database
Failed to successfully launch or connect to a child MSBuild. exe process. Verify that the MSBuild. exe
今日问题-2022/7/4 lambda体中修改String引用类型变量
Case development of landlord fighting game
Make Jar, Not War
golang中的WaitGroup实现原理