当前位置:网站首页>Machine learning: the difference between random gradient descent (SGD) and gradient descent (GD) and code implementation.
Machine learning: the difference between random gradient descent (SGD) and gradient descent (GD) and code implementation.
2022-07-07 01:21:00 【HanZee】
machine learning : Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) And gradient descent (GD) The difference between code implementation .
If you want to understand in detail :-》 Gradient descent method
Gradient descent method (GD)
Hypothesis function fx, Cost function cost, It has the following expression :
f ( x ) = w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + b c o s t ( w ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n ( f ( x i ) − y i ) w 1 = w 1 o l d − α ∂ c o s t ( w ) ∂ w 1 c o s t ( w ) w 2 = w 2 o l d − α ∂ c o s t ( w ) ∂ w 2 c o s t ( w ) \begin{aligned}f\left( x\right) =w_{1}x_{1}+w_{2}x_{2}+b\\ cost\left( w\right) =\dfrac{1}{n}\sum ^{n}_{i=1}\left( f(x_{i}\right) -y_{i}) \\ w_{1}=w_{1old}-\alpha \dfrac{\partial cos t\left( w\right) }{\partial w_{1}}cos t\left( w\right) \\ w _{2}=w_{2old}-\alpha \dfrac{\partial cos t\left( w\right) }{\partial w_{2}}cos t\left( w\right) \end{aligned} f(x)=w1x1+w2x2+bcost(w)=n1i=1∑n(f(xi)−yi)w1=w1old−α∂w1∂cost(w)cost(w)w2=w2old−α∂w2∂cost(w)cost(w)
From the above formula , We come to the conclusion that :
1. Parameters w,b Every update , It is necessary to calculate the partial derivative of all data to the corresponding parameters , This calculation is very large , The convergence speed of the function will be very slow when there is a large amount of data .
2. And SGD Different , Every time the parameter changes , Can guarantee cost It moves towards the global minimum .
3. If cost Nonconvex functions , Functions may fall into local optima .
And then the gradient goes down (SGD)
The formula is as follows :
f ( x ) = w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + b f\left( x\right) =w_{1}x_{1}+w_{2}x_{2}+b f(x)=w1x1+w2x2+b
f o r ( i = 0 , i < = n , i + + ) c o s t ( w ) = ( f ( x i ) − y i ) w 1 = w 1 o l d − α ∂ c o s t ( w ) ∂ w 1 c o s t ( w ) w 2 = w 2 o l d − α ∂ c o s t ( w ) ∂ w 2 c o s t ( w ) for (i=0,i<=n,i++)\\ cost\left( w\right) =(f(x_i)-y_i)\\ w_{1}=w_{1old}-\alpha \dfrac{\partial cos t\left( w\right) }{\partial w_{1}}cos t\left( w\right) \\ w _{2}=w_{2old}-\alpha \dfrac{\partial cos t\left( w\right) }{\partial w_{2}}cos t\left( w\right) for(i=0,i<=n,i++)cost(w)=(f(xi)−yi)w1=w1old−α∂w1∂cost(w)cost(w)w2=w2old−α∂w2∂cost(w)cost(w)
From the above formula , Come to the following conclusion :
- SGD Every time the parameter is updated , Only calculated 1 individual batch Gradient of ( The above formula assumes batch=1), It greatly accelerates the convergence speed of the function .
2.SGD Only one data is considered for each parameter update , It may not move in the direction of global optimization every time , Eventually, it may not converge to the minimum , But it will solve the problem of falling into local optimization .
