当前位置:网站首页>Can't you understand the code of linked list in C language? An article allows you to grasp the secondary pointer and deeply understand the various forms of parameter passing in the function parameter
Can't you understand the code of linked list in C language? An article allows you to grasp the secondary pointer and deeply understand the various forms of parameter passing in the function parameter
2022-07-07 01:39:00 【Autumn white leaves fall】
Author's brief introduction : Others regard dreams as horses , And I want to dream about yards . I am Ye Luo Qiu Bai , Try to learn from the back end
Personal home page : The homepage of autumn white leaves
Series column : Data structure dry goods sharing
Recommend a simulated interview 、 Brush Title artifact Enter the world of question brushing
Preface
This blog is about to solve the problem that you can't understand or write the basic operations of linked lists , For beginners , There are many places that must be incomprehensible . For example, functions parameter list The diversity of , Dynamic memory allocation function malloc etc. , In fact, these knowledge and The pointer Close ties , Especially the secondary pointer . Then start learning this blog well !
Catalog
Explanation of secondary pointer
The application of linked list
Define the structure of the double linked list
Pass in the first level pointer
A reference to an incoming pointer
Brush question network recommendation
Explanation of secondary pointer
sketch : In fact, one pointer points to another Address .
We all know that the pointer points to the address , But the pointer itself is also a Variable , Of course, it can also be pointed by the secondary pointer .
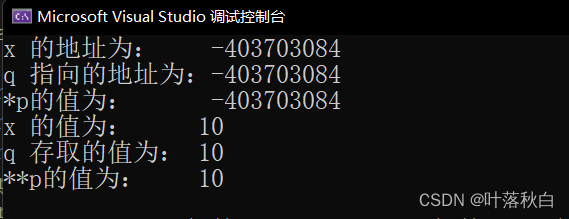
grammar : Form like int x = 10; int *q = &x; int **p = & q;
So here q Pointer to x The address of ,p The pointer points to the pointer q The address of ,*q You can get x Value ,*p You can get q The pointer itself ,**p You can also get x Value .
Code example :
int main(void)
{
int x = 10;
int* q = &x;
int** p = &q;
printf("x The address for : %d\n", &x);
printf("q The address pointed to is :%d\n", q);
printf("*p The value of is : %d\n", *p); //p Pointer q The address of , that *p Is a dereference operation ,
// It's equal to q In itself
printf("x The value of is : %d\n", x);
printf("q The accessed value is : %d\n", *q);
printf("**p The value of is : %d\n", **p); //**p It is equivalent to solving the reference twice , Get it first q In itself ,
// Get the second time q Point to the value of the address
return 0;
}Running results :
The application of linked list
Here take the double linked list of the leading node as an example
Define the structure of the double linked list
typedef int ElemType;// Rename the integer data to int
typedef int Status;// Rename integer to Status
// Data structure definition of double linked list
typedef struct DouNode {
ElemType data; // Data fields
struct DouNode* head; // Precursor pointer
struct DouNode* next; // Subsequent pointer
}DousList, * LinkList;// Node pointer Code interpretation :
utilize typedef Rename the data type , As long as you encounter it later ElemType and Status All integers are enough . The double linked list structure consists of three parts : Data fields 、 Precursor pointer 、 Subsequent pointer , The difference from the single linked list is that there is an additional precursor pointer . Then the end of the brace is also renamed , here DousList and DouNode The effect is the same , Are all structure names , then LinkList Is a pointer to a node .
Specific use :
LinkList L,L It's a pointer ,DousList *P,P It's also a pointer , There are two ways to create .
Create a double linked list
Use two correct forms of creating linked lists and one wrong form , Compare the memory creation methods
Pass in the first level pointer
This method cannot be successfully created
Code demonstration :
void CreateDouList(LinkList L, int n)
{
LinkList ptr;
int i;
L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(DousList)); // Apply for space for the head node
L->next = NULL;
L->head = NULL;
L->data = n;//L->data Record the number of nodes
ptr = L;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int value = 0;
scanf("%d",&value);
LinkList me = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(DouNode));
me->data = value; // Node data domain
me->next = NULL;
me->head = NULL;
ptr->next = me;
me->head = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next; // The tail interpolation method is used to build the table
}
}Code parsing :
The parameter list here is LinkList L and Integer data n,L Is the incoming chain header node pointer ,n It is used to record the number of inserted data , In the following for The number of times a cycle is used as a cycle . Next use malloc Function is L The linked list allocates memory space ,malloc Need to use The pointer To receive , The brackets on the left are allocated Pointer types , The bracket on the right is the allocated memory The size . After the space allocation is completed, the pre initialization and subsequent pointers are null , Data fields data Number of recorded data .ptr The pointer is initially equal to L The pointer , Next into n Secondary cycle , Create a node pointer to be inserted me And allocate memory space and initialize , The last three lines of code are used for tail interpolation to establish the linked list :
The tail interpolation :
First, let ptr The subsequent pointer of points to me, then me Of head Pointer to ptr, This is equivalent to putting me The node is inserted into the linked list , then ptr Point to this inserted new node , This ensures that each inserted node is after the last inserted node .
