当前位置:网站首页>Utilisation de hudi dans idea
Utilisation de hudi dans idea
2022-07-03 09:21:00 【Xiao Hu s'est - il amélioré aujourd'hui?】
Préparation environnementale
- Création Maven Projets
- Créer une connexion distante au serveur
Tools------Delployment-----Browse Remote Host
Les paramètres sont les suivants::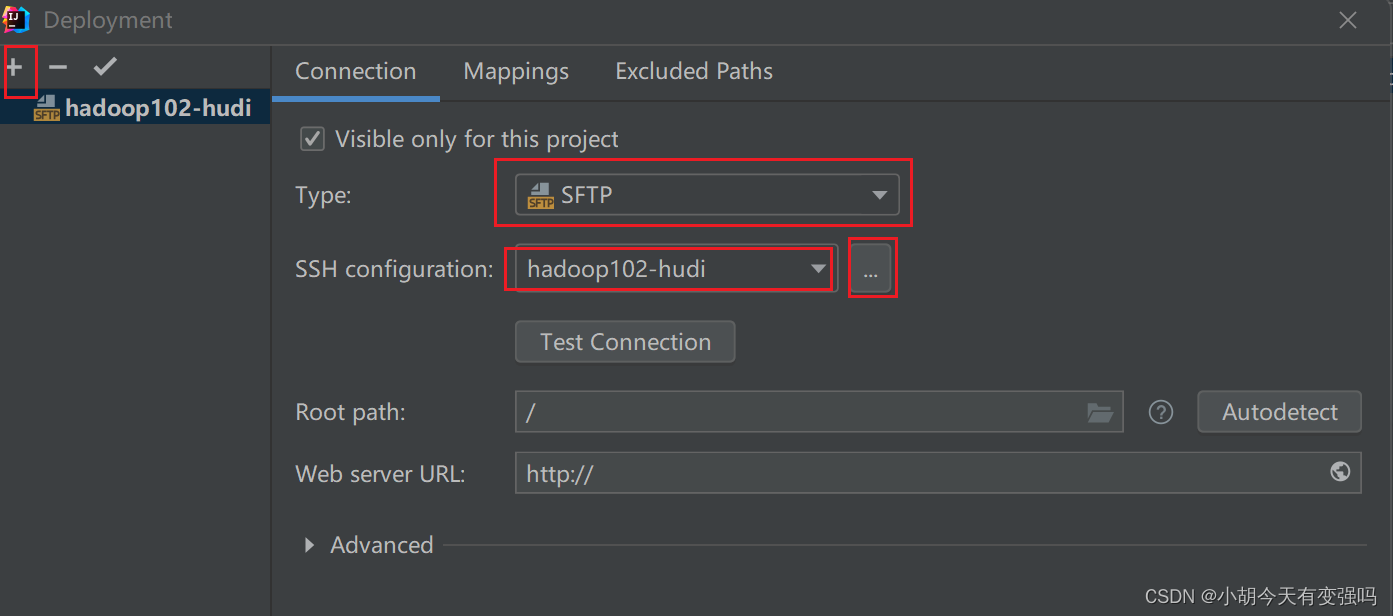
Saisissez ici le compte et le mot de passe du serveur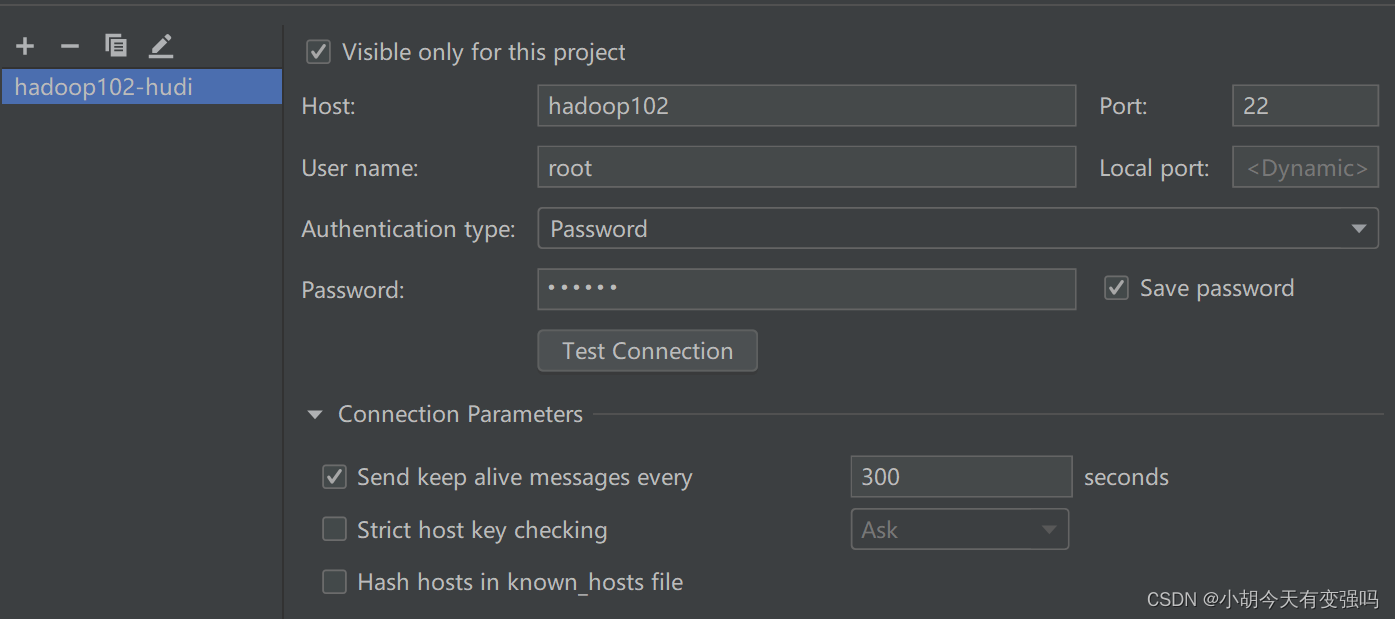
Cliquez surTest Connection,ConseilsSuccessfullyEt si,Cela signifie que la configuration est réussie.
- CopierHadoopDe core-site.xml、hdfs-site.xml Et log4j.properties Trois fichiers copiés àresourcesSous le dossier.
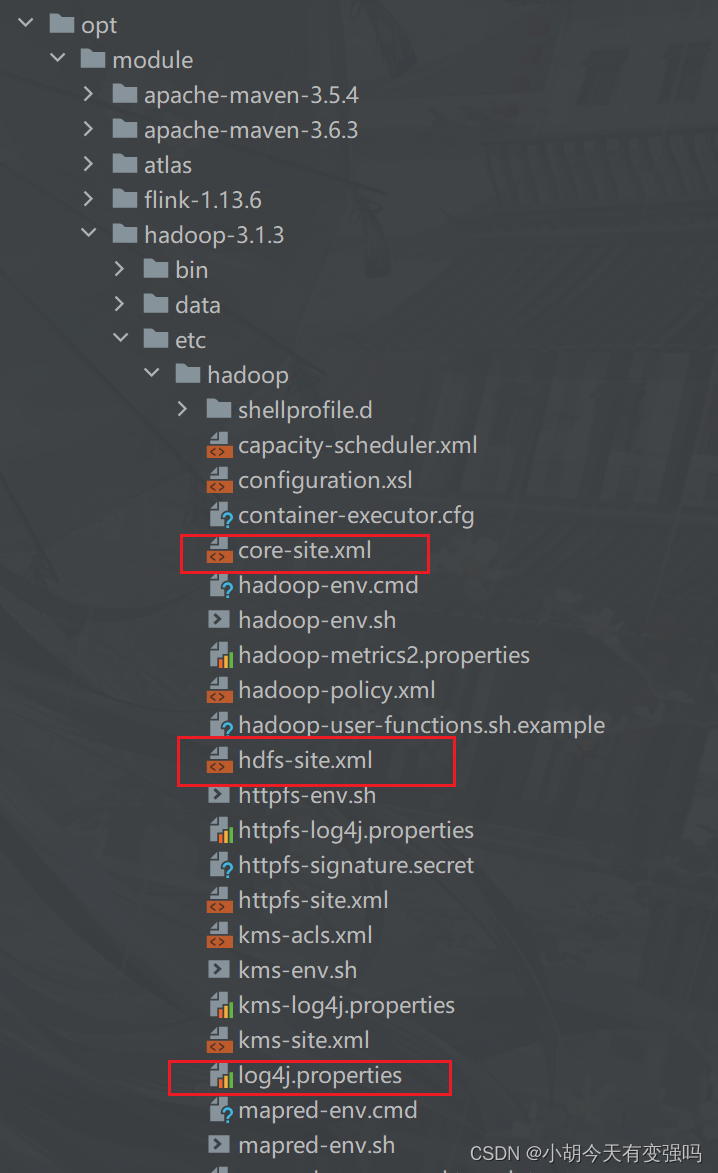
Paramètres log4j.properties Pour imprimer le message d'exception d'avertissement :
log4j.rootCategory=WARN, console
- Ajouter pom.xml Documentation
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>aliyun</id>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>cloudera</id>
<url>https://repository.cloudera.com/artifactory/cloudera-repos/</url>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>jboss</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<properties>
<scala.version>2.12.10</scala.version>
<scala.binary.version>2.12</scala.binary.version>
<spark.version>3.0.0</spark.version>
<hadoop.version>2.7.3</hadoop.version>
<hudi.version>0.9.0</hudi.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- DépendanceScalaLangues -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spark Core Dépendance -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spark SQL Dépendance -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-sql_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hadoop Client Dépendance -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>${hadoop.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- hudi-spark3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hudi</groupId>
<artifactId>hudi-spark3-bundle_2.12</artifactId>
<version>${hudi.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-avro_2.12</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<outputDirectory>target/classes</outputDirectory>
<testOutputDirectory>target/test-classes</testOutputDirectory>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
