当前位置:网站首页>Dark horse notes - create immutable sets and streams
Dark horse notes - create immutable sets and streams
2022-07-07 01:20:00 【Xiaofu taps the code】
Catalog
1.1 What is an immutable set ?
1.2 How to create immutable sets ?
Case study :Stream The role of flow
Stream The core of flow thinking :
2.3Stream The common use of stream API
Stream The common use of stream API( Intermediate operation method )
Stream Common end operations for streams
2.4Stream Comprehensive application of flow
Stream Stream collection operation
Stream Stream collection methods
Collectors Tool classes provide specific collection methods
1. Immutable set
1.1 What is an immutable set ?
Immutable set , Is a collection that cannot be modified .
At the time of data collection creation , And it's immutable throughout the life cycle . Otherwise, the report will be wrong .
Why create immutable sets ?
If a data cannot be modified , It's a good practice to copy it defensively into immutable sets .
Or when the collection object is called by an untrusted Library , Immutable forms are safe .
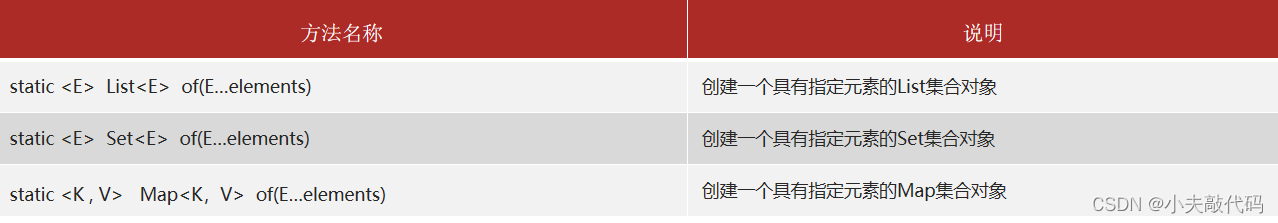
1.2 How to create immutable sets ?
stay List、Set、Map Interface , All exist of Method , You can create an immutable collection .
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
The goal is : Immutable set .
*/
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、 Immutable List aggregate
List<Double> lists = List.of(569.5, 700.5, 523.0, 570.5);
// lists.add(689.0);
// lists.set(2, 698.5);
// System.out.println(lists);
double score = lists.get(1);
System.out.println(score);
// 2、 Immutable Set aggregate
Set<String> names = Set.of(" Delireba ", " Deli hot nine ", " Marzaha ", " Karba " );
// names.add(" Third young master ");
System.out.println(names);
// 3、 Immutable Map aggregate
Map<String, Integer> maps = Map.of("huawei",2, "Java Development ", 1 , " watch ", 1);
// maps.put(" clothes ", 3);
System.out.println(maps);
}
}
This collection cannot be added , Can't delete , Do not modify .
summary :
Characteristics of immutable sets ?
Cannot be modified after the definition is completed , Or add 、 Delete
How to create immutable sets ?
List、Set、Map Interface , All exist of Method can create immutable collections .
2.Stream flow
2.1Stream An overview of flow
What is? Stream flow ?
stay Java 8 in , Thanks to the Lambda The functional programming that comes with it , Introduced a whole new Stream Flow concept .
Purpose : For simplifying set and array operations API.
Case study :Stream The role of flow
demand : Complete the creation and traversal of the collection according to the following requirements
Create a collection , Store multiple string elements
Put all the objects in the set with " Zhang " The first element is stored in a new collection
hold " Zhang " The length in the first set is 3 To a new collection
Traverse the element output in the set obtained in the previous step .