But does this really insert data into the linked list , Let's see the debugging results :
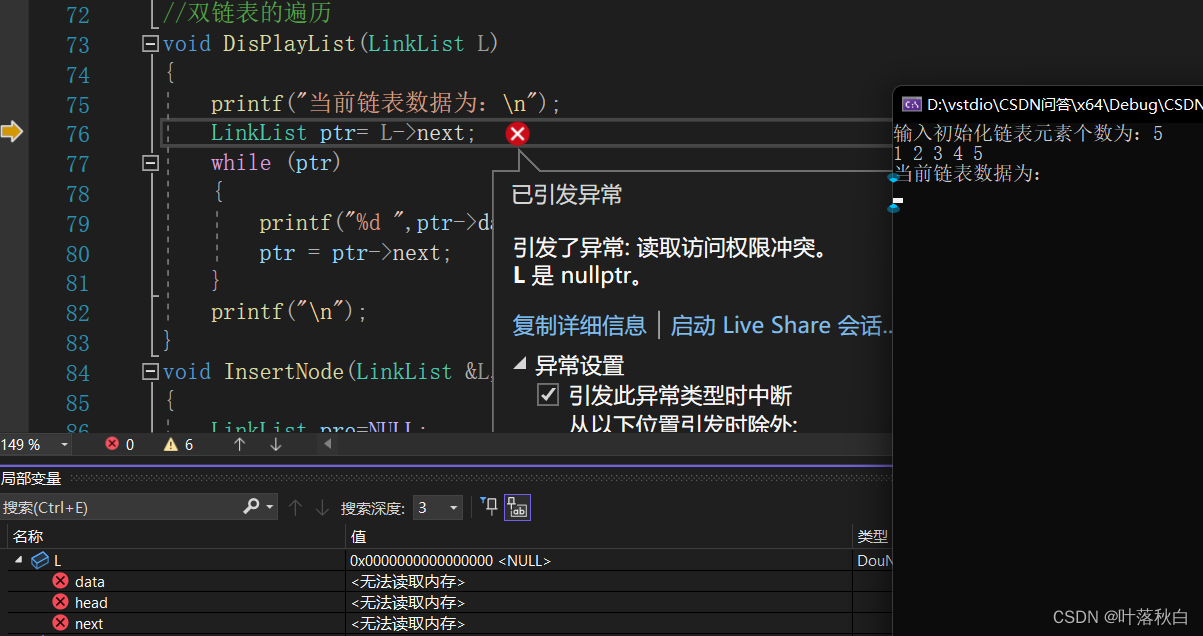
When entering the traversal program , Let's create ptr Pointer to L Successor of linked list , Immediately, a null pointer exception occurred , But the data is clearly inserted above , Why ? Obviously , The linked list here L Inserting data is not complete . This is because what we pass in the function of creating the linked list is only the pointer of the linked list L, Then in the function, this pointer is just a copy , Increasing the memory space here will not affect the actual parameter linked list , This is consistent with the value transfer and address transfer of ordinary data types .