<!-- Maven Plug - in compilé -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>testCompile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Pour annoter le code suivant généré lors de la création du projet , Sinon, la dépendance continue de signaler des erreurs :
<!-- <properties>-->
<!-- <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>-->
<!-- <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>-->
<!-- </properties>-->
Structure du Code: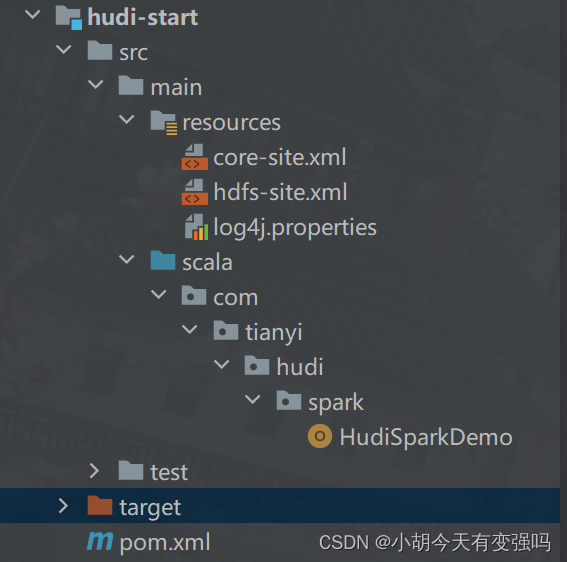
Code de base
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils.DataGenerator
import org.apache.spark.sql.{
DataFrame, SaveMode, SparkSession}
/** * Hudi Le cadre de Data Lake ,Basé surSparkMoteur de calcul,Effectuer les donnéesCURDFonctionnement, Données sur les déplacements en taxi générées à l'aide de simulations officielles * * Tâche 1:Données analogiques,InsérerHudiTableau,AdoptionCOWMode * Tâche 2: Snapshot mode Query (Snapshot Query)Données,AdoptionDSLComment * Tâche 3:Mise à jour(Update)Données * Tâche 4:Requête incrémentale(Incremental Query)Données,AdoptionSQLComment * Tâche 5:Supprimer(Delete)Données */
object HudiSparkDemo {
/** * Affaires officielles:La simulation génère des données,InsérerHudiTableau, Le type de tableau est COW */
def insertData(spark: SparkSession, table: String, path: String): Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
// No1Pas、Simulation des données de voyage
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
val dataGen: DataGenerator = new DataGenerator()
val inserts = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(100))
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
val insertDF: DataFrame = spark.read.json(
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts.asScala, 2).toDS()
)
// insertDF.printSchema()
// insertDF.show(10, truncate = false)
//Deuxième étape: Insérer les données dansHudiTableau
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
insertDF.write
.mode(SaveMode.Append)
.format("hudi")
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", 2)
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", 2)
//HudiParamètres des propriétés du tableau
.option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "ts")
.option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "uuid")
.option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "partitionpath")
.option(TBL_NAME.key(), table)
.save(path)
}
