Software engineering in code -- Yes menu Source code analysis of the project
brief introduction :
This article is based on Mr. Meng Ning's knowledge instruction in advanced software engineering class , It mainly records the adoption of VS Code To build a menu(https://github.com/mengning/menu) The experimental process of the project , And in the process of reading the project source code for software engineering ideas 、 Thinking about methods and design principles .
Reference material :
The reference materials of this paper are mainly :https://gitee.com/mengning997/se/blob/master/README.md#%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E8%BD%AF%E4%BB%B6%E5%B7%A5%E7%A8%8B
Experimental environment :
operating system :Windows 10、
Document editor :VS Code 1.51.0、
Compilers and debuggers :MinGW 8.1.0(gcc and gdb stay Windows Implementation version on the platform ).
Catalog :
One 、VS Code To build C/C++ The compiling and debugging environment of .
Two 、 Thinking about design art in software engineering .
3、 ... and 、 Summary of experiments .
One 、VS Code To build C/C++ The compiling and debugging environment of
1. install VS Code And C/C++ Developing a plug-in
VS Code(Visual Studio Code) It's a free product developed by Microsoft 、 Open source cross platform text ( Code ) Editor . Almost perfect editor .
Official website :https://code.visualstudio.com
file :https://code.visualstudio.com/docs
Source code :https://github.com/Microsoft/vscode
The project files used in this experiment are from C Written in language , To complete the construction of the project , You need to install VS Code And build on it C/C++ The compiler and development environment of . The specific operation is as follows :
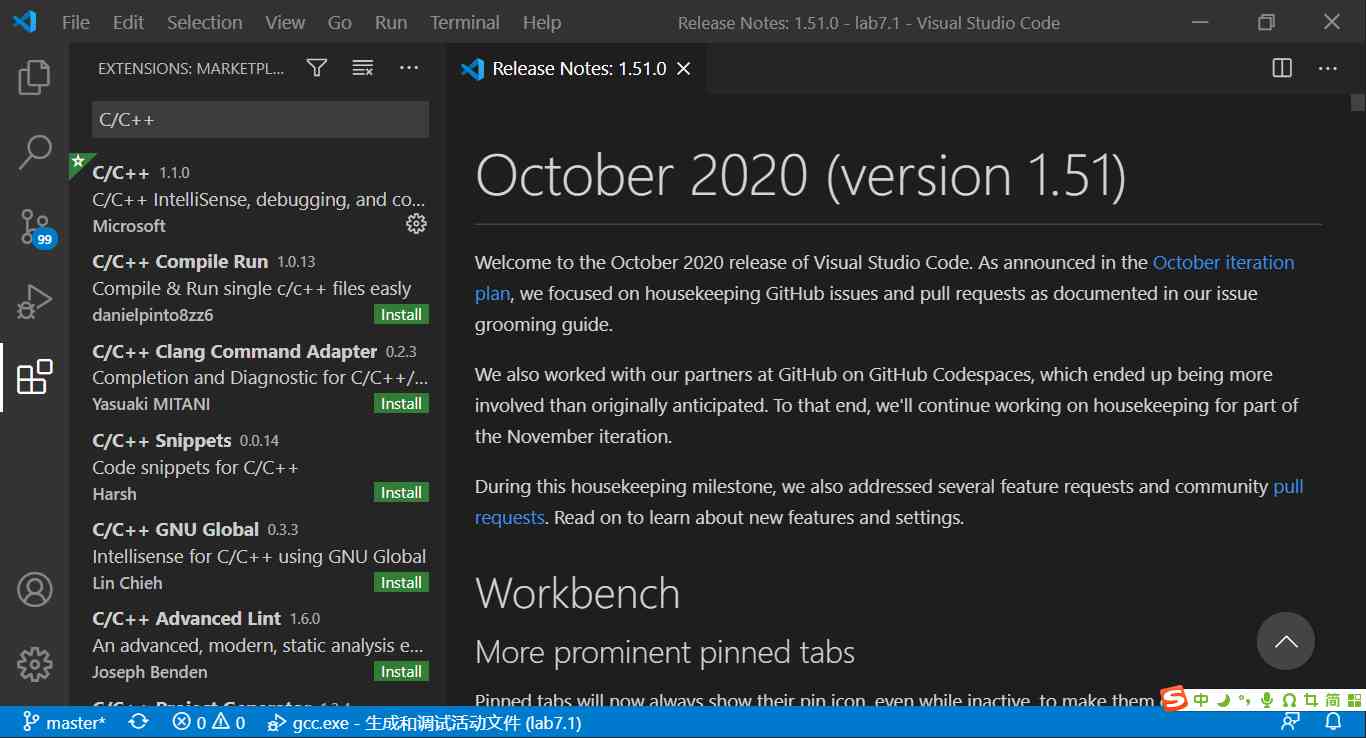
Come first VS Code Download and install VS Code, Open the software after installation , Click the manage expansion icon on the left , Enter in the input box C/C++ And select the plug-in to install . After successful installation, as shown in the figure :
