当前位置:网站首页>Multithreading basic part part 1
Multithreading basic part part 1
2022-06-27 05:55:00 【Gold content of Xiaobai】
Catalog
process : An execution of a program in a system
Threads : A subtask in the process
Difference between process and thread
Classes that describe Thread objects -Thread class
run Methods and start Differences in methods
Create thread :Java There are four ways to create a thread in
a. Inherit Thread class , overwrite run Method ( Ready made core task methods )
Use anonymous inner classes to create Tread Object writing
b. overwrite Runnable Interface , overwrite run Method
Use anonymous inner class to implement Runnable Interface
c. overwrite Callable Interface , overwrite call Method
d. Creating threads using thread pool
2.Thread The core properties of the class
3. The start thread calls Tread Class start Method
There are two ways to interrupt threads
There are two ways for a thread to receive a built-in interrupt notification
5. Wait for another thread -join Method
6. Get the currently executing thread object
8. Change the thread state from running state to ready state =>yield() Method
BLOCKED , WAITING , TIMED_WAITING
Processes and threads
process : An execution of a program in a system
The process is the resource allocation in the current operating system (CPU, Memory and other key system information ) Minimum unit of , Different processes are independent of each other .
This is the process in the task manager

Threads : A subtask in the process
A thread is an independent task in a process , For example, downloading the browser process , Listen to music, etc , Just some threads of the browser process
All threads of the same process share the process resources , Threads are operating system task execution ( System scheduling ) The basic unit of
Difference between process and thread
1. The process is os The basic unit of resource allocation , Thread is os The basic unit of system scheduling .
2. Creating and destroying a process is much more expensive than a thread ( The cost is equivalent to time ), Threads are lighter .
3. Scheduling a thread is also much faster than scheduling a process .( Launch the browser / Browser tags , The label must be fast )
4. The process contains threads , Each process contains at least one thread ( The main thread ).
5. Processes are relatively independent of each other , Different processes do not share memory space , Threads of the same process share memory space .
Classes that describe Thread objects -Thread class
The entrance to our program is main Method , All calls start with the main method , So the same , All thread tasks are also from the main method ( The main thread ) To begin .
Java The classes describing threads in are Thread class ——java.lang.Thread The core class of class thread , It's all through Thread Class to start a thread .
When we finish writing the subclass of the thread run Method , Invokes in the main method Thread object .start Method to start a thread .
All threads are parallel , At the same time, execute in the computer
Use jconsole Thread status can be observed , Used to compare threads
run Methods and start Differences in methods
run Method
run Method is the work task of thread class , in other words ,run Method determines what the thread does after it is started , When run Method execution completed (JVM start-up run Method ), The thread will enter the destroy state .
start Method
start The method is Thread Class to start the thread , Only thread objects call start Method will be scheduled by the system , Enter the running state .
Create thread :Java There are four ways to create a thread in
a. Inherit Thread class , overwrite run Method ( Ready made core task methods )
// Inherit Thread class
public static class Run2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" Inherit Thread class ");
}
}ps: adopt Thread Class start Start thread
a Thread and startup in mode
1. A subclass inheritance Thread class
2. overwrite run Method
3. Generate the current subclass object , And then call start Method to start the thread
Use anonymous inner classes to create Tread Object writing
// Inherit inner class creation Thread object
Thread thread3 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" Inheriting anonymous inner classes Thread object ");
}
};b. overwrite Runnable Interface , overwrite run Method
public static class Run implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" Realization Runnable Interface ");
}
}ps: adopt Thread Class start Start thread
b Thread and startup in mode
1. Realization Runnable Interface
2. overwrite run Method
3. establish Thread Class object , call start Method
Use anonymous inner class to implement Runnable Interface
// Inheriting anonymous inner classes Runnable
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(" Inheriting anonymous inner classes Runnable");
}
}," Xiao peng ");Use Lambda expression
Thread thread3 = new Thread(()-> {
System.out.println("Lambda Thread creation of expression ");
}," A Ming ");c. overwrite Callable Interface , overwrite call Method
d. Creating threads using thread pool
Thread Class
Thread Class is JVM Describes the classes that manage threads , Each thread corresponds to a unique Thread object
1. Construction method

Such as , Pass in Runnable The methods of interface classes are constructor methods
ps: The thread can be named after the interface is passed in

2.Thread The core properties of the class
A picture flow

3. The start thread calls Tread Class start Method

4. Interrupt threads
There are two ways to interrupt threads
a. Interrupt by sharing variables

b. adopt Thread.interrupted() Static methods or Thread Member method of object isInterrupted()
Thread There is a property of whether the thread is interrupted in the class

There are two ways for a thread to receive a built-in interrupt notification
a. When a thread calls sleep/wait/join When the method is blocked , Notice of interruption received thread.interrupt()
Throw interrupt exception InterruptedException
When an exception is thrown , The interrupt state of the current thread will be cleared
b. The thread does not call the above three methods , Receive interrupt notification when in normal operation state thread.interrupt()
Thread.interrupted() Determine whether the current thread is interrupted , If the interrupt status is true Clear interrupt flag