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
The goal is : Preliminary experience Stream Convenient and fast flow
*/
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, " Zhang Sanfeng "," zhang wuji "," Zhou Zhiruo "," Zhao Min "," Zhang Qiang ");
System.out.println(names);
//
// // 1、 Find the one surnamed Zhang from the set and put it in the new set
// List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
// for (String name : names) {
// if(name.startsWith(" Zhang ")){
// zhangList.add(name);
// }
// }
// System.out.println(zhangList);
//
// // 2、 Find a name whose length is 3 The name of
// List<String> zhangThreeList = new ArrayList<>();
// for (String name : zhangList) {
// if(name.length() == 3){
// zhangThreeList.add(name);
// }
// }
// System.out.println(zhangThreeList);
// 3、 Use Stream Realized
names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang ")).filter(s -> s.length() == 3).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}Stream The core of flow thinking :
1. Get the of a set or array first Stream flow ( It's a conveyor belt )
2. Put the elements on it
3. Then use this Stream Flow simplified API To facilitate the operation of elements .
summary :
Stream What is the function of flow , What technology is combined ?
Simplify the set 、 Array operations API. Combined with the Lambda expression .
say something Stream The idea and use steps of flow .
Get the of a set or array first Stream flow ( It's a conveyor belt ).
Put the elements on it .
Then use this Stream Flow simplified API To facilitate the operation of elements .
2.2Stream Stream acquisition
Stream Three methods of flow
obtain Stream flow
Create a pipeline , And put the data on the pipeline, ready to operate
The middle way
Operation on the assembly line . After one operation , You can continue with other operations .
Put an end to the method
One Stream A stream can only have one end method , It's the last operation on the pipeline
Stream The first step in manipulating a set or array is to get Stream flow , Then you can use the function of flow .
Gather to get Stream stream
have access to Collection Default method in interface stream() Generative flow

Array get Stream stream

import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
The goal is :Stream Stream acquisition
Stream The core of flow thinking :
Is to get the set or array first Stream flow ( It's a conveyor belt )
Then use this Stream Stream operates on the elements of a collection or array .
And then use Stream Flow simplifies the process of replacing collection operations API.
Collection gets the name of the stream API:
(1) default Stream<E> stream();
Summary :
Gather to get Stream Circulation : stream();
Array :Arrays.stream( Array ) / Stream.of( Array );
*/
public class StreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** --------------------Collection Gather to get the stream ------------------------------- */
Collection<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> s = list.stream();
/** --------------------Map Gather to get the stream ------------------------------- */
Map<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
// Bond flow
Stream<String> keyStream = maps.keySet().stream();
// Value flow
Stream<Integer> valueStream = maps.values().stream();
// Key value ( Take the whole )
Stream<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> keyAndValueStream = maps.entrySet().stream();
/** --------------------- Array get stream ------------------------------ */
String[] names = {" Zhao Min "," Small zhao "," extinction "," Zhou Zhiruo "};
Stream<String> nameStream = Arrays.stream(names);
Stream<String> nameStream2 = Stream.of(names);
}
}
2.3Stream The common use of stream API
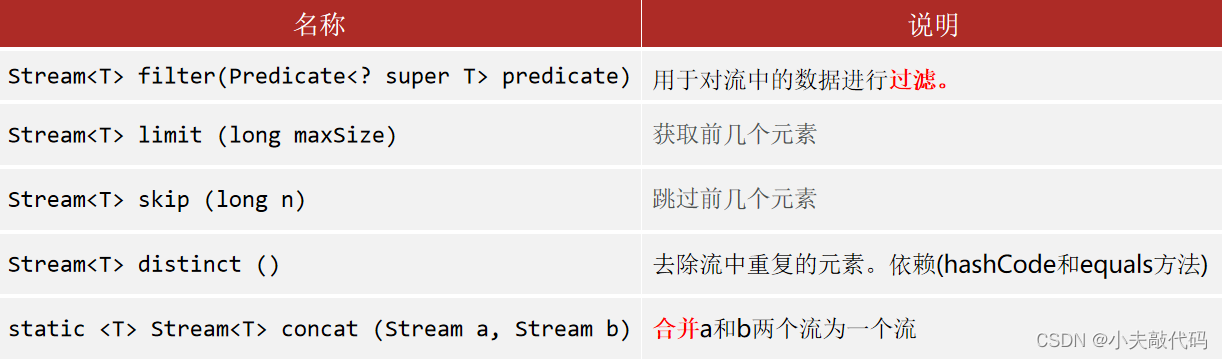
Stream The common use of stream API( Intermediate operation method )
Be careful :
Intermediate methods are also called non terminating methods , After the call is completed, a new Stream Stream can continue to use , Support Chain programming .
stay Stream The collection cannot be modified directly in the stream 、 Data in array .
Stream Common end operations for streams