/** * AdoptionSnapshot Query Snapshot pour interroger les données de la table */
def queryData(spark: SparkSession, path: String): Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
val tripsDF: DataFrame = spark.read.format("hudi").load(path)
// tripsDF.printSchema()
// tripsDF.show(10, truncate = false)
// Les frais de recherche sont supérieurs à 10,Moins de50 Données de voyage pour
tripsDF
.filter($"fare" >= 20 && $"fare" <=50)
.select($"driver", $"rider", $"fare", $"begin_lat", $"begin_lon", $"partitionpath", $"_hoodie_commit_time")
.orderBy($"fare".desc, $"_hoodie_commit_time".desc)
.show(20, truncate = false)
}
def queryDataByTime(spark: SparkSession, path: String):Unit = {
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._
//Mode 1:Spécifier la chaîne, Filtrer les données par date - heure
val df1 = spark.read
.format("hudi")
.option("as.of.instant", "20220610160908")
.load(path)
.sort(col("_hoodie_commit_time").desc)
df1.printSchema()
df1.show(numRows = 5, truncate = false)
//Mode 2:Spécifier la chaîne, Filtrer les données par date - heure
val df2 = spark.read
.format("hudi")
.option("as.of.instant", "2022-06-10 16:09:08")
.load(path)
.sort(col("_hoodie_commit_time").desc)
df2.printSchema()
df2.show(numRows = 5, truncate = false)
}
/** * Oui.DataGenerator Passer les données de génération comme paramètre */
def insertData(spark: SparkSession, table: String, path: String, dataGen: DataGenerator): Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
// No1Pas、Simulation des données de voyage
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
val inserts = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateInserts(100))
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
val insertDF: DataFrame = spark.read.json(
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(inserts.asScala, 2).toDS()
)
// insertDF.printSchema()
// insertDF.show(10, truncate = false)
//Deuxième étape: Insérer les données dansHudiTableau
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
insertDF.write
//Remplacer parOverwriteMode
.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite)
.format("hudi")
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", 2)
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", 2)
//HudiParamètres des propriétés du tableau
.option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "ts")