2. Download compiler MinGW-w64, Configure system environment variables
The compiler and debugger are not included in the development plug-in installed in the previous step , So we need MinGW-w64 As run C/C++ Project compilers and debuggers . Go to the official website first (https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw-w64/files/) Download the appropriate version of the installation package :
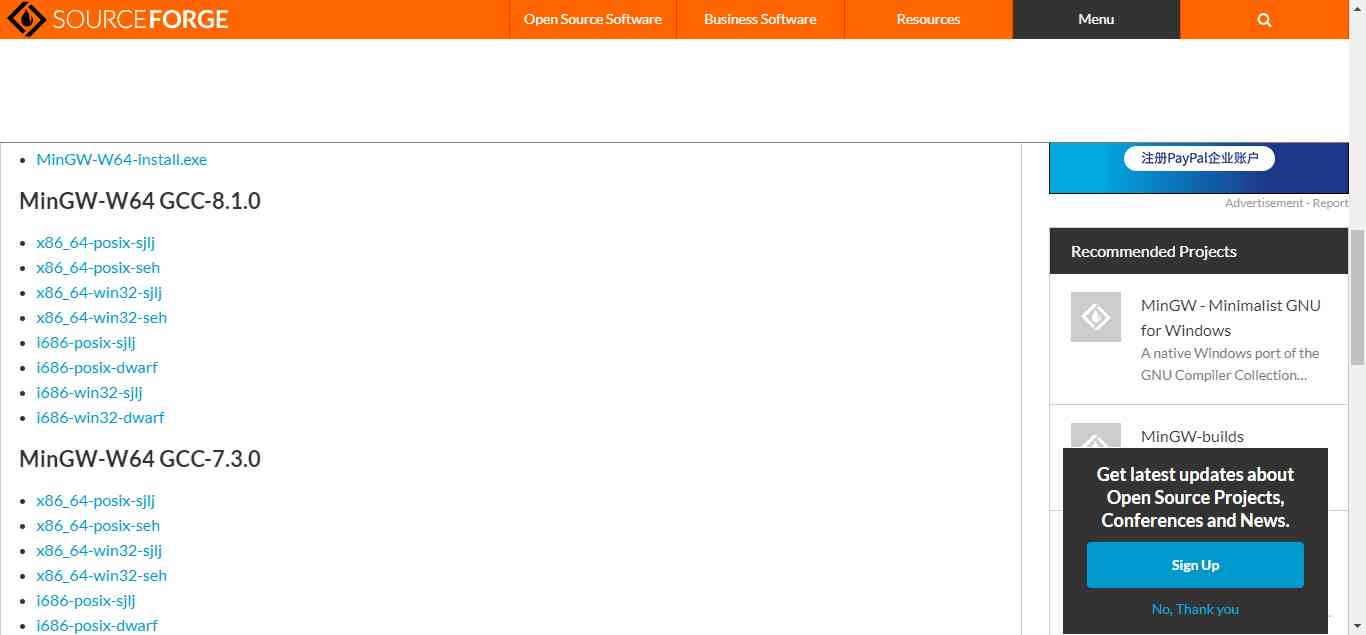
This experiment chooses MinGW-W64GCC-8.1.0 Under the x86_64-posix-seh Download , Unzip the folder to find a name of bin Folder :
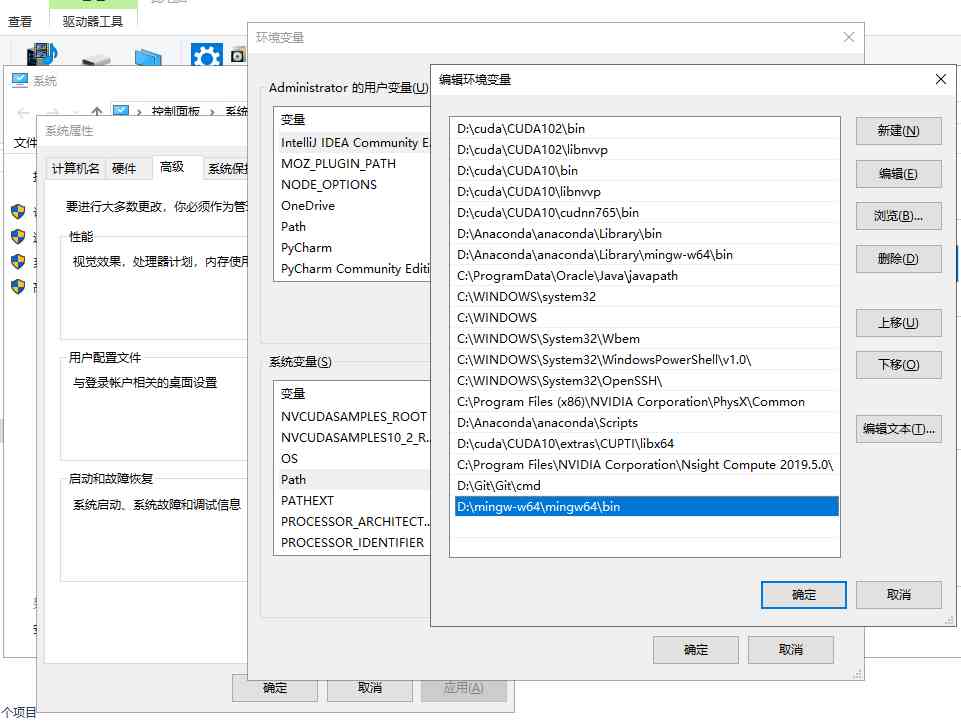
Then add the directory to the system environment variable :
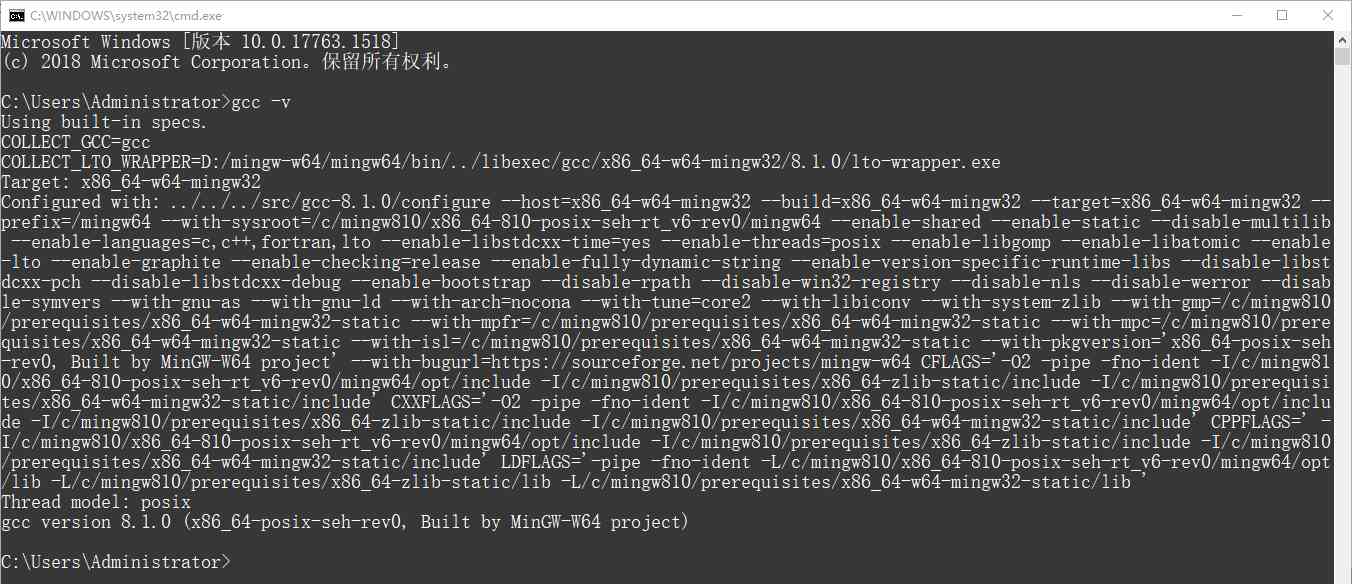
Enter... On the command line gcc -v, See the following results to show that the installation is successful .