Be careful : Termination operation method , After the call is completed, the flow can no longer be used , The reason is that it will not return Stream 了 .
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
The goal is :Stream The common use of stream API
forEach : One by one processing ( Traverse )
count: Number of Statistics
-- long count();
filter : Filter element
-- Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
limit : Take the first few elements
skip : Skip the first few
map : Processing method
concat : Combined flow .
*/
public class StreamDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(" zhang wuji ");
list.add(" Zhou Zhiruo ");
list.add(" Zhao Min ");
list.add(" Zhang Qiang ");
list.add(" Zhang Sanfeng ");
list.add(" Zhang Sanfeng ");
// Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang ")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
long size = list.stream().filter(s -> s.length() == 3).count();
System.out.println(size);
// list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang ")).limit(2).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
System.out.println("--------------------------");
list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang ")).limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang ")).skip(2).forEach(System.out::println);
// map Processing method : The first parameter is raw material -> The second parameter is the result of processing .
// Add a... To the front of the set element :zhangsan
list.stream().map(s -> "zhangsan" + s).forEach(a -> System.out.println(a));
// demand : Put all the names All processed into a student object .
list.stream().map(s -> new Student(s)).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// list.stream().map(Student::new).forEach(System.out::println); // Constructor reference Method reference
// Combined flow .
Stream<String> s1 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang "));
Stream<String> s2 = Stream.of("java1", "java2");
// public static <T> Stream<T> concat(Stream<? extends T> a, Stream<? extends T> b)
Stream<String> s3 = Stream.concat(s1 , s2);
s3.distinct().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}
summary :
What is the meaning of terminating and non terminating methods ?
After terminating the method, the stream cannot continue to be used , Non terminating methods will return a new stream , Support chain programming .
2.4Stream Comprehensive application of flow
Case study :
demand : The Development Department of a company , It is divided into development department I and Development Department II , Now we need to settle the mid year data .
analysis :
Employee information includes at least ( name 、 Gender 、 Wages 、 Bonus 、 Punishment record )
Develop a department with 4 Employees 、 The second development department has 5 Employees
Filter out 2 Information about the highest paid employees in a department , Encapsulated as an excellent employee object Topperformer
Count out 2 The average monthly income of each department , Ask for the removal of the maximum and minimum wages .
Statistics 2 The average salary of a development department as a whole , Remove the average of the minimum and maximum wages .
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamDemo04 {
public static double allMoney ;
public static double allMoney2 ; // 2 Remove the maximum wage from each department , The sum of the minimum wages
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> one = new ArrayList<>();
one.add(new Employee(" Pig eight quit ",' male ',30000 , 25000, null));
one.add(new Employee(" The Monkey King ",' male ',25000 , 1000, " Contradict your boss "));
one.add(new Employee(" Monk sha ",' male ',20000 , 20000, null));
one.add(new Employee(" Small white dragon ",' male ',20000 , 25000, null));
List<Employee> two = new ArrayList<>();
two.add(new Employee(" Wusong ",' male ',15000 , 9000, null));
two.add(new Employee(" Li Kui ",' male ',20000 , 10000, null));
two.add(new Employee(" ximen qing ",' male ',50000 , 100000, " Be beaten "));
two.add(new Employee(" Pan Jinlian ",' Woman ',3500 , 1000, " Be beaten "));
two.add(new Employee(" Wu Da Long ",' Woman ',20000 , 0, " Poison "));
// 1、 The highest paid employees in the development department .(API)
// Specify the size rule
// Employee e = one.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus(), e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus()))
// .get();
// System.out.println(e);
Topperformer t = one.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus(), e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus()))
.map(e -> new Topperformer(e.getName(), e.getSalary() + e.getBonus())).get();
System.out.println(t);
// 2、 Count the average wage , Remove the maximum wage and minimum wage
one.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus(), e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus()))
.skip(1).limit(one.size() - 2).forEach(e -> {
// Find the sum : The total salary of the remaining employees
allMoney += (e.getSalary() + e.getBonus());
});
System.out.println(" The average salary for developing a department is :" + allMoney / (one.size() - 2));
// 3、 Merge 2 A collection stream , Re statistics
Stream<Employee> s1 = one.stream();
Stream<Employee> s2 = two.stream();
Stream<Employee> s3 = Stream.concat(s1 , s2);
s3.sorted((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus(), e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus()))
.skip(1).limit(one.size() + two.size() - 2).forEach(e -> {
// Find the sum : The total salary of the remaining employees
allMoney2 += (e.getSalary() + e.getBonus());
});
// BigDecimal
BigDecimal a = BigDecimal.valueOf(allMoney2);
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf(one.size() + two.size() - 2);
System.out.println(" The average salary of the development department is :" + a.divide(b,2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
}
}
2.5 collect Stream flow
Stream Stream collection operation
collect Stream Meaning of flow : Is to put Stream The result data after stream operation is transferred back to the set or array .
Stream flow : Easy to operate set / Array means .
aggregate / Array : Is the purpose of development .
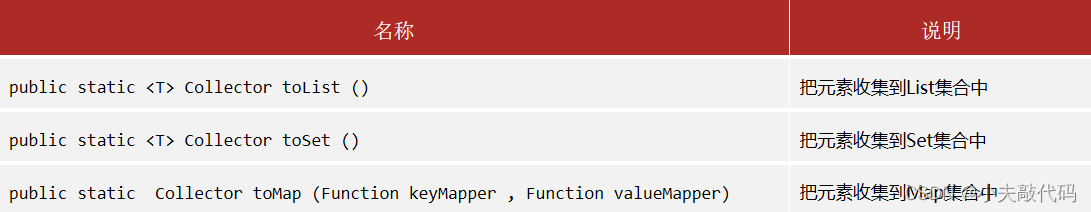
Stream Stream collection methods