.option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "uuid")
.option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "partitionpath")
.option(TBL_NAME.key(), table)
.save(path)
}
/** * Production analogique Hudi Mise à jour des données dans le tableau , Mise à jour vers HudiDans le tableau */
def updateData(spark: SparkSession, table: String, path: String, dataGen: DataGenerator):Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
// No1Pas、Simulation des données de voyage
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
// Produire des données mises à jour
val updates = convertToStringList(dataGen.generateUpdates(100))
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
val updateDF: DataFrame = spark.read.json(
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(updates.asScala, 2).toDS()
)
// TOOD: No2Pas、Insérer les données dansHudiTableau
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
updateDF.write
//Ajouter un mode
.mode(SaveMode.Append)
.format("hudi")
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", "2")
.option("hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism", "2")
// Hudi Paramètres de valeur des attributs pour le tableau
.option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "ts")
.option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "uuid")
.option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "partitionpath")
.option(TBL_NAME.key(), table)
.save(path)
}
/** * AdoptionIncremental Query Requête incrémentale de données , L'horodatage doit être spécifié */
def incrementalQueryData(spark: SparkSession, path: String): Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
// No1Pas、ChargementHudiDonnées du tableau,Accèscommit timeTemps, Comme seuil de données de requête incrémentale
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceReadOptions._
spark.read
.format("hudi")
.load(path)
.createOrReplaceTempView("view_temp_hudi_trips")
val commits: Array[String] = spark
.sql(
""" |select | distinct(_hoodie_commit_time) as commitTime |from | view_temp_hudi_trips |order by | commitTime DESC |""".stripMargin
)
.map(row => row.getString(0))
.take(50)
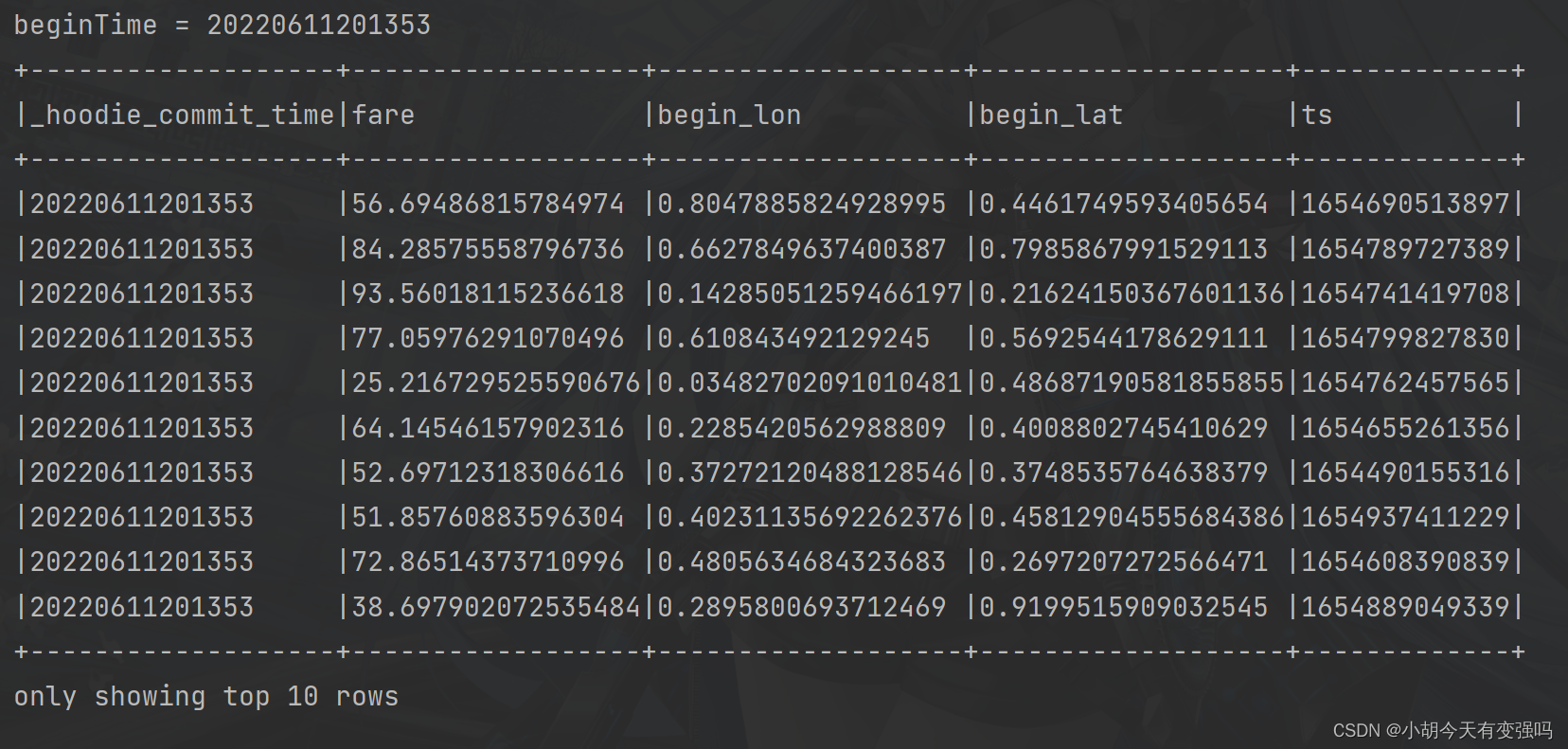
val beginTime = commits(commits.length - 1) // commit time we are interested in
println(s"beginTime = ${
beginTime}")