3. stay VS Code Configure the compilation path in the
Press shortcut key F5, Yes C The program compiles , Generate .vscode Folder ,VS Code It will be automatically generated in this folder launch.json file , modify launch.json The documents are as follows :
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "gcc.exe - Generate and debug active files ", // Configuration name , It will be displayed in the drop-down menu of startup configuration
"type": "cppdbg", // Configuration type , It's only for cppdbg
"request": "launch", // Request configuration type , It can be for launch( start-up ) or attach( additional )
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", // The path of the program to be debugged
"args": ["-std=c++11"], // Command line parameters passed to the program during program debugging , It is usually set to empty
"stopAtEntry": false, // Set to true When the program will be suspended at the program entrance , Generally set as false
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", // Working directory when debugging program , It's usually ${workspaceRoot} That is, the directory where the code is located workspaceRoot Has been abandoned , Now changed to workspaceFolder
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true, // Whether to display the console window when debugging , Generally set as true Display console
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/gdb.exe", // miDebugger The path of , Pay attention to the relationship between MinGw The path corresponds to
"preLaunchTask": "c/c++ g++.exe build active file", // Tasks performed before debugging session start , It's usually a compiler ,c++ by g++, c by gcc
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
When there is... In the project file .h Type of C Language header file , Need to put .h The file path where the file is located is added to the compilation path . At this time, you need to .vscode New under folder c_cpp_properties.json file , And modify the contents of the document as follows :
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceRoot}",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/include/**",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/backward",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include-fixed",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/../../../../x86_64-w64-mingw32/include",