We use the incoming pointer address to solve this problem , Two methods : Pointer quote and The secondary pointer
A reference to an incoming pointer
The implementation part of the function does not need to be modified at all , Just add a reference to the formal parameter list "&" that will do .
void CreateDouList(LinkList &L, int n);View debugging results :
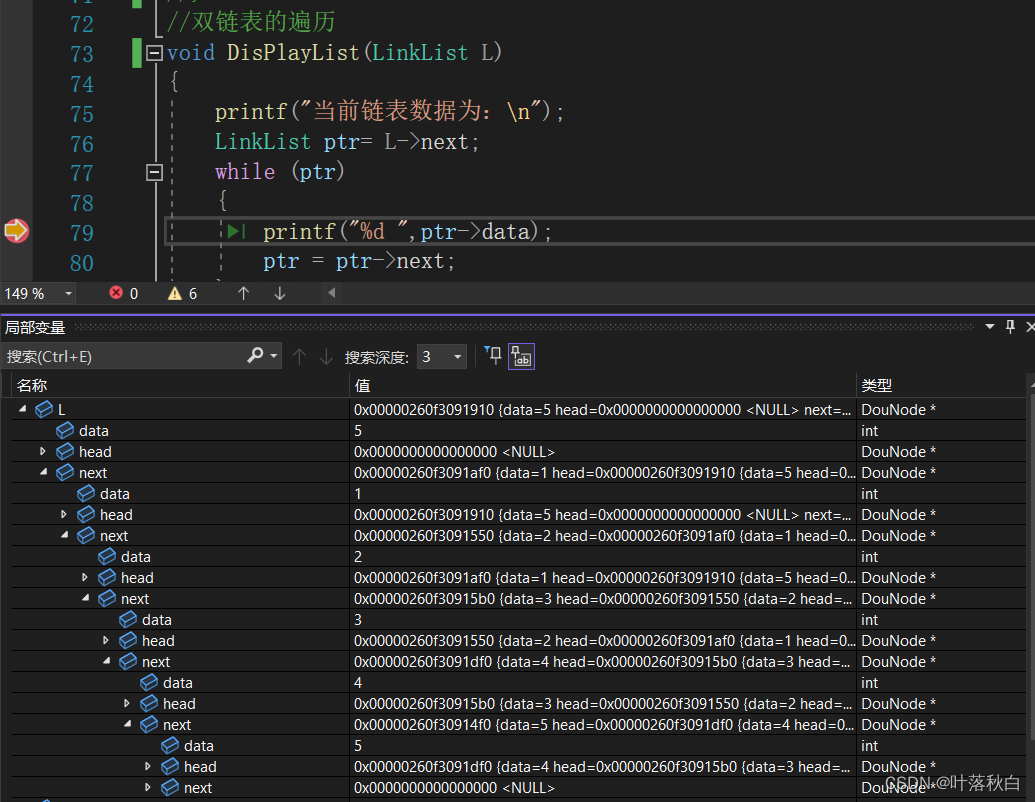
The same debugging method , You can see clearly after passing in the reference of the pointer L Of data be equal to 5, That is, five data are saved , Then the values of subsequent nodes are consistent with the results of tailoring , The subsequent pointer of the last node just points to NULL, Completely accord with Our design code .
After passing in the reference of the pointer , The spatial change of the linked list in the function will lead to the spatial change of the linked list in the argument , Only in this way can the insertion operation be completed , Insert the node into the linked list .
Pass in the secondary pointer
This is the same as the reference principle of pointer , I mainly share with you the forms used
Note that the arguments should be added when calling “&” operator , example :CreateDouList(&L,n);
void CreateDouList(LinkList *L, int n)
{
LinkList ptr;
int i;
*L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(DousList)); // Apply for space for the head node
(*L)->next = NULL;
(*L)->head = NULL;
(*L)->data = n;//L->data Record the number of nodes
ptr = (*L);
printf(" Start inserting data :\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int value = 0;
scanf("%d",&value);
LinkList me = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(DouNode));
me->data = value; // Node data domain
me->next = NULL;
me->head = NULL;
ptr->next = me;
me->head = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next; // The tail interpolation method is used to build the table
}
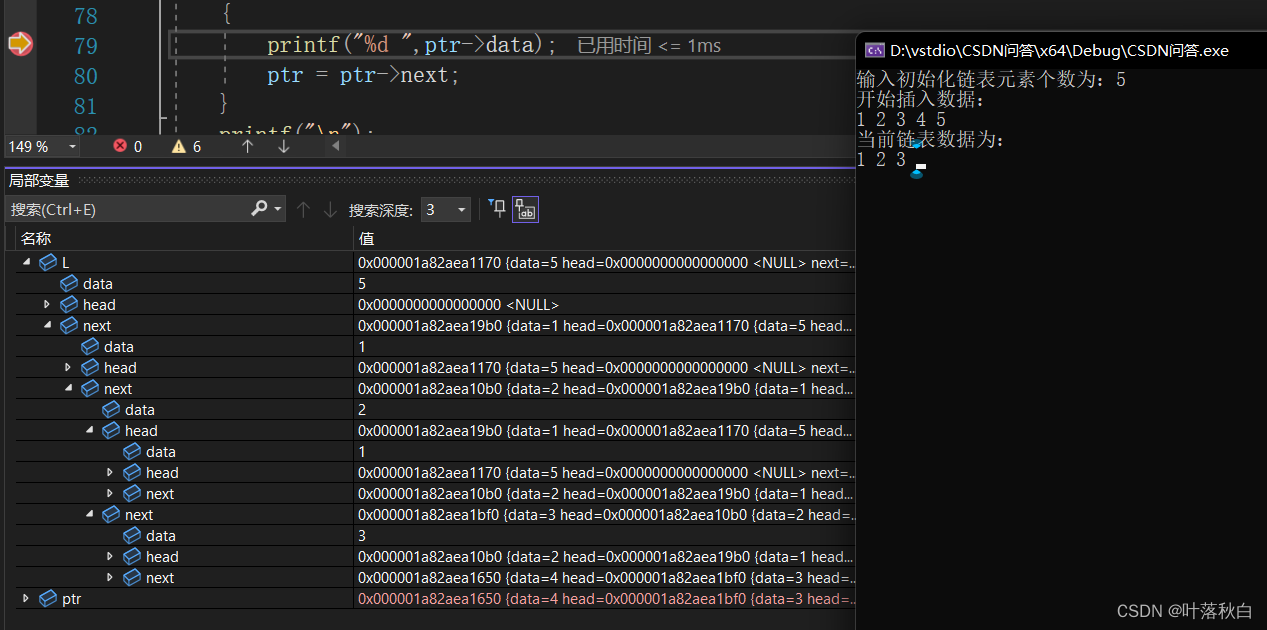
}Here the parameter of the formal parameter list is LinkList *L, and DousLIst **L The effect is the same , It's a The secondary pointer . If you use a pointer to the linked list, you need a reference operation , It's written in (*L) In the form of . Then allocate space 、 To initialize 、 Assign value to linked list pointer ptr Wait for the operation , In this way, the secondary pointer of the linked list L The change of will also change the linked list of arguments , You can view the debugging results .