Thread.currentThread.isInterrupted(); Judge whether the specified thread object is in interrupt state , If the state is true, The interrupt flag is not cleared

5. Wait for another thread -join Method
use join Method , When a thread calls another thread's join Method , Wait until the calling thread finishes executing , To continue executing subsequent code for this thread .

join A variation of the method

6. Get the currently executing thread object
Thread.currentThread() => Get the executing thread object
for example
Thread.currentThread().getName()Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()7. Hibernate current process
Thread.sleep(long millis) (ms) Method , Sleep the process in which it is used .
8. Change the thread state from running state to ready state =>yield() Method
call yield The thread of the method will voluntarily give up CPU resources , From running state to ready state , Waiting to be CPU Continue to dispatch .
When will you give up CPU, When was it CPU Reschedule , All are os The scheduling of , We have no choice .
There are two possibilities for this approach :
a. After the thread makes the operation in running state , Dispatch again soon

b. After the thread makes the operation in running state , Not scheduled for a long time
This method is completely controlled by CPU control , We can't control it , So I don't use much .
State of thread
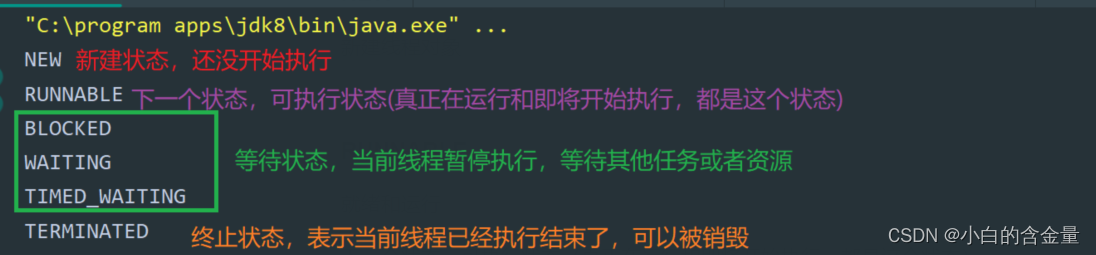 Attach a status chart , The following description will rely on the following figure
Attach a status chart , The following description will rely on the following figure

NEW
New thread object ,new One Thread Object is new state
New state , It hasn't started yet

RUNNABLE
Ready and running , Thread object .start Namely RUNNABLE state
Next state , Executable state ( Really running and about to start execution , All in this state )

BLOCKED , WAITING , TIMED_WAITING
Wait state , All three waiting states are blocked ( This thread needs to suspend execution , The reasons for the suspension of execution caused by these three factors are different )
TIMED_WAITING

Overtime waiting , Indicates that the thread needs to wait for a period of time before resuming execution
for example sleep The method is this kind of waiting

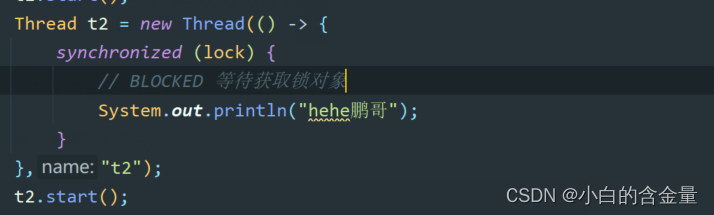
BLOCKED
When a thread is locked and waiting to acquire a lock object, it is BLOCKER state
WAITING
When threads use lock.wait() When the method is used , Description: enter the thread waiting state , That requires another thread lock.notify Method to unlock this thread

TERMINATED

run Method execution completed , Or throw an exception and execute abnormally
Termination status , Indicates that the current thread has finished executing , It can be destroyed
You can use the thread object of the main thread .isAlive() Method to determine whether the thread is alive

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

多线程基础部分Part3
Two position relay hjws-9440

思维的技术:如何破解工作生活中的两难冲突?

Gao Xiang slam14 lecture - note 1

Leetcode99 week race record

30个单片机常见问题及解决办法!

Kubesphere cluster configuration NFS storage solution - favorite

Codeforces Round #802 (Div. 2)

Junda technology - centralized monitoring scheme for multi brand precision air conditioners

Qt使用Valgrind分析内存泄漏
随机推荐
洛谷P4683 [IOI2008] Type Printer 题解
QListWidgetItem上附加widget
Database - index
Webrtc series - Nomination and ice of 7-ice supplement for network transmission_ Model
使用域名转发mqtt协议,避坑指南
Navigation [machine learning]
Spark 之 WholeStageCodegen
双位置继电器XJLS-8G/220
Two position relay rxmvb2 r251 204 110dc
How win 10 opens the environment variables window
Discussion on streaming media protocol (MPEG2-TS, RTSP, RTP, RTCP, SDP, RTMP, HLS, HDS, HSS, mpeg-dash)
Go log -uber open source library zap use
leetcode298周赛记录
Edge loads web pages in IE mode - edge sets ie compatibility
Code is data
Double position relay rxmd2-1mrk001984 dc220v
C语言实现定时器
Opencv implements object tracking
30个单片机常见问题及解决办法!
《汇编语言-王爽》第3章笔记及实验