"${workspaceFolder}/include" // Write your own .h The header file is placed in this directory
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"__GNUC__=6",
"__cdecl=__attribute__((__cdecl__))"
],
"intelliSenseMode": "msvc-x64",
"browse": {
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": "",
"path": [
"${workspaceRoot}",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/include/**",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/backward",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include-fixed",
"D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/../../../../x86_64-w64-mingw32/include"
]
},
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++20"
}
],
"version": 4
}
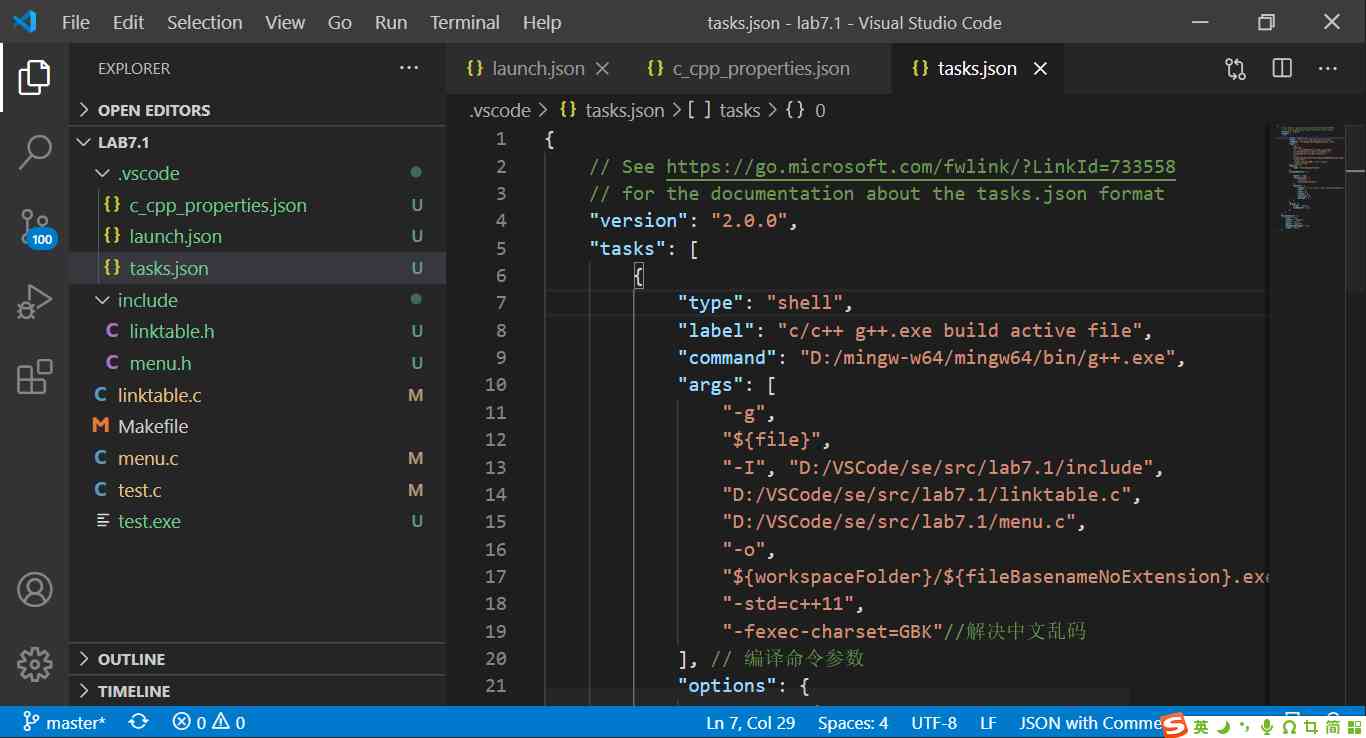
among D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/ yes MinGW-W64GCC-8.1.0 The installation path on my computer . In addition to the need to configure these two files , Still need to be in .vscode New under folder tasks.json file , The contents of the document are amended as follows :
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "c/c++ g++.exe build active file",
"command": "D:/mingw-w64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe",
"args": [
"-g",
"${file}",
"-I", "D:/VSCode/se/src/lab7.1/include",
"D:/VSCode/se/src/lab7.1/linktable.c",
"D:/VSCode/se/src/lab7.1/menu.c",
"-o",
"${workspaceFolder}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"-std=c++11",
"-fexec-charset=GBK"// Solve the Chinese garbled code
], // Compile command parameters
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}"
},
"problemMatcher": {
"owner": "cpp",
"fileLocation": [
"relative",
"${workspaceFolder}"
],
"pattern": {
"regexp": "^(.*):(/d+):(/d+):/s+(warning|error):/s+(.*)$",
"file": 1,
"line": 2,
"column": 3,
"severity": 4,
"message": 5
}
},
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
}
],
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": false,
"panel": "shared",
"showReuseMessage": true,
"clear": false
}
}
Here we are , The configuration of the environment is completed ,menu The directory structure of the project is as follows :
4. Run the project
Run the project test.c file , The results of project running are as follows :
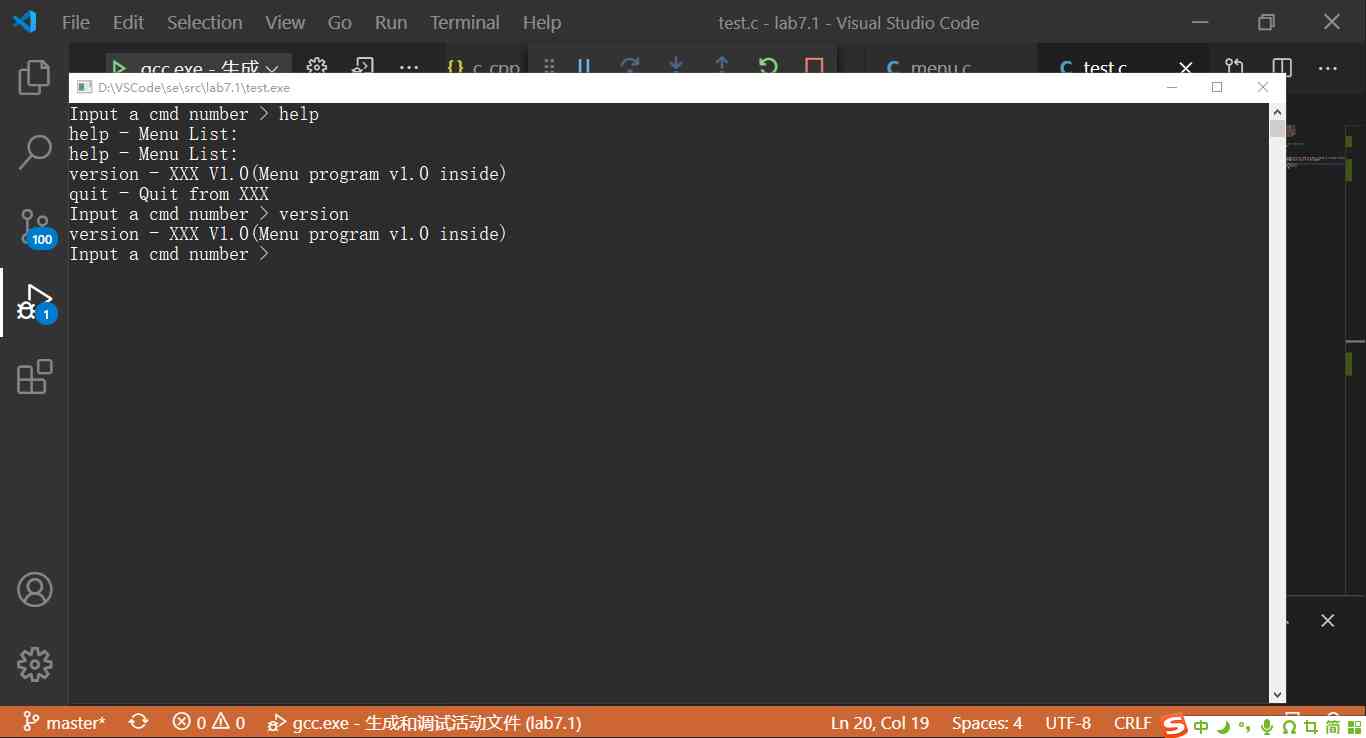
You can see from the above picture that test.c The file ran successfully , It is using VS Code build C/C++ The experiment of compiling and debugging environment is completed successfully .