Collectors Tool classes provide specific collection methods
summary :
1. collect Stream The role of flow ?
Stream A stream is a collection of operations / Array means
The result data of the operation should eventually be restored to the set or array .
import java.util.*;
import java.util.function.IntFunction;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
The goal is : collect Stream Stream data to In a collection or array .
*/
public class StreamDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(" zhang wuji ");
list.add(" Zhou Zhiruo ");
list.add(" Zhao Min ");
list.add(" Zhang Qiang ");
list.add(" Zhang Sanfeng ");
list.add(" Zhang Sanfeng ");
Stream<String> s1 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang "));
List<String> zhangList = s1.collect(Collectors.toList()); // Variable set
zhangList.add("java1");
System.out.println(zhangList);
// List<String> list1 = s1.toList(); // Get the immutable set
// list1.add("java");
// System.out.println(list1);
// Pay attention to pay attention to :“ Streams can only be used once ”
Stream<String> s2 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang "));
Set<String> zhangSet = s2.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(zhangSet);
Stream<String> s3 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith(" Zhang "));
// Object[] arrs = s3.toArray();
String[] arrs = s3.toArray(String[]::new); // Can be either , Expand your thinking !!
System.out.println("Arrays An array of content :" + Arrays.toString(arrs));
}
}边栏推荐
- Build your own website (17)
- In rails, when the resource creation operation fails and render: new is called, why must the URL be changed to the index URL of the resource?
- Oracle:CDB限制PDB资源实战
- table表格设置圆角
- pytorch之数据类型tensor
- 系统休眠文件可以删除吗 系统休眠文件怎么删除
- 树莓派/arm设备上安装火狐Firefox浏览器
- [batch dos-cmd command - summary and summary] - view or modify file attributes (attrib), view and modify file association types (Assoc, ftype)
- Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
- 负载均衡性能参数如何测评?
猜你喜欢

JTAG debugging experience of arm bare board debugging
线段树(SegmentTree)
界面控件DevExpress WinForms皮肤编辑器的这个补丁,你了解了吗?
Niuke cold training camp 6B (Freund has no green name level)
AI 从代码中自动生成注释文档
Anfulai embedded weekly report no. 272: 2022.06.27--2022.07.03
![[case sharing] basic function configuration of network loop detection](/img/d8/a367c26b51d9dbaf53bf4fe2a13917.png)
[case sharing] basic function configuration of network loop detection
UI控件Telerik UI for WinForms新主题——VS2022启发式主题
2022 Google CTF segfault Labyrinth WP

Analysis of mutex principle in golang
随机推荐
ARM裸板调试之JTAG调试体验
C# 计算农历日期方法 2022
【案例分享】网络环路检测基本功能配置
Segmenttree
Using the entry level of DVA in taro3.*
自旋与sleep的区别
golang中的atomic,以及CAS操作
Let's see through the network i/o model from beginning to end
Force buckle 1037 Effective boomerang
Rainstorm effect in levels - ue5
gnet: 一个轻量级且高性能的 Go 网络框架 使用笔记
[牛客] B-完全平方数
Part VI, STM32 pulse width modulation (PWM) programming
免费白嫖的图床对比
Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
Boot - Prometheus push gateway use
[100 cases of JVM tuning practice] 04 - Method area tuning practice (Part 1)
字节P7专业级讲解:接口测试常用工具及测试方法,福利文
pyflink的安装和测试
The cost of returning tables in MySQL