// No2Pas、ParamètresHudiDonnéesCommitTimeSeuil temporel, Effectuer une requête incrémentale de données
val tripsIncrementalDF = spark.read
.format("hudi")
// Définir le mode de données de requête à :incremental,Lecture incrémentale
.option(QUERY_TYPE.key(), QUERY_TYPE_INCREMENTAL_OPT_VAL)
// Définir l'heure de début de la lecture incrémentale des données
.option(BEGIN_INSTANTTIME.key(), beginTime)
.load(path)
// No3Pas、 Enregistrer les données de requête incrémentales comme une vue temporaire , Les frais de recherche sont supérieurs à 20Données
tripsIncrementalDF.createOrReplaceTempView("hudi_trips_incremental")
spark
.sql(
""" |select | `_hoodie_commit_time`, fare, begin_lon, begin_lat, ts |from | hudi_trips_incremental |where | fare > 20.0 |""".stripMargin
)
.show(10, truncate = false)
}
/** * SupprimerHudiDonnées du tableau, Selon la clé primaire uuidSupprimer,Si c'est une table partitionnée, Spécifier le chemin de partition */
def deleteData(spark: SparkSession, table: String, path: String): Unit = {
import spark.implicits._
// No1Pas、ChargementHudiDonnées du tableau, Obtenir le nombre d'entrées
val tripsDF: DataFrame = spark.read.format("hudi").load(path)
println(s"Raw Count = ${
tripsDF.count()}")
// No2Pas、 Simuler les données à supprimer ,DeHudiChargement des données,Obtenir quelques données, Convertir pour supprimer l'ensemble de données
val dataframe = tripsDF.limit(2).select($"uuid", $"partitionpath")
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
val dataGenerator = new DataGenerator()
val deletes = dataGenerator.generateDeletes(dataframe.collectAsList())
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
val deleteDF = spark.read.json(spark.sparkContext.parallelize(deletes.asScala, 2))
// No3Pas、Enregistrer les données dansHudiDans le tableau, Définir le type d'opération :DELETE
import org.apache.hudi.DataSourceWriteOptions._
import org.apache.hudi.config.HoodieWriteConfig._
deleteDF.write
.mode(SaveMode.Append)
.format("hudi")
.option("hoodie.insert.shuffle.parallelism", "2")
.option("hoodie.upsert.shuffle.parallelism", "2")
// Définir le type d'opération de données à delete,La valeur par défaut estupsert
.option(OPERATION.key(), "delete")
.option(PRECOMBINE_FIELD.key(), "ts")
.option(RECORDKEY_FIELD.key(), "uuid")
.option(PARTITIONPATH_FIELD.key(), "partitionpath")
.option(TBL_NAME.key(), table)
.save(path)