Two 、 Thinking about design art in software engineering
1. Yes menu The source code of each version of the project is analyzed
| Folder name | Sub file | Function description |
|---|---|---|
lab1 |
hello.c/menu.c |
hello.c The function of the file is to test whether the development environment is completed ,menu.c The document is the original structure of the project ( Pseudo code ). |
lab2 |
menu.c |
Yes menu.c To improve the , Be able to target help and quit The command completes the output . by menu.c Added file header comments . |
lab3.1 |
menu.c |
Organize instructions through linked lists , A function pointer is designed for each instruction to handle the operation corresponding to the instruction . |
lab3.2 |
menu.c |
Encapsulate the search operation of the linked list to FindCmd Among functions , Encapsulate the display operation of linked list to function ShowAllCmd among . |
lab3.3 |
linklist.c/linklist.h/menu.c |
Separate the declaration part from the implementation part of the linked list , Place them in linklist.h and linklist.c The file of ; Encapsulate business logic into menu.c In file . |
lab4 |
linktable.h/linketable.c/menu.c/test.c/testlinktable.c |
Introduced the dynamic creation of command chain list, including add, delete, modify and other functions , The semaphore is used to realize the mutual exclusion operation of the linked list in the multithreading environment , Unit test is carried out . |
lab5.1 |
linktable.h/linktable.c/menu.c/testlinktable.c |
Separate the initialization of the linked list from the business logic , Introduce callback function SearchCondition, Call function of callback function SearchLinkTableNode. |
lab5.2 |
linktable.h/linktable.c/menu.c/Makefile |
Introduce callback function to SearchLinkTableNode To transform , The coupling degree between data structure and logic code is reduced , Added makefile The file completes the compilation and linking program . |
lab7.1 |
linktable.h/linktable.c/menu.c/Makefile/menu.h/test.c |
Business logic menu Part of the function is separated into a separate module , Thus in test To realize the function module call in . |
lab7.2 |
lab7.1 Sub file of +readme.txt |
Added readme.txt file , It records the functions and instructions of the project . |
2. Yes menu Thinking about the software engineering thought embodied in the project
Modular design
(Modular design) So called modular design , Simply put, it is to combine some elements of the product , Constitute a subsystem with a specific function , Use this subsystem as a generic module to combine with other product elements , Form a new system , Produce many different functions or the same function 、 Series of products with different properties . Modular design is one of the green design methods , It has changed from concept to more mature design method . Combine green design idea with modular design method , It can meet the functional attributes and environmental attributes of the product at the same time , On the one hand, it can shorten the product development and manufacturing cycle , Add product line , Improve product quality , Respond quickly to market changes ; On the other hand , Adverse effects on the environment can be reduced or eliminated , Convenient reuse 、 upgrade 、 Repair and disassembly after product abandonment 、 Recycling and disposal .
stay menu In the project , The beginning is to define the data structure 、 The declaration and business logic are written in the same menu.c In file , from lab3.1 Start , The definition of data structure is gradually separated from the operation of data structure , Thus the data structure is modularized . from lab4 To lab5.2 It is the stage of gradually separating the business logic layer from the data definition layer , This decouples the business logic from the underlying data definition . from lab7.1 To lab7.2 It's the stage of gradually modularizing business logic , Finally, a simple and easy-to-use interface is formed for high-level call .