Debugging results :
Brush question network recommendation
The data structure is not particularly friendly to Xiaobai , A lot of knowledge will be forgotten if you don't look at it for a few days. You must consolidate the knowledge you have learned , Therefore, it is necessary to brush questions . Here I would like to introduce to you a question brushing platform that I think is more friendly to Xiaobai — Cattle from
These are classic linked list questions , More practice is sure to consolidate knowledge , Is it still a problem to pinch a linked list .
I hope you can make full use of your time , To consolidate what they have learned , Hit the big factory , Let's make progress together !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Your cache folder contains root-owned files, due to a bug in npm ERR! previous versions of npm which
Js逆向——捅了【马蜂窝】的ob混淆与加速乐

454-百度面经1
dvajs的基础介绍及使用
![[advanced C language] 8 written questions of pointer](/img/d4/c9bb2c8c9fd8f54a36e463e3eb2fe0.png)
[advanced C language] 8 written questions of pointer
Typical problems of subnet division and super network construction
Comparison of picture beds of free white whoring
从底层结构开始学习FPGA----FIFO IP的定制与测试

云呐|工单管理办法,如何开展工单管理
![[signal and system]](/img/aa/a65d6da1d1d9410254ca7b775e24a6.png)
[signal and system]
随机推荐
Set up [redis in centos7.x]
Wood extraction in Halcon
How to manage distributed teams?
Docker method to install MySQL
Appium foundation - appium inspector positioning tool (I)
js如何快速创建一个长度为 n 的数组
AcWing 1140. 最短网络 (最小生成树)
【芯片方案设计】脉搏血氧仪
C语言实例_3
405 method not allowed appears when the third party jumps to the website
Vocabulary in Data Book
安全保护能力是什么意思?等保不同级别保护能力分别是怎样?
AI automatically generates annotation documents from code
swiper组件中使用video导致全屏错位
AcWing 344. Solution to the problem of sightseeing tour (Floyd finding the minimum ring of undirected graph)
Mysqlbackup restores specific tables
Set WordPress pseudo static connection (no pagoda)
mysqlbackup 还原特定的表
C语言实例_4
移植DAC芯片MCP4725驱动到NUC980