// No4Pas、RechargerHudiDonnées du tableau,Nombre d'entrées statistiques, Voir si la réduction 2Données
val hudiDF: DataFrame = spark.read.format("hudi").load(path)
println(s"Delete After Count = ${
hudiDF.count()}")
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME","hty")
//CréationSparkSessionExemple d'objet,Définir les propriétés
val spark: SparkSession = {
SparkSession.builder()
.appName(this.getClass.getSimpleName.stripSuffix("$"))
.master("local[2]")
// Définir la méthode de sérialisation:Kryo
.config("spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer")
.getOrCreate()
}
//Définir les variables:Nom du tableau、Enregistrer le chemin
val tableName: String = "tbl_trips_cow"
val tablePath: String = "/hudi_warehouse/tbl_trips_cow"
//Construire un générateur de données, La simulation génère des données commerciales
import org.apache.hudi.QuickstartUtils._
//Tâche 1:Données analogiques,InsérerHudiTableau,AdoptionCOWMode
//insertData(spark, tableName, tablePath)
//Tâche 2: Snapshot mode Query (Snapshot Query)Données,AdoptionDSLComment
//queryData(spark, tablePath)
//queryDataByTime(spark, tablePath)
// Tâche 3:Mise à jour(Update)Données,No1Pas、La simulation génère des données,No2Pas、La simulation génère des données,Pour la Section1 Mise à jour de la valeur du champ de données Step ,
// No3Pas、Mettre à jour les données àHudiDans le tableau
val dataGen: DataGenerator = new DataGenerator()
//insertData(spark, tableName, tablePath, dataGen)
//updateData(spark, tableName, tablePath, dataGen)
//Tâche 4:Requête incrémentale(Incremental Query)Données,AdoptionSQLComment
//incrementalQueryData(spark, tablePath)
//Tâche 5:Supprimer(Delete)Données
deleteData(spark, tableName,tablePath)
//Fin de l'application,Fermer la ressource
spark.stop()
}
}
Tests
Mise en œuvre insertData(spark, tableName, tablePath) Méthode suivie d'une requête instantanée :
queryData(spark, tablePath)

Requête incrémentale(Incremental Query)Données:
incrementalQueryData(spark, tablePath)
Références
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sb4y1n7hK?p=21&vd_source=e21134e00867aeadc3c6b37bb38b9eee
边栏推荐
- [graduation season | advanced technology Er] another graduation season, I change my career as soon as I graduate, from animal science to programmer. Programmers have something to say in 10 years