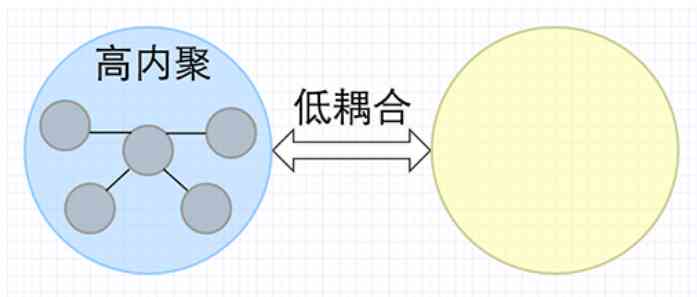
The gradual modularization of the project reduces the coupling between the modules , It is more suitable for scenarios where requirements are constantly changing , So as to achieve the project between the various modules “ High cohesion 、 Low coupling ” The design goal of .
Reusable interfaces
An interface is a contract between its implementation and its clients . The implementation must provide the functions specified in the interface , The client must use these functions according to the implicit and explicit rules described in the interface . Programming languages provide some implicit rules , To control the type declared in the interface 、 The use of functions and variables . for example ,C The language's type checking rules can catch errors in the type and number of parameters in an interface function . Generally speaking , The interface specification contains five basic elements : Purpose of the interface ; The conditions to be satisfied before using the interface , It is generally called a precondition or assumption ; Protocol specification to be followed by both parties using the interface ; The effect of using the interface , It's generally called a post condition ; The quality attribute implied in the interface .
With menu In the project linktable.c In the document SearchLinkTableNode Function as an example , In the formal parameter of the function Condition The parameter is a function pointer int Condition(tLinkTableNode* pNode, void* args), This parameter can use function callback to provide a more general interface for other modules , And this function doesn't use any business logic layer data , Only responsible for traversing the entire list , The judgment on whether to find the node of the specified condition is left to Condition The callback function pointed to is responsible for . When another module wants to call the interface , Just write according to your own needs Condition Function , This design , It encapsulates the implementation details of each module , The reusability of the code has been greatly improved .
function SearchLinkTableNode The implementation code of is as follows :
/*
* Search a LinkTableNode from LinkTable
* int Conditon(tLinkTableNode * pNode);
*/
tLinkTableNode * SearchLinkTableNode(tLinkTable *pLinkTable, int Conditon(tLinkTableNode * pNode, void * args), void * args)
{
if(pLinkTable == NULL || Conditon == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
tLinkTableNode * pNode = pLinkTable->pHead;
while(pNode != NULL)
{
if(Conditon(pNode,args) == SUCCESS)
{
return pNode;
}
pNode = pNode->pNext;
}
return NULL;
}
Business layer module menu.c The implementation and call of the interface in the file are as follows :
/* data struct and its operations */
typedef struct DataNode
{
tLinkTableNode * pNext;
char* cmd;
char* desc;
int (*handler)();
} tDataNode;
int SearchCondition(tLinkTableNode * pLinkTableNode, void * args)
{
char * cmd = (char*) args;
tDataNode * pNode = (tDataNode *)pLinkTableNode;
if(strcmp(pNode->cmd, cmd) == 0)
{
return SUCCESS;
}
return FAILURE;
}
/* find a cmd in the linklist and return the datanode pointer */
tDataNode* FindCmd(tLinkTable * head, char * cmd)
{
return (tDataNode*)SearchLinkTableNode(head,SearchCondition,(void*)cmd);
}
Reentrant functions and thread safety
Reentrant function : If a program or subroutine can “ Be interrupted at any time , Then the operating system schedules another piece of code , This code calls the subroutine again without error ”, It is called reentrant (reentrant or re-entrant) Of . in other words , When the subroutine is running , The execution thread can enter and execute it again , Still achieve the results expected at design time . Different from multithreading in thread safety , Reentrant emphasizes execution on a single thread , Re enter the same subroutine , It's still safe .
The conditions that reentrant functions should satisfy : It can't contain static ( overall situation ) Non constant data 、 Cannot return static ( overall situation ) The address of non constant data 、 Only data provided by the caller can be processed 、 Cannot rely on the lock of a single instance pattern resource 、 The called function must also be reentrant . The above condition requires that all variables used by the reentrant function be stored in the current function frame of the call stack (frame) On . therefore , When the same thread of execution returns to execute the function New function frame loaded , Does not conflict with the function frame used in the previous execution of the function 、 Don't cover each other , This ensures the security of reentrant execution .
Thread safety : When multiple threads access the same object , If you don 't have to consider the scheduling and alternate execution of these threads in the runtime environment , There's no need for extra synchronization , Or in any other way , The behavior of calling this object can get the correct result , So this object is thread safe .