Code implementation
Take Boston house price forecast as an example
Import data
import numpy as np
path = 'Desktop/ Boston prices /trian.csv'
data = np.loadtxt(path, delimiter = ",", skiprows=1)
data.shape
Split data
train = data[:int(data.shape[0]*0.8)]
test = data[int(data.shape[0]*0.8):]
print(train.shape, test.shape)
train_x = train[:,:-1]
train_y = train[:,13:]
test_x = test[:,:-1]
test_y = test[:,13:]
print(train_x.shape, train_y.shape)
class Network:
def __init__(self, num_weights):
self.num_weights = num_weights
self.w = np.random.rand(num_weights, 1)
self.b = 0
def forward(self, x):
z = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b
return z
def loss(self, z, y):
cost = (z-y)*(z-y)
cost = np.mean(cost)
return cost
def gradient(self, z, y):
w = (z-y)*train_x
w = np.mean(w, axis=0)
w = np.array(w).reshape([13, 1])
b = z-y
b = np.mean(b)
return w, b
def update(self, gradient_w, gradient_b, eta):
self.w = self.w - eta*gradient_w
self.b = self.b - eta*gradient_b
# gradient descent
def train_GD(self, items, eta):
for i in range(items):
z = self.forward(train_x)
loss = self.loss(z, train_y)
gradient_w, gradient_b = self.gradient(z, train_y)
self.update(gradient_w, gradient_b, eta)
# if i % 100 == 0:
test_loss = self.test()
print('item:', i, 'loss:', loss, 'test_loss:', test_loss)
# And then the gradient goes down
def train_SGD(self, num_epochs, batchsize, eta):
for epoch_id in range(num_epochs):
np.random.shuffle(train)
losses = []
for i in range(0, len(train), batchsize):
# print(i, batchsize+i)
mini_batchs = train[i:i + batchsize]
for iter_id, mini_batch in enumerate(mini_batchs):
# print(mini_batch)
x = mini_batch[:-1]
y = mini_batch[-1]
z = self.forward(x)
loss = self.loss(z, y)
gradient_w, gradient_b = self.gradient(z, y)
self.update(gradient_w, gradient_b, eta)
losses.append(loss)
sum = 0
for i in losses:
sum += i
loss_mean = sum/len(losses)
print('Epoch{}, loss{}, loss_mean{}'.format(epoch_id, loss, loss_mean))
def test(self):
z = self.forward(test_x)
loss = self.loss(z, test_y)
return loss
net = Network(13)
net.train_GD(100, eta=1e-9)
net.train_SGD(100, 5, 1e-9)
边栏推荐
- from . cv2 import * ImportError: libGL. so. 1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or direc
- The cost of returning tables in MySQL
- AI 从代码中自动生成注释文档
- Taro2.* applet configuration sharing wechat circle of friends
- THREE.AxesHelper is not a constructor
- Spark TPCDS Data Gen
- golang中的Mutex原理解析
- NEON优化:log10函数的优化案例
- Grc: personal information protection law, personal privacy, corporate risk compliance governance
- Case development of landlord fighting game
猜你喜欢
Installation of gazebo & connection with ROS
Js逆向——捅了【马蜂窝】的ob混淆与加速乐
Send template message via wechat official account
![[HFCTF2020]BabyUpload session解析引擎](/img/db/6003129bc16f943ad9868561a2d5dc.png)
[HFCTF2020]BabyUpload session解析引擎

微信公众号发送模板消息
2022 Google CTF SEGFAULT LABYRINTH wp
![[signal and system]](/img/aa/a65d6da1d1d9410254ca7b775e24a6.png)
[signal and system]
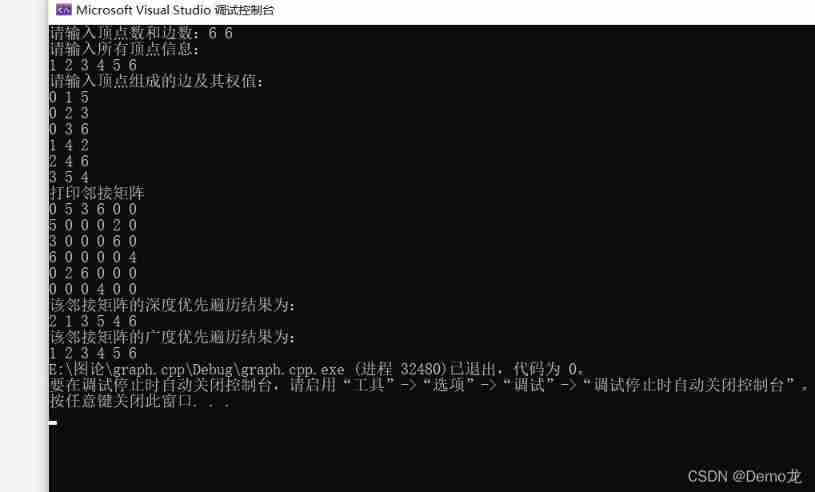
BFS realizes breadth first traversal of adjacency matrix (with examples)
boot - prometheus-push gateway 使用
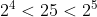
Typical problems of subnet division and super network construction
随机推荐
Openjudge noi 1.7 08: character substitution
taro3.*中使用 dva 入门级别的哦
ARM裸板调试之JTAG原理
Transformation transformation operator
Realize incremental data synchronization between MySQL and ES
Taro applet enables wxml code compression
golang中的atomic,以及CAS操作
剑指 Offer II 035. 最小时间差-快速排序加数据转换
Lldp compatible CDP function configuration
Spark TPCDS Data Gen
Taro2.* 小程序配置分享微信朋友圈
Neon Optimization: About Cross access and reverse cross access
Meet in the middle
移植DAC芯片MCP4725驱动到NUC980
Maidong Internet won the bid of Beijing life insurance to boost customers' brand value
Installation of gazebo & connection with ROS
黑马笔记---创建不可变集合与Stream流
C# 计算农历日期方法 2022
【芯片方案设计】脉搏血氧仪
Atomic in golang and CAS operations