- 【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版9】—Advanced Feature Learning on Point Clouds using Multi-resolution Features and Learni
- Wonderful review | i/o extended 2022 activity dry goods sharing
- [point cloud processing paper crazy reading frontier version 11] - unsupervised point cloud pre training via occlusion completion
- LeetCode 515. Find the maximum value in each tree row
- 剑指 Offer II 029. 排序的循环链表
- With low code prospect, jnpf is flexible and easy to use, and uses intelligence to define a new office mode
- [point cloud processing paper crazy reading classic version 7] - dynamic edge conditioned filters in revolutionary neural networks on Graphs
- npm install安装依赖包报错解决方法
- LeetCode 532. 数组中的 k-diff 数对
猜你喜欢

Digital management medium + low code, jnpf opens a new engine for enterprise digital transformation
AcWing 787. 归并排序(模板)

Hudi 集成 Spark 数据分析示例(含代码流程与测试结果)
2022-2-13 learn the imitation Niuke project - Project debugging skills

【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版12】—— Adaptive Graph Convolution for Point Cloud Analysis

LeetCode 715. Range module

Redis learning (I)

Crawler career from scratch (II): crawl the photos of my little sister ② (the website has been disabled)

干货!零售业智能化管理会遇到哪些问题?看懂这篇文章就够了

AcWing 786. Number k
随机推荐
Common penetration test range
LeetCode 715. Range module
Problems in the implementation of lenet
【点云处理之论文狂读经典版14】—— Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds
【点云处理之论文狂读经典版8】—— O-CNN: Octree-based Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Analysis
Crawler career from scratch (I): crawl the photos of my little sister ① (the website has been disabled)
Principles of computer composition - cache, connection mapping, learning experience
Crawler career from scratch (V): detailed explanation of re regular expression
C language programming specification
2022-2-14 learning xiangniuke project - generate verification code
Solve POM in idea Comment top line problem in XML file
浅谈企业信息化建设
Digital statistics DP acwing 338 Counting problem
Computing level network notes
[point cloud processing paper crazy reading classic version 8] - o-cnn: octree based revolutionary neural networks for 3D shape analysis
Sword finger offer II 029 Sorted circular linked list
【点云处理之论文狂读前沿版8】—— Pointview-GCN: 3D Shape Classification With Multi-View Point Clouds
我們有個共同的名字,XX工
Using variables in sed command
低代码起势,这款信息管理系统开发神器,你值得拥有!