Thread safety needs to be considered : Access shared variables or resources , There is a risk of concurrency , For example, the properties of an object , Static variables , Shared cache , Database etc. ; All timing dependent operations , Even if every step is thread safe , There is still the problem of concurrency ; When there is a binding relationship between different data . for example IP And port number . Just change it IP Just change the port number , otherwise IP It's also ineffective . So when it comes to this kind of operation , Be alert to atomic merging operations , Or all the changes are successful , Or all the modifications failed . When using other classes , If the class's comments state that it is not thread safe , Then it should not be used in multithreaded scenarios , Instead, consider the corresponding thread safe class , Or do some processing to ensure thread safety .
menu Application of thread safety in project :menu Modification of linked list in project 、 Delete and add operations due to access to shared variables or resources , There is a risk of concurrency . So in function CreateLinkTable()、DeleteLinkTable(tLinkTable *pLinkTable)、AddLinkTableNode(tLinkTable *pLinkTable,tLinkTableNode * pNode) and DelLinkTableNode(tLinkTable *pLinkTable,tLinkTableNode * pNode) Using thread mutex mechanism to ensure the code thread safety .
/*
* LinkTable Type
*/
struct LinkTable
{
tLinkTableNode *pHead;
tLinkTableNode *pTail;
int SumOfNode;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
};
/*
* Create a LinkTable
*/
tLinkTable * CreateLinkTable()
{
tLinkTable * pLinkTable = (tLinkTable *)malloc(sizeof(tLinkTable));
if(pLinkTable == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pLinkTable->pHead = NULL;
pLinkTable->pTail = NULL;
pLinkTable->SumOfNode = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&(pLinkTable->mutex), NULL);
return pLinkTable;
}
/*
* Delete a LinkTable
*/
int DeleteLinkTable(tLinkTable *pLinkTable)
{
if(pLinkTable == NULL)
{
return FAILURE;
}
while(pLinkTable->pHead != NULL)
{
tLinkTableNode * p = pLinkTable->pHead;
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
pLinkTable->pHead = pLinkTable->pHead->pNext;
pLinkTable->SumOfNode -= 1 ;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
free(p);
}
pLinkTable->pHead = NULL;
pLinkTable->pTail = NULL;
pLinkTable->SumOfNode = 0;
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
free(pLinkTable);
return SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Add a LinkTableNode to LinkTable
*/
int AddLinkTableNode(tLinkTable *pLinkTable,tLinkTableNode * pNode)
{
if(pLinkTable == NULL || pNode == NULL)
{
return FAILURE;
}
pNode->pNext = NULL;
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
if(pLinkTable->pHead == NULL)
{
pLinkTable->pHead = pNode;
}
if(pLinkTable->pTail == NULL)
{
pLinkTable->pTail = pNode;
}
else
{
pLinkTable->pTail->pNext = pNode;
pLinkTable->pTail = pNode;
}
pLinkTable->SumOfNode += 1 ;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
return SUCCESS;
}
/*
* Delete a LinkTableNode from LinkTable
*/
int DelLinkTableNode(tLinkTable *pLinkTable,tLinkTableNode * pNode)
{
if(pLinkTable == NULL || pNode == NULL)
{
return FAILURE;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
if(pLinkTable->pHead == pNode)
{
pLinkTable->pHead = pLinkTable->pHead->pNext;
pLinkTable->SumOfNode -= 1 ;
if(pLinkTable->SumOfNode == 0)
{
pLinkTable->pTail = NULL;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
return SUCCESS;
}
tLinkTableNode * pTempNode = pLinkTable->pHead;
while(pTempNode != NULL)
{
if(pTempNode->pNext == pNode)
{
pTempNode->pNext = pTempNode->pNext->pNext;
pLinkTable->SumOfNode -= 1 ;
if(pLinkTable->SumOfNode == 0)
{
pLinkTable->pTail = NULL;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
return SUCCESS;
}
pTempNode = pTempNode->pNext;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pLinkTable->mutex));
return FAILURE;
}
Be careful : The conditions for reentrant functions are only necessary for thread safety , Not a sufficient condition , When multithreading executes the same program, thread insecurity may occur outside the reentrant function .
3、 ... and 、 summary
Through a period of study , Finally completed this experiment , Not only have you learned to use VS Code complete C/C++ Build the development environment , Also by reading menu Project source code , Understand a lot of modular design in software engineering 、 Reusable interfaces 、 Knowledge of reentrant functions and thread safety , Benefit a lot .